Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Terasaka, Yuta; Iimoto, Takeshi*; Saso, Michitaka*; Fujita, Reiko*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 66(4), p.203 - 207, 2024/04
, 66(4), p.203 - 207, 2024/04
no abstracts in English
Iwamoto, Osamu; Fujita, Reiko*; Niita, Koji*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*
Kaku Deta Nyusu (Internet), (122), p.33 - 43, 2019/02
A program related to the transmutation of long-lived fission products (LLFPs) entitled "Reduction and Resource Recycling of High-level Radioactive Wastes through Nuclear Transmutation" has been conducted under the Impulsing Paradigm Change through Disruptive Technologies Program (ImPACT) organized by the Cabinet Office since 2014 and it will be finished in FY 2018. Various activities from acquisition of basic data to examination of transmutation scenario are being carried out as the five separated projects. R&Ds related to nuclear data are also conducted and many outcomes are being produced. This article describes results of the two projects related nuclear data with a short introduction of the whole project.
Koyama, Shinichi; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Ozawa, Masaki*; Kurosawa, Kiyoko*; Fujita, Reiko*; Mimura, Hitoshi*; Okada, Ken*; Morita, Yasuji; Fujii, Yasuhiko*
Procedia Chemistry, 7, p.222 - 230, 2012/00
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:77.60(Chemistry, Analytical)Adv.-ORIENT cycle strategy has been proposed as a basic concept for trinitarian research on separation, transmutation and utilization of nuclides and elements based on FBR fuel cycle. Validation of principal separation method and related safety research were performed from 2006 through 2011 as Phase I program. First, more than 90% of Cs could be recovered from the actual spent fuel [IXC(I) step]. The next is the adsorption of the platinum group metals (PGM), lanthanides, Am and Cm were separated by using a tertiary pyridine-type resin (TPR) as ion exchange steps [IXC(II, III, IV) steps]. The separated PGM metals will be supplied to the electrochemical extraction [CEE step]. As experiment for safety issues, Hastelloy-B at RT and Ta at 90 C were confirmed their anti-corrosive in highly concentrated HCl media. Thermo-chemical stability for TPR was verified. Issues to be solved for next phase based on the final results of phase I program.
C were confirmed their anti-corrosive in highly concentrated HCl media. Thermo-chemical stability for TPR was verified. Issues to be solved for next phase based on the final results of phase I program.
Koyama, Shinichi; Yamagishi, Isao; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Ozawa, Masaki*; Fujita, Reiko*; Okada, Ken*; Tatenuma, Katsuyoshi*; Mimura, Hitoshi*; Fujii, Yasuhiko
Proceedings of International Conference on Toward and Over the Fukushima Daiichi Accident (GLOBAL 2011) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/12
Effective separation of MA and LLFP, transmutation and utilization were the main directions of Advanced OREINT Cycle project. Study for each integrant technology was concluded as first trial of the project. TPR enabled to separate MA/Ln and then Am/Cm precisely from spent fuel in HCl and HNO media. CEE method could separate the light PGM and Tc by HCl media. Recovery of Cs from simulated HLLW coul be achieved more than 90 %. In addition, the perspective for next phase was proposed.
media. CEE method could separate the light PGM and Tc by HCl media. Recovery of Cs from simulated HLLW coul be achieved more than 90 %. In addition, the perspective for next phase was proposed.
Koyama, Shinichi; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Mimura, Hitoshi*; Fujita, Reiko*; Kurosawa, Kiyoko*; Okada, Ken*; Ozawa, Masaki
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 53(7), p.980 - 987, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:36.74(Nuclear Science & Technology)Individual basic researches of separation step were performed in the Advanced ORIENT Cycle project. High separation selectivity for Cs and Sr by novel nano adsorbents AMP-SG (D) and D18C6-MC were confirmed, respectively. TPR well adsorbed Pd and Tc in dilute HCl condition. Formation of rare metal fission product RMFP-deposit Pt electrodes from SHLLW was verified, and it was confirmed that high catalytic reactivity on electrolytic production of hydrogen. As experiment for engineering feasibility, Hastelloy-B at RT and Ta at 90 C were confirmed their anti-corrosive in highly concentrated HCl media. Thermo-chemical stability for TPR was verified in either HCl or HNO
C were confirmed their anti-corrosive in highly concentrated HCl media. Thermo-chemical stability for TPR was verified in either HCl or HNO media toward its practical use in the separation process. Issues to be solved for optimization based on the results of lab-scale experiment have revealed in this study.
media toward its practical use in the separation process. Issues to be solved for optimization based on the results of lab-scale experiment have revealed in this study.
Ozawa, Masaki; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Koyama, Shinichi; Yamagishi, Isao; Fujita, Reiko*; Okada, Ken*; Tatenuma, Katsuyoshi*; Mimura, Hitoshi*; Fujii, Yasuhiko*
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycle; Sustainable Options & Industrial Perspectives (Global 2009) (CD-ROM), p.1117 - 1126, 2009/09
Fujita, Reiko*; Nakamura, Hitoshi*; Mizuguchi, Koji*; Utsunomiya, Kazuhiro*; Amamoto, Ippei
Proceedings of 2008 Joint Symposium on Molten Salts (USB Flash Drive), p.886 - 891, 2008/10
Pyrochemical treatment in molten salts is a promising process for decontamination of radioactive wastes without producing large amounts of secondary waste. In this report, the fundamental experiment was carried out to treat the wastes which had complicated shapes such as Magnoxend corps, metallic waste contaminated by uranium, spent chemical trap fillers and spent Zircaloy channel boxs from BWR and acquired good results.
Ozawa, Masaki; Koyama, Shinichi; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Fujita, Reiko*; Mimura, Hitoshi*; Fujii, Yasuhiko*
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles and Systems (Global 2007) (CD-ROM), p.451 - 457, 2007/09
To minimize the ecological burden originating in nuclear fuel recycling, a new R&D strategy, Adv.-ORIENT (Advanced Optimization by Recycling Instructive ElemeNTs) cycle, was set forth. A key separation tool is ion exchange chromatography (IXC) by a tertiary pyridine resin having soft donor nitrogen atoms. This method has provided individual recovery of pure Am and Cm products with a Pu/U/Np fraction from irradiated fuel in just a 3-step separation. A catalytic electrolytic extraction (CEE) method by Pd has been employed to separate, purify and fabricate RMFP catalysts. High separation efficiency of RMFP proved hydrochloric acid as a suitable media for their recovery. Different functioned ion exchangers, e.g., ammonium molybdophosphate (AMP), have been investigated for the separation of Cs
has been employed to separate, purify and fabricate RMFP catalysts. High separation efficiency of RMFP proved hydrochloric acid as a suitable media for their recovery. Different functioned ion exchangers, e.g., ammonium molybdophosphate (AMP), have been investigated for the separation of Cs . Theoretical and laboratory studies on the isotope separation of LLFPs were begun for
. Theoretical and laboratory studies on the isotope separation of LLFPs were begun for  Se,
Se,  Sn and
Sn and  Cs.
Cs.
Hayashi, Hirokazu; Akabori, Mitsuo; Minato, Kazuo; Mizuguchi, Koji*; Kawabe, Akihiro*; Fujita, Reiko*
Denki Kagaku Oyobi Kogyo Butsuri Kagaku, 75(7), p.528 - 534, 2007/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Electrochemistry)The simulation code for the pyrochemical processing of spent nuclear fuels was developed to analyze experimental data, to predict experimental results, and to propose adequate conditions and processes. The Simulation code for Pyrochemical Reprocessing (SPR) is based on calculations of chemical equilibrium and electrochemical reactions. The code also includes the calculations of the current-potential distribution between the electrodes. Some calculations were made to simulate the experimental results on the electro-codeposition process of UO and PuO
and PuO . The phenomena of the redox reactions between Pu
. The phenomena of the redox reactions between Pu and Pu
and Pu ions and those between Fe
ions and those between Fe and Fe
and Fe ions were theoretically analyzed; these redox reactions cause the low current efficiency in the electro-codeposition process. The calculated current-potential distribution around the cathode corresponds to the observed distribution of the oxide deposited on the cathode.
ions were theoretically analyzed; these redox reactions cause the low current efficiency in the electro-codeposition process. The calculated current-potential distribution around the cathode corresponds to the observed distribution of the oxide deposited on the cathode.
Ozawa, Masaki; Fujita, Reiko*; Koyama, Shinichi; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Fujii, Yasuhiko*
Proceedings of 9th OECD/NEA Information Exchange Meeting on Actinide and Fission Product Partitioning and Transmutation, p.315 - 324, 2007/00
Catalytic Electrolytic extraction method has been studied as a separation tool for rare metal fission products, RMFP in the spent nuclear fuel. In an employed CEE process, Pd cation itself would not only be easily deposited from various nitric acid solutions, but enhance also the deposition of co-existing RuNO
cation itself would not only be easily deposited from various nitric acid solutions, but enhance also the deposition of co-existing RuNO , ReO
, ReO
 and
and  TcO
TcO
 by acting as a catalyst. The quaternary-, Pd-Ru-Rh-Re, deposit Pt or Ti electrode, fabricated by CEE, suggested the highest cathodic current corresponding to the hydrogen generation reaction in both alkaline solution and sea water. Advanced ORIENT Cycle, where ion exchange chromatography using tertiary pyridine resin and the CEE employ as mainstay separation technology, will enhance separation and utilization of actinide and fission product, and thus be expected to realize ultimate reducing radioactive wastes.
by acting as a catalyst. The quaternary-, Pd-Ru-Rh-Re, deposit Pt or Ti electrode, fabricated by CEE, suggested the highest cathodic current corresponding to the hydrogen generation reaction in both alkaline solution and sea water. Advanced ORIENT Cycle, where ion exchange chromatography using tertiary pyridine resin and the CEE employ as mainstay separation technology, will enhance separation and utilization of actinide and fission product, and thus be expected to realize ultimate reducing radioactive wastes.
; Utsunomiya, Kazuhiro*; ; ; Fujita, Reiko*
JNC TJ6400 2002-006, 173 Pages, 2003/03
None
; ; ; ; Fujita, Reiko*
JNC TJ6400 2001-011, 35 Pages, 2002/02
no abstracts in English
; Sato, Fuminori; ; Mizuguchi, Koji*; Omori, Takashi*; Fujita, Reiko*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 1(3), p.312 - 316, 2002/00
None
; Fujita, Reiko*; Yahata, Hidetsugu*; ; Utsunomiya, Kazuhiro*
JNC TJ8400 2001-029, 52 Pages, 2001/01
Pyrochemical reprocessing is one of a successful candidate of good economy for spent fuel reprocessing. Metallic fuel reprocessing process based on Argonne National Laboratory technology needs a reduction process from oxide fuel to metallic fuel to be applied to oxide fuel reprocessing. This study has examined the reduction process using metallic Li as a reducing agent for UO which is comparatively estimated with the results of U
which is comparatively estimated with the results of U O
O examined last year after investigating the material of mesh basket with literature. The mesh basket made of Ti and W for oxide container, which are selected by investigating the material of mesh basket with literature, were both broken during reduction. However, the mesh basket made of several layers of stainless steel was not broken at the same reduction condition. The reduction ratio of UO
examined last year after investigating the material of mesh basket with literature. The mesh basket made of Ti and W for oxide container, which are selected by investigating the material of mesh basket with literature, were both broken during reduction. However, the mesh basket made of several layers of stainless steel was not broken at the same reduction condition. The reduction ratio of UO was estimated to be about 80-100% by a gas bullet method or an acidic pretreatment method. The influence of simulated fission products (FPs) on the reduction ratio of UO
was estimated to be about 80-100% by a gas bullet method or an acidic pretreatment method. The influence of simulated fission products (FPs) on the reduction ratio of UO was nothing, however the reduction products were mixed with the simulated FPs. A further study such as investigating the behavior of FPs in the Li reduction conditions and establishing the separation process of FPs from the reduction products of UO
was nothing, however the reduction products were mixed with the simulated FPs. A further study such as investigating the behavior of FPs in the Li reduction conditions and establishing the separation process of FPs from the reduction products of UO is necessary.
is necessary.
Fujita, Reiko*; ; Kondo, Naruhito*; Utsunomiya, Kazuhiro*
JNC TJ8420 2000-004, 41 Pages, 2000/03
no abstracts in English
Fujita, Reiko*; Yahata, Hidetsugu*; Kondo, Naruhito*; Utsunomiya, Kazuhiro*
JNC TJ8400 2000-066, 45 Pages, 2000/03
no abstracts in English
Yamaoka, Mitsuaki*; Fujita, Reiko*
PNC TJ9164 97-002, 105 Pages, 1997/03
As a study on technology utilization of advanced fast reactors, a core study on burning technology of actinides and FPs by fast reactors is carried out together with a research on material characteristics of fuels and targets for Pu/FP Burning. In the core study, a Pu-burning fast reactor corc was studied which can also burn minor actinides and FPs based upon the 600MWe Pu-burning fast reactor core with high Pu enrichment ( 40%). The criteria of core design were no significant change of core specification and small sodium void reactivity, and so on. In the core, minor actinides and FPs are loaded in the following way. (a)Core region ; loading of Pu/Np (Oxide fuel, Pu enrichment of
40%). The criteria of core design were no significant change of core specification and small sodium void reactivity, and so on. In the core, minor actinides and FPs are loaded in the following way. (a)Core region ; loading of Pu/Np (Oxide fuel, Pu enrichment of  40%) (b)Outside of core region ; the first layer
40%) (b)Outside of core region ; the first layer  loading of Am/Cm/rate earths mixed with ZrH
loading of Am/Cm/rate earths mixed with ZrH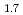 the second laycr
the second laycr  loading of Tc-99 mixed with ZrH
loading of Tc-99 mixed with ZrH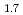 . The operation cycle length is 5 months and the averagc discharge burnup is about 80GWd/t. The burning capability of Pu, minor actinides and FPs is as follows ; (1)Pu burning rate ;
. The operation cycle length is 5 months and the averagc discharge burnup is about 80GWd/t. The burning capability of Pu, minor actinides and FPs is as follows ; (1)Pu burning rate ;  390kg/Year(
390kg/Year( 74kg/TWhe) (2)Burning rate of minor actinides;
74kg/TWhe) (2)Burning rate of minor actinides;  4.2%/Year(
4.2%/Year( 43kg/Year) (3)Burning rate of Tc-99;
43kg/Year) (3)Burning rate of Tc-99;  3.7%/Year(
3.7%/Year( 6.5kg/Year) The sodium void reactivity is very small. (0.1%
6.5kg/Year) The sodium void reactivity is very small. (0.1%  k/kk'=40cent) It is much smaller than that of the conventional fast reactors. This is the advantage of the core concept. The recent progress of material investigation of Pu, minor actinides and FP burning fuels was summaried. Also, basic characteristics of targets for FP burning was summalized, and the compatibility of the targets with ZrH
k/kk'=40cent) It is much smaller than that of the conventional fast reactors. This is the advantage of the core concept. The recent progress of material investigation of Pu, minor actinides and FP burning fuels was summaried. Also, basic characteristics of targets for FP burning was summalized, and the compatibility of the targets with ZrH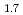 is evaluated.
is evaluated.
; Kawashima, Masatoshi*; ; Yamaoka, Mitsuaki*; Fujita, Reiko*
PNC TJ9164 96-008, 189 Pages, 1996/12
In the first reactor, sodium void reactivity and and sodium coolant temperature reavtivity are increased, and Doppler coefficient is decreased when MA is recycled. It is important to improve these reactivities in terms of safety features. In the study, Analysis was conducted of the effect on the sodium void reduction without deteriorating the core performance by mixing nuclides that give large absorption reactions in the higher energy region, where neutrons are increased at the neutron spectrum is hardened. Effect of higher Pu isotopes was also analyzed with parameters for improving Doppler coefficient. In the analysis of reduced sodium void reactivity core usig the threshold reaction, dominant energy region was identified for the sodium void reactivity by analyzing the core neutron spectra with parameters of MA mixing and core size. Furthermore, effect on reducing void reactivity was analyzed with parameters of inventory amounts and kinds of absorber nuclides. As a result, it was found that the sodium void reactivity of the MOX core with oxide-17 was about half of that of the core with natural oxide. In the analysis of reduced Doppler reactivity core, effect of improving the Doppler effect was analyzed for the nitride fuel core with higher Pu isotopes and resonance absorbers. Applicability and properties required for core analysis were also examined for candidates of base inert material, and the properties of fuel with those materials were preliminary surveyed. As a result, it was found that characteristics including Doppler coefficients can be improved with nuclides of structure material as metal form.
Yamaoka, Mitsuaki*; ; Kawashima, Masatoshi*; Fujita, Reiko*
PNC TJ9164 95-009, 231 Pages, 1995/03
To enhance plutonium burning capability in fast reactors, one of the effective means is to use materials other than uranium for dilution of plutonium. A feasibility study was made to build a 600MWe-class core concept within the do-main of sodium-cooled fast reactors. The analysis covered core static and transient characteristics, including fuel material surveys. The candidate fuels were chosen as plutonium oxide with diluen materials, such as Al O
O and BeO, to keep the Doppler coefficients negative large enough, condisering the TOP-type transisnts results from the FY1993 study. Core nuclear analysis showed that use of fuel without uranium considerably increases burnup swing and power mismatch between fresh and burnt fuels, aiming at the long cycle length as the 600MWe MOX core design. The core characteristics under ULOF- and UTOP-transients were compared with those in the 600MWe-MOX core. The study showed that the 9-month cycle core burned 59% fissile plutonium with negative sodium void worth (-1 $) under the plant condition for sodium inlet 390 C-deg. and the outlet temperature 510 C-deg. This study revealed that core neutronic feasibility has shown for such an innovative core concept with selecting appropriate diluent fuel materials combining core specifications. This means that sodium-cooled fast reactor has additional larger flexibility associated with plutonium utilization in the future.
and BeO, to keep the Doppler coefficients negative large enough, condisering the TOP-type transisnts results from the FY1993 study. Core nuclear analysis showed that use of fuel without uranium considerably increases burnup swing and power mismatch between fresh and burnt fuels, aiming at the long cycle length as the 600MWe MOX core design. The core characteristics under ULOF- and UTOP-transients were compared with those in the 600MWe-MOX core. The study showed that the 9-month cycle core burned 59% fissile plutonium with negative sodium void worth (-1 $) under the plant condition for sodium inlet 390 C-deg. and the outlet temperature 510 C-deg. This study revealed that core neutronic feasibility has shown for such an innovative core concept with selecting appropriate diluent fuel materials combining core specifications. This means that sodium-cooled fast reactor has additional larger flexibility associated with plutonium utilization in the future.
Nishihara, Kenji; Kawashima, Masatoshi*; Fujita, Reiko*
no journal, ,
In this project, research and development of elemental technologies has been promoted for separation and transmutation. In this research, we integrated HLW volume reduction and resource recycling system and evaluated the overall material balance. In addition, we examined the disposal method of generated waste and the possibility of recycled materials.