Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Qin, T. Y.*; Hu, F. F.*; 徐 平光; Zhang, R.*; Su, Y. H.; Ao, N.*; Li, Z. W.*; 篠原 武尚; 菖蒲 敬久; Wu, S. C.*
International Journal of Fatigue, 202, p.109233_1 - 109233_16, 2026/01
The surface induction-hardened S38C medium carbon steel shows a good balance of strength and toughness, but complicates the evaluation of fatigue resistance, mainly because of gradient residual stress (RS) and grains. An integrated fatigue resistance assessment (AIFA) framework was proposed to consider the residual stress relief under stochastic loads. To this end, quasi-in situ neutron diffraction and Bragg-edge imaging were combined to probe the evolution of residual stress during crack propagation. Firstly, a rigid-flexible coupled vehicle dynamics model was adopted to obtain the time-domain variable amplitude loading spectrum. Then, Fortran subroutines were developed to assign these data into full-scale S38C axle model, and the remaining life was predicted using the damage tolerance approach. The results demonstrate that crack propagation would accelerate when residual stress is considered in the case of the crack depth exceeding 3.0 mm. It is, for the first time, found that 15 mm- and 5 mm-thickness fan-shaped specimens can retain the axial and hoop residual strain in terms of diffraction angle variation, respectively, for full-scale structural S38C steel axles. In the absence of RS, the remaining life of the axle decreases sharply from 624,800 to 51,300 km as the crack depth increases from 3.0 to 16 mm. Compared with the standard method under constant amplitude loading without residual stress relief, the present AIFA method provides the more accurate but conservative fatigue life prediction.
深津 勇太; Hu, Q.*; 舘 幸男
Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 276, p.104789_1 - 104789_12, 2026/01
This study investigated the diffusion and sorption behavior of Cs in granitic rocks by conducting through-diffusion experiments using tonalite, granodiorite, and granite samples. The effective diffusion coefficients (De) and distribution coefficients (Kd) of Cs
in granitic rocks by conducting through-diffusion experiments using tonalite, granodiorite, and granite samples. The effective diffusion coefficients (De) and distribution coefficients (Kd) of Cs were evaluated under various KCl concentrations, as potassium is a key competing cation for Cs
were evaluated under various KCl concentrations, as potassium is a key competing cation for Cs sorption. In addition, elemental mapping and mineralogical characterization of solid samples were conducted using laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry and X-ray diffraction, to support the interpretation of Cs
sorption. In addition, elemental mapping and mineralogical characterization of solid samples were conducted using laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry and X-ray diffraction, to support the interpretation of Cs transport. The results showed that rocks with higher biotite content exhibited higher De values and, in some cases, higher Kd values under high KCl conditions (1
transport. The results showed that rocks with higher biotite content exhibited higher De values and, in some cases, higher Kd values under high KCl conditions (1 10
10 mol L
mol L ). At this concentration, formation of a dual profile, characterized by localized Cs enrichment near the inlet boundary, was suppressed. This suppression may be explained by the disappearance of a hydrobiotite peak observed in XRD spectra, suggesting that structural modification of biotite to hydrobiotite was inhibited. As a result, the number of high affinity of Cs
). At this concentration, formation of a dual profile, characterized by localized Cs enrichment near the inlet boundary, was suppressed. This suppression may be explained by the disappearance of a hydrobiotite peak observed in XRD spectra, suggesting that structural modification of biotite to hydrobiotite was inhibited. As a result, the number of high affinity of Cs sorption sites near the sample boundaries was reduced. Furthermore, in all rock types, the De values for Cs
sorption sites near the sample boundaries was reduced. Furthermore, in all rock types, the De values for Cs exceeded those of deuterated water as a neutral tracer. This trend indicates cation excess diffusion, in which Cs
exceeded those of deuterated water as a neutral tracer. This trend indicates cation excess diffusion, in which Cs diffusivity is enhanced by its accumulation in the electrical double layer adjacent to negatively charged surfaces of biotite, occur. Although structural modifications of biotite depending on KCl concentration may have influenced Cs
diffusivity is enhanced by its accumulation in the electrical double layer adjacent to negatively charged surfaces of biotite, occur. Although structural modifications of biotite depending on KCl concentration may have influenced Cs transport, the systematic correlation between biotite content and Cs
transport, the systematic correlation between biotite content and Cs diffusivity provides a consistent explanation in the understanding of matrix diffusion and sorption behaviors among various granitic rock types. These findings demonstrate that cation excess diffusion associated with biotite is a critical mechanism in the control of Cs
diffusivity provides a consistent explanation in the understanding of matrix diffusion and sorption behaviors among various granitic rock types. These findings demonstrate that cation excess diffusion associated with biotite is a critical mechanism in the control of Cs transport in the matrix of crystalline rocks and should be considered in predictive models for repository safety assessments.
transport in the matrix of crystalline rocks and should be considered in predictive models for repository safety assessments.
Zhao, X.*; Zhang, Z.*; 服部 高典; Wang, J.*; Li, L.*; Jia, Y.*; Li, W.*; Xue, J.*; Fan, X.*; Song, R.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 16, p.7713_1 - 7713_8, 2025/08
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00熱効果は、固体状態の冷凍技術の一つの解決策の基盤を成すもので、通常は固体状態の相転移付近で発生し、冷凍温度範囲が限定されている。ここでは、前例のない概念である「全温度帯バロカロリック効果」を導入し実現する。すなわち、KPF において77.5Kから300Kの極めて広い温度範囲(潜在的に4Kまで)で観測される顕著なバカカロリック効果である。この温度範囲は、一般的な室温、液体窒素、液体水素、液体ヘリウムの冷却領域をカバーしている。直接測定されたバーカロリック断熱温度変化は、250MPaの圧力を解放した際に、室温で12K、77.5Kで2.5Kに達する。この効果は、圧力依存性の中性子粉末回折、ラマン散乱解析、第一原理計算により示されるように、菱面体高圧相への持続的な相転移に起因する。構造的不安定性を考慮した熱力学的エネルギーランドスケープを記述する。この独自の全温度帯バロカロリック効果は、従来の多段式シナリオを超えた、高度に適用可能な固体状態冷凍技術への新たなアプローチを提供する。
において77.5Kから300Kの極めて広い温度範囲(潜在的に4Kまで)で観測される顕著なバカカロリック効果である。この温度範囲は、一般的な室温、液体窒素、液体水素、液体ヘリウムの冷却領域をカバーしている。直接測定されたバーカロリック断熱温度変化は、250MPaの圧力を解放した際に、室温で12K、77.5Kで2.5Kに達する。この効果は、圧力依存性の中性子粉末回折、ラマン散乱解析、第一原理計算により示されるように、菱面体高圧相への持続的な相転移に起因する。構造的不安定性を考慮した熱力学的エネルギーランドスケープを記述する。この独自の全温度帯バロカロリック効果は、従来の多段式シナリオを超えた、高度に適用可能な固体状態冷凍技術への新たなアプローチを提供する。
Hu, F. F.*; Qin, T. Y.*; Su, Y. H.; He, L. H.*; Ao, N.*; Parker, J. D.*; 篠原 武尚; Wu, S. C.*
International Journal of Fatigue, 193, p.108826_1 - 108826_14, 2025/04
The relaxation behaviors of residual stress and the influence on the fatigue resistance of S38C axles with induction hardening were investigated by using advanced Bragg-edge transmission imaging and neutron diffraction as well as XFEM-based numerical modeling. The Bragg-edge imaging results indicate that lattice parameters change as the crack develops, which then leads to a decrease of residual strain. In addition, it was observed from neutron diffraction results that all three residual stress components decrease with the crack growth. By contrast, the compressive residual stress in the axle surface was almost fully released when the crack propagated to the matrix material zone. Furthermore, residual stress relaxation was validated by the extended finite element method. These new insights confirm stress relaxation in railway S38C axles during crack propagation, which must be considered while carrying out the structural integrity assessment.
Hu, F.-F.*; Qin, T.-Y.*; Ao, N.*; 徐 平光; Su, Y. H.; Parker, J. D.*; 篠原 武尚; 菖蒲 敬久; Kang, G.-Z.*; Ren, M.-M.; et al.
Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 25(2), p.75 - 93, 2025/04
To accurately predict the remaining lifetime of surface-strengthened railway axles, a damage tolerance method considering three-dimensional (3D) residual stresses was proposed. By taking the induction-hardened carbon steel S38C axle as an example, two-dimensional (2D) distribution characterization of residual strain and 3D residual stress measurement were performed through comprehensive application of the neutron Bragg-edge transmission imaging and angle-dispersive neutron diffraction experiments. A numerical method was employed to implant the 3D residual stress into the axle model, and the remaining lifetime of the full-scale axle was studied by coupling the measured load spectrum, press-fit loads, and residual stresses. Experimental results shows that, both axial and hoop directions present a compressive residual strain gradient layer of about 3 mm, with a maximum compressive residual strain of up to -4500 
 in the surface layer, yet a maximum tensile strain of up to 1000
in the surface layer, yet a maximum tensile strain of up to 1000 
 in the core. The maximum axial and hoop compressive stresses of the axle are about -500 MPa and -303 MPa respectively, while radial stresses overall fluctuate in the zero mean stress range. At depths beyond 4.5 mm from the surface layer, all three components are tensile stresses. The axle surface layer is subjected to compressive residual stresses, and crack propagation does not occur if the crack depth is less than 4.5 mm. Nevertheless, cracks propagate accelerates when the crack depth is greater than 4.5 mm. Different crack propagation depth thresholds lead to a larger calculated remaining lifetime for the residual stress-free condition than for the case where 3D residual stresses are taken into account. However, the axle remaining service mileage of the axle of 227000 Km under the most conservative conditions exceeds 3.5 non-destructive inspection (NDI) cycles, with a large safety margin. The experimental results can provide a scientific reference for the development and optimization of NDI cycles for surface-strengthened railway axles.
in the core. The maximum axial and hoop compressive stresses of the axle are about -500 MPa and -303 MPa respectively, while radial stresses overall fluctuate in the zero mean stress range. At depths beyond 4.5 mm from the surface layer, all three components are tensile stresses. The axle surface layer is subjected to compressive residual stresses, and crack propagation does not occur if the crack depth is less than 4.5 mm. Nevertheless, cracks propagate accelerates when the crack depth is greater than 4.5 mm. Different crack propagation depth thresholds lead to a larger calculated remaining lifetime for the residual stress-free condition than for the case where 3D residual stresses are taken into account. However, the axle remaining service mileage of the axle of 227000 Km under the most conservative conditions exceeds 3.5 non-destructive inspection (NDI) cycles, with a large safety margin. The experimental results can provide a scientific reference for the development and optimization of NDI cycles for surface-strengthened railway axles.
Rajeev, H. S.*; Hu, X.*; Chen, W.-L.*; Zhang, D.*; Chen, T.*; 古府 麻衣子*; 梶本 亮一; 中村 充孝; Chen, A. Z.*; Johnson, G. C.*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 94(3), p.034602_1 - 034602_14, 2025/03
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:66.92(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Two-dimensional hybrid organic-inorganic perovskites (HOIPs) have emerged as promising materials for light-emitting diode applications. In this study, by using time-of-flight neutron spectroscopy we identified and quantitatively separated the lattice vibrational and molecular rotational dynamics of two perovskites, butylammonium lead iodide (BA) PbI
PbI and phenethyl-ammonium lead iodide (PEA)
and phenethyl-ammonium lead iodide (PEA) PbI
PbI . By examining the corresponding temperature dependence, we found that the lattice vibrations, as evidenced by neutron spectra, are consistent with the lattice dynamics obtained from Raman scattering. We revealed that the rotational dynamics of organic molecules in these materials tend to suppress their photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) while the vibrational dynamics did not show predominant correlations with the same. Additionally, we observed photoluminescence emission peak splitting for both systems, which becomes prominent above certain critical temperatures where the suppression of PLQY begins. This study suggests that the rotational motions of polarized molecules may lead to a reduction in exciton binding energy or the breaking of degeneracy in exciton binding energy levels, enhancing non-radiative recombination rates, and consequently reducing photoluminescence yield. These findings offer a deeper understanding of fundamental interactions in 2D HOIPs and could guide the design of more efficient light-emitting materials for advanced technological applications.
. By examining the corresponding temperature dependence, we found that the lattice vibrations, as evidenced by neutron spectra, are consistent with the lattice dynamics obtained from Raman scattering. We revealed that the rotational dynamics of organic molecules in these materials tend to suppress their photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) while the vibrational dynamics did not show predominant correlations with the same. Additionally, we observed photoluminescence emission peak splitting for both systems, which becomes prominent above certain critical temperatures where the suppression of PLQY begins. This study suggests that the rotational motions of polarized molecules may lead to a reduction in exciton binding energy or the breaking of degeneracy in exciton binding energy levels, enhancing non-radiative recombination rates, and consequently reducing photoluminescence yield. These findings offer a deeper understanding of fundamental interactions in 2D HOIPs and could guide the design of more efficient light-emitting materials for advanced technological applications.
 -orbital transition metal multielemental alloy nanoparticles by atomically dispersed 4
-orbital transition metal multielemental alloy nanoparticles by atomically dispersed 4 -orbital Pd for a 100-fold extended lifetime
-orbital Pd for a 100-fold extended lifetimeZhu, B.*; Huang, S.*; Seo, O.*; Cao, M.*; 松村 大樹; Gu, H.*; Wu, D.*
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 147(13), p.11250 - 11256, 2025/02
Earth-abundant 3 -orbital late transition metals are the most used and highly desired catalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) but are prone to quick oxidative dissolution, leading to poor durability. We first report that FeCoNiCu multielemental alloy nanoparticles (MEANPs) can be stabilized with only 0.3 at.%Pd, a 4
-orbital late transition metals are the most used and highly desired catalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) but are prone to quick oxidative dissolution, leading to poor durability. We first report that FeCoNiCu multielemental alloy nanoparticles (MEANPs) can be stabilized with only 0.3 at.%Pd, a 4 -orbital element. Although pure Pd is known for extremely poor OER activity and durability, Pd-FeCoNiCu sustains 1000 h at 10 mA cm
-orbital element. Although pure Pd is known for extremely poor OER activity and durability, Pd-FeCoNiCu sustains 1000 h at 10 mA cm . In an accelerating durability test (ADT) at 100 mA cm
. In an accelerating durability test (ADT) at 100 mA cm , it exhibits a mere 8.9 mV increase over 25 h with a degradation rate of 0.356 mVh
, it exhibits a mere 8.9 mV increase over 25 h with a degradation rate of 0.356 mVh , which is 1/350th that of FeCoNiCu (125 mVh
, which is 1/350th that of FeCoNiCu (125 mVh ) and among the most stable OER catalysts reported so far. Aberration-corrected HAADF-STEM and X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) reveal that atomically dispersed Pd atoms, surrounded by Fe, Co, Ni, and Cu atoms, contributed to a more delocalized electronic structure and stronger bonding via strong
) and among the most stable OER catalysts reported so far. Aberration-corrected HAADF-STEM and X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) reveal that atomically dispersed Pd atoms, surrounded by Fe, Co, Ni, and Cu atoms, contributed to a more delocalized electronic structure and stronger bonding via strong  -
- /
/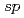 hybridization and the vibronic coupling induced by atomic displacement. The altered local density of states (LDOS) of Fe, Co, Ni, and Cu mitigates the oxidation of FeCoNiCu in OER by over 50%, quantified by hard X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (HAXPES), making the combination of these five dissoluble elements a durable catalyst.
hybridization and the vibronic coupling induced by atomic displacement. The altered local density of states (LDOS) of Fe, Co, Ni, and Cu mitigates the oxidation of FeCoNiCu in OER by over 50%, quantified by hard X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (HAXPES), making the combination of these five dissoluble elements a durable catalyst.
Liu, P.-F.*; Li, X.*; Li, J.*; Zhu, J.*; Tong, Z.*; 古府 麻衣子*; 楡井 真実; Xu, J.*; Yin, W.*; Wang, F.*; et al.
National Science Review, 11(12), p.nwae216_1 - nwae216_10, 2024/12
被引用回数:16 パーセンタイル:91.80(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Crystalline solids exhibiting inherently low lattice thermal conductivity ( ) are of great importance in applications such as thermoelectrics and thermal barrier coatings. However,
) are of great importance in applications such as thermoelectrics and thermal barrier coatings. However,  cannot be arbitrarily low and is limited by the minimum thermal conductivity related to phonon dispersions. In this work, we report the liquid-like thermal transport in a well-ordered crystalline CsAg
cannot be arbitrarily low and is limited by the minimum thermal conductivity related to phonon dispersions. In this work, we report the liquid-like thermal transport in a well-ordered crystalline CsAg Te
Te , which exhibits an extremely low
, which exhibits an extremely low  value of
value of  0.18 Wm
0.18 Wm K
K . On the basis of first-principles calculations and inelastic neutron scattering measurements, we find that there are lots of low-lying optical phonon modes at
. On the basis of first-principles calculations and inelastic neutron scattering measurements, we find that there are lots of low-lying optical phonon modes at  3.1 meV hosting the avoided-crossing behavior with acoustic phonons. These strongly localized modes are accompanied by weakly bound rattling Ag atoms with thermally induced large amplitudes of vibrations. Using the two-channel model, we demonstrate that coupling of the particle-like phonon modes and the heat-carrying wave-like phonons is essential for understanding the low
3.1 meV hosting the avoided-crossing behavior with acoustic phonons. These strongly localized modes are accompanied by weakly bound rattling Ag atoms with thermally induced large amplitudes of vibrations. Using the two-channel model, we demonstrate that coupling of the particle-like phonon modes and the heat-carrying wave-like phonons is essential for understanding the low  , which is heavily deviated from the
, which is heavily deviated from the 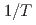 temperature dependence of the standard Peierls theory. In addition, our analysis indicates that the soft structural framework with liquid-like motions of the fluctuating Ag atoms is the underlying cause that leads to the suppression of the heat conduction in CsAg
temperature dependence of the standard Peierls theory. In addition, our analysis indicates that the soft structural framework with liquid-like motions of the fluctuating Ag atoms is the underlying cause that leads to the suppression of the heat conduction in CsAg Te
Te . These factors synergistically account for the ultralow
. These factors synergistically account for the ultralow  value. Our results demonstrate that the liquid-like heat transfer could indeed exist in a well-ordered crystal.
value. Our results demonstrate that the liquid-like heat transfer could indeed exist in a well-ordered crystal.
 SR study on the noncentrosymmetric superconductor NbGe
SR study on the noncentrosymmetric superconductor NbGe
Jiao, J. C.*; Chen, K. W.*; Hillier, A. D.*; 伊藤 孝; 髭本 亘; Li, Z.*; Lv, B.*; Xu, Z.-A.*; Shu, L.*
Physical Review B, 110(21), p.214516_1 - 214516_9, 2024/12
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We report on a muon spin relaxation ( SR) study on the polycrystalline noncentrosymmetric superconductor NbGe
SR) study on the polycrystalline noncentrosymmetric superconductor NbGe with superconducting transition temperature
with superconducting transition temperature  = 2.0-2.1 K. The zero-field
= 2.0-2.1 K. The zero-field  SR experiment indicates the absence of a spontaneous magnetic field in the superconducting state, showing the preservation of time-reversal symmetry in the superconducting state. The transverse-field
SR experiment indicates the absence of a spontaneous magnetic field in the superconducting state, showing the preservation of time-reversal symmetry in the superconducting state. The transverse-field  SR experiment is performed to map the phase diagram of NbGe
SR experiment is performed to map the phase diagram of NbGe , from which clear evidence of both type-I and type-II superconductivities is obtained. More importantly, we clearly delineate the region in the phase diagram where type-I and type-II superconductivities coexist.
, from which clear evidence of both type-I and type-II superconductivities is obtained. More importantly, we clearly delineate the region in the phase diagram where type-I and type-II superconductivities coexist.
Zhu, M.*; Romerio, V.*; Steiger, N.*; Nabi, S. D.*; 村井 直樹; 河村 聖子; Povarov, K. Y.*; Skourski, Y.*; Sibille, R.*; Keller, L.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 133(18), p.186704_1 - 186704_6, 2024/11
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:93.48(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Magnetic, thermodynamic, neutron diffraction and inelastic neutron scattering are used to study spin correlations in the easy-axis XXZ triangular lattice magnet K Co(SeO
Co(SeO )
) . Despite the presence of quasi-2D supersolid magnetic order, the low-energy excitation spectrum contains no sharp modes and is instead a broad and structured multiparticle continuum. Applying a weak magnetic field drives the system into an m = 1/3 fractional magnetization plateau phase and restores sharp spin wave modes. To some extent, the behavior at zero field can be understood in terms of spin wave decay. However, the presence of clear excitation minima at the M points of the Brillouin zone suggest that the spinon language may provide a more adequate description, and signals a possible proximity to a Dirac spin liquid state.
. Despite the presence of quasi-2D supersolid magnetic order, the low-energy excitation spectrum contains no sharp modes and is instead a broad and structured multiparticle continuum. Applying a weak magnetic field drives the system into an m = 1/3 fractional magnetization plateau phase and restores sharp spin wave modes. To some extent, the behavior at zero field can be understood in terms of spin wave decay. However, the presence of clear excitation minima at the M points of the Brillouin zone suggest that the spinon language may provide a more adequate description, and signals a possible proximity to a Dirac spin liquid state.
 -
- transitions
transitionsYang, Q.*; Yang, X.*; Wang, Y.*; Fei, Y.*; Li, F.*; Zheng, H.*; Li, K.*; Han, Y.*; 服部 高典; Zhu, P.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.7778_1 - 7778_9, 2024/09
被引用回数:16 パーセンタイル:91.89(Multidisciplinary Sciences)明るい一重項励起子と三重項励起子を同時に発現する発光材料は、オプトエレクトロニクス、サイネージ、情報暗号化において大きな可能性を秘めている。しかしながら、高性能の白色発光を実現するためには、蛍光と燐光の寄与が不均衡であることが大きな障害となっている。ここでは、水素結合の協同効果による圧力処理エンジニアリングによって、n- -
- 遷移の混合を実現し、イソフタル酸(IPA)中で三重項状態の発光を7%から40%に高めることで、この課題に対処した。加圧処理したIPAでは、蛍光と燐光のハイブリッドに基づく優れた白色発光が得られ、フォトルミネッセンス量子収率は当初の19%(青色発光)から75%に増加した。その場での高圧IRスペクトル、X線回折、中性子回折から、圧力の上昇に伴い水素結合が連続的に強化されることが明らかになった。さらに、この強化された水素結合は、圧力処理後も常圧条件下まで保持され、バランスの取れた一重項/三重項励起子集団のための効率的な系間交差を目的としたIPAに与え、効率的な白色発光をもたらした。この研究は、有機低分子の三重項状態を明るくするルートを提案するだけでなく、一重項励起子と三重項励起子の比率を調節して、高性能の白色発光を構築するものである。
遷移の混合を実現し、イソフタル酸(IPA)中で三重項状態の発光を7%から40%に高めることで、この課題に対処した。加圧処理したIPAでは、蛍光と燐光のハイブリッドに基づく優れた白色発光が得られ、フォトルミネッセンス量子収率は当初の19%(青色発光)から75%に増加した。その場での高圧IRスペクトル、X線回折、中性子回折から、圧力の上昇に伴い水素結合が連続的に強化されることが明らかになった。さらに、この強化された水素結合は、圧力処理後も常圧条件下まで保持され、バランスの取れた一重項/三重項励起子集団のための効率的な系間交差を目的としたIPAに与え、効率的な白色発光をもたらした。この研究は、有機低分子の三重項状態を明るくするルートを提案するだけでなく、一重項励起子と三重項励起子の比率を調節して、高性能の白色発光を構築するものである。
Zhu, L.*; He, H.*; Naeem, M.*; Sun, X.*; Qi, J.*; Liu, P.*; Harjo, S.; 中島 健次; Li, B.*; Wang, X.-L.*
Physical Review Letters, 133(12), p.126701_1 - 126701_6, 2024/09
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:70.50(Physics, Multidisciplinary)It has long been suspected that magnetism could play a vital role in the phase stability of multi- component high-entropy alloys. However, the nature of the magnetic order, if any, has remained elusive. Here, by using elastic and inelastic neutron scattering, we demonstrate evidence of antiferromagnetic order below  80 K and strong spin fluctuations persisting to room temperature in a single-phase face-centered cubic (fcc) CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy. Despite the chemical complexity, the magnetic structure in CrMnFeCoNi can be described as
80 K and strong spin fluctuations persisting to room temperature in a single-phase face-centered cubic (fcc) CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy. Despite the chemical complexity, the magnetic structure in CrMnFeCoNi can be described as  -Mn-like, with the magnetic moments confined in alternating (001) planes and pointing toward the
-Mn-like, with the magnetic moments confined in alternating (001) planes and pointing toward the 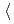 111
111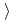 direction. Combined with first-principles calculation results, it is shown that the antiferromagnetic order and spin fluctuations help stabilized the fcc phase in CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy.
direction. Combined with first-principles calculation results, it is shown that the antiferromagnetic order and spin fluctuations help stabilized the fcc phase in CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy.
Ying, H.*; Yang, X.*; He, H.*; Yan, A.*; An, K.*; Ke, Y.*; Wu, Z.*; Tang, S.*; Zhang, Z.*; Dong, H.*; et al.
Scripta Materialia, 250, p.116181_1 - 116181_7, 2024/09
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:75.30(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Nanoscale chemical fluctuations and their effect on the deformation behavior of CrFeCoNi-based high-entropy alloys (HEAs) were investigated using small-angle scattering and in situ neutron diffraction measurements. Small-angle scattering results demonstrated the presence of nano ( 10 nm) chemical fluctuations in the as-prepared CrFeCoNiPd HEAs, which was attributed to the negative mixing of enthalpy and the significant atomic radius difference between Pd and the constituent elements in the CrFeCoNi-based alloys. Subsequent tensile tests demonstrated that the yield and tensile strengths of the as-prepared CrFeCoNiPd HEA surpass those of the as-prepared CrMnFeCoNi HEA. Neutron diffraction data analysis revealed an anomalous response of dislocation evolution with the strain.
10 nm) chemical fluctuations in the as-prepared CrFeCoNiPd HEAs, which was attributed to the negative mixing of enthalpy and the significant atomic radius difference between Pd and the constituent elements in the CrFeCoNi-based alloys. Subsequent tensile tests demonstrated that the yield and tensile strengths of the as-prepared CrFeCoNiPd HEA surpass those of the as-prepared CrMnFeCoNi HEA. Neutron diffraction data analysis revealed an anomalous response of dislocation evolution with the strain.
Hu, F. F.*; Qin, T. Y.*; Ao, N.*; Su, Y. H.; Zhou, L.*; 徐 平光; Parker, J. D.*; 篠原 武尚; Chen, J.*; Wu, S. C.*
Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 306, p.110267_1 - 110267_18, 2024/08
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:35.05(Mechanics)Non-destructive and quantitative mapping of gradient residual strain distribution in surface-hardened railway S38C axles could provide a positive reference for determining service lifetime and maintenance strategy. To tackle this concern, time-of-flight neutron Bragg-edge transmission imaging was employed by real axle samples with and without impacted crater. A novel and simple procedure to formulate the residual strain field was also developed in this work, with the transmission batch code in Appendix A. By mapping the global two- dimensional residual strains, it can be verified that the residual strains into the axle are uniformly distributed in the hoop direction. Subsequently, it was revealed that the axial and hoop residual strains, respectively in the cylinder and the long strip samples prepared from a real S38C hollow axle, indicated a gradient evolution distribution with a depth of  8 mm, covering a range of -5500
8 mm, covering a range of -5500  1000
1000 
 for axial strains and -6500
for axial strains and -6500  1000
1000 
 for hoop strains. More importantly, the maximum compressive lattice strain of the cylinder sample was increased by 15.61%, and 22.35% at the impacting speeds of 100, and 125 m/s, respectively; and that of the long strip sample increased by 29.17%, and 43.70%, respectively. It can thus be concluded that lattice strains have redistributed around the impact crater, demonstrating the local alteration of the residual strain field. These new findings suggest the localized variation in residual strains should be taken into account while evaluating the service damage evolution of railway axles, especially those affected by high-speed impacts during operation.
for hoop strains. More importantly, the maximum compressive lattice strain of the cylinder sample was increased by 15.61%, and 22.35% at the impacting speeds of 100, and 125 m/s, respectively; and that of the long strip sample increased by 29.17%, and 43.70%, respectively. It can thus be concluded that lattice strains have redistributed around the impact crater, demonstrating the local alteration of the residual strain field. These new findings suggest the localized variation in residual strains should be taken into account while evaluating the service damage evolution of railway axles, especially those affected by high-speed impacts during operation.
Qin, T. Y.*; Hu, F. F.*; 徐 平光; Zhang, H.*; Zhou, L.*; Ao, N.*; Su, Y. H.; 菖蒲 敬久; Wu, S. C.*
International Journal of Fatigue, 185, p.108336_1 - 108336_13, 2024/08
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:89.19(Engineering, Mechanical)Gradient distribution of triaxial residual stresses to a depth of several millimeters is retained in middle carbon steel S38C axles after high-frequency induction hardening, which has become a critical concern for fatigue structural integrity. To address this, the axial, hoop, and radial gradient residual strains inside the axles were measured for the first time by advanced neutron diffraction. The SIGINI Fortran subroutine was then adopted to reconstruct the global initial residual stress field from the measured data. Experimental and simulation results show that residual stresses of about -520 MPa (axial), -710 MPa (hoop), and -40 MPa (radial) residual stress were retained below the axle surface. Subsequently, the fatigue crack propagation behavior of S38C axles was numerically investigated in the framework of fracture mechanics. The calculated results clearly show that the compressive residual stresses at a depth of 0?3 mm from the axle surface lead to a low crack growth driving force, and that fatigue cracks do not propagate as long as the crack depth is less than 3.7 mm for hollow S38C axles. These results further indicate that the maximum defect size allowed in routine inspections is acceptable from a safety and economic point of view. Accurate measurement and characterization of the global gradient residual stress field through experiments and simulations can provide an important reference for optimizing the mileage intervals of nondestructive testing (NDT) of surface defects in these surface-strengthened railway axles.
 Tc separation/concentration technology from
Tc separation/concentration technology from  Mo by (n,
Mo by (n,  ) method, 2
) method, 2藤田 善貴; Hu, X.*; Yang, Y.*; 北川 大凱*; 藤原 靖幸*; 吉永 尚生*; 堀 順一*; Do, T. M. D.*; 鈴木 達也*; 末松 久幸*; et al.
KURNS Progress Report 2023, P. 122, 2024/07
核セキュリティ等の観点から放射化法((n, )法)による
)法)による Mo製造の研究開発が進められている。この方法を
Mo製造の研究開発が進められている。この方法を Mo/
Mo/ Tcジェネレータに適用するためには、Mo吸着材として用いられるアルミナ(Al
Tcジェネレータに適用するためには、Mo吸着材として用いられるアルミナ(Al O
O )の特性改善が不可欠である。本報告では、高いMo吸着特性を有すると報告されている2つの文献を基に3種類のアルミナを合成し、ジェネレータへの適用性を評価した。京都大学研究用原子炉(KUR)で照射したMoO
)の特性改善が不可欠である。本報告では、高いMo吸着特性を有すると報告されている2つの文献を基に3種類のアルミナを合成し、ジェネレータへの適用性を評価した。京都大学研究用原子炉(KUR)で照射したMoO を溶解した溶液(Mo濃度10g/L、pH4)に、アルミナを添加し3時間静置した。静置後のアルミナをカラムに移し、24時間ごとに2日間ミルキングを実施した。その結果、全てのアルミナで現行のジェネレータに使用されているアルミナを大きく上回る90mg-Mo/g以上のMo吸着量を得た。一方で、表面に均一な細孔が観察されたアルミナではミルキングにおけるMo脱離量も多かった。したがって、本試験条件においては、アルミナの表面状態はMo吸着特性よりもMo保持能力に大きな影響を与える可能性が示唆された。今後、より実用的な条件下でのジェネレータへの適用性を評価する。
を溶解した溶液(Mo濃度10g/L、pH4)に、アルミナを添加し3時間静置した。静置後のアルミナをカラムに移し、24時間ごとに2日間ミルキングを実施した。その結果、全てのアルミナで現行のジェネレータに使用されているアルミナを大きく上回る90mg-Mo/g以上のMo吸着量を得た。一方で、表面に均一な細孔が観察されたアルミナではミルキングにおけるMo脱離量も多かった。したがって、本試験条件においては、アルミナの表面状態はMo吸着特性よりもMo保持能力に大きな影響を与える可能性が示唆された。今後、より実用的な条件下でのジェネレータへの適用性を評価する。
Zhou, L.*; Zhang, H.*; Qin, T. Y.*; Hu, F. F.*; 徐 平光; Ao, N.*; Su, Y. H.; He, L. H.*; Li, X. H.*; Zhang, J. R.*; et al.
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 55(7), p.2175 - 2185, 2024/07
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:50.84(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)High-speed railway S38C axles undergo surface induction hardening for durability, but are susceptible to fatigue cracks from foreign object impact. The neutron diffraction method was employed to measure the residual strain in S38C axles, obtaining microscopic lattice distortion data, for the gradient layer at a depth of 8 mm under the surface. The results showed that after induction-hardening, the microscopic lattice distortion had a gradient distribution, decreasing with the distance from the surface. However, in the case of impacting speed of 600 km/m, the average microscopic lattice distortion increased with the distance from the surface, reaching a maximum augmentation of 55 pct. These findings indicate a strong experimental basis, and improve our understanding of the relationship between macroscopic residual stress and decision-making, in regard to operation and maintenance.
Ma, Y.*; Naeem, M.*; Zhu, L.*; He, H.*; Sun, X.*; Yang, Z.*; He, F.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Wang, X.-L.*
Acta Materialia, 270, p.119822_1 - 119822_13, 2024/05
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:91.62(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We report an in situ neutron diffraction study of 316 L that reveals an extraordinary work-hardening rate (WHR) of  7 GPa at 15 K. Detailed analyses show that the major contribution to the excellent strength and ductility comes from the transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) effect, introduced by the austenite-to-martensite (
7 GPa at 15 K. Detailed analyses show that the major contribution to the excellent strength and ductility comes from the transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) effect, introduced by the austenite-to-martensite ( -to-
-to- ') phase transition. A dramatic increase in the WHR is observed along with the transformation; the WHR declined when the austenite phase is exhausted. During plastic deformation, the volume-fraction weighted phase stress and stress contribution from the
') phase transition. A dramatic increase in the WHR is observed along with the transformation; the WHR declined when the austenite phase is exhausted. During plastic deformation, the volume-fraction weighted phase stress and stress contribution from the  '-martensite increase significantly. The neutron diffraction data further suggest that the
'-martensite increase significantly. The neutron diffraction data further suggest that the  -to-
-to- ' phase transformation was mediated by the
' phase transformation was mediated by the  -martensite, as evidenced by the concurrent decline of the
-martensite, as evidenced by the concurrent decline of the  phase with the
phase with the  phase.
phase.
Hu, X.*; 藤田 善貴; 土谷 邦彦; 福谷 哲*; 堀 順一*; 鈴木 達也*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 333(11), p.6057 - 6063, 2024/05
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Chemistry, Analytical)難溶性である多孔質MoO ターゲットを使用した新しい
ターゲットを使用した新しい Mo/
Mo/ Tcジェネレータの製造方法を開発している。本方法では、水への溶解度の違いを利用してMoO
Tcジェネレータの製造方法を開発している。本方法では、水への溶解度の違いを利用してMoO から
から Tcを抽出する。まず、作製した多孔質MoO
Tcを抽出する。まず、作製した多孔質MoO ペレットをKUR(京都大学研究用原子炉)を用いて中性子照射した。照射した多孔質MoO
ペレットをKUR(京都大学研究用原子炉)を用いて中性子照射した。照射した多孔質MoO を水へ浸漬させ、
を水へ浸漬させ、 Tcの抽出率を調べた。この結果、MoO
Tcの抽出率を調べた。この結果、MoO から比較的低い
から比較的低い Mo/
Mo/ Tc比で
Tc比で Tcが抽出され、MoO
Tcが抽出され、MoO の水への溶解度は極めて低かった。さらに、
の水への溶解度は極めて低かった。さらに、 Moの溶解度はその他のモリブデンの安定同位体よりも高く、(n,
Moの溶解度はその他のモリブデンの安定同位体よりも高く、(n, )反応により生成された
)反応により生成された Moの溶解におけるホットアトム効果を明らかにした。本方法は、MoO
Moの溶解におけるホットアトム効果を明らかにした。本方法は、MoO ターゲットの再利用も可能で、製造プロセスの持続可能性を有するものであり、(n,
ターゲットの再利用も可能で、製造プロセスの持続可能性を有するものであり、(n, )反応で生成された
)反応で生成された Moを利用した水抽出による
Moを利用した水抽出による Mo/
Mo/ Tcジェネレータの実現が期待できる。
Tcジェネレータの実現が期待できる。
Yuan, X.*; Hu, Q. H.*; Fang, X.*; Wang, Q. M.*; Ma, Y.*; 舘 幸男
Sedimentary Geology, 465, p.106633_1 - 106633_14, 2024/05
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Geology)Archie's cementation factor, m, is a critical parameter for petrophysical studies, and the value is influenced by several factors such as the shape, type, and size of grains, degrees of diagenesis, and associated pore structure. Using integrated experimental and theoretical approaches, the goal of this study is to obtain the cementation factor of rocks (both reservoir rock and caprock) and assess the impact of diagenesis processes on the values of the cementation factor. Thirteen samples of geologically diverse rocks (six mudstones, four fossiliferous limestones, two marbles, and one sandstone) were selected to achieve these research objectives. Two approaches, the diffusion of gas tracers and the Bosanquet formula calculation using pore-throat sizes from mercury intrusion porosimetry analyses, were used to derive the cementation factors of these rock samples. These rocks were categorized into two groups based on the correlation between average pore-throat diameter and diffusivity, and an exponential-law relationship between the cementation factor and porosity was determined for these sample groups. In addition, thin-section petrography and field emission-scanning electron microscopy observations were utilized to investigate diagenetic processes, with four diagenetic patterns being established: (1) strong compaction, strong cementation, and weak dissolution-diagenesis pattern; (2) weak compaction, medium cementation, and weak dissolution-diagenesis pattern; (3) weak compaction, medium cementation, and strong dissolution-diagenesis pattern; and (4) fracture-matrix pattern. The results indicated that diagenetic processes and microfractures contribute to the variability in the cementation factors in these rock samples.