Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Co
Co )Sn studied by
)Sn studied by  SR
SRCai, Y.*; Yoon, S.*; Sheng, Q.*; Zhao, G.*; Seewald, E. F.*; Ghosh, S.*; Ingham, J.*; Pasupathy, A. N.*; Queiroz, R.*; Lei, H.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 111(21), p.214412_1 - 214412_17, 2025/06
We study the magnetic properties of the metallic kagome system (Fe Co
Co )Sn by a combination of muon spin relaxation (
)Sn by a combination of muon spin relaxation ( SR), magnetic susceptibility, and scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) measurements in single crystal specimens with Co concentrations
SR), magnetic susceptibility, and scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) measurements in single crystal specimens with Co concentrations  = 0, 0.11, 0.8. In the undoped antiferromagnetic compound FeSn, we find possible signatures for a previously unidentified phase that sets in at
= 0, 0.11, 0.8. In the undoped antiferromagnetic compound FeSn, we find possible signatures for a previously unidentified phase that sets in at 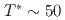 ~K, well beneath the Neel temperature
~K, well beneath the Neel temperature 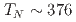 ~K as indicated by a peak in the relaxation rate 1/
~K as indicated by a peak in the relaxation rate 1/ observed in zero field (ZF) and longitudinal field (LF)
observed in zero field (ZF) and longitudinal field (LF)  SR measurements, with a corresponding anomaly in the ac and dc susceptibility, and an increase in the static width 1/
SR measurements, with a corresponding anomaly in the ac and dc susceptibility, and an increase in the static width 1/ in ZF-
in ZF- SR measurements. No signatures of spatial symmetry breaking are found in STM down to 7~K. Related to the location and motion of muons in FeSn, we confirmed a previous report that about 40% of the implanted muons reside at a field-cancelling high symmetry site at
SR measurements. No signatures of spatial symmetry breaking are found in STM down to 7~K. Related to the location and motion of muons in FeSn, we confirmed a previous report that about 40% of the implanted muons reside at a field-cancelling high symmetry site at  ~K, while an onset of thermal hopping changes the site occupancy at higher temperatures. In Fe
~K, while an onset of thermal hopping changes the site occupancy at higher temperatures. In Fe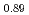 Co
Co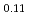 Sn, where disorder eliminated the field-cancellation effect, all the implanted muons exhibit precession and/or relaxation in the ordered state. In Fe
Sn, where disorder eliminated the field-cancellation effect, all the implanted muons exhibit precession and/or relaxation in the ordered state. In Fe Co
Co Sn, we find canonical spin glass behavior with freezing temperature
Sn, we find canonical spin glass behavior with freezing temperature 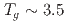 ~K; the ZF and LF-
~K; the ZF and LF- SR time spectra exhibit results similar to those observed in dilute alloy spin glasses CuMn and AuFe, with a critical behavior of
SR time spectra exhibit results similar to those observed in dilute alloy spin glasses CuMn and AuFe, with a critical behavior of  at
at 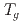 and
and 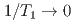 as
as 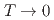 . The absence of spin dynamics at low temperatures makes a clear contrast to the spin dynamics observed by
. The absence of spin dynamics at low temperatures makes a clear contrast to the spin dynamics observed by  SR in many geometrically frustrated spin systems on insulating kagome, pyrochlore, and triangular lattices. The spin glass behavior of CoSn doped with dilute Fe moments is shown to originate primarily from the randomness of doped Fe moments rather than due to geometrical frustration of the underlying lattice.
SR in many geometrically frustrated spin systems on insulating kagome, pyrochlore, and triangular lattices. The spin glass behavior of CoSn doped with dilute Fe moments is shown to originate primarily from the randomness of doped Fe moments rather than due to geometrical frustration of the underlying lattice.
 CoSi
CoSi山内 宏樹; Sari, D. P.*; 安井 幸夫*; 坂倉 輝俊*; 木村 宏之*; 中尾 朗子*; 大原 高志; 本田 孝志*; 樹神 克明; 井川 直樹; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(1), p.013144_1 - 013144_9, 2024/02
 -Mn-type family alloys Mn
-Mn-type family alloys Mn
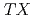 have three-dimensional antiferromagnetic (AFM) corner-shared triangular network. The antiferromagnet Mn
have three-dimensional antiferromagnetic (AFM) corner-shared triangular network. The antiferromagnet Mn RhSi shows magnetic short-range order (SRO) over a wide temperature range of approximately 500 K above the N
RhSi shows magnetic short-range order (SRO) over a wide temperature range of approximately 500 K above the N el temperature
el temperature  = 190 K. Mn
= 190 K. Mn CoSi has the smallest lattice parameter and the lowest
CoSi has the smallest lattice parameter and the lowest  in the family compounds. The quantum critical point (QCP) from AFM to the quantum paramagnetic state is expected near a cubic lattice parameter of 6.15
in the family compounds. The quantum critical point (QCP) from AFM to the quantum paramagnetic state is expected near a cubic lattice parameter of 6.15 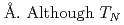 of Mn
of Mn CoSi is only 140 K, quantum critical behavior is observed in Mn
CoSi is only 140 K, quantum critical behavior is observed in Mn CoSi as the enhancement of the electronic specific heat coefficient
CoSi as the enhancement of the electronic specific heat coefficient  . We study how the magnetic SRO appears in Mn
. We study how the magnetic SRO appears in Mn CoSi by using neutron scattering,
CoSi by using neutron scattering,  SR, and physical property measurements. The experimental results show that the neutron scattering intensity of the magnetic SRO does not change much regardless of the suppressed magnetic moment in the long-range magnetic ordered state compared to those of Mn
SR, and physical property measurements. The experimental results show that the neutron scattering intensity of the magnetic SRO does not change much regardless of the suppressed magnetic moment in the long-range magnetic ordered state compared to those of Mn RhSi. The initial asymmetry drop ratio of
RhSi. The initial asymmetry drop ratio of  SR above
SR above  becomes small, and the magnetic SRO temperature
becomes small, and the magnetic SRO temperature 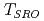 is suppressed to 240 K. The results suggest that the Mn
is suppressed to 240 K. The results suggest that the Mn CoSi is close to the QCP in the Mn
CoSi is close to the QCP in the Mn
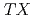 system.
system.
山田 椋平*; 玉熊 佑紀*; 桑田 遥*; 三枝 裕美*; 渡邊 裕貴; 廣田 誠子*; Jin, Q.*; Cai, Y.*
保健物理(インターネット), 58(3), p.169 - 177, 2023/11
本報告は、2023年6月29日と30日の2日間にわたり開催された第1回日本保健物理学会・日本放射線安全管理学会合同シンポジウム(オンライン)の概要について報告するものである。
 100 MeV/nucleon
100 MeV/nucleonPohl, T.*; Sun, Y. L.*; Obertelli, A.*; Lee, J.*; G mez-Ramos, M.*; 緒方 一介*; 吉田 数貴; Cai, B. S.*; Yuan, C. X.*; Brown, B. A.*; et al.
mez-Ramos, M.*; 緒方 一介*; 吉田 数貴; Cai, B. S.*; Yuan, C. X.*; Brown, B. A.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 130(17), p.172501_1 - 172501_8, 2023/04
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:88.25(Physics, Multidisciplinary)大きなフェルミ面非対称性を持つ陽子過剰な O原子核からの100MeV/nucleonでの陽子による陽子・中性子除去反応について報告した。この結果は、quasi-freeノックアウト反応、非弾性散乱、核子移行反応を含む複数の反応機構の定量的寄与を初めて示すものである。このようなエネルギー領域では通常無視される非弾性散乱と核子移行の寄与が、弱束縛陽子と強束縛中性子の除去反応断面積にそれぞれ約50%と30%寄与していることが示された。
O原子核からの100MeV/nucleonでの陽子による陽子・中性子除去反応について報告した。この結果は、quasi-freeノックアウト反応、非弾性散乱、核子移行反応を含む複数の反応機構の定量的寄与を初めて示すものである。このようなエネルギー領域では通常無視される非弾性散乱と核子移行の寄与が、弱束縛陽子と強束縛中性子の除去反応断面積にそれぞれ約50%と30%寄与していることが示された。
 ;
;  SR studies and charge-spin percolation model
SR studies and charge-spin percolation modelSheng, Q.*; 金子 竜也*; Yamakawa, Kohtaro*; Guguchia, Z.*; Gong, Z.*; Zhao, G.*; Dai, G.*; Jin, C.*; Guo, S.*; Fu, L.*; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 4(3), p.033172_1 - 033172_14, 2022/09
A pyrite system NiS Se
Se exhibits a bandwidth controlled Mott transition via (S,Se) substitutions in a two-step process: the antiferromagnetic insulator (AFI) to antiferromagnetic metal (AFM) transition at
exhibits a bandwidth controlled Mott transition via (S,Se) substitutions in a two-step process: the antiferromagnetic insulator (AFI) to antiferromagnetic metal (AFM) transition at 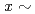 0.45 followed by the AFM to paramagnetic metal (PMM) transition at
0.45 followed by the AFM to paramagnetic metal (PMM) transition at 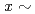 1.0. Among a few other Mott systems which exhibit similar two-step transitions, Ni(S,Se)
1.0. Among a few other Mott systems which exhibit similar two-step transitions, Ni(S,Se) is of particular interest because a large intermediate AFM region in the phase diagram would provide unique opportunities to study the interplay between the spin and charge order. By comparing and combining our muon spin relaxation studies and previous neutron scattering studies, here we propose a picture where the spin order is maintained by the percolation of "nonmetallic" localized and dangling Ni moments surrounded by S, while the charge transition from AFI to AFM is caused by the percolation of the conducting paths generated by the Ni-Se-Ni bonds.
is of particular interest because a large intermediate AFM region in the phase diagram would provide unique opportunities to study the interplay between the spin and charge order. By comparing and combining our muon spin relaxation studies and previous neutron scattering studies, here we propose a picture where the spin order is maintained by the percolation of "nonmetallic" localized and dangling Ni moments surrounded by S, while the charge transition from AFI to AFM is caused by the percolation of the conducting paths generated by the Ni-Se-Ni bonds.
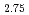 GeTe
GeTe
Bao, S.*; Wang, W.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Cai, Z.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Huang, Z.*; Si, W.*; Ma, Z.*; 梶本 亮一; 池内 和彦*; et al.
Physical Review X, 12(1), p.011022_1 - 011022_15, 2022/02
被引用回数:35 パーセンタイル:93.99(Physics, Multidisciplinary)In the local or itinerant extreme, magnetic excitations can be described by the Heisenberg model which treats electron spins as localized moments, or by the itinerant-electron model where the exchange interaction between electrons leads to unequal numbers of electrons with up and down spins. However, the nature of the magnetic excitations has been elusive when both local moments and itinerant electrons are present in the intermediate range. Using inelastic neutron scattering, we provide direct spectroscopic evidence on the coexistence of and interplay between local moments and itinerant electrons in a van der Waals metallic ferromagnet Fe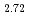 GeTe
GeTe , which can sustain tunable room-temperature ferromagnetism down to the monolayer limit. We find that there exist ferromagnetic spin-wave excitations dispersing from the zone center at low energies resulting from local moments and a columnlike broad continuum at the zone boundary at high energies up to over 100 meV resulting from itinerant electrons. Unlike the two-dimensional crystal structure, the low-energy mode exhibits a three-dimensional nature, and the high-energy mode also has an out-of-plane dependence. Both modes persist well above the Curie temperature of 160 K. Our neutron spectroscopic data reveal that the low-energy spin waves at 100 K are more coherent than those at 4 K, which is evidence of the weakening of the Kondo screening at high temperatures. These results unambiguously demonstrate the coexistence of local moments and itinerant electrons and the Kondo effect between these two components in Fe
, which can sustain tunable room-temperature ferromagnetism down to the monolayer limit. We find that there exist ferromagnetic spin-wave excitations dispersing from the zone center at low energies resulting from local moments and a columnlike broad continuum at the zone boundary at high energies up to over 100 meV resulting from itinerant electrons. Unlike the two-dimensional crystal structure, the low-energy mode exhibits a three-dimensional nature, and the high-energy mode also has an out-of-plane dependence. Both modes persist well above the Curie temperature of 160 K. Our neutron spectroscopic data reveal that the low-energy spin waves at 100 K are more coherent than those at 4 K, which is evidence of the weakening of the Kondo screening at high temperatures. These results unambiguously demonstrate the coexistence of local moments and itinerant electrons and the Kondo effect between these two components in Fe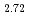 GeTe
GeTe . Such behaviors are generally expected in heavy-fermion systems with heavy
. Such behaviors are generally expected in heavy-fermion systems with heavy  electrons but are rarely clearly observed in materials with light
electrons but are rarely clearly observed in materials with light  electrons. These findings shed light on the understanding of magnetism in transition-metal compounds.
electrons. These findings shed light on the understanding of magnetism in transition-metal compounds.
 Cu
Cu TeO
TeO
Shangguan, Y.*; Bao, S.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Cai, Z.*; Wang, W.*; Huang, Z.*; Ma, Z.*; Liao, J.*; Zhao, X.*; 梶本 亮一; et al.
Physical Review B, 104(22), p.224430_1 - 224430_8, 2021/12
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:10.80(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Dimerized magnets forming alternating Heisenberg chains exhibit quantum coherence and entanglement and thus can find potential applications in quantum information and computation. However, magnetic systems typically undergo thermal decoherence at finite temperatures. Here, we show inelastic neutron scattering results on an alternating antiferromagnetic-ferromagnetic chain compound Na Cu
Cu TeO
TeO that the excited quasiparticles can counter thermal decoherence and maintain strong correlations at elevated temperatures. At low temperatures, we observe clear dispersive singlet-triplet excitations arising from the dimers formed along the crystalline
that the excited quasiparticles can counter thermal decoherence and maintain strong correlations at elevated temperatures. At low temperatures, we observe clear dispersive singlet-triplet excitations arising from the dimers formed along the crystalline  -axis. The excitation gap is of
-axis. The excitation gap is of  18 meV and the bandwidth is about half of the gap. The band top energy has a weak modulation along the [100] direction, indicative of a small interchain coupling. The gap increases while the bandwidth decreases with increasing temperature, leading to a strong reduction in the available phase space for the triplons. As a result, the Lorentzian-type energy broadening becomes highly asymmetric as the temperature is raised. These results are associated with a strongly correlated state resulting from hard-core constraint and quasiparticle interactions. We consider these results to be not only evidence for strong correlations at finite temperatures in Na
18 meV and the bandwidth is about half of the gap. The band top energy has a weak modulation along the [100] direction, indicative of a small interchain coupling. The gap increases while the bandwidth decreases with increasing temperature, leading to a strong reduction in the available phase space for the triplons. As a result, the Lorentzian-type energy broadening becomes highly asymmetric as the temperature is raised. These results are associated with a strongly correlated state resulting from hard-core constraint and quasiparticle interactions. We consider these results to be not only evidence for strong correlations at finite temperatures in Na Cu
Cu TeO
TeO , but also for the universality of the strongly correlated state in a broad range of quantum magnetic systems.
, but also for the universality of the strongly correlated state in a broad range of quantum magnetic systems.
Yao, Y.*; Cai, R.*; Yang, S.-H.*; Xing, W.*; Ma, Y.*; 森 道康; Ji, Y.*; 前川 禎通; Xie, X.-C.*; Han, W.*
Physical Review B, 104(10), p.104414_1 - 104414_6, 2021/09
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:42.22(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We report the experimental observation of half-integer Shapiro steps in the strong ferromagnetic Josephson junction (Nb-NiFe-Nb) by investigating the current-phase relation under radio-frequency microwave excitation. The half-integer Shapiro steps are robust in a wide temperature range from T = 4 to 7 K. The half-integer Shapiro steps could be attributed to co-existence of 0- and  -states in the strong ferromagnetic NiFe Josephson junctions with the spatial variation of the NiFe thickness. This scenario is also supported by the high-resolution transmission electron microscopy characterization of the Nb/NiFe/Nb junction.
-states in the strong ferromagnetic NiFe Josephson junctions with the spatial variation of the NiFe thickness. This scenario is also supported by the high-resolution transmission electron microscopy characterization of the Nb/NiFe/Nb junction.
Lam, T.-N.*; Lee, S. Y.*; Tsou, N.-T.*; Chou, H.-S.*; Lai, B.-H.*; Chang, Y.-J.*; Feng, R.*; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.; Liaw, P. K.*; et al.
Acta Materialia, 201, p.412 - 424, 2020/12
被引用回数:43 パーセンタイル:90.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We examined fatigue-crack-growth behaviors of CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloys (HEAs) under as-fatigued and tensile-overloaded conditions using neutron-diffraction measurements coupled with diffraction peak-profile analyses. We applied both high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) and neutron-diffraction strain mapping for the complementary microstructure examinations. Immediately after a single tensile overload, the crack-growth-retardation period was obtained by enhancing the fatigue resistance, as compared to the as-fatigued condition. The combined mechanisms of the overload-induced larger plastic deformation, the enlarged compressive residual stresses and plastic-zone size, the crack-tip blunting ahead of the crack tip, and deformation twinning governed the pronounced macroscopic crack-growth-retardation behavior following the tensile overload.
 TeO
TeO
Bao, S.*; Cai, Z.*; Si, W.*; Wang, W.*; Wang, X.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Ma, Z.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; 梶本 亮一; 池内 和彦*; et al.
Physical Review B, 101(21), p.214419_1 - 214419_8, 2020/06
被引用回数:21 パーセンタイル:72.45(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We perform thermodynamic and inelastic neutron scattering (INS) measurements to study the lattice dynamics (phonons) of a cubic collinear antiferromagnet Cu TeO
TeO which hosts topological spin excitations (magnons). While the specific heat and thermal conductivity results show that the thermal transport is dominated by phonons, the deviation of the thermal conductivity from a pure phononic model indicates that there is a strong coupling between magnons and phonons. In the INS measurements, we find a mode in the excitation spectra at 4.5 K, which exhibits a slight downward dispersion around the Brillouin zone center. This mode disappears above the N
which hosts topological spin excitations (magnons). While the specific heat and thermal conductivity results show that the thermal transport is dominated by phonons, the deviation of the thermal conductivity from a pure phononic model indicates that there is a strong coupling between magnons and phonons. In the INS measurements, we find a mode in the excitation spectra at 4.5 K, which exhibits a slight downward dispersion around the Brillouin zone center. This mode disappears above the N el temperature and thus cannot be a phonon. Furthermore, the dispersion is distinct from that of a magnon. Instead, it can be explained by the magnon-polaron mode, collective excitations resulting from the hybridization between magnons and phonons. We consider the suppression of the thermal conductivity and emergence of the magnon-polaron mode to be evidence for magnon-phonon coupling in Cu
el temperature and thus cannot be a phonon. Furthermore, the dispersion is distinct from that of a magnon. Instead, it can be explained by the magnon-polaron mode, collective excitations resulting from the hybridization between magnons and phonons. We consider the suppression of the thermal conductivity and emergence of the magnon-polaron mode to be evidence for magnon-phonon coupling in Cu TeO
TeO .
.
 Mn
Mn Sb
Sb
Cai, Z.*; Bao, S.*; Wang, W.*; Ma, Z.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Wang, J.*; Ran, K.*; Li, S.*; 蒲沢 和也*; et al.
Physical Review B, 101(13), p.134408_1 - 134408_10, 2020/04
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:35.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)ディラック物質は量子現象と共にキャリアの役割を探索するのに良い系で、磁気ワイル半金属のSr Mn
Mn Sb
Sb はワイルフェルミオンとマグノンの関係を研究する良い舞台である。本研究では、Sr
はワイルフェルミオンとマグノンの関係を研究する良い舞台である。本研究では、Sr Mn
Mn Sb
Sb の単結晶の中性子非弾性散乱実験を行い、磁性Mn層の分散は約76meVまで広がり、層間の分散は6meVの狭いバンド幅を持つことを見出した。また、これらの実験結果はハイゼンベルグ・スピンハミルトニアンを用いた線形スピン波理論によって再現可能である。本研究では、ワイルフェルミオンとマグノンが共存しているにもかかわらず、Sr
の単結晶の中性子非弾性散乱実験を行い、磁性Mn層の分散は約76meVまで広がり、層間の分散は6meVの狭いバンド幅を持つことを見出した。また、これらの実験結果はハイゼンベルグ・スピンハミルトニアンを用いた線形スピン波理論によって再現可能である。本研究では、ワイルフェルミオンとマグノンが共存しているにもかかわらず、Sr Mn
Mn Sb
Sb 中のワイルフェルミオンが磁気ダイナミクスに影響を与えているという明確な証拠は得られなかった。これは、ワイルフェルミオンとマグノンがSb層とMn層に別々に存在し、この擬二次元性による層間結合の弱さに起因するもの考えられる。
中のワイルフェルミオンが磁気ダイナミクスに影響を与えているという明確な証拠は得られなかった。これは、ワイルフェルミオンとマグノンがSb層とMn層に別々に存在し、この擬二次元性による層間結合の弱さに起因するもの考えられる。
 Bi
Bi Se
Se
Wang, J.*; Ran, K.*; Li, S.*; Ma, Z.*; Bao, S.*; Cai, Z.*; Zhang, Y.*; 中島 健次; 河村 聖子;  erm
erm k, P.*; et al.
k, P.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 10, p.2802_1 - 2802_6, 2019/06
被引用回数:22 パーセンタイル:77.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Superconductivity mediated by phonons is typically conventional, exhibiting a momentum-independent  -wave pairing function, due to the isotropic interactions between electrons and phonons along different crystalline directions. Here, by performing inelastic neutron scattering measurements on a superconducting single crystal of Sr
-wave pairing function, due to the isotropic interactions between electrons and phonons along different crystalline directions. Here, by performing inelastic neutron scattering measurements on a superconducting single crystal of Sr Bi
Bi Se
Se , a prime candidate for realizing topological superconductivity by doping the topo-logical insulator Bi
, a prime candidate for realizing topological superconductivity by doping the topo-logical insulator Bi Se
Se , we found that there exist singular phonons, with the linewidths of the acoustic phonons increasing substantially at long wavelengths, but only for those along the [001] direction. This observation indicates a large and singular electron-phonon coupling at small momenta, which we propose to give rise to the exotic
, we found that there exist singular phonons, with the linewidths of the acoustic phonons increasing substantially at long wavelengths, but only for those along the [001] direction. This observation indicates a large and singular electron-phonon coupling at small momenta, which we propose to give rise to the exotic  -wave nematic superconducting pairing in the MxBi
-wave nematic superconducting pairing in the MxBi Se
Se (M = Cu, Sr, Nb) superconductor family. Therefore, we show that these superconductors may be the first examples where electron-phonon interaction can induce more exotic superconducting pairing than the
(M = Cu, Sr, Nb) superconductor family. Therefore, we show that these superconductors may be the first examples where electron-phonon interaction can induce more exotic superconducting pairing than the  -wave.
-wave.
 T
T As
As (
( = Co,Ni)
= Co,Ni)Tam, D. M.*; Song, Y.*; Man, H.*; Cheung, S. C.*; Yin, Z.*; Lu, X.*; Wang, W.*; Frandsen, B. A.*; Liu, L.*; Gong, Z.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 95(6), p.060505_1 - 060505_6, 2017/02
被引用回数:24 パーセンタイル:68.68(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We use neutron diffraction and muon spin relaxation to study the effect of in-plane uniaxial pressure on the antiferromagnetic (AF) orthorhombic phase in BaFe T
T As
As and its Co- and Ni-substituted members near optimal superconductivity. In the low-temperature AF ordered state, uniaxial pressure necessary to detwin the orthorhombic crystals also increases the magnetic ordered moment, reaching an 11% increase under 40 MPa for BaFe
and its Co- and Ni-substituted members near optimal superconductivity. In the low-temperature AF ordered state, uniaxial pressure necessary to detwin the orthorhombic crystals also increases the magnetic ordered moment, reaching an 11% increase under 40 MPa for BaFe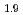 Co
Co As
As , and a 15% increase for BaFe
, and a 15% increase for BaFe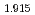 Ni
Ni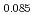 As
As . We also observe an increase of the AF ordering temperature (
. We also observe an increase of the AF ordering temperature (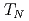 ) of about 0.25 K/MPa in all compounds, consistent with density functional theory calculations that reveal better Fermi surface nesting for itinerant electrons under uniaxial pressure. The doping dependence of the magnetic ordered moment is captured by combining dynamical mean field theory with density functional theory, suggesting that the pressure-induced moment increase near optimal superconductivity is closely related to quantum fluctuations and the nearby electronic nematic phase.
) of about 0.25 K/MPa in all compounds, consistent with density functional theory calculations that reveal better Fermi surface nesting for itinerant electrons under uniaxial pressure. The doping dependence of the magnetic ordered moment is captured by combining dynamical mean field theory with density functional theory, suggesting that the pressure-induced moment increase near optimal superconductivity is closely related to quantum fluctuations and the nearby electronic nematic phase.
Frandsen, B. A.*; Liu, L.*; Cheung, S. C.*; Guguchia, Z.*; Khasanov, R.*; Morenzoni, E.*; Munsie, T. J. S.*; Hallas, A. M.*; Wilson, M. N.*; Cai, Y.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 7, p.12519_1 - 12519_8, 2016/08
被引用回数:36 パーセンタイル:76.64(Multidisciplinary Sciences)RENiO (RE = rare-earth element) and V
(RE = rare-earth element) and V O
O are archetypal Mott insulator systems. When tuned by chemical substitution (RENiO
are archetypal Mott insulator systems. When tuned by chemical substitution (RENiO ) or pressure (V
) or pressure (V O
O ), they exhibit a quantum phase transition (QPT) between an antiferromagnetic Mott insulating state and a paramagnetic metallic state. Because novel physics often appears near a Mott QPT, the details of this transition, such as whether it is first or second order, are important. Here, we demonstrate through muon spin relaxation/rotation experiments that the QPT in RENiO
), they exhibit a quantum phase transition (QPT) between an antiferromagnetic Mott insulating state and a paramagnetic metallic state. Because novel physics often appears near a Mott QPT, the details of this transition, such as whether it is first or second order, are important. Here, we demonstrate through muon spin relaxation/rotation experiments that the QPT in RENiO and V
and V O
O is first order: the magnetically ordered volume fraction decreases to zero at the QPT, resulting in a broad region of intrinsic phase separation, while the ordered magnetic moment retains its full value until it is suddenly destroyed at the QPT. These findings bring to light a surprising universality of the pressure-driven Mott transition, revealing the importance of phase separation and calling for further investigation into the nature of quantum fluctuations underlying the transition.
is first order: the magnetically ordered volume fraction decreases to zero at the QPT, resulting in a broad region of intrinsic phase separation, while the ordered magnetic moment retains its full value until it is suddenly destroyed at the QPT. These findings bring to light a surprising universality of the pressure-driven Mott transition, revealing the importance of phase separation and calling for further investigation into the nature of quantum fluctuations underlying the transition.
 Cu
Cu N
N O
O as seen via resonant inelastic X-ray scattering
as seen via resonant inelastic X-ray scattering石井 賢司; 筒井 健二; 池内 和彦*; Jarrige, I.; 水木 純一郎; 平賀 晴弘*; 山田 和芳*; 遠山 貴己*; 前川 禎通; 遠藤 康夫*; et al.
Physical Review B, 85(10), p.104509_1 - 104509_5, 2012/03
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:13.88(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We perform a resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS) study of Ni-substituted La CuO
CuO and Cu-substituted La
and Cu-substituted La NiO
NiO .Resonantly enhanced charge-transfer excitations are successfully observed by tuning the incident photon energy to the
.Resonantly enhanced charge-transfer excitations are successfully observed by tuning the incident photon energy to the  -edge of the substituted element. These excitations display a very weak momentum dependence, evidencing their local character. We find a shift in the energy of the onset edge of these features compared with the non-substituted compounds La
-edge of the substituted element. These excitations display a very weak momentum dependence, evidencing their local character. We find a shift in the energy of the onset edge of these features compared with the non-substituted compounds La CuO
CuO and La
and La NiO
NiO . This shift is quantitatively reproduced by exact diagonalization calculations of the RIXS spectra. RIXS is shown to be a powerful tool to probe the electronic states of substituted elements and to understand their interaction with surrounding atoms.
. This shift is quantitatively reproduced by exact diagonalization calculations of the RIXS spectra. RIXS is shown to be a powerful tool to probe the electronic states of substituted elements and to understand their interaction with surrounding atoms.
 Cu
Cu Ni
Ni O
O
石井 賢司; 池内 和彦*; Jarrige, I.; 水木 純一郎; 平賀 晴弘*; 山田 和芳*; 筒井 健二; 遠山 貴己*; 前川 禎通*; 遠藤 康夫*; et al.
Physica C, 470(Suppl.1), p.S155 - S157, 2010/12
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Applied)Substitution of a specific element for a component is often used to elucidate its role in the superconductors. For a complete understanding of the substitution effect not only on the superconductivity but also on the electronic states, element-selective experiments are required. In this respect, resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS) has proven to be a powerful experimental technique enabling element-selective diagnosis of charge excitations. By tuning the incident photon energy to a given absorption edge of the element, the excitations involving the element are resonantly enhanced. In addition, RIXS has the advantage that momentum dependence can be measured. Using RIXS, we have measured the electronic excitations at the substituting sites in La Cu
Cu Ni
Ni O
O and La
and La Ni
Ni Cu
Cu O
O . Near the absorption edge of the substituting element, namely the Ni
. Near the absorption edge of the substituting element, namely the Ni  -edge for La
-edge for La Cu
Cu Ni
Ni O
O and the Cu
and the Cu  -edge for La
-edge for La Ni
Ni Cu
Cu O
O , charge transfer excitations from the 2
, charge transfer excitations from the 2 level of neighboring oxygen to the upper Hubbard band of the substituted Ni/Cu are observed. Experimental spectra are qualitatively reproduced by a theoretical calculation based on a
level of neighboring oxygen to the upper Hubbard band of the substituted Ni/Cu are observed. Experimental spectra are qualitatively reproduced by a theoretical calculation based on a  -
- model.
model.
Jarrige, I.; Cai, Y. Q.*; 石井 啓文*; 平岡 望*; Bleuzen, A.*
Applied Physics Letters, 93(5), p.054101_1 - 054101_3, 2008/08
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:35.59(Physics, Applied)Charge-transfer excitation is at the source of the photoinduced magnetism observed in several Prussian blue molecule-based magnets. Using resonant inelastic X-ray scattering and X-ray absorption spectroscopy, we probe directly the thermally-activated charge transfer in a photomagnetic Fe-Co cyanide, Cs Co
Co [Fe(CN)
[Fe(CN) ]
]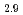 [V]
[V]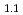 . 16H
. 16H O, where [V] represents [Fe(CN)
O, where [V] represents [Fe(CN) ] vacancies. The temperature dependence of both Co and Fe valence ratios is estimated for the first time in one cooling run, thus yielding a more complete picture of the temperature-induced cooperative electronic modifications. This novel approach, benefiting from relatively short acquisition times, opens the possibility for realtime characterization of the photoinduced magnetism in molecule-based magnets.
] vacancies. The temperature dependence of both Co and Fe valence ratios is estimated for the first time in one cooling run, thus yielding a more complete picture of the temperature-induced cooperative electronic modifications. This novel approach, benefiting from relatively short acquisition times, opens the possibility for realtime characterization of the photoinduced magnetism in molecule-based magnets.
 における圧力下金属絶縁体転移のX線発光と吸収分光法の測定
における圧力下金属絶縁体転移のX線発光と吸収分光法の測定Jarrige, I.; Shieh, S.*; 石井 啓文*; 平岡 望*; Cai, Y.*
no journal, ,
Here we report on a spectroscopic investigation of the intricate interplays between electronic, magnetic and structural properties of LaMnO across its pressure-induced insulator to metal transition (IMT) at 32 GPa. We measure the Mn K-beta fluorescence line by X-ray emission spectroscopy (XES) and the Mn K-egde by X-ray absorption spectroscopy in the partial fluorescence yield mode (PFY-XAS). The XES spectra disclose a high-spin to low-spin transition accompanying the IMT that points to strongly interwoven charge and spin degrees of freedom, which is reminiscent of the Mott perspective. On the other hand, close insight is gained on the structure from the Mn K pre-edge region, where evidence is found for a complete suppression of the Jahn-Teller distortions at the IMT. This is congruent with the scenario that the gap closure results from the progressive pressure-induced degeneracy of the majority-spin eg band, thus suggesting that the IMT in LaMnO
across its pressure-induced insulator to metal transition (IMT) at 32 GPa. We measure the Mn K-beta fluorescence line by X-ray emission spectroscopy (XES) and the Mn K-egde by X-ray absorption spectroscopy in the partial fluorescence yield mode (PFY-XAS). The XES spectra disclose a high-spin to low-spin transition accompanying the IMT that points to strongly interwoven charge and spin degrees of freedom, which is reminiscent of the Mott perspective. On the other hand, close insight is gained on the structure from the Mn K pre-edge region, where evidence is found for a complete suppression of the Jahn-Teller distortions at the IMT. This is congruent with the scenario that the gap closure results from the progressive pressure-induced degeneracy of the majority-spin eg band, thus suggesting that the IMT in LaMnO is not a plain Mott transition.
is not a plain Mott transition.
 CuO
CuO の共鳴非弾性X線散乱
の共鳴非弾性X線散乱石井 賢司; 池内 和彦; Jarrige, I.; 水木 純一郎; 平賀 晴弘*; 山田 和芳*; 筒井 健二; 遠山 貴己*; 前川 禎通*; 石井 啓文*; et al.
no journal, ,
これまでに高温超伝導体のCuをNiに置換した系は非常に数多くの研究がなされてきた。その多くはCu (
(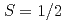 )をNi
)をNi (
(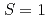 )に置換したと考え、Niを磁性不純物として着目したものであったが、Ni置換は電子状態にも何らかの影響があると予想される。今回、共鳴非弾性X線散乱(RIXS)の元素選択性を利用することによりNi周りの電子状態を抽出することに成功したのでその結果について報告する。本研究で用いた
)に置換したと考え、Niを磁性不純物として着目したものであったが、Ni置換は電子状態にも何らかの影響があると予想される。今回、共鳴非弾性X線散乱(RIXS)の元素選択性を利用することによりNi周りの電子状態を抽出することに成功したのでその結果について報告する。本研究で用いた 吸収端のRIXSでは、CuまたはNiの
吸収端のRIXSでは、CuまたはNiの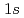 -
-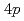 遷移に対応するエネルギーのX線を利用することで、電荷ギャップを越える励起が観測できる。例えば、Niの
遷移に対応するエネルギーのX線を利用することで、電荷ギャップを越える励起が観測できる。例えば、Niの 吸収端でLa
吸収端でLa Cu
Cu Ni
Ni O
O の測定を行うと、中間状態で生成されたNiの
の測定を行うと、中間状態で生成されたNiの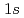 正孔を遮蔽するために周りの酸素
正孔を遮蔽するために周りの酸素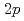 軌道からNiの
軌道からNiの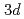 軌道へ電子が遷移する。酸素
軌道へ電子が遷移する。酸素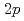 軌道にできたホールはCuとZhang-Rice siglet(ZRS)を形成するので、ZRSとNi(
軌道にできたホールはCuとZhang-Rice siglet(ZRS)を形成するので、ZRSとNi(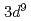 )が存在するような励起状態を観測することになる。同様に、La
)が存在するような励起状態を観測することになる。同様に、La CuO
CuO をCuの
をCuの 吸収端で測定すると、ZRSとCu(
吸収端で測定すると、ZRSとCu(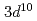 )が生じる励起状態が観測される。今回、La
)が生じる励起状態が観測される。今回、La Cu
Cu Ni
Ni O
O の
の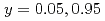 の測定を行い、既に報告されている
の測定を行い、既に報告されている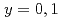 のスペクトルと比較することで、Ni, Cuそれぞれに特徴的な電子状態の議論を行う。
のスペクトルと比較することで、Ni, Cuそれぞれに特徴的な電子状態の議論を行う。
石井 賢司; 筒井 健二; 池内 和彦*; Jarrige, I.; 水木 純一郎; 平賀 晴弘*; 山田 和芳*; 遠山 貴己*; 前川 禎通; 石井 啓文*; et al.
no journal, ,
It is widely recognized that inelastic scattering of neutron and X-ray is a powerful tool to investigate dynamical properties of electrons in the energy-momentum space. Especially, inelastic X-ray scattering has become available in the last decade by utilizing brilliant synchrotron radiation X-rays. When the incident X-ray energy is tuned to an absorption edge of a constituent element of materials, resonantly enhanced electronic excitations are observed, which is called resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS). An additional characteristic arises from the resonant process, namely, the specific element selectively get involved in the observed excitations. While neutron scattering is predominantly sensitive to spin excitations, one can complementarily measure various excitations of electronic degrees of freedom, charge, spin, and orbital, with the RIXS technique. In our presentation, we show an explicit application of the element selectivity: resonant inelastic X-ray scattering of Ni-substituted La CuO
CuO and Cu-substituted La
and Cu-substituted La NiO
NiO . Resonantly enhanced charge-transfer excitations are successfully observed by tuning the incident photon energy to the K-edge of the substituted element. Combined with theoretical calculations, we will discuss the local electronic states around the substituted element which are affected through the interaction with surrounding atoms.
. Resonantly enhanced charge-transfer excitations are successfully observed by tuning the incident photon energy to the K-edge of the substituted element. Combined with theoretical calculations, we will discuss the local electronic states around the substituted element which are affected through the interaction with surrounding atoms.