Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...

 atoms (J-PARC E03, E07 and future)
atoms (J-PARC E03, E07 and future)Yamamoto, Takeshi; Fujita, Manami; Gogami, Toshiyuki*; Harada, Takeshi*; Hayakawa, Shuhei*; Hosomi, Kenji; Ichikawa, Yudai; Ishikawa, Yuji*; Kamata, K.*; Kanauchi, H.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 271, p.03001_1 - 03001_5, 2022/11
Gogami, Toshiyuki*; Ebata, Kengo; Fujita, Manami; Harada, Takeshi; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hosomi, Kenji; Ichikawa, Yudai; Imai, Kenichi*; Kim, S.; Nanamura, Takuya; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 271, p.11002_1 - 11002_7, 2022/11
Miwa, Koji*; Fujita, Manami; Harada, Takeshi; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hosomi, Kenji; Ichikawa, Masaya; Imai, Kenichi*; Sako, Hiroyuki; Sato, Susumu; Tamura, Hirokazu; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 271, p.04001_1 - 04001_7, 2022/11
Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu; Hayashi, Naoki; Saha, P. K.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Tani, Norio; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(9), p.1174 - 1205, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:74.40(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, the purpose of the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) is to accelerate a 1 MW, high-intensity proton beam. To achieve beam operation at a repetition rate of 25 Hz at high intensities, the RCS was elaborately designed. After starting the RCS operation, we carefully verified the validity of its design and made certain improvements to establish a reliable operation at higher power as possible. Consequently, we demonstrated beam operation at a high power, namely, 1 MW. We then summarized the design, actual performance, and improvements of the RCS to achieve a 1 MW beam.
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Harada, Hiroyuki; Kabumoto, Hiroshi; Kamiya, Junichiro; Matsuda, Makoto; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Tamura, Jun; Kako, Eiji*; Domae, Takeshi*; Sakai, Hiroshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 20th International Conference on RF Superconductivity (SRF 2021) (Internet), p.299 - 302, 2021/10
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) tandem booster is one of the pioneering superconducting heavy ion linac in the world. It consists of 40 QWRs with an operation frequency of 130 MHz and 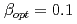 , and has potential to accelerate various ions up to Au to 10 MeV/u. The user operation was started in 1994, however, it has been suspended since the Great East Japan Earthquake in 2011. Recently, in addition to the efforts to restart the tandem booster, activities to develop new lower-beta cavities to improve the acceleration efficiency of heavier ions such as Uranium has been launched. In this work, the current status of the design study of the QWRS for the JAEA tandem facility is presented. Electro-magnetic design using simulation code was performed and acceleration gradient of 5.7 MV/m and 6.6 MV/m was obtained for 130-MHz and 65-MHz QWRs, respectively.
, and has potential to accelerate various ions up to Au to 10 MeV/u. The user operation was started in 1994, however, it has been suspended since the Great East Japan Earthquake in 2011. Recently, in addition to the efforts to restart the tandem booster, activities to develop new lower-beta cavities to improve the acceleration efficiency of heavier ions such as Uranium has been launched. In this work, the current status of the design study of the QWRS for the JAEA tandem facility is presented. Electro-magnetic design using simulation code was performed and acceleration gradient of 5.7 MV/m and 6.6 MV/m was obtained for 130-MHz and 65-MHz QWRs, respectively.
Parker, J. D.*; Harada, Masahide; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Hiroi, Kosuke; Kai, Tetsuya; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Nakatani, Takeshi; Oikawa, Kenichi; Segawa, Mariko; Shinohara, Takenao; et al.
Materials Research Proceedings, Vol.15, p.102 - 107, 2020/05
Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Oikawa, Kenichi; Nakatani, Takeshi; Segawa, Mariko; Hiroi, Kosuke; Su, Y. H.; Oi, Motoki; Harada, Masahide; Iikura, Hiroshi; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 91(4), p.043302_1 - 043302_20, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:77 Percentile:97.23(Instruments & Instrumentation)Shobuda, Yoshihiro; Saha, P. K.; Hotchi, Hideaki; Harada, Hiroyuki; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Tamura, Fumihiko; Tani, Norio; Togashi, Tomohito; Toyama, Takeshi*; Watanabe, Yasuhiro; et al.
Proceedings of 8th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '17) (Internet), p.2946 - 2949, 2017/05
no abstracts in English
Shobuda, Yoshihiro; Chin, Y. H.*; Saha, P. K.; Hotchi, Hideaki; Harada, Hiroyuki; Irie, Yoshiro*; Tamura, Fumihiko; Tani, Norio; Toyama, Takeshi*; Watanabe, Yasuhiro; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2017(1), p.013G01_1 - 013G01_39, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:68.21(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS), whose beam energy ranges from 400 MeV to 3 GeV and which is located in the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, is a kicker-impedance dominant machine, which violates the impedance budget from a classical viewpoint. Contrary to conventional understanding, we have succeeded to accelerate a 1-MW equivalent beam. The machine has some interesting features: for instance, the beam tends to be unstable for the smaller transverse beam size, the beam is stabilized by increasing the peak current 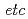 . Space charge effects play an important role in the beam instability at the RCS. In this study, a new theory has been developed to calculate the beam growth rate with the head-tail and coupled-bunch modes (
. Space charge effects play an important role in the beam instability at the RCS. In this study, a new theory has been developed to calculate the beam growth rate with the head-tail and coupled-bunch modes (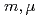 ) while taking space charge effects into account. The theory sufficiently explains the distinctive features of the beam instabilities at the RCS.
) while taking space charge effects into account. The theory sufficiently explains the distinctive features of the beam instabilities at the RCS.
Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Oikawa, Kenichi; Segawa, Mariko; Harada, Masahide; Nakatani, Takeshi; Oi, Motoki; Aizawa, Kazuya; Sato, Hirotaka*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 746, p.012007_1 - 012007_6, 2016/00
Times Cited Count:59 Percentile:99.77(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Tomoya; Takao, Koichiro*; Kawasaki, Takeshi*; Harada, Masayuki*; Nogami, Masanobu*; Ikeda, Yasuhisa*
Polyhedron, 96, p.102 - 106, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:52.61(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)We have determined crystal structures of UO (NO
(NO )
) (
(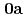 )
) (
(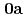 : 2-imidazolidone), UO
: 2-imidazolidone), UO (NO
(NO )
) (
(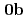 )
) (
(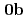 : tetrahydro-2-pyrimidone) and UO
: tetrahydro-2-pyrimidone) and UO (NO
(NO )
) (
(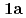 )
) (
(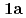 : 1-methyl-2-imidazolidone) by using single crystal X-ray analysis, and examined correlations between melting points (mps) and intermolecular hydrogen bonds (HBs) of UO
: 1-methyl-2-imidazolidone) by using single crystal X-ray analysis, and examined correlations between melting points (mps) and intermolecular hydrogen bonds (HBs) of UO (NO
(NO )
) (CU)
(CU) (CU: cyclic urea derivatives) and UO
(CU: cyclic urea derivatives) and UO (NO
(NO )
) (NRP)
(NRP) (NRP: pyrrolidone derivative).
(NRP: pyrrolidone derivative).
 S
SGo, Shintaro*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Yokoyama, Rin*; Kobayashi, Motoki*; Kisamori, Keiichi*; Takaki, Motonobu*; Miya, Hiroyuki*; Ota, Shinsuke*; Michimasa, Shinichiro*; Shimoura, Susumu*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 6, p.030005_1 - 030005_4, 2015/06
Yamamoto, Kazami; Hayashi, Naoki; Okabe, Kota; Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Hatakeyama, Shuichiro; Hotchi, Hideaki; Hashimoto, Yoshinori*; Toyama, Takeshi*
Proceedings of 54th ICFA Advanced Beam Dynamics Workshop on High-Intensity, High Brightness and High Power Hadron Beams (HB 2014) (Internet), p.278 - 282, 2015/03
Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS) of Japan Proton Accelerator Complex (J-PARC) is providing more than 300 kW of proton beam to Material and Life science Facility (MLF) and Main Ring (MR). Last summer shutdown, a new ion source was installed to increase output power to 1 MW. In order to achieve reliable operation of 1 MW, we need to reduce beam loss as well. Beam quality of such higher output power is also important for users. Therefore we developed new monitors that can measure the halo with higher accuracy. We present beam monitor systems for these purposes.
Hayashi, Naoki; Harada, Hiroyuki; Horino, Koki; Hotchi, Hideaki; Kamiya, Junichiro; Kinsho, Michikazu; Saha, P. K.; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Tani, Norio; et al.
Proceedings of 4th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '13) (Internet), p.3833 - 3835, 2014/07
no abstracts in English
Umeda, Takahide*; Okamoto, Mitsuo*; Arai, Ryo*; Sato, Yoshihiro*; Kosugi, Ryoji*; Harada, Shinsuke*; Okumura, Hajime*; Makino, Takahiro; Oshima, Takeshi
Materials Science Forum, 778-780, p.414 - 417, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:70.22(Crystallography)Interface defects of Metal-Oxide-Semiconductors (MOSFETs) fabricated on Carbone (C) face 4H-SiC were investigated by Electrically Detected Magnet Resistance (EDMR). Gate oxide of the MOSFETs was formed by either wet-oxidation and H annealing or dry-oxidation. The values of channel mobility for MOSFETS with wet gate oxide and dry gate oxide are less than 1 and 90 cm
annealing or dry-oxidation. The values of channel mobility for MOSFETS with wet gate oxide and dry gate oxide are less than 1 and 90 cm /Vs, respectively. By EDMR measurement under low temperature (less than 20 K), EDMR signals related to C were detected. The peak height of the signals increased with increasing
/Vs, respectively. By EDMR measurement under low temperature (less than 20 K), EDMR signals related to C were detected. The peak height of the signals increased with increasing  -ray doses, and the channel mobility decreased. From this result, it is assumed that hydrogen atoms passivating C dangling bonds are released by
-ray doses, and the channel mobility decreased. From this result, it is assumed that hydrogen atoms passivating C dangling bonds are released by  -rays and the channel mobility decreases with increasing the C related defects.
-rays and the channel mobility decreases with increasing the C related defects.
Sugai, Mitsunobu*; Harada, Jiro*; Imaizumi, Mitsuru*; Sato, Shinichiro; Oshima, Takeshi
Proceedings of 39th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (PVSC-39) (CD-ROM), p.0715 - 0720, 2013/06
no abstracts in English
 -ray irradiation in HNO
-ray irradiation in HNO media
mediaNogami, Masanobu*; Sugiyama, Yuichi*; Kawasaki, Takeshi*; Harada, Masayuki*; Kawata, Yoshihisa*; Morita, Yasuji; Kikuchi, Toshiaki*; Ikeda, Yasuhisa*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 296(1), p.423 - 427, 2013/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:41.67(Chemistry, Analytical)Stability of polyvinylpolypyrrolidone (PVPP), a resin with adsorption selectivity to U(VI) in nitric acid media, against  -ray irradiation has been examined using HNO
-ray irradiation has been examined using HNO solutions of various concentrations. As the result, no clear decrease in the capacity was observed for any samples. Or rather, it was found that the capacity increased by approximately 50% for the PVPP slurry irradiated in 6 M HNO
solutions of various concentrations. As the result, no clear decrease in the capacity was observed for any samples. Or rather, it was found that the capacity increased by approximately 50% for the PVPP slurry irradiated in 6 M HNO . The infrared spectroscopic study indicates that PVPP degrades by
. The infrared spectroscopic study indicates that PVPP degrades by  -ray irradiation in HNO
-ray irradiation in HNO from the cleavage of the pyrrolidone ring by the addition of oxygen atom originating from HNO
from the cleavage of the pyrrolidone ring by the addition of oxygen atom originating from HNO , followed by the formation of chain monoamides with multiple coordinative atoms by the continuous addition of oxygen, finally leading to the generation of primary-amine type anion exchange resin. It is also indicated that all generated functional groups possess adsorptivity to U(VI) in 3 M HNO
, followed by the formation of chain monoamides with multiple coordinative atoms by the continuous addition of oxygen, finally leading to the generation of primary-amine type anion exchange resin. It is also indicated that all generated functional groups possess adsorptivity to U(VI) in 3 M HNO .
.
 -ray irradiation
-ray irradiationNogami, Masanobu*; Sugiyama, Yuichi*; Kawasaki, Takeshi*; Harada, Masayuki*; Kawata, Yoshihisa*; Morita, Yasuji; Kikuchi, Toshiaki*; Ikeda, Yasuhisa*
Science China; Chemistry, 55(9), p.1739 - 1745, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:19.06(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Stability of N-alkylated pyrrolidone derivatives (NRPs) against radiation was examined by irradiation tests with  Co
Co  -ray. We have been developed a novel reprocessing system using NRPs which have precipitation ability to haxa- and tetravalent actinides in nitric acid media. Degradation rates of NRPs are evaluated by irradiation in 3M nitric acid solutions and mechanism of degradation are discussed in the present paper.
-ray. We have been developed a novel reprocessing system using NRPs which have precipitation ability to haxa- and tetravalent actinides in nitric acid media. Degradation rates of NRPs are evaluated by irradiation in 3M nitric acid solutions and mechanism of degradation are discussed in the present paper.
Honda, Junichi; Matsui, Hiroki; Harada, Akio; Obata, Hiroki; Tomita, Takeshi
JAEA-Technology 2012-022, 35 Pages, 2012/07
The advanced utilization of Light Water Reactor (LWR) fuel is progressed in Japan to save the power generating cost and the volume of nuclear wastes. The electric power companies have been continued the approach to extend the burnup and to rise up the thermal power of the commercial fuel. The government should be accumulating the detailed information of the newest technologies to make the regulations and guidelines for the safety of the advanced nuclear fuels. The remote controlled Electron Prove Micro Analyzer attached with crystal orientation analyzer (EPMA) has been developed in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to evaluate the fuel behavior effected by the cladding microstructure under the accident condition. The device was modified to the airtight and earthquake resistant structure for the examination of high radioactive elements. This paper describes the specification of EPMA and the test results of the cold mock-up to confirm their performances and reliabilities.
Honda, Junichi; Matsui, Hiroki; Harada, Akio; Obata, Hiroki; Tomita, Takeshi
JAEA-Technology 2012-021, 17 Pages, 2012/07
The advanced utilization of Light Water Reactor (LWR) fuel is progressed in Japan to save the power generating cost and the volume of nuclear wastes. The electric power companies have been continued the approach to extend the burnup and to rise up the thermal power of the commercial fuel. The government should be accumulating the detailed information of the newest technologies to make the regulations and guidelines for the safety of the advanced nuclear fuels. The ion milling for post irradiation examination has been developed in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to investigate cladding microstructure. This device has been modified to operate the high radioactive elements remotely and have the performance of earthquake resistant. This paper describes the specification of the device which were specialized for post irradiation examination and the test results of the cold mock-up to confirm their performances and reliabilities.