Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
岩本 ちひろ*; 高村 正人*; 上野 孝太*; 片岡 美波*; 栗原 諒*; 徐 平光; 大竹 淑恵*
ISIJ International, 62(5), p.1013 - 1022, 2022/05
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:32.54(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Neutron diffraction is a powerful non-destructive method for evaluating the microscopic structure and internal stress of metal plates as a bulk average. Precise neutron diffraction measurements with a high intensity neutron beam have already been carried out at large-scale neutron facilities. However, it is not easy to provide users with enough experimental opportunities. We are working on upgrading the neutron diffractometer with techniques of time-of-flight to enable stress measurements at RIKEN accelerator-driven compact neutron source (RANS). To improve neutron diffraction resolution, delayed neutrons, which expand neutron beam pulse width, should be suppressed. However, it is difficult to separate the delayed neutrons experimentally. In this study, a new analysis method has been proposed to deconvolute the diffraction peak from the delayed neutron component. Moreover, a new collimator system, called decoupled collimator system, has been developed to reduce the number of delayed neutrons. The diffraction patterns from a powder sample of pure body-centered cubic iron were measured with the decoupled collimator and the diffraction peak of {211} reflection was analyzed by the new analysis method using a model function of a single exponential decay function convoluted with a Gaussian function. By this method, the decoupled collimator system has been confirmed to achieve a smaller measurement limit of lattice strain 
 than a small-aperture polyethylene collimator system and a non-collimator system. The currently available
than a small-aperture polyethylene collimator system and a non-collimator system. The currently available 
 was 6.7
was 6.7 10
10 , this means that the internal stress up to 130 MPa can be well evaluated for steel materials with a Young's modulus of 200 GPa at RANS.
, this means that the internal stress up to 130 MPa can be well evaluated for steel materials with a Young's modulus of 200 GPa at RANS.
角田 龍之介*; 高村 正人*; 徐 平光; 岩本 ちひろ*; 高梨 宇宙*; 大竹 淑恵*; 栗原 諒*; 高橋 進*; 鈴木 裕士
no journal, ,
During the production of high-strength steel structural parts, the residual stress is necessary to be well controlled for the better dimensional accuracy and the longer service life. The neutron diffraction measurement is a good candidate to monitor the microscopic lattice strain of polycrystalline materials in bulk average. RANS (Riken Accelerator-driven Compact Neutron Source) has been developed and upgraded aiming at in-house, on-site and on-demand measurements to meet with industrial needs. Recently, the phase volume fractions and the bulk textures of steel materials have been measured successfully at RANS. In order to measure the lattice strain at RANS, it is required to improve the energy resolution to observe slight peak shift, and the decoupled moderator is thought as a good solution method for that. In this study, a new decoupled moderator consisting of polyethylene with 20 cmm thickness and B C rubber was designed and fabricated, and its neutron beam characteristic was investigated in order to improve the time energy resolution to realize in-house neutron stress measurement at RANS. Here, the preliminary results of the resolutions comparing between the new decoupled moderator and the traditional coupled moderators with 20 and 40 mm thickness polyethylene will be reported together with the scattering angle dependent instrumental resolution of the linear neutron position-sensitive detector.
C rubber was designed and fabricated, and its neutron beam characteristic was investigated in order to improve the time energy resolution to realize in-house neutron stress measurement at RANS. Here, the preliminary results of the resolutions comparing between the new decoupled moderator and the traditional coupled moderators with 20 and 40 mm thickness polyethylene will be reported together with the scattering angle dependent instrumental resolution of the linear neutron position-sensitive detector.
高村 正人*; 岩本 ちひろ*; 徐 平光; 角田 龍之介*; 栗原 諒*; 箱山 智之*; 池田 義雅*; 鈴木 裕士; 大竹 淑恵*
no journal, ,
High strength steels are becoming more and more important in automotive body structures for good weight reduction, providing further requirement in the balance between strength and formability. Numerical models in forming simulations taking into account the texture evolution may accurately analyze macroscopic plastic behavior, through referring to local surface texture measurement using Electron backscatter diffraction or X-ray diffraction. In contrast, neutron diffraction may measure the microstructure factors including bulk-averaged texture, enable to more deeply understand the mechanisms of deformation behavior. Such neutron diffraction studies usually require large-scale experimental facilities like a reactor and a large accelerator, so meet certain difficulty in the instrumental accessibility. To solve these problems, Riken Accelerator-driven Compact Neutron Source (RANS) has been developed. On-site evaluation of microstructural factors enables us to analyze metal deformation processes more efficiently. Authors have recently succeeded in accurately measuring the texture evolution of an IF steel and also in determining the retained austenite volume fraction of multi-phase steels, by optimizing the beam condition and layout of collimators, samples, detectors, etc. These results show the possibility of practical use of an in-house compact neutron source in laboratories of universities, research institutes and industrial firms.
高村 正人*; 岩本 ちひろ*; 徐 平光; 上野 孝太*; 栗原 諒*; 鈴木 裕士; 大竹 淑恵*
no journal, ,
Plastic forming processes of metallic sheets, 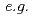 , forging, rolling, bending, pressing, drawing, and extruding, are important manufacturing methods to produce complex mechanical parts. Numerical simulation using the finite element method based on the crystal plasticity theory has been thought valuable to improve the forming accuracy and reduce the forming defects, especially for high strength automotive metallic sheets. For the realization of reliable numerical modelling and the development of strength-formability well-balanced novel metallic sheets, the bulk average microstructure information closely related to the mechanical characteristics is highly expected to be on-site available, or at least may be measured in time through neutron diffraction. Towards these on-site neutron diffraction measurement requirements from forming process designers and materials researchers, RIKEN has developed an accelerator-driven compact neutron source (RANS) and realized the texture and phase fraction measurement at a good precision level. Recently, a novel residual measurement technique using RANS is being carried out.
, forging, rolling, bending, pressing, drawing, and extruding, are important manufacturing methods to produce complex mechanical parts. Numerical simulation using the finite element method based on the crystal plasticity theory has been thought valuable to improve the forming accuracy and reduce the forming defects, especially for high strength automotive metallic sheets. For the realization of reliable numerical modelling and the development of strength-formability well-balanced novel metallic sheets, the bulk average microstructure information closely related to the mechanical characteristics is highly expected to be on-site available, or at least may be measured in time through neutron diffraction. Towards these on-site neutron diffraction measurement requirements from forming process designers and materials researchers, RIKEN has developed an accelerator-driven compact neutron source (RANS) and realized the texture and phase fraction measurement at a good precision level. Recently, a novel residual measurement technique using RANS is being carried out.
岩本 ちひろ*; 高村 正人*; 上野 孝太*; 栗原 諒*; 徐 平光; 鈴木 裕士; 大竹 淑恵*
no journal, ,
理化学研究所小型中性子源RANSでは、これまでに飛行時間法による中性子回折測定の開発を行っており、集合組織や体積率の測定を成功させてきた。さらに、残留応力測定への高度化として回折線分解能を向上するために、大型施設で利用されている非結合型中性子減速材の導入によって、結合型中性子減速材の場合と比較してBCC鉄粉の211結晶面からの回折線分解能が若干改善された。本研究では、回折線強度を増やし、かつバックグラウンドを低減するためのビームライン開発を行った。まず、空間的・時間的に広がった中性子ビームがサンプルへ照射されることを防ぐため、また広がった中性子ビームが実験室内床面などから散乱されることで発生するバックグランドを抑えるため、減速材から中性子取り出し口までの開口部内壁に、熱中性子遮蔽材であるB Cゴムシートを貼りつけた。さらに、サンプルへのビーム強度を増加させるため、これまで中性子取り出し口からサンプルまでの間に設置していた長さ3m、開口50
Cゴムシートを貼りつけた。さらに、サンプルへのビーム強度を増加させるため、これまで中性子取り出し口からサンプルまでの間に設置していた長さ3m、開口50 50mm
50mm のポリエチレンコリメータを外し、長さ3m、開口250
のポリエチレンコリメータを外し、長さ3m、開口250 250mm
250mm のボロン含有ポリエチレン(BPE)導管を設置した。この導管の下流側開口部には、上流からのビーム由来のバックグラウンドを低減するために、BPE導管の最下流に開口50mm角、厚さ15mmのB
のボロン含有ポリエチレン(BPE)導管を設置した。この導管の下流側開口部には、上流からのビーム由来のバックグラウンドを低減するために、BPE導管の最下流に開口50mm角、厚さ15mmのB Cゴムシートで作成したコリメータを設置した。この改善後のセットアップを用いてBCC鉄粉回折線を測定し、改善前のセットアップ時における回折線分布と比較した。200結晶面以外の回折線ピークにおいて、セットアップ改善後の回折線強度が増加し、また回折線ピークの形状も鋭い形状をしている結果が得られている。この改善により、RANSにおける残留応力測定のS/N向上及び測定時間短縮化が可能となることが示された。
Cゴムシートで作成したコリメータを設置した。この改善後のセットアップを用いてBCC鉄粉回折線を測定し、改善前のセットアップ時における回折線分布と比較した。200結晶面以外の回折線ピークにおいて、セットアップ改善後の回折線強度が増加し、また回折線ピークの形状も鋭い形状をしている結果が得られている。この改善により、RANSにおける残留応力測定のS/N向上及び測定時間短縮化が可能となることが示された。
徐 平光; 岩本 ちひろ*; 高村 正人*; 大竹 淑恵*; 栗原 諒*; 上野 孝太*; 片岡 美波*; 山本 和喜; Harjo, S.; 菖蒲 敬久
no journal, ,
Neutron diffraction can collect sample-volume averaged diffraction patterns due to the excellent penetrability and the coarse beam spot, valuable for investigating bulk microstructure changes of polycrystalline materials. In recent years, several neutron instruments in Japan have been employed for precise bulk texture evaluation. The engineering materials diffractometer attached with large sample stage and precise radial collimators at J-PARC has realized a reliably combined Rietveld texture evaluation, simultaneously providing crystallographic textures and other profile-analysis-related material parameters such as crystal structures, stress tensors. The RANS compact neutron source has enabled reliable bulk texture evaluation of steel materials through reasonably using a high stereographic angle resolution and a large sample-gauge volume. As a feed-back from the texture measurement technique based on RANS compact neutron source, recently, weak diffraction patterns step-by-step collected in very short time from RESA neutron diffractometer at JRR-3 have been utilized to realize the precise texture evaluation of various polycrystalline materials, 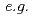 , a standard rock material, and different steel materials.
, a standard rock material, and different steel materials.
岩本 ちひろ*; 高村 正人*; 上野 孝太*; 片岡 美波*; 栗原 諒*; 徐 平光; 大竹 淑恵*
no journal, ,
Neutron diffraction is a powerful non-destructive method for evaluating the microscopic structure and internal stress of metallic materials and related semi-finished parts as a bulk average. To implement on-site stress measurements via the neutron diffraction at laboratories and factories frequently and even daily, we are establishing and upgrading the novel measurement and analysis methodology of time-of-flight neutron diffraction at RIKEN accelerator-driven compact neutron source (RANS). In this study, we have proposed two methods to improve the determination resolution of the diffraction peak position by focusing on delayed neutrons due to background scattering from devices such as reflector surrounding the neutron moderator and the polyethylene collimator. First, an analysis method has been proposed to deconvolute original diffraction peak from the delayed neutron component by defining a new model function to well describe the profile shape of delayed neutron diffraction. Second, a new decoupled collimator system has been developed to reduce the number of delayed neutrons. The diffraction patterns from a powder sample of pure body-centered cubic iron were measured with the decoupled collimator and the diffraction peak of {211} reflection was analyzed by the new analysis method using the neutron diffraction profile model function,  , a single exponential decay function convoluted with a Gaussian function. By this method, the decoupled collimator system has been confirmed to achieve a smaller measurement limit of lattice strain
, a single exponential decay function convoluted with a Gaussian function. By this method, the decoupled collimator system has been confirmed to achieve a smaller measurement limit of lattice strain 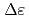 than a small-aperture polyethylene collimator system and a non-collimator system. The currently available
than a small-aperture polyethylene collimator system and a non-collimator system. The currently available 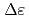 was 6.7
was 6.7 10
10 , which means that the internal stress up to 130 MPa can be well evaluated at RANS for steel materials with a Young's modulus of 200 GPa.
, which means that the internal stress up to 130 MPa can be well evaluated at RANS for steel materials with a Young's modulus of 200 GPa.
岩本 ちひろ*; 栗原 諒*; 高村 正人*; 高橋 進*; 鈴木 康介*; 徐 平光; 大竹 淑恵*
no journal, ,
中性子回折測定は、鉄鋼材料に溶接加工や鍛造加工を施した際に発生する残留応力を非破壊かつ定量的に測定できる最適な手法である。小型中性子源による中性子回折測定の実現は、このような測定のものづくり現場でのオンサイト測定を可能にし、材料加工研究開発のさらなる加速要望に応えるために必須である。一方で、中性子回折による応力測定には、回折線ピークの微小なシフトを測定するために高い回折線測定分解能が必要である。回折線分解能向上のためには、チョッパー機構やポイズンモデレータなどの短パルス化デバイス導入が一般的である。しかしながら、これらのデバイスは、ビーム強度の低下に直結し、かつ追加遮蔽導入によるシステムの大型化にもつながるため、中性子ビーム強度の低い小型中性子源の現場導入を前提とした開発には不向きである。本研究では、線源より下流側で中性子ビームの長パルス化を引き起こす"遅延中性子"に着目し、中性子ビーム強度と回折線測定分解能の間のトレードオフの関係を打開するための2つの開発を行なった。ひとつは、遅延中性子の発生を防ぐ非結合型コリメータシステムの開発、もうひとつは遅延中性子による長パルス化の影響を分離できる新しい回折線フィッティング関数を導入した解析法である。理化学研究所の小型加速器中性子源RANSのビームラインで、これらの手法を取り入れて、S45C試料に応力を付加させた既知応力サンプルからの中性子回折線を測定した。その結果500MPaの圧縮応力を格子ひずみから同定することに成功した。
岩本 ちひろ*; 高村 正人*; 栗原 諒*; 徐 平光; 鈴木 康介*; 高橋 進*; 山本 和喜; 菖蒲 敬久; 大竹 淑恵*
no journal, ,
中性子回折による応力測定には、回折線ピークの微小なシフトを測定するために高い回折線測定分解能が必要である。大型施設では、回折線測定分解能向上のためにチョッパー機構やポイズンモデレータなどの短パルス化デバイス導入が一般的である。しかしながら、これらのデバイスは、ビーム強度を低下させ、かつ追加遮蔽導入によるシステムの大型化にもつながる。そのため中性子ビーム強度の低い小型中性子源の現場導入を前提とした開発には不向きである。本研究では、中性子線源より下流側で中性子ビームの長パルス化を引き起こす"遅延中性子"に着目し、中性子ビーム強度と回折線測定分解能の間のトレードオフの関係を打開するための2つの開発を行なった。ひとつは、遅延中性子の発生を防ぐ非結合型コリメータシステムの開発、もうひとつは遅延中性子による長パルス化の影響を分離できる新しい回折線フィッティング関数を導入した解析法である。理化学研究所の小型加速器中性子源RANSのビームラインにおいて、これらの手法を取り入れてBCC鉄粉回折線を測定し、改善前のセットアップ時における回折線分布と比較した結果を図2に示す。(211)格子面からの回折ピークに対して、検出された回折中性子収量が非結合型コリメータシステムを使用することで2倍増加させながら、ひずみ分解能6.8 10
10 を達成した。これはヤング率が約200GPaの鉄鋼材料の応力を130MPaまで測定可能であることを示している。また、S45C試料に応力を付加させた既知応力サンプルからの回折中性子トライアル測定を行った。その結果500MPa
を達成した。これはヤング率が約200GPaの鉄鋼材料の応力を130MPaまで測定可能であることを示している。また、S45C試料に応力を付加させた既知応力サンプルからの回折中性子トライアル測定を行った。その結果500MPa 200MPaの圧縮応力を格子ひずみから同定することに成功した。
200MPaの圧縮応力を格子ひずみから同定することに成功した。
岩本 ちひろ*; 栗原 諒*; 高村 正人*; 高橋 進*; 鈴木 康介*; 徐 平光; 大竹 淑恵*
no journal, ,
Neutron diffraction is a powerful non-destructive method for evaluating the microscopic structure and internal stress of metal as a bulk average. To implement on-site stress measurements via the neutron diffraction at laboratories and factories frequently and even daily, we are working on improving the method of the neutron diffraction measurement and analysis with techniques of time-of-flight to at RIKEN accelerator-driven compact neutron source (RANS). In this study, we have proposed two methods to improve the determination resolution of the diffraction peak position by focusing on delayed neutrons due to scattering from devices such as reflector surrounding the moderator and the polyethylene collimator. First, an analysis method has been proposed to deconvolute original diffraction peak from the delayed neutron component by defining a model function describing the delayed neutron shape. Second, a new collimator system, called decouple collimator, to reduce the number of delayed neutrons has been developed. In this presentation, we will show following two results: First, the performances of these new methods were evaluated to measure diffraction patterns from a powder sample of pure body-centered cubic iron with the decouple collomator, and to analyze the diffraction peak of {211} reflection by the new analysis method using a model function of a single exponential decay function convoluted with a Gaussian function. The diffracted neutron yield increased by a factor of 2 comapred with a traditional small-apperture polyethylene collimator system while the diffraction peak was successfully separated clearly from the delayed neutron component. Second, a trial stress measurement of a carbon steel specimen applied to as-known compressive stress was performed. At present, the applied stress can be measured with an error of up to 200 MPa for the specimen with applied stress of 500 MPa.