Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
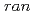 -butadiene) rubbers
-butadiene) rubbersYamaguchi, Daisuke; Yuasa, Takeshi*; Sone, Takuo*; Tominaga, Tetsuo*; Noda, Yohei*; Koizumi, Satoshi*; Hashimoto, Takeji*
Macromolecules, 50(19), p.7739 - 7759, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:53.53(Polymer Science)We elucidated the spatial distribution of filler particles in cross-linked poly(styrene-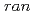 -butadiene) rubbers (SBR) developed under a typical fillers/rubbers compounding process as one of dissipative structures formed under a stress field imposed on the given system. The dispersion state of the fillers in SBR was clarified on the basis of hierarchical structures consisting of five structure levels. More specifically, it has the following characteristics depending on the specific interactions: Small, compact clusters build up compact mass-fractal structures, while large, loose clusters build up open mass-fractal structures.
-butadiene) rubbers (SBR) developed under a typical fillers/rubbers compounding process as one of dissipative structures formed under a stress field imposed on the given system. The dispersion state of the fillers in SBR was clarified on the basis of hierarchical structures consisting of five structure levels. More specifically, it has the following characteristics depending on the specific interactions: Small, compact clusters build up compact mass-fractal structures, while large, loose clusters build up open mass-fractal structures.
Teshima, Naoya; Aoyagi, Tetsuo; Hashimoto, Kiyoharu*; Manabe, Atsushi*; Yuasa, Fukuko*; Nakajima, Norihiro
JAEA-Data/Code 2009-004, 24 Pages, 2009/06
The authentication System Group of J-PARC Information System Group carried out the feasibility study about PKI authentication method that used IC card. Its purpose was that we validated its practical utility to choose an authentication method to adjust a security level desired at the information system of J-PARC. As a target of the feasibility studies, we chose following four validation items. (1) "The EAP-TLS wireless LAN authentication method" (2) "The Web-SSL client authentication method when accessed via SSL-VPN device" (3) "The PKI authentication method that used IC card stored the certificate which issued by NAREGI-CA software. (4) "The PKI authentication method that used Dual card type FeliCa". We established validation point for each validation item, and carried out it. So, we got the results and useful information. This report is that we organized a validation procedure, result and knowledge that we got by feasibility studies.
Koizumi, Satoshi; Zhao, Y.; Tomita, Yoko*; Kondo, Tetsuo*; Iwase, Hiroki; Yamaguchi, Daisuke; Hashimoto, Takeji
European Physical Journal E, 26(1-2), p.137 - 142, 2008/05
Times Cited Count:58 Percentile:86.23(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Fujita, Hiroki; Hashimoto, Tetsuo*
Radiation Measurements, 42(2), p.156 - 162, 2007/02
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:36.27(Nuclear Science & Technology)Red thermoluminescence (RTL), electron spin resonance (ESR) centers and kinetic parameter for RTL electron trap were investigated in combination with annealing experiments. The ESR for Ti-centers was measured in conjunction with Al-centers at 77 K upon warming up to room temperature. Only three kinds of Ti-centers were experimentally observed as the electron-trapped center in the ESR measurement. The [TiO / H
/ H ]
] , the [TiO
, the [TiO / Li
/ Li ]
] and the [TiO
and the [TiO / Na
/ Na ]
] centers were affected by annealing treatment. The [TiO
centers were affected by annealing treatment. The [TiO / H
/ H ]
] centers behaved just like radical H
centers behaved just like radical H atoms derived from radiolysis of H-related impurities. Tendency of [TiO
atoms derived from radiolysis of H-related impurities. Tendency of [TiO / Na
/ Na ]
] centers was resemble to the changes of RTL-intensities associated with annealing temperatures. The phenomena were supported by both the results of RTL measurement as well as kinetic parameters, which were determined by RTL measurement were also influenced by the annealing temperatures and were found to be correlated with broadening of RTL peak after annealing treatments.
centers was resemble to the changes of RTL-intensities associated with annealing temperatures. The phenomena were supported by both the results of RTL measurement as well as kinetic parameters, which were determined by RTL measurement were also influenced by the annealing temperatures and were found to be correlated with broadening of RTL peak after annealing treatments.
Fujita, Hiroki; Hashimoto, Tetsuo*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 123(2), p.143 - 147, 2007/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:41.54(Environmental Sciences)To develop retrospective dosimetry of unexpected radiation accident, the basic studies on violet thermoluminescence (VTL) phenomena were conducted using natural quartz grains. All VTL glowcurves of as-received samples exhibited no peaks below 250  C, although there remained VTL peaks in the temperature region below 250
C, although there remained VTL peaks in the temperature region below 250  C for artificially irradiated quartz samples. Therefore, accident doses could be estimated without interference of naturally accumulated doses by VTL measurement from natural quartz. The mean lives of VTL were evaluated by the various heating rates method and then the range of values was between some days and ten thousands of years depending on each peak. Especially, the mean life of VTL peak at 200
C for artificially irradiated quartz samples. Therefore, accident doses could be estimated without interference of naturally accumulated doses by VTL measurement from natural quartz. The mean lives of VTL were evaluated by the various heating rates method and then the range of values was between some days and ten thousands of years depending on each peak. Especially, the mean life of VTL peak at 200  C was years order. Furthermore, the lower detection limit was calculated to be tens of mGy from the response curve. This value was lower than that of other methods such as ESR dosimetry. From these results, VTL dosimetry would be preferable for accidental evaluation.
C was years order. Furthermore, the lower detection limit was calculated to be tens of mGy from the response curve. This value was lower than that of other methods such as ESR dosimetry. From these results, VTL dosimetry would be preferable for accidental evaluation.
Sanada, Yukihisa; Kobayashi, Hirohide; Furuta, Sadaaki; Nemoto, Kazuhiko*; Kawai, Keiichi*; Hashimoto, Tetsuo*
Radioisotopes, 55(12), p.727 - 734, 2006/12
The purpose of this study is to develop new measurement methods of radon progenies that discharged alpha-ray focused on pulse time interval. It is calculated that a delayed coincidence method, time-interval-analysis (TIA), has been applied to decay events on the microsecond time-scale (164microsecond). The measurement system with silicon detectors was produced and examined a basic performance of the system by using  Th electrodeposited sources. This system was designed that it have shorter dead times. The results were as follows. (1) The theory of measurement
Th electrodeposited sources. This system was designed that it have shorter dead times. The results were as follows. (1) The theory of measurement  Po using TIA methods was established. (2) Development of the system that measured
Po using TIA methods was established. (2) Development of the system that measured  Po. (3) Suggested that methods to examine a basic performance by using
Po. (3) Suggested that methods to examine a basic performance by using  Th electrodeposited sources. It is scheduled to examine the method of subtracting the progenies of the thorium series, and to reflect this system in an actual work of radiation control in the future.
Th electrodeposited sources. It is scheduled to examine the method of subtracting the progenies of the thorium series, and to reflect this system in an actual work of radiation control in the future.
Sanada, Yukihisa; Kobayashi, Hirohide; Hashimoto, Tetsuo*
Proceedings of 2nd Asian and Oceanic Congress Radiological Protection (AOCRP-2) (CD-ROM), p.313 - 317, 2006/10
The dust monitor for rapid detection of artificial nuclides such as Plutonium with Rn-progeny background compensation system was developed to apply a time interval analysis (TIA). The TIA method was applied to beta and  decay events with microsecond scale (half-life of
decay events with microsecond scale (half-life of  Po: 164 microsecond). In actual experiments, dust sample on the filter (HE-40T pore size: 8micrometer) was collected in a workspace at the JAEA reprocessing facility to compensate
Po: 164 microsecond). In actual experiments, dust sample on the filter (HE-40T pore size: 8micrometer) was collected in a workspace at the JAEA reprocessing facility to compensate  Bi-
Bi- Po correlated events. As a result, total alpha-ray counting rate except for
Po correlated events. As a result, total alpha-ray counting rate except for  Po was 0
Po was 0  0.05 cps. The small
0.05 cps. The small  Am source with dust sampling was measured for simulation of unexpected additional
Am source with dust sampling was measured for simulation of unexpected additional  -ray emitted radionuclides. The increment for
-ray emitted radionuclides. The increment for  -ray counting rate due to the
-ray counting rate due to the  Am source could be clearly detected. The present method will apply for on-line monitoring of
Am source could be clearly detected. The present method will apply for on-line monitoring of  -ray measurement, because the method is able to detect artificial nuclides by compensating any changes of background due to Rn-progeny.
-ray measurement, because the method is able to detect artificial nuclides by compensating any changes of background due to Rn-progeny.
Fujita, Hiroki; Hashimoto, Tetsuo*
Radioisotopes, 55(3), p.117 - 123, 2006/03
The causes of the different optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) sensitivities for quartz aliquots from different origins were investigated concerning influence of radioluminescence (RL) during artificial irradiation. All RL spectra from red-thermoluminescence (RTL) quartz grains consist of two broad RL emission peaks, assignable to a violet region (V-RL) of a 400 nm peak and a red one (R-RL) of a 630 nm one from an on-line RL-spectrometric analysis. The OSL sensitivities were affected on the total amounts of V-RL intensities during irradiation of a fixed total dose (20 Gy) with different dose rates. Additionally, the bleaching effects of RL with shorter wavelength than blue-region were assured from another experiment with the combination of quartz slices and optical filter. Conclusively, it is suggested that the V-RL emissions appreciably affect the residual or naturally accumulated doses when OSL/SAR protocol was applied.
 -ray measurement methods with radon suppression focused on pulse time interval
-ray measurement methods with radon suppression focused on pulse time intervalSanada, Yukihisa; Nohara, Naofumi*; Adachi, Yasuyuki*; Nemoto, Kazuhiko*; Kawai, Keiichi*; Kobayashi, Hirohide; Hashimoto, Tetsuo*
JAEA-Technology 2005-009, 33 Pages, 2006/01
An  -ray measurement methods based on analyzing the time interval of pulses was newly developed. This method was developed aiming to suppress the background counts originated in progeny of uranium series. A delayed coincidence and time interval analysis (TIA) methods have been applied to measure a-b decay successive events (correlated events) on microsecond time-scale (164
-ray measurement methods based on analyzing the time interval of pulses was newly developed. This method was developed aiming to suppress the background counts originated in progeny of uranium series. A delayed coincidence and time interval analysis (TIA) methods have been applied to measure a-b decay successive events (correlated events) on microsecond time-scale (164 s). The measurement system have such functions with silicon detectors was developed intending to shorten the dead time. The basic performance of the system was examined by using
s). The measurement system have such functions with silicon detectors was developed intending to shorten the dead time. The basic performance of the system was examined by using  Th electrodeposited sources. Follows were obtained in this work : The theory of measurement
Th electrodeposited sources. Follows were obtained in this work : The theory of measurement  Po using TIA methods was established. Measurement system of
Po using TIA methods was established. Measurement system of  Po was developed. Conformation methods of correlated events by using
Po was developed. Conformation methods of correlated events by using  Th electrodeposited sources was suggested. The efficiency of correlated events in aerosol samples was estimated. The methods to measure correlated events was indicated by addition of
Th electrodeposited sources was suggested. The efficiency of correlated events in aerosol samples was estimated. The methods to measure correlated events was indicated by addition of  Th. The method of subtracting the progenies of the thorium series are to examine.
Th. The method of subtracting the progenies of the thorium series are to examine.
Fujita, Hiroki; Hashimoto, Tetsuo*
11th International Conference on Luminescence and Electron Spin Resonance Dating (LED 2005), Book of Abstracts, p.68, P. 68, 2005/07
Radioluminescence (RL) phenomena can be observed from many insulating minerals including quartz during radiation-irradiation. The RL attracts much attention to the purpose of both the alternative dosimetry and the elucidation of luminescence mechanism.RL spectrum consists of two RL emission regions assigned to emission peaks at 400 (violet region) and 630nm (Red region) on natural quartz by using an on-line spectrometric system. Increment of RL intensities was observed by increasing dose rate. When the sample was irradiated beforehand, the RL emission intensities depended on the predoses. The above phenomena will lead to a possibility to determine doses using RL measurement. The RL emission peak at 400nm was almost close to stimulated wavelength (470nm) on optically stimulated luminescence (OSL)-measurements. Therefore OSL source would be stimulated by the RL emission wavelength. Overestimated or underestimated OSL-doses were occurred by measuring conditions (high- and low-dose rate), and quartz origins, compared with applied dose. The OSL-doses was related to violet-RL (V-RL) emission intensity but red-RL (R-RL). This result suggested that OSL source would be stimulated by V-RL emission within quartz grain. However, estimated doses by red-TL (RTL) and blue-TL (BTL) measurements were less or not affected by dose rate. These results imply that RL emission is more effective to OSL measurement than TL measurement.
Uezu, Yasuhiro; Hashimoto, Tetsuo*
Saikuru Kiko Giho, (24), p.39 - 45, 2004/00
One kind of discrimination with swiftness and precision of artificial long-lived such as plutonium from natural short-lived such as progenies of radon without chemical separation is time interval analysis (TIA) based on difference existences of time intervals of radiation pulses between short and long lived. The probability of extraction of short lived is higher than long lived within optional fixed time.Lower limit of detection applied to a probability theory was examined in this report adding to principle of TIA theory, measuring system and results of trial tests.
; Koarashi, Jun; Sanada, Yukihisa; Hashimoto, Tetsuo
International Symposium on Transfer of Radionuclides in Biosphere, 0 Pages, 2002/00
None
Ara, Hiroshige*; Fukumitsu, Kenji*; Iizuka, Yunosuke*; Ishii, Takashi*; Izumiya, Yasushi*; Imazu, Masanori*; Utsugida, Yoshizo*; Hasegawa, Makoto*; Maeda, Masaya*; Yabe, Yukio*; et al.
PNC TJ199 84-04VOL1, 20 Pages, 1984/03
None
Koizumi, Satoshi; Tomita, Yoko*; Zhao, Y.; Iwase, Hiroki*; Yamaguchi, Daisuke; Kondo, Tetsuo*; Hashimoto, Takeji; Masui, Tomomi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Zhao, Y.; Koizumi, Satoshi; Hashimoto, Takeji; Tomita, Yoko*; Kondo, Tetsuo*
no journal, ,
Noda, Yohei; Yamaguchi, Daisuke; Hashimoto, Takeji; Koizumi, Satoshi; Tominaga, Tetsuo*; Sone, Takuo*; Yuasa, Takeshi*
no journal, ,
For silica-filled styrene-butdiene rubber samples, we measured small angle neutron scattering with the proton spins in the samples being aligned to one direction. As a result, we precisely determined the silica particles' dispersion by the abstracted partial scattering function.
Noda, Yohei; Yamaguchi, Daisuke; Hashimoto, Takeji; Shamoto, Shinichi; Koizumi, Satoshi; Yuasa, Takeshi*; Tominaga, Tetsuo*; Sone, Takuo*
no journal, ,
We have developed a proton spin contrast variation technique. It has been known that a good DNP performance is achieved in a polyethylene sample absorbed a vapor of TEMPO radical as an electron spin source. We recently applied this technique to silica-filled SBR rubber, which is used for tread rubber of fuel-efficient tires. Finally, we successfully evaluated silica particles' dispersion state precisely, which is supposed to have great effect on tire's fuel efficiency.
 /
/ surveymeter
surveymeterHokama, Tomonori; Fujita, Hiroki; Hashimoto, Tetsuo*
no journal, ,
It is aimed for environmental radiation monitoring to develop the system which detects Plutonium using  /
/ surveymeter and time interval analysis.
surveymeter and time interval analysis.