Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
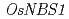 gene in rice via targeted mutagenesis using the CRISPR/Cas9 system
gene in rice via targeted mutagenesis using the CRISPR/Cas9 system雑賀 啓明*; 三上 雅史*; 遠藤 真咲*; 坂本 綾子; 土岐 精一*
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 97, 2016/02
Arabidopsis thaliana cells, in which DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) have occurred, select either DNA repair, cell death or endocycle. Avoidance of entry into endocycle even under genotoxic conditions, rice (Oryza sativa L.) is more suitable than Arabidopsis for the study of DSBs repair in plants. Nijmegen breakage syndrome 1 (NBS1) protein consists of the Mre11/Rad50/NBS1 (MRN) complex plays an important role in response to DNA damage in mammal. Although rice has a homologue of NBS1, OsNBS1, its function remains unclear. Here, we attempted to knockout the OsNBS1 gene using the recently developed clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat (CRISPR)-associated endonuclease 9 (CRISPR/Cas9) system. Rice (cv. Nipponbare) cells were transformed via Agrobacterium and obtained 72 lines of cali. Cleaved amplified polymorphic sequences (CAPS) analysis detected mutations in 58 lines. Biallelic mutations in theOsNBS1 gene were induced in 24 lines. Sequence analyses of PCR products in #2 and #4 detected not only small mutations but also large modifications at the expected cleavage site. The large insertions involved one or two fragments that seem to be copied from sequences around the cleavage site. These mutations are thought to be repaired by a synthesis-dependent strand annealing (SDSA)-like system as proposed in a previous report in barley.
雑賀 啓明*; 吉原 亮平*; 坂本 綾子; 土岐 精一*
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 99, 2013/01
To date, many commercial varieties of various kinds of plants have been developed by ion beam breeding. However, to further improve the ion beam breeding system, it is important to gather more basic information on the mutagenic effects of ion beams in plants. To this end, we try to establish a novel mutation detection system using a conditional negative selection marker to stop cell growth. Cultured cell such as callus that can clonally propagate efficiently and easily are well-suited to this system. In this study, we checked the sensitivity of callus of the model plants Arabidopsis and rice to carbon ion beams.

吉原 亮平; 野澤 樹; 雑賀 啓明*; 寺西 美佳*; 土岐 精一*; 日出間 純*; 坂本 綾子
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 74, 2011/01
This study aimed to elucidate the effects of ion beams on  . We focus on (1) what kinds of damage are produced by ion beams, and (2) what kinds of cellular processes are involved in turn the damage into mutations. Our results suggest that 220 MeV carbon ions may induce more numbers of DNA lesions or more severe types of DNA lesions than
. We focus on (1) what kinds of damage are produced by ion beams, and (2) what kinds of cellular processes are involved in turn the damage into mutations. Our results suggest that 220 MeV carbon ions may induce more numbers of DNA lesions or more severe types of DNA lesions than  -rays and 50 MeV helium ions. Our results also suggest that the considerable amount of DNA lesions induced by
-rays and 50 MeV helium ions. Our results also suggest that the considerable amount of DNA lesions induced by  -rays and 50 MeV helium ions are repaired by non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) repair mechanism, but the majority of DNA lesions induced by 220 MeV carbon ions are not repaired by NHEJ.
-rays and 50 MeV helium ions are repaired by non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) repair mechanism, but the majority of DNA lesions induced by 220 MeV carbon ions are not repaired by NHEJ.
雑賀 啓明*; 吉原 亮平; 坂本 綾子; 土岐 精一*
no journal, ,
突然変異は、イオンビーム照射によって誘発されるDNA損傷が正確に修復されなかった結果として生じる。よって、イオンビームの照射によって生じる突然変異のスペクトラムと、その原因となるDNA損傷修復機構との関係が明らかになれば、突然変異スペクトラムを制御できると考えられる。われわれは、DNA損傷と変異スペクトラムの関係を明らかにするために、モデル植物であるシロイヌナズナやイネのカルスを用いて新規の突然変異スペクトラム解析実験系の構築を試みた。シロイヌナズナの葉及び根から誘導したカルスを用いてイオンビームに対する感受性を調べたところ、7.5Gyより高い線量を照射した場合では、シュートの再生効率が10%未満に低下することが明らかとなった。一方、イネカルスを用いた感受性試験では、照射していないカルスや2.5-15Gyのイオンビームを照射したカルスの新鮮重は30-35mgであったのに対し、20-40Gyの高い線量を照射したカルスでは15-20mgとなり、増殖が抑制されていることが明らかとなった。今後は、これらの条件を参考に変異スペクトラム解析実験系を構築し、イオンビームによって誘発される突然変異のスペクトラム解析を行うとともに、その誘発にかかわるDNA修復機構の解析を行いたいと考えている。
日出間 純*; 寺西 美佳*; 土岐 精一*; 雑賀 啓明*; 坂本 綾子; 吉原 亮平
no journal, ,
イオンビームを用いた植物の突然変異誘発の研究は、原子力機構が研究拠点となり、高崎量子応用研究所のイオン照射装置(TIARA)を利用して、世界に先駆けて行われてきた。イオンビームによる突然変異体育種の特徴として、(1)低LET放射線と比較して、突然変異誘発率が高く、変異スペクトラムが広いこと、(2)1つの形質のみに変異が生じ、変異形質が安定している、等が知られている。しかし、従来の方法と同様に、イオンビーム育種においても突然変異の方向性はランダムかつ偶発的であり、また多大な労力が必要とされるため、より有効な技術が望まれていた。本研究では、モデル植物を利用して、さまざまなDNA修復系とそれが関与する突然変異スペクトラムとの関係を明らかにすることにより、これまでランダムで偶発的と考えられてきた突然変異の誘発に関して、その誘発機構を制御することにより、より効率的な育種素材を創成することを目指している。
寺西 美佳*; 日出間 純*; 雑賀 啓明*; 土岐 精一*; 吉原 亮平*; 野澤 樹; 長谷 純宏; 坂本 綾子
no journal, ,
これまで「突然変異は偶発的に生じる」という立場から、目的の変異体獲得のためには最適な選抜条件の設定と選抜規模の拡大が必須とされてきた。しかし、「突然変異はDNA損傷に対して細胞内での修復機構が作用することで生じる」という点に着目すると、細胞内でのDNA修復機構を人為的に制御できれば、より自由に突然変異の効率や方向性をデザインできる可能性がある。そこで、このような新技術の開発のための第一歩として、シロイヌナズナのDNA修復欠損株を作製し、イオンビーム誘発変異における幾つかのDNA修復機構の果たす役割の解明を試みた。