Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
挽野 真一*; 森 道康; 前川 禎通
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 83(7), p.074704_1 - 074704_5, 2014/07
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:28.33(Physics, Multidisciplinary)AC Josephson current in a Josephson junction with voltage bias is spatially modulated by an external magnetic field, and induces an electromagnetic (EM) field inside the junction. The current-voltage (I-V) curve exhibits peaks due to the resonance between the EM field and the spatially modulated AC Josephson current. This is called  . Such a spatially modulated Josephson current can be also induced by a non-uniform insulating barrier and the Fiske resonance appears without external magnetic field. This is called zero-field Fiske resonance (ZFFR). In this paper, we theoretically study the ZFFR coupled with spin-waves in a superconductor/ferromagnetic insulator/superconductor junction (ferromagnetic Josephson junction) with a non-uniform ferromagnetic insulating barrier. The resonant mode coupled with spin-waves can be induced without external magnetic field. We find that the I-V curve shows resonant peaks associated with composite excitations of spin-waves and the EM field in the junction. The voltage at the resonance is obtained as a function of the normal modes of EM field. We show several current-density dependences of the ZFFRs coupled with spin-waves.
. Such a spatially modulated Josephson current can be also induced by a non-uniform insulating barrier and the Fiske resonance appears without external magnetic field. This is called zero-field Fiske resonance (ZFFR). In this paper, we theoretically study the ZFFR coupled with spin-waves in a superconductor/ferromagnetic insulator/superconductor junction (ferromagnetic Josephson junction) with a non-uniform ferromagnetic insulating barrier. The resonant mode coupled with spin-waves can be induced without external magnetic field. We find that the I-V curve shows resonant peaks associated with composite excitations of spin-waves and the EM field in the junction. The voltage at the resonance is obtained as a function of the normal modes of EM field. We show several current-density dependences of the ZFFRs coupled with spin-waves.
森 道康; 小椎八重 航*; 挽野 真一*; 前川 禎通
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 26(25), p.255702_1 - 255702_5, 2014/06
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:14.73(Physics, Condensed Matter)A magnetic domain wall (DW) behaves as a massive particle with elasticity. Sliding and oscillation of the DW have been observed experimentally, whereas vibration of a width in the DW, "breathing mode", has not been measured so far. We theoretically propose how to observe the breathing mode by the Josephson junction having a ferromagnetic layer between superconducting electrodes. The current-voltage ( -
- ) curve is calculated by an equivalent circuit of the resistively shunted junction model. The breathing mode is identified by stepwise structures in the
) curve is calculated by an equivalent circuit of the resistively shunted junction model. The breathing mode is identified by stepwise structures in the  -
- curve, which appear at the voltages
curve, which appear at the voltages  =
=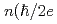 )
) with the fundamental constant
with the fundamental constant 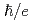 , integer number
, integer number  , and the frequency of the breathing mode
, and the frequency of the breathing mode  .
.
挽野 真一*; 森 道康; 小椎八重 航*; 前川 禎通
Applied Physics Letters, 100(15), p.152402_1 - 152402_3, 2012/04
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:22.57(Physics, Applied)We theoretically propose a principle for precise measurement of oscillatory domain wall (DW) by a ferromagnetic Josephson junction, which is composed of a ferromagnetic wire with DW and two superconducting electrodes. The current-voltage curve exhibits stepwise structures, only when DW oscillates in the ferromagnetic wire. The voltage step appears at 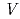 =
=  (
( /2
/2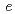 )
) 
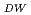 with the fundamental constant
with the fundamental constant  /
/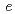 , integer number
, integer number  , and the DW frequency
, and the DW frequency 
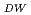 . Since
. Since 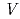 can be determined in the order of 10
can be determined in the order of 10 accuracy, the oscillatory DW will be measured more precisely than present status by conventional method.
accuracy, the oscillatory DW will be measured more precisely than present status by conventional method.
挽野 真一*; 森 道康; 高橋 三郎; 前川 禎通
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 80(7), p.074707_1 - 074707_8, 2011/07
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:47.32(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Coupling of Josephson-phase and spin-waves is theoretically studied in a superconductor/ferromagnetic insulator/superconductor (S/FI/S) junction. Electromagnetic (EM) field inside the junction and the Josephson current coupled with spin-waves in FI are calculated by combining Maxwell and Landau-Lifshitz-Gilbert equations. In the S/FI/S junction, it is found that the current-voltage (I-V) characteristic shows two resonant peaks for each mode of the EM field. Voltages at the resonant peaks are obtained as a function of the normal modes of EM field, which indicates a composite excitation of the EM field and spin-waves in the S/FI/S junction. We also examine another type of junction, in which a nonmagnetic insulator (I) is located at one of interfaces between S and FI. In such an S/I/FFI/S junction, three resonant peaks appear in the I-V curve, since the Josephson-phase couples to the EM field in the I layer.
挽野 真一*; 森 道康; 高橋 三郎*; 前川 禎通
Superconductor Science and Technology, 24(2), p.024008_1 - 024008_5, 2011/02
被引用回数:13 パーセンタイル:44.66(Physics, Applied)We study the supercurrent resulting from coupling of the Josephson-phase and the spin-wave excited by microwave radiation in a ferromagnetic Josephson junction, in which two superconductors are separated by a ferromagnet. To explore how the spin wave excitation affects the current-voltage curve, the resistively shunted junction model, which is an equation of motion for the Josephson-phase, is extended by considering the gauge invariance including magnetization. When the magnetization is driven by the microwave adjusted to the ferromagnetic resonance frequency, the dc supercurrent is induced in the junction, and the current-voltage curve shows step structures as a function of applied voltage. The position of each step in voltage is proportional to the microwave frequency multiplied by even number. This means that the even number of magnons is necessary for the singlet Cooper pair to go through the ferromagnetic layer. The magnitudes of step-height can be controlled by tuning the shape of interface. Our results present a new route to observe the spin-wave excitation by the Josephson effect.
森 道康; 挽野 真一*; 高橋 三郎; 前川 禎通
no journal, ,
Nano-structure composed of superconductor (S) and magnetic materials shows various interesting phenomena. We study the supercurrent resulting from coupling of the Josephson-phase and the spin-wave excited by microwave radiation in a ferromagnetic Josephson junction, in which two S's are separated by a ferromagnet (F). To explore how the spin wave excitation affects the current-voltage curve, the resistively shunted junction model, which is an equation of motion for the Josephson-phase, is extended by considering the gauge invariance including magnetization. When the magnetization is driven by the microwave adjusted to the ferromagnetic resonance frequency, the dc supercurrent is induced in the junction, and the current-voltage curve shows step structures as a function of applied voltage. The position of each step in voltage is proportional to the microwave frequency multiplied by even number. This means that the even number of magnons is necessary for the singlet Cooper pair to go through the ferromagnetic layer. The magnitudes of step-height can be controlled by tuning the shape of interface. Our results present a new route to observe the spin-wave excitation by the Josephson effect.
森 道康; 挽野 真一*; 高橋 三郎; 前川 禎通
no journal, ,
Coupling of Josephson-phase and spin-waves is theoretically studied in a ferromagnetic Josephson junction, in which two superconductors (S's) are separated by a ferromagnet (F). Electromagnetic (EM) field inside the junction and the Josephson current coupled with spin-waves in F are calculated by combining Maxwell and Landau-Lifshitz-Gilbert equations. In the SFS junction, it is found that the current-voltage ( -
- ) characteristic shows
) characteristic shows 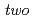 resonant peaks. Voltages at the resonant peaks are obtained as a function of the normalmodes of EM field, which indicates a composite excitation of the EM field and spin-waves in the ferromagnetic Josephson junction. We examine a ferromagnetic Josephson junction, in which an insulator (I) is inserted in one of interfaces between S and F. In such an SIFS junction,
resonant peaks. Voltages at the resonant peaks are obtained as a function of the normalmodes of EM field, which indicates a composite excitation of the EM field and spin-waves in the ferromagnetic Josephson junction. We examine a ferromagnetic Josephson junction, in which an insulator (I) is inserted in one of interfaces between S and F. In such an SIFS junction, 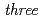 resonant peaks appear in the
resonant peaks appear in the  -
- curve, since the Josephson-phase couples to the EM field in the insulating layer.
curve, since the Josephson-phase couples to the EM field in the insulating layer.
森 道康; 挽野 真一*; 小椎八重 航*; 前川 禎通
no journal, ,
Nano-scale magnetic materials for spintronics devices are extensively studied due to many advantages. Non-volatile memory using a magnetic domain wall (DW) is one example of such devices, and the oscillatory DW is examined toward several applications. Once such devices are realized in a microscopic circuit, one needs to measure the DW motion more precisely. In this talk, we discuss the transport properties characterized by a magnetic domain wall (DW) motion in a ferromagnetic Josephson junction, which is composed of a ferromagnetic wire with DW and two superconducting electrodes. Our previous theory is developed to include the DW motion into the Josephson current. By supposing a simplified DW structure, we find that the current-voltage curve exhibits stepwise structures, when DW oscillates in the ferromagnetic wire. The mechanism behind this result is common to the electric field generated by the vortex motion in the superconductor.
森 道康; 挽野 真一*; 小椎八重 航*; 前川 禎通
no journal, ,
Nano-scale magnetic materials for spintronics devices are extensively studied due to many advantages such as enhanced operationspeed, low power consumption, and high integration of memory cell. Non-volatile memory using a magnetic domain wall (DW) is one example of such devices, and many studies are devoted to control DW. Among those studies, the oscillatory DW is experimentally observed and is examined toward applications, e.g. high sensitive magnetic sensor, nano-scale telecommunication, rf-assisted writing of magnetic bit, and microwave generator. Once such devices are realized in a microscopic circuit, one needs to measure the DW frequency more precisely. We theoretically propose a principle for precise measurement of oscillatory domain wall (DW) by a ferromagnetic Josephson junction,which is composed of a ferromagnetic wire with DW and two superconducting electrodes. The current-voltage curve exhibits stepwisestructures, only when DW oscillates in the ferromagnetic wire. The voltage step appears at V=n(h/2e)f with the fundamental constant h/e,integer number n, and the DW frequency f. Since V can be determined in the order of 10 accuracy, the oscillatory DW will be measured more precisely than present status by conventional method.
accuracy, the oscillatory DW will be measured more precisely than present status by conventional method.
森 道康; 挽野 真一*; 小椎八重 航*; 前川 禎通
no journal, ,
強磁性体で隔てられた超伝導体の接合を考え、その強磁性体中で磁壁が振動運動している場合の電流電圧特性を理論的に導いた。その結果、磁壁の振動数の整数倍に比例定数をかけた電圧のところで、電流電圧特性が階段状に変化しうることを見いだした。比例係数がプランク定数と素電荷で与えられ、電圧はジョセフソン接合を用いて極めて高い精度で規定されているので、磁壁の振動数の高精度な観測が可能になると期待される。
森 道康; 小椎八重 航*; 挽野 真一*; 前川 禎通
no journal, ,
強磁性体で隔てられた超伝導体の接合を考え、その強磁性体中に磁壁が含まれている場合の電流電圧特性を理論的に導いた。振動運動している場合の電流電圧特性を理論的に導いた。その結果、磁壁の振動数の整数倍に比例定数をかけた電圧のところで、電流電圧特性が階段状に変化しうることを見出した。比例係数がプランク定数と素電荷で与えられ、電圧はジョセフソン接合を用いて極めて高い精度で規定されているので、磁壁の振動数の高精度な観測が可能になると期待される。
森 道康; 小椎八重 航*; 挽野 真一*; 前川 禎通
no journal, ,
We theoretically propose how to observe the breathing mode by the Josephson junction having a ferromagnetic layer between superconducting electrodes. The current-voltage (I-V) curve is calculated by an equivalent circuit of the resistively shunted junction model. The breathing mode is identified by stepwise structures in the I-V curve, which appear at the voltages V=n( /2e) with the fundamental constant
/2e) with the fundamental constant  /2e, integer number n, and the frequency of the breathing mode. This is the most feasible method to observe the breathing mode of the DW due to the sensitivity of the Josephson junction. In principle, magnetic resonance methods are also possible to measure the breathing mode. However, owing to their low sensitivity, the resonance measurements would be limited to a sample containing huge numbers of DWs or a specific structure of a ferromagnet. Although such a measurement is realized in the Skyrmion lattice, in which the rotational and the breathing modes are observed, it has not been done on the breathing mode of the DW so far. Our method is accessible to the breathing mode of a single DW due to the sensitivity of the Josephson junction.
/2e, integer number n, and the frequency of the breathing mode. This is the most feasible method to observe the breathing mode of the DW due to the sensitivity of the Josephson junction. In principle, magnetic resonance methods are also possible to measure the breathing mode. However, owing to their low sensitivity, the resonance measurements would be limited to a sample containing huge numbers of DWs or a specific structure of a ferromagnet. Although such a measurement is realized in the Skyrmion lattice, in which the rotational and the breathing modes are observed, it has not been done on the breathing mode of the DW so far. Our method is accessible to the breathing mode of a single DW due to the sensitivity of the Josephson junction.
森 道康; 小椎八重 航*; 挽野 真一*; 前川 禎通
no journal, ,
We theoretically propose how to observe the breathing mode by the Josephson junction having a ferromagnetic layer between superconducting electrodes. The current-voltage (I-V) curve is calculated by an equivalent circuit of the resistively shunted junction model. The breathing mode is identified by stepwise structures in the I-V curve, which appear at the voltages V=n( /2e)w with the fundamental constant
/2e)w with the fundamental constant  /2e, integer number n, and the frequency of the breathing mode w. This is the most feasible method to observe the breathing mode of the DW due to the sensitivity of the Josephson junction. In principle, magnetic resonance methods are also possible to measure the breathing mode. However, owing to their low sensitivity, theresonance measurements would be limited to a sample containing huge numbers of DWs or a specific structure of a ferromagnet. Although such ameasurement is realized in the Skyrmion lattice, in which the rotational and the breathing modes are observed, it has not been done on the breathing mode of the DW so far. Our method is accessible to the breathing mode of a single DW due to the sensitivity of the Josephson junction.
/2e, integer number n, and the frequency of the breathing mode w. This is the most feasible method to observe the breathing mode of the DW due to the sensitivity of the Josephson junction. In principle, magnetic resonance methods are also possible to measure the breathing mode. However, owing to their low sensitivity, theresonance measurements would be limited to a sample containing huge numbers of DWs or a specific structure of a ferromagnet. Although such ameasurement is realized in the Skyrmion lattice, in which the rotational and the breathing modes are observed, it has not been done on the breathing mode of the DW so far. Our method is accessible to the breathing mode of a single DW due to the sensitivity of the Josephson junction.