Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:60 Percentile:96.18(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Ozawa, Kazumi; Morisada, Yoshiaki*; Noh, S.*; Fujii, Hidetoshi*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 98-99, p.2080 - 2084, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:71.70(Nuclear Science & Technology)The vacuum plasma spray (VPS) technique has been investigated as the most practical method to form Tungsten (W) layer as a plasma facing material in fusion devices. The issues are the thermal conductivity and the strength of VPS-W, i.e., the thermal conductivity of VPS-W were significantly lower than that of the bulk W, and the hardness of VPS-W is much less than that of the bulk W. These are mainly caused by the porous structure of VPS-W. In order to solve these issues, friction stir processing (FPS) was applied on VPS-W in this study. It was suggested that FSP can contribute to significant improvement both in mechanical and thermal properties of VPS-W coating.
Ozawa, Kazumi; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Morisada, Yoshiaki*; Fujii, Hidetoshi*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 98-99, p.2054 - 2057, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.75(Nuclear Science & Technology)Reduced activation ferritic/martensitic steel, as typified by F82H, is a promising candidate for structural material of DEMO fusion reactors. To prevent plasma sputtering, tungsten (W) coating was essentially required. This study aims to examine the irradiation effects on hardness and microstructure of vacuum-plasma-spray coated W-F82H steel, with a special emphasis on the impacts of grain-refining induced by frictional stir processing (FSP). It was revealed that the hardness of the VPS-FSP W after ion-irradiation to 5.4 dpa at 800 C were not remarkably changed, where bulk W usually exhibited significant irradiation hardening.
C were not remarkably changed, where bulk W usually exhibited significant irradiation hardening.
 Pd and stable
Pd and stable 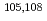 Pd nuclei at J-PARC/MLF/ANNRI
Pd nuclei at J-PARC/MLF/ANNRINakamura, Shoji; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitatani, Fumito; Ota, Masayuki; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Goko, Shinji*; Hara, Kaoru; Harada, Hideo; Hirose, Kentaro; Kin, Tadahiro*; et al.
Nuclear Data Sheets, 119, p.143 - 146, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:55.01(Physics, Nuclear)We have started the measurements of the neutron-capture cross sections for stable 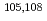 Pd nuclei as well as the radioactive
Pd nuclei as well as the radioactive  Pd. The neutron-capture cross-section measurements by the time-of flight method were performed using an apparatus called "Accurate Neutron-Nucleus Reaction measurement Instrument (ANNRI)" installed at the neutron Beam Line No.4 of the Materials and Life science experimental Facility (MLF) in the J-PARC. The neutron-capture cross sections of
Pd. The neutron-capture cross-section measurements by the time-of flight method were performed using an apparatus called "Accurate Neutron-Nucleus Reaction measurement Instrument (ANNRI)" installed at the neutron Beam Line No.4 of the Materials and Life science experimental Facility (MLF) in the J-PARC. The neutron-capture cross sections of  Pd and
Pd and 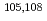 Pd have been measured in the neutron energy range from thermal to 300 eV. Some new information was obtained for resonances of these Pd nuclei.
Pd have been measured in the neutron energy range from thermal to 300 eV. Some new information was obtained for resonances of these Pd nuclei.
 Am(n,
Am(n, ) at J-PARC/MLF/ANNRI
) at J-PARC/MLF/ANNRIHarada, Hideo; Ota, Masayuki; Kimura, Atsushi; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Hirose, Kentaro; Hara, Kaoru; Kin, Tadahiro*; Kitatani, Fumito; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Nakamura, Shoji; et al.
Nuclear Data Sheets, 119, p.61 - 64, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:73.90(Physics, Nuclear)Nakamura, Shoji; Ota, Masayuki; Oshima, Masumi; Kitatani, Fumito; Kimura, Atsushi; Kin, Tadahiro; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Goko, Shinji*; Toh, Yosuke; Hara, Kaoru; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2012-001, p.147 - 152, 2012/07
 Cm and
Cm and 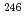 Cm measured with an array of large germanium detectors in the ANNRI at J-PARC/MLF
Cm measured with an array of large germanium detectors in the ANNRI at J-PARC/MLFKimura, Atsushi; Fujii, Toshiyuki*; Fukutani, Satoshi*; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Goko, Shinji*; Hara, Kaoru; Harada, Hideo; Hirose, Kentaro; Hori, Junichi*; Igashira, Masayuki*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 49(7-8), p.708 - 724, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:52 Percentile:95.69(Nuclear Science & Technology)Hori, Junichi*; Fujii, Toshiyuki*; Fukutani, Satoshi*; Furusaka, Michihiro*; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Goko, Shinji*; Harada, Hideo; Hiraga, Fujio*; Igashira, Masayuki*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2011-002, p.29 - 34, 2011/09
The neutron capture cross sections of  Zr,
Zr,  Tc and
Tc and  Pd have been measured relative to the
Pd have been measured relative to the  B(n,
B(n,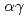 ) standard cross section by the neutron time-of-flight (TOF) method. Neutron capture
) standard cross section by the neutron time-of-flight (TOF) method. Neutron capture  rays were measured with a 4
rays were measured with a 4 Ge spectrometer as a part of the Accurate Neutron-Nucleus Reaction measurement Instrument (ANNRI) installed at the neutron Beam Line No.4 (BL04) of the Material and Life science experimental Facility (MLF) in the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). This paper presents the preliminary results.
Ge spectrometer as a part of the Accurate Neutron-Nucleus Reaction measurement Instrument (ANNRI) installed at the neutron Beam Line No.4 (BL04) of the Material and Life science experimental Facility (MLF) in the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). This paper presents the preliminary results.
Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Kino, Koichi*; Furusaka, Michihiro*; Hiraga, Fujio*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Kato, Kiyoshi*; Igashira, Masayuki*; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Mizumoto, Motoharu*; Oshima, Masumi; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 59(2), p.1781 - 1784, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:61.03(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The project of the comprehensive nuclear data research for the development of the advanced reactor systems had been executed successfully by eight organizations from 2005 to 2009. In this project, we constructed the pulsed neutron beamline that was aimed to obtain neutron capture cross-sections of long-lived fission products and minor actinides accurately. The energy spectra, spatial distributions, and pulses of the beam were studied by measurements and simulation calculations, and they were found to be consistent with those of the beamline design. In this paper, we present the overview of the project and the properties of the neutron beam provided by this beam line.
Nakamura, Shoji; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Goko, Shinji; Harada, Hideo; Kimura, Atsushi; Kin, Tadahiro; Kitatani, Fumito; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Ota, Masayuki; Oshima, Masumi; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 59(2), p.1773 - 1776, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:38.01(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A series of neutron-capture cross-section measurements using the time-of flight method has been started at the J-PARC/MLF/ANNRI. As a part of the measurements, we have measured the neutron-capture cross-sections of Pd isotopes such as 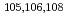 Pd.
Pd.
 Ge spectrometer
Ge spectrometerHarada, Hideo; Goko, Shinji*; Kimura, Atsushi; Ota, Masayuki*; Oshima, Masumi; Kitatani, Fumito; Toh, Yosuke; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Kin, Tadahiro; Koizumi, Mitsuo; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 59(2), p.1547 - 1552, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:52.46(Physics, Multidisciplinary)For the improvement of the accuracy on the neutron capture cross sections, a 4 Ge spectrometer was developed. The 4
Ge spectrometer was developed. The 4 Ge spectrometer is a unique tool due to its superior energy resolution for studying properties on neutron capture reactions, not only capture cross sections but also resonance identification,
Ge spectrometer is a unique tool due to its superior energy resolution for studying properties on neutron capture reactions, not only capture cross sections but also resonance identification,  -ray intensity distribution, and spin-parity assignment. For example, its performance on the resonance identification was demonstrated using a
-ray intensity distribution, and spin-parity assignment. For example, its performance on the resonance identification was demonstrated using a  Ag sample. On the measurement of a
Ag sample. On the measurement of a  -ray intensity distribution for each resonance, the results of
-ray intensity distribution for each resonance, the results of  U will be shown. Using the 4
U will be shown. Using the 4 Ge spectrometer, the measurements of neutron capture cross sections were started at the J-PARC/MLF/ANNRI. The preliminary results on the measurements of neutron capture cross sections will be discussed mainly based on measurements of neutron capture cross sections for
Ge spectrometer, the measurements of neutron capture cross sections were started at the J-PARC/MLF/ANNRI. The preliminary results on the measurements of neutron capture cross sections will be discussed mainly based on measurements of neutron capture cross sections for  Am, together with related techniques.
Am, together with related techniques.
 Cm and
Cm and 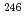 Cm at J-PARC/MLF/ANNRI
Cm at J-PARC/MLF/ANNRIKimura, Atsushi; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Goko, Shinji*; Harada, Hideo; Kin, Tadahiro; Kitatani, Fumito; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Nakamura, Shoji; Ota, Masayuki*; Oshima, Masumi; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 59(2), p.1828 - 1831, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:26.60(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Harada, Hideo; Oshima, Masumi; Kimura, Atsushi; Goko, Shinji*; Ota, Masayuki*; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Kin, Tadahiro; Kitatani, Fumito; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Nakamura, Shoji; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2010-005, p.9 - 14, 2010/12
The neutron-nucleus reaction instrument (NNRI) was installed at the J-PARC MLF BL04, which was designed for measuring neutron cross sections with a neutron time-of-flight technique. This includes two kinds of capture  -ray spectrometers: the 4
-ray spectrometers: the 4 Ge spectrometer and the NaI spectrometers. The measurements of neutron capture cross sections for minor actinides and fission products have been started at the NNRI using these spectrometers since 2009. In this paper, the preliminary results and future perspectives are discussed.
Ge spectrometer and the NaI spectrometers. The measurements of neutron capture cross sections for minor actinides and fission products have been started at the NNRI using these spectrometers since 2009. In this paper, the preliminary results and future perspectives are discussed.
 Cm resonances using NNRI
Cm resonances using NNRIGoko, Shinji*; Kimura, Atsushi; Harada, Hideo; Oshima, Masumi; Ota, Masayuki*; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Kin, Tadahiro; Kitatani, Fumito; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Nakamura, Shoji; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 47(12), p.1097 - 1100, 2010/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:39.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)To obtain the accurate nuclear data of minor actinides required for a nuclear transmutation system or an innovative nuclear fuel cycle system, measurement of neutron-capture cross section of  Cm was performed using NNRI installed at beam line No.4 (BL04) of MLF in J-PARC. Using "4
Cm was performed using NNRI installed at beam line No.4 (BL04) of MLF in J-PARC. Using "4 Ge spectrometer" that is a component of NNRI, neutron time of flight spectra and prompt
Ge spectrometer" that is a component of NNRI, neutron time of flight spectra and prompt  ray spectra were measured. Then neutron-capture cross section ratios of
ray spectra were measured. Then neutron-capture cross section ratios of  Cm resonances were derived and compared with the evaluated values of JENDL-3.3. The previous experimental data was measured using a nuclear explosion as a pulsed neutron source, and the present result is the first time in the world that such measurements have been carried out at an accelerator facility. By developing techniques for more detailed analysis and improvement of the experimental conditions, the absolute values of capture cross section are expected to be obtained.
Cm resonances were derived and compared with the evaluated values of JENDL-3.3. The previous experimental data was measured using a nuclear explosion as a pulsed neutron source, and the present result is the first time in the world that such measurements have been carried out at an accelerator facility. By developing techniques for more detailed analysis and improvement of the experimental conditions, the absolute values of capture cross section are expected to be obtained.
Sanada, Hiroyuki; Niunoya, Sumio*; Matsui, Hiroya; Fujii, Yoshiaki*
Journal of MMIJ, 125(10,11), p.521 - 529, 2009/11
This paper shows the results obtained from the laboratory tests and microscopic observation of Horonobe siliceous rocks. The consolidated undrained and drained triaxial compression tests showed different behaviors of strain-softening, pore pressure and dilatancy between diatomaceous and siliceous mudstones. Stress-strain behavior changed from strain-softening to ductile behavior under high confining pressure and pore pressure increased gradually even after peak strength for diatomaceous mudstone. Diatomaceous mudstone yielded under hydrostatic pressure of 10 MPa in isotropic consolidation test. This yielding was regarded as pore collapse based on the variation of hydraulic conductivity which was estimated from variation of volumetric strain in isotropic consolidation test, effective porosity and microscopic observation before and after the yielding.
Sanada, Hiroyuki; Niunoya, Sumio*; Matsui, Hiroya; Fujii, Yoshiaki*
Journal of MMIJ, 125(10,11), p.530 - 539, 2009/10
Understanding initial stress in underground is important for construction of HLW repository. Evaluation of initial stress around Horonobe URL was carried out in order to understand initial stress condition and applicability of AE, DSCA and hydraulic fracturing (HF) methods to Neogene sedimentary rock. Initial stress values obtained from AE method is smaller than overburden pressure due to time dependency of Kaizer effect. Principal stress values by DSCA are similar to those by HF tests. Directions of maximum horizontal principal stresses are approximately in E-W and corresponded to HF results. Horizontal maximum and minimum principal stresses increase linearly in HF results. Deviatoric stress is acting at shallow depth. Initial stress condition approaches hydrostatic condition with depth. Direction of maximum horizontal principal stress was in E-W direction which was similar to tectonic movement around Horonobe URL by triangular surveying.
Sanada, Hiroyuki; Sugita, Yutaka; Fujii, Yoshiaki*
Proceedings of 3rd International Workshop and Conference on Earth Resources Technology 2009 (CD-ROM), p.149 - 158, 2009/05
EDZ is considered to be important issues in repositories since this is relevant to plug design, support design etc. As a part of the research and development on the geological isolation, JAEA has been implementing the Horonobe URL Project. Deformation and failure behavior around a shaft in URL is described in the paper. Tunnel shape are being measured by a laser displacement sensor to clarify dimension and mechanism of breakouts along the shaft wall. Displacement measurement by extensometers are being carried out to understand deformation behavior in the surrounding rock mass. Breakouts of about 50 cm deep in N-S direction are more frequently observed with excavation depth. The breakout direction was consistent with the maximum horizontal stress which was estimated to be approximately in E-W direction by hydrofracturing tests. Compressive deformation of rock mass also increased with excavation depth. Most part of the deformation occurred within 1 m from the shaft wall.
Sanada, Hiroyuki; Matsui, Hiroya; Fujii, Yoshiaki*
Proceedings of International Symposium on Rock Mechanics "Rock Characterization, Modelling and Engineering Design Methods" (SINOROCK 2009) (CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2009/05
This paper shows the results obtained from triaxial and isotropic consolidation test to select mechanical behavior of Horonobe siliceous rocks. The consolidated undrained and drained triaxial compression tests showed different behaviors of strain-softening, pore pressure and dilatancy between diatomaceous and siliceous mudstones. Stress-strain behavior changed from strain-softening to ductile behavior under high confining pressure and pore pressure increased gradually even after peak strength for diatomaceous mudstone. Diatomaceous mudstone yielded under hydrostatic pressure of 10 MPa in isotropic consolidation test. This yielding was regarded as pore collapse based on the variation of hydraulic conductivity which was estimated from variation of volumetric strain in isotropic consolidation test, effective porosity and microscopic observation before and after the yielding.
Sanada, Hiroyuki; Matsui, Hiroya; Fujii, Yoshiaki*
Dai-12-Kai Iwa No Rikigaku Kokunai Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (CD-ROM), p.703 - 708, 2008/09
This paper shows the result of rock mechanical investigations which have been carried out as a part of the investigations of Horonobe Underground Research Project. The results of the investigations are summarized as follows. Uniaxial compression and tensile strength of siliceous rock distributed in Wakkanai formation is larger than diatomaceous mudstone distributed in Koetoi formation. Stress-strain curve shows strain softening behavior from results of tri-axial compression test. Pore pressure and dilatancy behavior show different trends as compared with diatomaceous mudstone and siliceous rock.
Sanada, Hiroyuki; Matsui, Hiroya; Yamamoto, Takuya*; Aoki, Tomoyuki*; Ogawa, Toyokazu*; Jo, Mayumi*; Fujii, Yoshiaki*
Heisei-19-Nendo Shigen, Sozai Gakkai Hokkaido Shibu Sokai Oyobi Shunki Koenkai Koen Yoshishu, p.9 - 10, 2007/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been conducting the Horonobe Underground Reseach Laboratory Project as a part of geological isolation research and development at Horonobe-town in Hokkaido, Japan. The rocks around URL have high porosity and low permeability. Therefore, the excess pore pressure caused by URL excavation is possible to affect to the stability of surrounding rock. In this point of view, the authors carried out a stress-seepage coupled analysis to understand the process of the pore pressure change due to excavation and the influence to the stability of surrounding rock and support system. As a result, the large excess pore pressure causes a part in surrounding rock on excavation in an anisotropic initial stress condition and it dissipates with time. The pore pressure change causes the complex deformation in the surrounding rock as well. However, the phenomena are not significant influence to the stability of the surrounding rock and support system.