Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Watanabe, Osamu*; Oyama, Kazuhiro*; Endo, Junji*; Doda, Norihiro; Ono, Ayako; Kamide, Hideki; Murakami, Takahiro*; Eguchi, Yuzuru*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(9), p.1102 - 1121, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:71.70(Nuclear Science & Technology)A natural circulation (NC) evaluation methodology has been developed to ensure the safety of a sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR) of 1500MW adopting the NC decay heat removal system (DHRS). The methodology consists of a 1D safety analysis which can evaluate the core hot spot temperature taking into account the temperature flattening effect in the core, a 3D fluid flow analysis which can evaluate the thermal-hydraulics for local convections and thermal stratifications in the primary system and DHRS, and a statistical safety evaluation method. The safety analysis method and the 3D analysis method have been validated using results of a 1/10 scaled water test simulating the primary system of the SFR and a 1/7 scaled sodium test simulating the primary system and the DHRS, and the applicability of the safety analysis for the SFR has been confirmed by comparing with the 3D analysis. Finally, a statistical safety evaluation has been performed for the SFR using the safety analysis method.
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Tanaka, Nobuatsu*; Eguchi, Yuzuru*; Nishimura, Motohiko*; Kunugi, Tomoaki*; Uchibori, Akihiro; Ito, Kei; Sakai, Takaaki
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 11(4), p.316 - 328, 2012/12
It is of importance for stable operations of sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs) to prevent gas entrainment (GE) phenomena due to free surface vortices. Therefore, the authors have been developing an evaluation method for GE based on computational fluid dynamics (CFD) methods. In this study, we determine the suitable CFD method for GE phenomena from several candidates through some numerical benchmarks. As the results, we obtain the following guideline for the vortex-induced gas entrainment. Free vortex flow around the vortex core can be correctly evaluated by using the appropriate numerical models such as enough mesh resolution, suitable advection solver, suitable turbulence and free surface modeling.
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Eguchi, Yuzuru*; Kunugi, Tomoaki*; Kamide, Hideki; Sakai, Takaaki; Ito, Kei
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 11(4), p.329 - 339, 2012/12
For the stable operation of fast breeder reactors (FBRs), the occurrences of gas entrainment (GE) phenomena should be suppressed below an allowance level. Therefore, a reliable evaluation method for the GE phenomena is necessary to determine the operating conditions of FBRs. In this paper, the authors propose a GE evaluation method in which free surface vortices are identified from velocity fields by using the second invariant of velocity gradient tensor, and the GE evaluation parameters, e.g. gas core length, are calculated by using the Burgers vortex model. In addition, the standard for prevention of three kinds of the vortex-type GE are shown in consideration of experimental data, evaluation results with the proposed method and the comparison results of them. Finally, it is confirmed that the onset conditions of the vortex-type GE can be evaluated by the proposed method.
Murakami, Takahiro*; Eguchi, Yuzuru*; Tanaka, Masaaki; Yamano, Hidemasa
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu, B, 78(792), p.1388 - 1391, 2012/08
In a conceptual design of Japan Sodium-cooled Fast Reactor (JSFR), short-elbow pipings with large-diameter are adopted for cooling system, in which the coolant flow causes periodical pressure fluctuation at the short-elbow. However, the mechanism of the periodical pressure fluctuation has not been clarified yet. In this paper, unsteady three-dimensional analysis by a finite element large-eddy-simulation (LES) code is carried out in order to explore the mechanism of the periodical pressure fluctuation in short-elbow pipings, based on visualizations of dynamic flow structure in the numerical results.
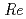 flow in a short-elbow pipe with undisturbed inlet velocity
flow in a short-elbow pipe with undisturbed inlet velocityEguchi, Yuzuru*; Murakami, Takahiro*; Tanaka, Masaaki; Yamano, Hidemasa
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 241(11), p.4368 - 4378, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:58.47(Nuclear Science & Technology)The paper is concerned with a large-eddy simulation (LES) for a high-Reynolds-number flow in a short-elbow pipe, which can potentially be employed in the primary piping system of the Japan Sodium-cooled Fast Reactor (JSFR). The basic performance of the LES is studied for an elbow pipe flow without turbulence at inlet boundary at 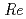 = 1.2
= 1.2 10
10 by comparison with a flow observed in a 1/3-scale water experiment, where the flow disturbance at the pipe inlet is small. In setting up the computational conditions, special care was taken to ensure that the mesh subdivision was suitable for the simulation of the pipe flow through a theoretical consideration. We discuss the effects of the turbulence model (Smagorinsky model, WALE model) and the inlet velocity profile on the results. The mechanism of the pressure fluctuation and the origin of the fluid force are also discussed with the aid of spectral analysis and the visualization of essential hydraulic quantities.
by comparison with a flow observed in a 1/3-scale water experiment, where the flow disturbance at the pipe inlet is small. In setting up the computational conditions, special care was taken to ensure that the mesh subdivision was suitable for the simulation of the pipe flow through a theoretical consideration. We discuss the effects of the turbulence model (Smagorinsky model, WALE model) and the inlet velocity profile on the results. The mechanism of the pressure fluctuation and the origin of the fluid force are also discussed with the aid of spectral analysis and the visualization of essential hydraulic quantities.
Ito, Kei; Sakai, Takaaki; Eguchi, Yuzuru*; Monji, Hideaki*; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Uchibori, Akihiro; Xu, Y.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 47(9), p.771 - 778, 2010/09
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:65.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)A gas entrainment (GE) prediction method has been developed to establish design criteria for the large-scale sodium-cooled fast reactor (JSFR) systems. In this paper, the evaluation accuracy of gas core lengths is improved by introducing the surface tension effects into the prototype GE prediction method. For the improvement, the mechanical balance between gravitational, centrifugal, and surface tension forces is considered. The improved GE prediction method is validated by analyzing the gas core lengths observed in simple experiments. Results show that the analytical gas core lengths calculated by the improved GE prediction method become shorter in comparison to the prototype GE prediction method, and are in good agreement with the experimental data. In addition, the experimental data under different temperature and surfactant concentration conditions are reproduced by the improved GE prediction method.
Kamide, Hideki; Miyakoshi, Hiroyuki; Watanabe, Osamu*; Eguchi, Yuzuru*; Koga, Tomonari*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu, B, 76(763), p.460 - 462, 2010/03
Fully natural circulation system is adopted in a decay heat removal system (DHRS) of the designs of Japan Sodium Cooled Fast Reactor (JSFR). Several investigations of experiments and simulation methods on this DHRS are performed. Water experiments are carried out for the primary heat transportation system including a reactor vessel and heat exchangers of DHRS using a 1/10 model. As for the DHRS loop, sodium experiments were carried out, especially for a heat exchanger installed in an Intermediate Heat Exchanger (IHX). Here, several results of the sodium experiments were described. Transient characteristics during the start up in the air system of the air cooler, secondary loop of DHRS, and the primary loop were examined by the sodium experiments. Smooth increase of natural circulation flow rates in all systems of air and sodium was confirmed. Verifications of numerical simulation methods are planned based on the water and sodium experiments in this investigation plan.
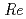 -number short-elbow pipe flow
-number short-elbow pipe flowEguchi, Yuzuru*; Murakami, Takahiro*; Tanaka, Masaaki; Yamano, Hidemasa
Proceedings of 13th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-13) (CD-ROM), 14 Pages, 2009/09
Since unsteady force possibly generated by fluid motion in a short-elbow pipe needs evaluating in the JSFR plant design, applicability of large-eddy simulation (LES) method to a high 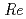 number water test is studied with an in-house LES code in the paper. First, requirement for mesh subdivision at high-
number water test is studied with an in-house LES code in the paper. First, requirement for mesh subdivision at high-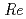 LES computation is theoretically studied. Then, the effects of turbulence model and boundary conditions are numerically studied using the Smagorinsky model and the WALE (Wall-adapting local eddy-viscosity) model with various inlet and outlet boundary conditions at
LES computation is theoretically studied. Then, the effects of turbulence model and boundary conditions are numerically studied using the Smagorinsky model and the WALE (Wall-adapting local eddy-viscosity) model with various inlet and outlet boundary conditions at 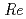 = 1.2
= 1.2 10
10 . It has turned out that the Smagorinsky model excels the WALE model and that an inlet velocity profile has a considerable impact on the separation features at the elbow curvature. It was also revealed that the outlet boundary condition is likely to have an effect on the separation features especially if the distance between the elbow and the outlet is rather short, which is the case of the present computation. Basic features of the pressure and the wall force fluctuations are also discussed with the aid of computational visualization and spectral analysis.
. It has turned out that the Smagorinsky model excels the WALE model and that an inlet velocity profile has a considerable impact on the separation features at the elbow curvature. It was also revealed that the outlet boundary condition is likely to have an effect on the separation features especially if the distance between the elbow and the outlet is rather short, which is the case of the present computation. Basic features of the pressure and the wall force fluctuations are also discussed with the aid of computational visualization and spectral analysis.
Kamide, Hideki; Miyakoshi, Hiroyuki; Watanabe, Osamu*; Eguchi, Yuzuru*; Koga, Tomonari*
Dai-14-Kai Doryoku, Enerugi Gijutsu Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu, p.427 - 428, 2009/06
Fully natural circulation system is adopted in a decay heat removal system (DHRS) of the designs of Japan Sodium Cooled Fast Reactor (JSFR). Several investigations of experiments and simulation methods on this DHRS are performed. Water experiments were carried out for the primary heat transportation system including a reactor vessel and heat exchangers of DHRS using a 1/10 model. As for the DHRS loop, sodium experiments were carried out, especially for a heat exchanger installed in an Intermediate Heat Exchanger (IHX). Here, several results of the sodium experiments were described. Transient characteristics during the start up in the air system of the air cooler, secondary loop of DHRS, and the primary loop were examined by the sodium experiments. Smooth increase of natural circulation flow rates in all systems of air and sodium were confirmed. Verifications of numerical simulation methods are planned based on the water and sodium experiments in this investigation plan.
Eguchi, Yuzuru*; Murakami, Takahiro*; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Yamano, Hidemasa; Kotake, Shoji
Proceedings of 6th Japan-Korea Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS-6) (USB Flash Drive), 8 Pages, 2008/11
The unsteady turbulent flow in a short-elbow pipe to be employed in a Japanese sodium-cooled fast breeder reactor was computed to examine the fundamental features of the flow, especially, pressure fluctuation to cause unsteady fluid force on the pipe. An FEM-based large-eddy simulation code, named SMART-fem, was used for the computation. The results at Re=3.2 10
10 and 1.2
and 1.2 10
10 show that two separation regions exist on the inner urvature of the elbow around 45-degree (middle of elbow) and 90-degree (end of elbow) positions. The statistical quantities of pressure fluctuation such as deviation, skewness and flatness were computed and analyzed, showing that there exist two symmetric regions of significant pressure fluctuation on the wall of inner curvature of the elbow. It has turned out that the pressure loss coefficient of the elbow pipe agrees well among the computation, experiment and authoritative reference data.
show that two separation regions exist on the inner urvature of the elbow around 45-degree (middle of elbow) and 90-degree (end of elbow) positions. The statistical quantities of pressure fluctuation such as deviation, skewness and flatness were computed and analyzed, showing that there exist two symmetric regions of significant pressure fluctuation on the wall of inner curvature of the elbow. It has turned out that the pressure loss coefficient of the elbow pipe agrees well among the computation, experiment and authoritative reference data.
Ito, Kei; Eguchi, Yuzuru*; Monji, Hideaki*; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Uchibori, Akihiro; Xu, Y.*
Proceedings of 6th Japan-Korea Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS-6) (USB Flash Drive), 8 Pages, 2008/11
A gas entrainment (GE) evaluation method presented at the previous symposium can predict a gas core length by applying local instant values (obtained from CFD results) to the extension vortex theory. However, in the GE evaluation method, a surface tension effect was not introduced. Therefore, it is valid to consider that gas core lengths were overestimated. In this study, the prediction accuracy of gas core lengths is improved by introducing the surface tension effects into the GE evaluation method. For that purpose, the mechanical balance between gravitational, centrifugal and surface tension forces are considered. The improved method was validated by predicting the gas core lengths in basic experiments. As the results, the predicted gas core length values by the improved evaluation method gave better agreements with the experimental results than the original evaluation method.
Sakai, Takaaki; Eguchi, Yuzuru*; Monji, Hideaki*; Ito, Kei; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Heat Transfer Engineering, 29(8), p.731 - 739, 2008/08
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:81.25(Thermodynamics)Design criteria for gas entrainments (GE) from the liquid surface in a fast breeder reactor system were proposed in this paper for the two types of GE phenomena from a vortex dimple based on a computational fluid dynamics (CFD) method. The first gas entrainment phenomenon is a gas core extension directly to the outlet piping level, which induces large amount of GE to the flow system. The second is continuous bubble detachments from the tip of the vortex dimple. Based on CFD calculations for elemental experiments of the surface vortex, local CFD non-dimensional numbers were defined as the design criteria to prevent GE. In conclusion, it was found that the CFD non-dimensional numbers are useful for the design parameters of GE prevention.
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Sakai, Takaaki; Kamide, Hideki; Kimura, Nobuyuki; Ezure, Toshiki; Uchibori, Akihiro; Ito, Kei; Kunugi, Tomoaki*; Okamoto, Koji*; Tanaka, Nobuatsu*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2008-049, 44 Pages, 2008/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has conducted a conceptional design study of a sodium-cooled fast reactor in a frame work of the FBR feasibility study. The plant system concept for a commercial step is intended to minimize a vessel diameter to achieve an economical competitiveness. Therefore, the coolant in the vessel has relatively higher velocity and gas entrainment (GE) prevention from a liquid surface in the reactor vessel becomes one of important issues for the thermal-hydraulic design. In order to establish a design criteria for the GE prevention, the GE from vortex dimples at the liquid surface was investigated by a working group. The 1st proposal of "Design Guideline for Gas Entrainment Prevention Using CFD Method" was established based on the knowledge gained from the working group activities. This report introduces each study in the working group to clarify the basis of the design guideline.
Eguchi, Yuzuru*; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Sakai, Takaaki; Yamaguchi, Akira*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 6(3), p.298 - 311, 2007/09
For numerical prediction of gas entrainment from a free surface in an upper plenum of a sodium-cooled fast breeder reactor, accurate computation of a swirling flow or vortices is one of the crucial ingredients. In this study, a multiscale LES code, MISTRAL, is applied to a swirl flow in a cylindrical vessel to examine the effects of the multiscale turbulence models on the accuracy of vortex prediction. The numerical results are compared with experimental results and another numerical results computed with a conventional LES code. The comparison indicates that the multiscale LES code is able to resolve the fine vortex core structure more accurately than the conventional one. Especially, elimination of eddy viscosity in the large-scale equations can improve the accuracy in computing a circumferential velocity around the vortex core. It has also turned out that a use of coarse mesh suppresses the peak value of circumferential velocity, which suggests us to employ an extrapolation method such as a vortex model in practice for quantitative estimate of unresolved vortex features.
Sakai, Takaaki; Eguchi, Yuzuru*; Monji, Hideaki*; Iwasaki, Takashi*; Ito, Kei; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 5th Korea-Japan Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS-5), p.406 - 413, 2006/11
Design criteria for gas entrainments (GE) from the liquid surface in a fast breeder reactor system were proposed in this paper for the two types of GE phenomena from a vortex dimple based on a computational fluid dynamics (CFD) method. The first gas entrainment phenomenon is a gas core extension directly to the outlet piping level, which induces large amount of GE to the flow system. The second is continuous bubble detachments from the tip of the vortex dimple. Based on CFD calculations for elemental experiments of the surface vortex, local CFD non-dimensional numbers were defined as the design criteria to prevent GE. In conclusion, it was found that the CFD non-dimensional numbers are useful for the design parameters of GE prevention.
Sakai, Takaaki; Monji, Hideaki*; Eguchi, Yuzuru*; Iwasaki, Takashi*; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 2006 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP '06) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2006/06
Design method for gas entrainment (GE) from liquid surfaces in a sodium-cooled fast breeder reactor (FBR) was studied. As one of trials to develop the design method by a computation fluid dynamics (CFD) technique, prediction of the GE condition from a surface vortex dimple in a cylindrical tank was performed by using a conventional CFD method. The CFD results showed reasonable agreements with the measured velocity profiles in experiments. Non-dimensional numbers by using the CFD results were proposed for the criteria of GE prevention. The GE design map was drawn by the CFD non-dimensional numbers for the existing CFD database. It was prospective that the gas entrainment can be evaluated by using the map of CFD non-dimensional numbers.
Eguchi, Yuzuru*
JNC TJ9400 2005-003, 87 Pages, 2005/07
The report is concerned with the evaluation of applicability of numerical modelling methods for the prediction of gas entrainment in an upper plenum of a sodium-cooled fast breeder reactor (FBR). Special attention was paid to applicability of variational multiscale (VMS) modelling in the context of the Finite Element Method. Two flow problems, which were experimentally shown to induce gas entrainment, are solved by a VMS code (MISTRAL). First, computing a benchmark problem of a gas entrainment swirl flow in a cylindrical vessel has led to the following results;(1) the VMS solution is able to resolve the precise vortex core structure more accurately than the non-VMS solution. The circumferential velocity obtained from VMS computation rises almost double in comparison with the non-VMS solution, though it still underestimates the experimental values.(2) the half-value radius of the negative region of the second invariant of velocity gradient matches well between the VMS and the non-VMS solutions.(3) the negative/positive boundary of the second invariant obtained from the VMS solution is closer to the vortex core radius observed in the experiment than that of the non-VMS solution, though the vortex dip length computed from the VMS result is shorter than the experimental value. Second, computing a benchmark problem of open channel flow with a square pillar and downstream suction pipe has led to the following results;(4) 2Dx-type spatial oscillation was observed due to lack of mesh subdivisions.(5) the distributional profile of the second invariant is similar to that of the first problem, characterized by a strong negative region surrounded by a weak positive region. As a possible future plan, it may be necessary to more precisely analyze the features of unsteady vortices obtained in the second benchmark problem and to identify the difference from the steady vortex of the first benchmark problem.
Sakai, Takaaki; Iwasaki, Takashi*; Eguchi, Yuzuru*; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
JNC TN9400 2004-017, 79 Pages, 2004/04
Numerical analysis was performed to validate a design method for a gas entrainment occurrence from a steady free surface vortex. In conclusion, it was clarified that the design method predicted the gas core lengths sufficiently conservative to the experimental data. If the gas entrainment criterion was supposed to be 50mm of the gas core length, it showed good agreement with experimental data.
Eguchi, Yuzuru*
JNC TJ9400 2004-005, 67 Pages, 2004/02
Numerical modelling methods are reviewed to identify suitable schemes for the prediction or evaluation of gas entrainment phenomena in an upper plenum of a sodium-cooled fast breeder reactor (FBR). Based on these review results, a possibly suitable numerical scheme is formulated for practical and accurate evaluation of the gas entrainment in a sodium-cooled FBR. To evaluate the selected numerical schemes, a benchmark problem of a gas entrainment swirl flow in a cylindrical vessel was solved with the method.
Sakai, Takaaki; Eguchi, Yuzuru*; Iwasaki, Takashi*; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Yamaguchi, Akira
Proceedings of 4th Japan-Korea Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS-4), p.171 - 178, 2004/00
Design method to prevent the gas entrainment from a steady vortex in a cylinder is discussed. The gas core length of the surface vortex dimple is used as a measure of the criterion of the gas entrainment. Burgers vortex model is applied compensationally to predict the gas core length with the practical CFD method. Practical CFD method that did not consider the liquid surface deformation was validated. Macroscopic flow parameters predicted by the CFD method showed reasonable agreements with the measured data in a cylindrical tank. In addition, predicted gas core lengths by using the CFD results showed conservatively longer length than the measured data. The criterion of the gas core length to prevent the gas entrainment was tried to evaluate for the Baum data in order to see the prospects of the design method. In conclusion, it may say that the CFD method has a possibility to evaluate the gas entrainment from a surface vortex.