Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Gu, G. H.*; Jeong, S. G.*; Heo, Y.-U.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Cho, J.*; Kim, H. S.*; 他4名*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 223, p.308 - 324, 2025/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Face-centered cubic (FCC) equi-atomic multi-principal element alloys (MPEAs) exhibit excellent mechanical properties from cryogenic to room temperatures. At room temperature, deformation is dominated by dislocation slip, while at cryogenic temperatures (CTs), reduced stacking fault energy enhances strain hardening with twinning. This study uses in-situ neutron diffraction to analyze the temperature-dependent deformation behavior of Al (CoNiV)
(CoNiV)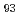 , a dual-phase (FCC/BCC) medium-entropy alloy (MEA). At liquid nitrogen temperature (LNT), deformation twinning in the FCC matrix leads to additional strain hardening through the dynamic Hall-Petch effect, giving the appearance of improved strengthening at LNT. In contrast, BCC precipitates show dislocation slip at both 77 K and 298 K, with temperature-dependent lattice friction stress playing a significant role in strengthening. The study enhances understanding of deformation behaviors and provides insights for future alloy design.
, a dual-phase (FCC/BCC) medium-entropy alloy (MEA). At liquid nitrogen temperature (LNT), deformation twinning in the FCC matrix leads to additional strain hardening through the dynamic Hall-Petch effect, giving the appearance of improved strengthening at LNT. In contrast, BCC precipitates show dislocation slip at both 77 K and 298 K, with temperature-dependent lattice friction stress playing a significant role in strengthening. The study enhances understanding of deformation behaviors and provides insights for future alloy design.
Go, J.*; Park, M.-H.*; Gao, S.*; 松宮 久*; Gong, W.; 辻 伸泰*
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 1014, p.178749_1 - 178749_10, 2025/02
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:89.83(Chemistry, Physical)In Mg alloys, basal dislocation slip is the preferential slip system that is activated at room temperature, while non-basal slips are typically difficult to activate owing to their high critical resolved shear stress. Until now, minimal focus has been directed towards the influence of loading direction on slip behavior in pre-twinned AZ31 alloys. This study employed transmission electron microscopy to demonstrate that non-basal slips, specifically prismatic and pyramidal I slips, are activated under deformation conditions where de-twinning is difficult in a pre-twinned AZ31 Mg alloy. When the tensile loading direction is parallel to the precompression direction, de-twinning and basal slip are the primary deformation modes. Conversely, when the tensile loading direction is perpendicular to the precompression direction, where de-twinning is challenging to activate, both basal and non-basal slips, such as prismatic and pyramidal I slips, emerge as the primary deformation modes. These results indicate that the pre-twinned AZ31 Mg alloy cannot deform solely through basal slips, and the activation of either de-twinning or non-basal slips is necessary to satisfy the von Mises criterion. Our findings in this study demonstrate the impact of non-basal slip activity on macroscopic yield stress and overall deformation, hence enhancing the understanding of magnesium alloy deformation mechanisms.
Naeem, M.*; Ma, Y.*; Tian, J.*; Kong, H.*; Romero-Resendiz, L.*; Fan, Z.*; Jiang, F.*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Wu, Z.*; et al.
Materials Science & Engineering A, 924, p.147819_1 - 147819_10, 2025/02
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Face-centered cubic (fcc) medium-/high-entropy alloys (M/HEAs) typically enhance strength and ductility at cryogenic temperatures via stacking faults, twinning, or martensitic transformation. However, in-situ neutron diffraction on VCoNi MEA at 15 K reveals that strain hardening is driven solely by rapid dislocation accumulation, without these mechanisms. This results in increased yield strength, strain hardening, and fracture strain. The behavior, explained by the Orowan equation, challenges conventional views on cryogenic strengthening in fcc M/HEAs and highlights the role of dislocation-mediated plasticity at low temperatures.
 neutron diffraction
neutron diffractionNaeem, M.*; Ma, Y.*; Knowles, A. J.*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Wang, X.-L.*; Romero Resendiz, L.*; 他6名*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 916, p.147374_1 - 147374_8, 2024/11
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:63.37(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Heterostructured materials (HSMs) improve the strength-ductility trade-off of alloys, but their cryogenic performance under real-time deformation is unclear. We studied heterostructured CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy via  neutron diffraction at 77 K and 293 K. A significant mechanical mismatch between fine and coarse grains led to an exceptional yield strength of 918 MPa at 293 K, increasing to 1244 MPa at 77 K with a uniform elongation of 34%. This strength-ductility synergy at 77 K is attributed to high dislocation pile-up density, increased planar faults, and martensitic transformation. Compared to homogeneous alloys, HSMs show promise for enhancing cryogenic mechanical performance in medium-/high-entropy alloys.
neutron diffraction at 77 K and 293 K. A significant mechanical mismatch between fine and coarse grains led to an exceptional yield strength of 918 MPa at 293 K, increasing to 1244 MPa at 77 K with a uniform elongation of 34%. This strength-ductility synergy at 77 K is attributed to high dislocation pile-up density, increased planar faults, and martensitic transformation. Compared to homogeneous alloys, HSMs show promise for enhancing cryogenic mechanical performance in medium-/high-entropy alloys.
Wang, S.*; Wang, J.*; Zhang, S.*; Wei, D.*; Chen, Y.*; Rong, X.*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Liu, X.*; Jiao, Z.*; et al.
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 185, p.245 - 258, 2024/06
被引用回数:15 パーセンタイル:97.90(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Nanoprecipitates and nanoscale retained austenite (RA) with suitable stability play crucial roles in determining the yield strength (YS) and ductility of ultrahigh strength steels (UHSSs). However, owing to the kinetics incompatibility between nanoprecipitation and austenite reversion, it is highly challenging to simultaneously introduce high-density nanoprecipitates and optimized RA in UHSSs. In this work, through the combination of austenite reversion treatment (ART) and subsequent flash austenitizing (FA), nanoscale chemical heterogeneity was successfully introduced into a low-cost UHSS prior to the aging process. This chemical heterogeneity involved the enrichment of Mn and Ni in the austenite phase. The resulting UHSS exhibited dual-nanoprecipitation of Ni(Al,Mn) and (Mo,Cr) C and nanoscale austenite stabilized via Mn and Ni enrichment. The hard martensitic matrix strengthened by high-density dual-nanoprecipitates constrains the plastic deformation of soft RA with a relatively low fraction, and the presence of relatively stable nanoscale RA with adequate Mn and Ni enrichment leads to a marginal loss in YS but keeps a persistent transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) effect. As a result, the newly-developed UHSS exhibits an ultrahigh YS of 1.7 GPa, an ultimate tensile strength (UTS) of 1.8 GPa, a large uniform elongation (UE) of 8.5 percent, and a total elongation (TE) of 13 percent. The strategy of presetting chemical heterogeneity to introduce proper metastable phases before aging can be extended to other UHSSs and precipitation-hardened alloys.
C and nanoscale austenite stabilized via Mn and Ni enrichment. The hard martensitic matrix strengthened by high-density dual-nanoprecipitates constrains the plastic deformation of soft RA with a relatively low fraction, and the presence of relatively stable nanoscale RA with adequate Mn and Ni enrichment leads to a marginal loss in YS but keeps a persistent transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) effect. As a result, the newly-developed UHSS exhibits an ultrahigh YS of 1.7 GPa, an ultimate tensile strength (UTS) of 1.8 GPa, a large uniform elongation (UE) of 8.5 percent, and a total elongation (TE) of 13 percent. The strategy of presetting chemical heterogeneity to introduce proper metastable phases before aging can be extended to other UHSSs and precipitation-hardened alloys.
Guo, B.*; Chen, H.*; Chong, Y.*; Mao, W.; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Zhang, Z.*; Jonas, J. J.*; 辻 伸泰*
Acta Materialia, 268, p.119780_1 - 119780_11, 2024/04
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:92.77(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)This paper focused on the characterization and mechanism of the dynamic transformation from the alpha to beta phase during the hot deformation of Ti-6Al-4V alloy and pure titanium. The investigation employed in-situ neutron diffraction and atomistic simulations for a comprehensive understanding of the process. Dynamic transformations were observed during deformation of the Ti-6Al-4V alloy and pure titanium below the beta transus temperatures. During isothermal holding after unloading, the in-situ neutron diffraction results for Ti-6Al-4V and pure titanium indicated a sluggish reverse transformation from the beta to alpha phase. The mechanism of dynamic transformation was explored through in-situ neutron diffraction and atomistic simulations, which revealed twofold effects of deformation on dynamic transformation. Firstly, deformation led to a significant rise in the Gibbs energy of the alpha phase relative to the beta phase, expanding the beta phase region and diminishing the alpha phase region. Secondly, deformation lowered the energy barriers associated with dynamic transformation, facilitating the activation of dynamic transformation more readily than in the equilibrium state before deformation.
 neutron diffraction
neutron diffractionZhou, Y.*; Song, W.*; Zhang, F.*; Wu, Y.*; Lei, Z.*; Jiao, M.*; Zhang, X.*; Dong, J.*; Zhang, Y.*; Yang, M.*; et al.
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 971, p.172635_1 - 172635_7, 2024/01
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:12.80(Chemistry, Physical)The grain orientation-dependent lattice strain evolution of a (TiZrHfNb)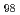
 refractory high-entropy alloy (HEA) during tensile loading has been investigated using
refractory high-entropy alloy (HEA) during tensile loading has been investigated using  neutron diffraction. The equivalent strain-hardening rate of each of the primary
neutron diffraction. The equivalent strain-hardening rate of each of the primary 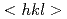 -oriented grain families was found to be relatively low, manifesting the macroscopically weak work-hardening ability of such a body-centered cubic (BCC)-structured HEA. This finding is indicative of a dislocation planar slip mode that is confined in a few single-slip planes and leads to in-plane softening by high pile-up stresses.
-oriented grain families was found to be relatively low, manifesting the macroscopically weak work-hardening ability of such a body-centered cubic (BCC)-structured HEA. This finding is indicative of a dislocation planar slip mode that is confined in a few single-slip planes and leads to in-plane softening by high pile-up stresses.
Kwon, H.*; Sathiyamoorthi, P.*; Gangaraju, M. K.*; Zargaran, A.*; Wang, J.*; Heo, Y.-U.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Lee, B.-J.*; Kim, H. S.*
Acta Materialia, 248, p.118810_1 - 118810_12, 2023/04
被引用回数:48 パーセンタイル:99.21(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Maraging steels, known for ultrahigh strength and good fracture toughness, derive their superior properties from lath martensite structure with high-density nanoprecipitates. In this work, we designed a novel Fe-based medium-entropy alloy with a chemical composition of Fe Co
Co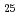 Ni
Ni Mo
Mo in atomic% by utilizing the characteristics of the maraging steels. By a single-step aging of only 10 min at 650
in atomic% by utilizing the characteristics of the maraging steels. By a single-step aging of only 10 min at 650  C, the alloy showed microstructures consisting of a very high number density of (Fe, Co, Ni)
C, the alloy showed microstructures consisting of a very high number density of (Fe, Co, Ni) Mo
Mo -type nanoprecipitates in lath martensite structure and reverted FCC phase, which led to ultrahigh yield strength higher than 2 GPa. This work demonstrates a novel direction to produce strong and ductile materials by expanding the horizons of material design with the aid of high-entropy concept and overcoming the limits of conventional materials.
-type nanoprecipitates in lath martensite structure and reverted FCC phase, which led to ultrahigh yield strength higher than 2 GPa. This work demonstrates a novel direction to produce strong and ductile materials by expanding the horizons of material design with the aid of high-entropy concept and overcoming the limits of conventional materials.
 phase to
phase to  phase in zirconium alloy revealed by in-situ neutron diffraction during high temperature deformation
phase in zirconium alloy revealed by in-situ neutron diffraction during high temperature deformationGuo, B.*; Mao, W.; Chong, Y.*; 柴田 曉伸*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Chen, H.*; Jonas, J. J.*; 辻 伸泰*
Acta Materialia, 242, p.118427_1 - 118427_11, 2023/01
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:70.10(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Dynamic transformation from alpha (HCP) to beta (BCC) phase in a zirconium alloy was revealed by the use of in-situ neutron diffraction during hot compression. The dynamic transformation was unexpectedly detected during isothermal compression at temperatures of 900 C and 950
C and 950 C (alpha + beta two-phase region) and strain rates of 0.01 s
C (alpha + beta two-phase region) and strain rates of 0.01 s and 0.001 s
and 0.001 s , even though equilibrium two-phase states were achieved prior to the hot compression. Dynamic transformation was accompanied by diffusion of Sn from beta to alpha phase, which resulted in changes of lattice parameters and a characteristic microstructure of alpha grains. The details of dynamic transformation are discussed using the evolution of lattice constants.
, even though equilibrium two-phase states were achieved prior to the hot compression. Dynamic transformation was accompanied by diffusion of Sn from beta to alpha phase, which resulted in changes of lattice parameters and a characteristic microstructure of alpha grains. The details of dynamic transformation are discussed using the evolution of lattice constants.
Wei, D.*; Gong, W.; 都留 智仁; Lobzenko, I.; Li, X.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Do, H.-S.*; Bae, J. W.*; Wagner, C.*; et al.
International Journal of Plasticity, 159, p.103443_1 - 103443_18, 2022/12
被引用回数:105 パーセンタイル:99.79(Engineering, Mechanical)Face-centered cubic single-phase high-entropy alloys (HEAs) containing multi-principal transition metals have attracted significant attention, exhibiting an unprecedented combination of strength and ductility owing to their low stacking fault energy (SFE) and large misfit parameter that creates severe local lattice distortion. Increasing both strength and ductility further is challenging. In the present study, we demonstrate via meticulous experiments that the CoCrFeNi HEA with the addition of the substitutional metalloid Si can retain a single-phase FCC structure while its yield strength (up to 65%), ultimate strength (up to 34%), and ductility (up to 15%) are simultaneously increased, owing to a synthetical effect of the enhanced solid solution strengthening and a reduced SFE. The dislocation behaviors and plastic deformation mechanisms were tuned by the addition of Si, which improves the strain hardening and tensile ductility. The present study provides new strategies for enhancing HEA performance by targeted metalloid additions.
 neutron diffraction and electron microscopy study
neutron diffraction and electron microscopy studyZheng, R.*; Gong, W.; Du, J.-P.*; Gao, S.*; Liu, M.*; Li, G.*; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.; Ma, C.*; 尾方 成信*; et al.
Acta Materialia, 238, p.118243_1 - 118243_15, 2022/10
被引用回数:43 パーセンタイル:96.32(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Grain refinement can lead to the strengthening of metallic materials according to the Hall-Petch relationship. However, our recent results suggested that grain boundary sliding is the dominant deformation mode in bulk ultrafine grained (UFG) pure Mg at room temperature, leading to softening. Here, for the first time, we report that the Hall-Petch strengthening can be regained in bulk UFG pure Mg at cryogenic temperature. At 77K, the UFG pure Mg with a mean grain size of 0.6  m exhibited ultrahigh tensile yield strength and ultimate tensile strength of 309 MPa and 380 MPa, respectively. Combined
m exhibited ultrahigh tensile yield strength and ultimate tensile strength of 309 MPa and 380 MPa, respectively. Combined  neutron diffraction and electron microscopy investigation indicated that residual dislocation structures and deformation twins hardly formed in the UFG specimen during tensile test at 298K. In contrast, fast accumulation of lattice defects and remarkable reorientation were evident at 77K, suggesting that the grain-boundary-mediated process was suppressed and the plastic deformation was dominated by dislocation slip and deformation twinning. In addition, all the pure Mg specimens exhibited pronounced strain hardening at 77 K, which was mainly attributed to the suppressed grain boundary sliding and dynamic recovery. The mean dislocation density and relative fractions of dislocations with various Burgers vectors of the UFG specimen deformed at 77K were determined quantitatively from neutron diffraction data.
neutron diffraction and electron microscopy investigation indicated that residual dislocation structures and deformation twins hardly formed in the UFG specimen during tensile test at 298K. In contrast, fast accumulation of lattice defects and remarkable reorientation were evident at 77K, suggesting that the grain-boundary-mediated process was suppressed and the plastic deformation was dominated by dislocation slip and deformation twinning. In addition, all the pure Mg specimens exhibited pronounced strain hardening at 77 K, which was mainly attributed to the suppressed grain boundary sliding and dynamic recovery. The mean dislocation density and relative fractions of dislocations with various Burgers vectors of the UFG specimen deformed at 77K were determined quantitatively from neutron diffraction data.
 ;
;  SR studies and charge-spin percolation model
SR studies and charge-spin percolation modelSheng, Q.*; 金子 竜也*; Yamakawa, Kohtaro*; Guguchia, Z.*; Gong, Z.*; Zhao, G.*; Dai, G.*; Jin, C.*; Guo, S.*; Fu, L.*; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 4(3), p.033172_1 - 033172_14, 2022/09
A pyrite system NiS Se
Se exhibits a bandwidth controlled Mott transition via (S,Se) substitutions in a two-step process: the antiferromagnetic insulator (AFI) to antiferromagnetic metal (AFM) transition at
exhibits a bandwidth controlled Mott transition via (S,Se) substitutions in a two-step process: the antiferromagnetic insulator (AFI) to antiferromagnetic metal (AFM) transition at 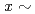 0.45 followed by the AFM to paramagnetic metal (PMM) transition at
0.45 followed by the AFM to paramagnetic metal (PMM) transition at 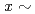 1.0. Among a few other Mott systems which exhibit similar two-step transitions, Ni(S,Se)
1.0. Among a few other Mott systems which exhibit similar two-step transitions, Ni(S,Se) is of particular interest because a large intermediate AFM region in the phase diagram would provide unique opportunities to study the interplay between the spin and charge order. By comparing and combining our muon spin relaxation studies and previous neutron scattering studies, here we propose a picture where the spin order is maintained by the percolation of "nonmetallic" localized and dangling Ni moments surrounded by S, while the charge transition from AFI to AFM is caused by the percolation of the conducting paths generated by the Ni-Se-Ni bonds.
is of particular interest because a large intermediate AFM region in the phase diagram would provide unique opportunities to study the interplay between the spin and charge order. By comparing and combining our muon spin relaxation studies and previous neutron scattering studies, here we propose a picture where the spin order is maintained by the percolation of "nonmetallic" localized and dangling Ni moments surrounded by S, while the charge transition from AFI to AFM is caused by the percolation of the conducting paths generated by the Ni-Se-Ni bonds.
Liu, M.*; Gong, W.; Zheng, R.*; Li, J.*; Zhang, Z.*; Gao, S.*; Ma, C.*; 辻 伸泰*
Acta Materialia, 226, p.117629_1 - 117629_13, 2022/03
被引用回数:80 パーセンタイル:99.44(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)One hopeful path to realize good comprehensive mechanical properties in metallic materials is to accomplish homogeneous nanocrystalline (NC) or ultrafine grained (UFG) structure with low dislocation density. In this work, high pressure torsion deformation followed by appropriate annealing was performed on 316 stainless steel (SS). For the first time, we successfully obtained NC/UFG 316 SS having uniform microstructures with various average grain sizes ranging from 46 nm to 2.54  m and low dislocation densities. Among the series, an un-precedentedly high yield strength (2.34 GPa) was achieved at the smallest grain size of 46 nm, in which dislocation scarcity induced hardening accounting for 57% of the strength. On the other hand, exceptional strength-ductility synergy with high yield strength (900 MPa) and large uniform elongation (27%) was obtained in the fully recrystallized specimen having the grain size of 0.38
m and low dislocation densities. Among the series, an un-precedentedly high yield strength (2.34 GPa) was achieved at the smallest grain size of 46 nm, in which dislocation scarcity induced hardening accounting for 57% of the strength. On the other hand, exceptional strength-ductility synergy with high yield strength (900 MPa) and large uniform elongation (27%) was obtained in the fully recrystallized specimen having the grain size of 0.38  m. The high yield stress and scarcity of dislocation sources in recrystallized UFGs activated stacking faults and deformation twins nucleating from grain boundaries during straining, and their interaction with dislocations allowed for sustainable strain hardening, which also agreed with the plaston concept recently proposed. The multiple deformation modes activated, together with the effective strengthening mechanisms, were responsible for the outstanding comprehensive mechanical performance of the material.
m. The high yield stress and scarcity of dislocation sources in recrystallized UFGs activated stacking faults and deformation twins nucleating from grain boundaries during straining, and their interaction with dislocations allowed for sustainable strain hardening, which also agreed with the plaston concept recently proposed. The multiple deformation modes activated, together with the effective strengthening mechanisms, were responsible for the outstanding comprehensive mechanical performance of the material.
Wei, D.*; Wang, L.*; Zhang, Y.*; Gong, W.; 都留 智仁; Lobzenko, I.; Jiang, J.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Bae, J. W.*; et al.
Acta Materialia, 225, p.117571_1 - 117571_16, 2022/02
被引用回数:96 パーセンタイル:99.64(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Recently-developed high-entropy alloys (HEAs) containing multiple principal metallic elements have ex-tended the compositional space of solid solutions and the range of their mechanical properties. Here we show that the realm of possibilities can be further expanded through substituting the constituent metals with metalloids, which are desirable for tailoring strength/ductility because they have chemical interactions and atomic sizes distinctly different from the host metallic elements. Specifically, the metalloid substitution increases local lattice distortion and short-range chemical inhomogeneities to elevate strength, and in the meantime reduces the stacking fault energy to discourage dynamic recovery and encourage defect accumulation via partial-dislocation-mediated activities. These impart potent dislocation storage to improve the strain hardening capability, which is essential for sustaining large tensile elongation. As such, metalloid substitution into HEAs evades the normally expected strength-ductility trade-off, enabling an unusual synergy of high tensile strength and extraordinary ductility for these single-phase solid solutions.
Kong, L.*; Gong, J.*; Hu, Q.*; Capitani, F.*; Celeste, A.*; 服部 高典; 佐野 亜沙美; Li, N.*; Yang, W.*; Liu, G.*; et al.
Advanced Functional Materials, 31(9), p.2009131_1 - 2009131_12, 2021/02
被引用回数:32 パーセンタイル:82.55(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)有機-無機ハロゲン化物ペロブスカイトは非常に柔らかいために、圧力などの外部刺激により格子定数を容易に変化させることができ、有用な光電特性を引き出すのに有効である。一方でこの特性は、多少の加圧でも、格子を歪ませてしまい、光と物質の相互作用を弱め、それによる性能の低下を引き起こす。そこで本研究では、代表的な物質であるヨウ化メチルアンモニウム鉛に対して圧力効果および同位体効果を調べ、それらが格子歪を抑制することが分かった。このことは、それらが、これまで得られなかったような光学的,機械的特性を持つ物質を得る手段として有効であることを示している。
 As
As
Xie, T.*; Wei, Y.*; Gong, D.*; Fennell, T.*; Stuhr, U.*; 梶本 亮一; 池内 和彦*; Li, S.*; Hu, J.*; Luo, H.*
Physical Review Letters, 120(26), p.267003_1 - 267003_7, 2018/06
被引用回数:40 パーセンタイル:86.41(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We report an inelastic neutron scattering study on the spin resonance in the bilayer iron-based superconductor CaKFe As
As . In contrast to its quasi-two-dimensional electron structure, three strongly
. In contrast to its quasi-two-dimensional electron structure, three strongly  -dependent modes of spin resonance are found below
-dependent modes of spin resonance are found below  = 35 K. The mode energies are below and linearly scale with the total superconducting gaps summed on the nesting hole and electron pockets, essentially in agreement with the results in cuprate and heavy fermion superconductors. This observation supports the sign-reversed Cooper-pairing mechanism under multiple pairing channels and resolves the long-standing puzzles concerning the broadening and dispersive spin resonance peak in iron pnictides. More importantly, the triple resonant modes can be classified into odd and even symmetries with respect to the distance of Fe-Fe planes within the Fe-As bilayer unit. Thus, our results closely resemble those in the bilayer cuprates with nondegenerate spin excitations, suggesting that these two high-
= 35 K. The mode energies are below and linearly scale with the total superconducting gaps summed on the nesting hole and electron pockets, essentially in agreement with the results in cuprate and heavy fermion superconductors. This observation supports the sign-reversed Cooper-pairing mechanism under multiple pairing channels and resolves the long-standing puzzles concerning the broadening and dispersive spin resonance peak in iron pnictides. More importantly, the triple resonant modes can be classified into odd and even symmetries with respect to the distance of Fe-Fe planes within the Fe-As bilayer unit. Thus, our results closely resemble those in the bilayer cuprates with nondegenerate spin excitations, suggesting that these two high- superconducting families share a common nature.
superconducting families share a common nature.
Su, Y. H.; 及川 健一; 篠原 武尚; 甲斐 哲也; 廣井 孝介; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Gong, W.; Zhang, S. Y.*; Parker, J. D.*; et al.
Physics Procedia, 88, p.42 - 49, 2017/06
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:87.16(Instruments & Instrumentation)The influences of bending deformation and subsequent subzero treatment on the martensite transformation behaviors in a metastable austenitic alloy Fe-25Ni-0.4C were investigated by the time-of-flight (TOF) neutron Bragg-edge transmission (BET) imaging method. Two-dimensional (2D) maps of martensite phase volume fractions and texture variations due to residual stress and lowering the temperature of the bent samples before and after subzero treatment were obtained by Bragg-edge spectral analysis. The obtained phase volume fractions were quantitatively compared with those determined by neutron diffraction.
 T
T As
As (
( = Co,Ni)
= Co,Ni)Tam, D. M.*; Song, Y.*; Man, H.*; Cheung, S. C.*; Yin, Z.*; Lu, X.*; Wang, W.*; Frandsen, B. A.*; Liu, L.*; Gong, Z.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 95(6), p.060505_1 - 060505_6, 2017/02
被引用回数:24 パーセンタイル:68.68(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We use neutron diffraction and muon spin relaxation to study the effect of in-plane uniaxial pressure on the antiferromagnetic (AF) orthorhombic phase in BaFe T
T As
As and its Co- and Ni-substituted members near optimal superconductivity. In the low-temperature AF ordered state, uniaxial pressure necessary to detwin the orthorhombic crystals also increases the magnetic ordered moment, reaching an 11% increase under 40 MPa for BaFe
and its Co- and Ni-substituted members near optimal superconductivity. In the low-temperature AF ordered state, uniaxial pressure necessary to detwin the orthorhombic crystals also increases the magnetic ordered moment, reaching an 11% increase under 40 MPa for BaFe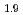 Co
Co As
As , and a 15% increase for BaFe
, and a 15% increase for BaFe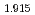 Ni
Ni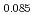 As
As . We also observe an increase of the AF ordering temperature (
. We also observe an increase of the AF ordering temperature (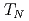 ) of about 0.25 K/MPa in all compounds, consistent with density functional theory calculations that reveal better Fermi surface nesting for itinerant electrons under uniaxial pressure. The doping dependence of the magnetic ordered moment is captured by combining dynamical mean field theory with density functional theory, suggesting that the pressure-induced moment increase near optimal superconductivity is closely related to quantum fluctuations and the nearby electronic nematic phase.
) of about 0.25 K/MPa in all compounds, consistent with density functional theory calculations that reveal better Fermi surface nesting for itinerant electrons under uniaxial pressure. The doping dependence of the magnetic ordered moment is captured by combining dynamical mean field theory with density functional theory, suggesting that the pressure-induced moment increase near optimal superconductivity is closely related to quantum fluctuations and the nearby electronic nematic phase.
 neutron diffraction experiment
neutron diffraction experiment川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; 相澤 一也; 岩橋 孝明; Shi, Z.*; Li, J.*; 友田 陽*; Ung r, T.*
r, T.*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 8, p.031009_1 - 031009_5, 2015/09
鉄鋼材料に代表される金属材料の力学的特性を理解するためには、弾性ひずみだけでなく、転位の密度や配列状態など微細構造を評価することが重要である。これらの情報はX線や中性子回折パターンに表れるBraggピークの形状を詳しく解析することで得ることができる。透過能の高い中性子を用いることでバルク状態の材料内部の微細構造に関する情報を得ることができるが、これまで中性子(特にパルス中性子)はあまり適用されてこなかった。我々はJ-PARC物質生命科学実験施設BL19に設置された工学材料回折装置 匠を用いてマルテンサイト鋼の引張り試験その場中性子回折測定を行い、CMWP法と呼ばれる解析法を用いてこの材料の微細構造を調べた。その結果、巨視的なひずみの増加に伴う転位密度の増加は比較的小さく、転位配列の顕著な規則化が観測された。
Ding, F.*; Luo, G.-N.*; Pitts, R.*; Litnovsky, A.*; Gong, X.*; Ding, R.*; Mao, H.*; Zhou, H.*; Wampler, W. R.*; Stangeby, P. C.*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 455(1-3), p.710 - 716, 2014/12
被引用回数:28 パーセンタイル:88.43(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)A movable material probe system (Material and Plasma Evaluation System: MAPES) with an independent pumping system and a sample exchange chamber has been developed and installed on a horizontal port of the EAST tokamak for studies of plasma material interaction (PMI). In the 2012 experimental campaign, deposition and erosion were studied for three samples: mock-up of the outer first wall panels (FWPs) in ITER, castellated tungsten, and molybdenum mirrors. The FWPs with carbon deposition layer were exposed to helium plasmas. The maximum erosion rate of the carbon was valuated to be 8 nm/s. The castellated tungsten with rectangular cells and roof-like shaped cells was exposed to deuterium plasmas to compare amount of deposits on the gap surface. The amount of carbon and boron impurities on the gap surface of the roof-like shaped cells were reduced to less than 30% compared with that of the rectangular cells. The molybdenum mirrors of which protective ducts are installed in front were exposed to deuterium plasmas in order to investigate effects of length of the ducts. It was found that the reflectivity of the mirrors with 60 mm-long protective ducts is kept the initial reflectivity.