Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
余語 覚文*; Lan, Z.*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; Wei, T.*; 森 隆人*; Golovin, D.*; 早川 岳人*; 岩田 夏弥*; et al.
Physical Review X, 13(1), p.011011_1 - 011011_12, 2023/01
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:88.42(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Neutrons are powerful tools for investigating the structure and properties of materials used in science and technology. Recently, laser-driven neutron sources (LDNS) have attracted the attention of different communities, from science to industry, in a variety of applications, including radiography, spectroscopy, security, and medicine. However, the laser-driven ion acceleration mechanism for neutron generation and for establishing the scaling law on the neutron yield is essential to improve the feasibility of LDNS. In this paper, we report the mechanism that accelerates ions with spectra suitable for neutron generation. We show that the neutron yield increases with the fourth power of the laser intensity, resulting in the neutron generation of 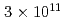 in
in 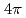 at a maximum, with
at a maximum, with 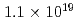 Wcm
Wcm , 900 J, 1.5 ps lasers. By installing a "hand-size" moderator, which is specially designed for the LDNS, it is demonstrated that the efficient generation of epithermal (0.1-100 eV) neutrons enables the single-shot analysis of composite materials by neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA). We achieve the energy resolution of 2.3% for 5.19-eV neutrons 1.8 m downstream of the LDNS. This leads to the analysis of elements and isotopes within sub-
, 900 J, 1.5 ps lasers. By installing a "hand-size" moderator, which is specially designed for the LDNS, it is demonstrated that the efficient generation of epithermal (0.1-100 eV) neutrons enables the single-shot analysis of composite materials by neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA). We achieve the energy resolution of 2.3% for 5.19-eV neutrons 1.8 m downstream of the LDNS. This leads to the analysis of elements and isotopes within sub- s times and allows for high-speed nondestructive inspection.
s times and allows for high-speed nondestructive inspection.
Naeem, M.*; He, H.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Lin, W.*; Kai, J.-J.*; Wu, Z.*; Lan, S.*; Wang, X.-L.*
Acta Materialia, 221, p.117371_1 - 117371_18, 2021/12
被引用回数:31 パーセンタイル:94.34(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We studied the deformation behavior of CrFeCoNi high-entropy alloy by in situ neutron diffraction at room temperature, intermediate low temperature of 140 K, low temperatures of 40 K (no serrated deformation) and 25 K (with massive serrations). The contributions from different deformation mechanisms to the yield strength and strain hardening have been estimated. The athermal contributions to the yield strength were  183 MPa at all temperatures, while the Peierls stress increased significantly at low temperatures (from 148 MPa at room temperature to 493 MPa at 25 K). Dislocations contributed to
183 MPa at all temperatures, while the Peierls stress increased significantly at low temperatures (from 148 MPa at room temperature to 493 MPa at 25 K). Dislocations contributed to  94% strain hardening at room temperature. Although the dislocation strengthening remained the major hardening mechanism at very low temperatures, the planar faults contribution increased steadily from 6% at room temperature to 28% at 25 K.
94% strain hardening at room temperature. Although the dislocation strengthening remained the major hardening mechanism at very low temperatures, the planar faults contribution increased steadily from 6% at room temperature to 28% at 25 K.
Naeem, M.*; Zhou, H.*; He, H.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Lan, S.*; Wu, Z.*; Zhu, Y.*; Wang, X.-L.*
Applied Physics Letters, 119(13), p.131901_1 - 131901_7, 2021/09
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:62.1(Physics, Applied)We investigated the in situ deformation behavior of the CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy at a cryogenic temperature of 140 K and compared it with deformation at room temperature. The sample exhibited higher strength and larger ductility at the cryogenic temperature. The CrCoNi alloy remained single-phase face-centered cubic at room temperature, while deformation at 140 K resulted in a martensitic transformation to the hexagonal close-packed structure. The phase transformation, an additional deformation mechanism to stacking faults, twinning, and dis- location slip, resulted in a higher work hardening at cryogenic temperature. The study addresses the structure metastability in the CrCoNi alloy, which led to the formation of epsilon-martensite from the intrinsic stacking faults.
He, H.*; Naeem, M.*; Zhang, F.*; Zhao, Y.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Wang, B.*; Wu, X.*; Lan, S.*; Wu, Z.*; et al.
Nano Letters, 21(3), p.1419 - 1426, 2021/02
被引用回数:41 パーセンタイル:95.34(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)In CrCoNi, a so-called medium-entropy alloy, an fcc-to-hcp phase transformation has long been anticipated. Here, we report an in situ loading study with neutron diffraction, which revealed a bulk fcc-to-hcp phase transformation in CrCoNi at 15 K under tensile loading. By correlating deformation characteristics of the fcc phase with the development of the hcp phase, it is shown that the nucleation of the hcp phase was triggered by intrinsic stacking faults. The confirmation of a bulk phase transformation adds to the myriads of deformation mechanisms available in CrCoNi, which together underpin the unusually large ductility at low temperatures.
Naeem, M.*; He, H.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Zhang, F.*; Wang, B.*; Lan, S.*; Wu, Z.*; Wu, Y.*; Lu, Z.*; et al.
Scripta Materialia, 188, p.21 - 25, 2020/11
被引用回数:56 パーセンタイル:97.51(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)The deformation behavior of CrMnFeCoNi high entropy alloy was investigated by in situ neutron diffraction at an ultralow temperature of 15 K. Analysis of the diffraction peak widths showed an extremely high dislocation density at 15 K, reaching  10
10 m
m . In addition, the dislocation density was found to closely follow the development of texture caused by deformation. In contrast to deformation by dislocation slip at room temperature, the ultralow-temperature deformation also involved stacking faults, twinning and serrations. The deformation pathway at ultralow temperature is outlined which is responsible for the extraordinary strength-ductility combination.
. In addition, the dislocation density was found to closely follow the development of texture caused by deformation. In contrast to deformation by dislocation slip at room temperature, the ultralow-temperature deformation also involved stacking faults, twinning and serrations. The deformation pathway at ultralow temperature is outlined which is responsible for the extraordinary strength-ductility combination.
Naeem, M.*; He, H.*; Zhang, F.*; Huang, H.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Wang, B.*; Lan, S.*; Wu, Z.*; Wang, F.*; et al.
Science Advances (Internet), 6(13), p.eaax4002_1 - eaax4002_8, 2020/03
被引用回数:145 パーセンタイル:99.09(Multidisciplinary Sciences)High-entropy alloys exhibit exceptional mechanical properties at cryogenic temperatures, due to the activation of twinning in addition to dislocation slip. The coexistence of multiple deformation pathways raises an important question regarding how individual deformation mechanisms compete or synergize during plastic deformation. Using in situ neutron diffraction, we demonstrate the interaction of a rich variety of deformation mechanisms in high-entropy alloys at 15 K, which began with dislocation slip, followed by stacking faults and twinning, before transitioning to inhomogeneous deformation by serrations. Quantitative analysis showed that the cooperation of these different deformation mechanisms led to extreme work hardening. The low stacking fault energy plus the stable face-centered cubic structure at ultralow temperatures, enabled by the high-entropy alloying, played a pivotal role bridging dislocation slip and serration.
Lan, Z.*; 余語 覚文*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; 早川 岳人*; 小泉 光生; Wei, T.*; Shi, B.*; 石本 崇*; Golovin, D.*; 森 隆人*; et al.
no journal, ,
High penetration power of neutrons is potentially useful for realizing opaque object analysis in non-destructive way. Large-scale particle accelerators and nuclear reactors are mostly used for development of neutron analyzing method. A Laser-Driven Neutron Source (LDNS) has been proposed as a new approach of neutron generation for non-destructive analysis. Demonstration experiments on neutron resonance measurement ware performed at ILE, Osaka Univ., Japan. The Peta-watt laser LFEX was used to shoot a CD (deuterated plastic) foil target to produce accelerated charged deuterons. Neutrons are generated by nuclear reaction between a cylindrical beryllium and the accelerated deuteron, and then moderated by a high-density polyethylene (HDP). Neutrons of 1 20 eV were observed with a neutron detector at a 1.8 m using neutron resonance diagnosis technology. This report describes the results of the first experimental demonstration.
20 eV were observed with a neutron detector at a 1.8 m using neutron resonance diagnosis technology. This report describes the results of the first experimental demonstration.
余語 覚文*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; 岩本 晃史*; 早川 岳人*; 小泉 光生; Golovin, D.*; 森 隆人*; Lan, Z.*; et al.
no journal, ,
大阪大学のLFEXレーザー施設において、大強度レーザーを用いたパルス中性子源(LDNS)の開発およびそれを利用した応用研究を進めている。レーザーは、パルス巾が1.5psで、最大出力は、1kJ(1.5 10
10 Wcm
Wcm である。開発した中性子源は1cm程度の大きさで、数十マイクロメータに収束したレーザーをターゲットに照射し、それによって生成したMeVもの高速イオン(水素や重水素粒子)を直径5mmのベリリウムに当てて、核反応により中性子を生成するものである。中性子の生成量は、1ショットあたり10
である。開発した中性子源は1cm程度の大きさで、数十マイクロメータに収束したレーザーをターゲットに照射し、それによって生成したMeVもの高速イオン(水素や重水素粒子)を直径5mmのベリリウムに当てて、核反応により中性子を生成するものである。中性子の生成量は、1ショットあたり10 で、この生成量は、入射エネルギーの4乗で増加することが分かった。さらに、生成した中性子を数cmの大きさのモデレータで減速させ、離れた位置に設置した中性子検出器により、中性子発生から検出までの飛行時間を測定するTOF測定を行った。試料を透過させて中性子の減衰を調べる実験を行った結果、核反応の共鳴による減衰の観測に成功した。
で、この生成量は、入射エネルギーの4乗で増加することが分かった。さらに、生成した中性子を数cmの大きさのモデレータで減速させ、離れた位置に設置した中性子検出器により、中性子発生から検出までの飛行時間を測定するTOF測定を行った。試料を透過させて中性子の減衰を調べる実験を行った結果、核反応の共鳴による減衰の観測に成功した。
余語 覚文*; Lan, Z.*; 早川 岳人*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; 小泉 光生; 森 隆人*; Wei, T.*; 藤岡 慎介*; et al.
no journal, ,
レーザー駆動中性子源は、高強度レーザーパルスを薄膜の1次ターゲットに集光して、プラズマの作る瞬間的な電場でMeVエネルギーイオン(陽子・重陽子)を発生し、それを2次ターゲット(ベリリウム等)に照射して、短パルスの高速中性子を発生する。2次ターゲットに小型の減速材を取り付けて、パルス熱外中性子を発生し、1.8mのビームラインで飛行時間法によるエネルギースペクトルを分析した。ビームラインに銀(Ag),タンタル(Ta),インジウム(In)の合板を設置したところ、3.81eV ( In), 4.28eV (
In), 4.28eV ( Ta), 5.19eV (
Ta), 5.19eV ( Ag)に共鳴吸収によるディップを計測した。これらの共鳴吸収スペクトルは、レーザー1パルスで発生する中性子で計測されたものである。講演では、実験結果の詳細と、将来的なシングルショット分析への応用可能性について議論する。
Ag)に共鳴吸収によるディップを計測した。これらの共鳴吸収スペクトルは、レーザー1パルスで発生する中性子で計測されたものである。講演では、実験結果の詳細と、将来的なシングルショット分析への応用可能性について議論する。
Lan, Z.*; 余語 覚文*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; 小泉 光生; 早川 岳人*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; Golovin, D.*; 森 隆人*; Wei, T.*; et al.
no journal, ,
Neutron resonance diagnosis technology has been developed on reactors and accelerators for over ten years. By employing neutron beams with high transmittance, it is possible to analyse elementary composition, internal temperature and shock waves of thick objects in a non-destructive way. We developed a new approach to generate short-pulse epithermal neutron beams using relativistic intensity laser for the neutron resonance spectral diagnosis, which is known as Laser-driven Epithermal Neutron Source (LDENS). The neutron resonance measuring experiment was implemented at ILE, Osaka Univ. with peta-watt laser LFEX. The experimental results in 2020 demonstrated that LDENS is applicable for neutron resonance measurement. In 2021 experiments, we developed the system to record neutron spectrum with higher quality. Multiple resonance peaks of various isotopes with different temperature were clearly measured. The presentation will introduce the experimental results and discussions including characteristic evaluation of LDENS and temperature dependency of neutron resonance peaks.
Lan, Z.*; 余語 覚文*; 早川 岳人*; Wei, T.*; 加美山 隆*; 佐藤 博隆*; 有川 安信*; Mirfayzi, R.*; 小泉 光生; 安部 勇輝*; et al.
no journal, ,
Neutron resonance diagnosis technology has been developed worldwide for over ten years. By employing neutron beams with high transmittance, it is possible to measure the resonance spectral of samples in the neutron beam-line. We developed a new approach to generate short pulse epithermal neutron beams using relativistic intensity laser for the neutron resonance spectral diagnosis, which is known as Laser-Driven Epithermal Neutron Source (LDENS). Benefit from highly focused laser, the LDENS can provide high temporal accuracy with a compact volume of the source. Therefore, the minimal change of neutron resonance peaks caused by Doppler broadening effect of atom temperature could be detected via single pulse of LDENS. In experiment, we measured resonance at 4.28eV of a 0,1mm Ta plate with serial temperature points (300K-600K) and another resonance at 5.18eV of an Ag plate was recorded as a reference of the neutron signal. The experimental data shows the feasibility of isotope-discriminating atomic thermometer using a single shot of LDENS. More results will be reported in the presentation.
Lan, Z.*; Wei, T.*; 早川 岳人*; 加美山 隆*; 佐藤 博隆*; 有川 安信*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; 小泉 光生; 安部 勇輝*; Morace, A.*; et al.
no journal, ,
A Laser-Driven Neutron Source (LDNS) is a novel neutron that provides neutron beam of ultra-short pulse duration and high flux. This technique would be useful for neutron resonance non-destructive diagnosis application. A demonstration experiment was carried out using an LDNS developed for the LFEX laser of Institute of Laser Engineering, Osaka University. A neutron resonance spectrum was observed with a single laser shot. The technique can be used as a "nuclear thermometer" because the resonance shape is broadened as a function of the sample material temperature.
Lan, Z.*; 早川 岳人*; Wei, T.*; 加美山 隆*; 佐藤 博隆*; 有川 安信*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; 小泉 光生; 安部 勇輝*; 森 隆人*; et al.
no journal, ,
As a new approach of neutron generation with the ultra-short pulse duration and high flux, a Laser-Driven Neutron Source (LDNS) has been studied. A demonstration experiment of neutron resonance spectroscopy using a LDNS has been performed using the petawatt laser LFEX at the Institute of Laser Engineering, Osaka University. A CD foil target was used for an high-density plasma generation. Neutrons were produced by the impact of the high energy ions on a boron converter. A high-density polyethylene surrounding the boron converter slowed down neutron energy to epithermal temperature. A single shot neutron resonance experiment was carried out at a neutron beam line of 1.8m. The neutron resonance peak at 4.28 eV of Ta was measured with different temperature.
余語 覚文*; Lan, Z.*; 有川 安信*; 早川 岳人*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; Wei, T.*; 巽 湧太*; 佐藤 博隆*; 加美山 隆*; 小泉 光生
no journal, ,
高強度レーザーで加速した陽子・重陽子をBe等のコンバータで中性子に変換するレーザー駆動中性子源を開発しており、これまでにレーザー1ショットで発生した単一パルスの中性子で、中性子共鳴スペクトルの計測に成功している。本発表では、サンプルを300-600Kの範囲で昇温し、共鳴吸収ピークのドップラー広がりが温度の平方根に依存する結果を得たので報告する。