Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 CoSi
CoSiYamauchi, Hiroki; Sari, D. P.*; Yasui, Yukio*; Sakakura, Terutoshi*; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Nakao, Akiko*; Ohara, Takashi; Honda, Takashi*; Kodama, Katsuaki; Igawa, Naoki; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(1), p.013144_1 - 013144_9, 2024/02
Yamashita, Takuya; Honda, Takeshi*; Mizokami, Masato*; Nozaki, Kenichiro*; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*; Pellegrini, M.*; Sakai, Takeshi*; Sato, Ikken; Mizokami, Shinya*
Nuclear Technology, 209(6), p.902 - 927, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:90.12(Nuclear Science & Technology)Yamamura, Sota*; Fujiwara, Kota*; Honda, Kota*; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Horiguchi, Naoki; Kaneko, Akiko*; Abe, Yutaka*
Physics of Fluids, 34(8), p.082110_1 - 082110_13, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:41.08(Mechanics)Liquid spreading and atomization due to jet impingement in liquid-liquid systems are considered to be crucial for understanding the cooling behavior of high-temperature molten material in a shallow water pool. This phenomenon takes place when a liquid jet enters a pool filled with other immiscible liquid. The jet spreads radially after impinging on the floor while forming a thin liquid film and atomizing droplets. In this paper, we explain the result to quantify the unsteady three-dimensional behavior of the spreading jet by the employment of 3D-LIF measurements and 3-dimensional reconstruction. Under high flow velocity conditions, the phenomena of hydraulic jump and atomization of the liquid film occurred along with the spreading. To evaluate the spreading behavior, a comparison of the jump radius position of the liquid-liquid system as the representative value was made with the one calculated by the existing theory of a gas-liquid system. As the result, the spreading of the liquid film in the liquid-liquid system was suppressed compared with that in the gas-liquid system. Furthermore, the PTV method was successfully used to measure the velocity boundary layer and velocity profile in the liquid film, which are important factors that affect the spreading mechanism of the liquid film. These results revealed that in liquid-liquid systems, shear stress at the liquid-liquid interface causes a decrease in the flow velocity and suppressed the development of the velocity boundary layer. Also, to evaluate the atomization behavior, the number and diameter distribution of the droplets were measured from the acquired 3-dimensional shape data of the jet. As the result, the number of droplets increased with the flow velocity. Based on these results, we concluded that the spreading of the liquid film is affected by such atomization behavior.
Komuro, Michiyasu; Kanazawa, Hiroyuki; Kokusen, Junya; Shimizu, Osamu; Honda, Junichi; Harada, Katsuya; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Nakada, Masami; Inagawa, Jun
JAEA-Technology 2021-042, 197 Pages, 2022/03
Plutonium Research Building No.1 was constructed in 1960 for the purpose of establishing plutonium handling technology and studying its basic physical properties. Radiochemical research, physicochemical research and analytical chemistry regarding solutions and solid plutonium compounds had been doing for the research program in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). In 1964, the laboratory building was expanded and started the researching plutonium-uranium mixed fuel and reprocessing of plutonium-based fuel, playing an advanced role in plutonium-related research in Japan. Since then, the research target has been expanded to include transplutonium elements, and it has functioned as a basic research facility for actinides. The laboratory is constructed by concrete structure and it has the second floor, equipped with 15 glove boxes and 4 chemical hoods. Plutonium Research Building No.1 was decided as one of the facilities to be decommissioned by Japan Atomic Energy Agency Reform Plan in September 2014. So far, the contamination survey of the radioactive materials in the controlled area, the decontamination of glove boxes, and the consideration of the equipment dismantling procedure have been performed as planned. The radioisotope and nuclear fuel materials used in the facility have been transfer to the other facilities in JAEA. The decommissioning of the facility is proceeding with the goal of completing by decommissioning the radiation controlled area in 2026. In this report, the details of the decommissioning plan and the past achievements are reported with the several data.
Oda, Chie; Kawama, Daisuke*; Shimizu, Hiroyuki*; Benbow, S. J.*; Hirano, Fumio; Takayama, Yusuke; Takase, Hiroyasu*; Mihara, Morihiro; Honda, Akira
Journal of Advanced Concrete Technology, 19(10), p.1075 - 1087, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Construction & Building Technology)Concrete in a transuranic (TRU) waste repository is considered a suitable material to ensure safety, provide structural integrity and retard radionuclide migration after the waste containers fail. In the current study, coupling between chemical, mass-transport and mechanical, so-called non-linear processes that control concrete degradation and crack development were investigated by coupled numerical models. Application of such coupled numerical models allows identification of the dominant non-linear processes that will control long-term concrete degradation and crack development in a TRU waste repository.
 Fe and
Fe and  Pu deposited on Earth constrain the r-process yields of recent nearby supernovae
Pu deposited on Earth constrain the r-process yields of recent nearby supernovaeWallner, A.*; Froehlich, M. B.*; Hotchkis, M. A. C.*; Kinoshita, N.*; Paul, M.*; Martschini, M.*; Pavetich, S.*; Tims, S. G.*; Kivel, N.*; Schumann, D.*; et al.
Science, 372(6543), p.742 - 745, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:96.93(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Half of the chemical elements heavier than iron are produced by the rapid neutron capture process (r-process). The sites and yields of this process are disputed, with candidates including some types of supernovae (SNe) and mergers of neutron stars. We search for two isotopic signatures in a sample of Pacific Ocean crust-iron-60 ( Fe) (half-life, 2.6 million years), which is predominantly produced in massive stars and ejected in supernova explosions, and
Fe) (half-life, 2.6 million years), which is predominantly produced in massive stars and ejected in supernova explosions, and  Pu (half-life, 80.6 million years), which is produced solely in r-process events. We detect two distinct influxes of
Pu (half-life, 80.6 million years), which is produced solely in r-process events. We detect two distinct influxes of  Fe to Earth in the last 10 million years and accompanying lower quantities of
Fe to Earth in the last 10 million years and accompanying lower quantities of  Pu. The
Pu. The  Pu/
Pu/ Fe influx ratios are similar for both events. The
Fe influx ratios are similar for both events. The  Pu influx is lower than expected if SNe dominate r-process nucleosynthesis, which implies some contribution from other sources.
Pu influx is lower than expected if SNe dominate r-process nucleosynthesis, which implies some contribution from other sources.
Kokusen, Junya; Akasaka, Shingo*; Shimizu, Osamu; Kanazawa, Hiroyuki; Honda, Junichi; Harada, Katsuya; Okamoto, Hisato
JAEA-Technology 2020-011, 70 Pages, 2020/10
The Uranium Enrichment Laboratory in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) was constructed in 1972 for the purpose of uranium enrichment research. The smoke emitting accident on 1989 and the fire accident on 1997 had been happened in this facility. The research on uranium enrichment was completed in JFY1998. The decommissioning work was started including the transfer of the nuclear fuel material to the other facility in JFY2012. The decommissioning work was completed in JFY2019 which are consisting of removing the hood, dismantlement of wall and ceiling with contamination caused by fire accident. The releasing the controlled area was performed after the confirmation of any contamination is not remained in the target area. The radioactive waste was generated while decommissioning, burnable and non-flammable are 1.7t and 69.5t respectively. The Laboratory will be used as a general facility for cold experiments.
Yamashita, Takuya; Sato, Ikken; Honda, Takeshi*; Nozaki, Kenichiro*; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*; Pellegrini, M.*; Sakai, Takeshi*; Mizokami, Shinya*
Nuclear Technology, 206(10), p.1517 - 1537, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:86.19(Nuclear Science & Technology)Benbow, S. J.*; Kawama, Daisuke*; Takase, Hiroyasu*; Shimizu, Hiroyuki*; Oda, Chie; Hirano, Fumio; Takayama, Yusuke; Mihara, Morihiro; Honda, Akira
Crystals (Internet), 10(9), p.767_1 - 767_33, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:26.57(Crystallography)Details are presented of the development of a coupled modeling simulator for assessing the evolution in the near-field of a geological repository for radioactive waste disposal where concrete is used as a backfill. The simulator uses OpenMI, a standard for exchanging data between simulation software programs at run-time, to form a coupled chemical-mechanical-hydrogeological model of the system. The approach combines a tunnel scale stress analysis finite element model, a discrete element model for accurately modeling the patterns of emerging cracks in the concrete, and a finite element and finite volume model of the chemical processes and alteration in the porous matrix and cracks in the concrete, to produce a fully coupled model of the system. Combining existing detailed simulation software in this way with OpenMI has the benefit of not relying on simplifications that might be necessary to combine all of the modeled processes in a single piece of software.
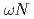 scattering length from
scattering length from  photoproduction on the proton near the reaction threshold
photoproduction on the proton near the reaction thresholdIshikawa, Takatsugu*; Fujimura, Hisako*; Fukasawa, Hiroshi*; Hashimoto, Ryo*; He, Q.*; Honda, Yuki*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Iwata, Takahiro*; Kaida, Shun*; Kasagi, Jirota*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(5), p.052201_1 - 052201_6, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:45.12(Physics, Nuclear)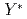 in nuclei through C
in nuclei through C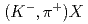 spectrum at 1.8 GeV/
spectrum at 1.8 GeV/ in the J-PARC E05 experiment
in the J-PARC E05 experimentHonda, Ryotaro*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hayakawa, Shuhei; Hosomi, Kenji; Imai, Kenichi; Ichikawa, Yudai; Nanamura, Takuya; Naruki, Megumi; Sako, Hiroyuki; Sato, Susumu; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 26, p.023014_1 - 023014_4, 2019/11
Takada, Shoji; Honda, Yuki*; Inaba, Yoshitomo; Sekita, Kenji; Nemoto, Takahiro; Tochio, Daisuke; Ishii, Toshiaki; Sato, Hiroyuki; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Sawa, Kazuhiro*
Proceedings of 9th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2018) (USB Flash Drive), 7 Pages, 2018/10
Nuclear heat utilization systems connected to HTGRs will be designed on the basis of non-nuclear grade standards for easy entry of chemical plant companies, requiring reactor operations to continue even if abnormal events occur in the systems. The inventory control is considered as one of candidate methods to control reactor power for load following operation for siting close to demand area, in which the primary gas pressure is varied while keeping the reactor inlet and outlet coolant temperatures constant. Numerical investigation was carried out based on the results of nuclear heat supply fluctuation tests using HTTR by non-nuclear heating operation to focus on the temperature transient of the reactor core bottom structure by imposing stepwise fluctuation on the reactor inlet temperature under different primary gas pressures below 120C. As a result, it was emerged that the fluctuation absorption characteristics are not deteriorated by lowering pressure. It was also emerged that the reactor outlet temperature did not reach the scram level by increasing the reactor inlet temperature 10 C stepwise at 80% of the rated power as same with the full power case.
Honda, Yuki; Sato, Hiroyuki; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Ohashi, Hirofumi
Journal of Nuclear Engineering and Radiation Science, 4(3), p.031013_1 - 031013_11, 2018/07
There is growing interest in uncertainty analysis for probabilistic risk assessment (PRA). The focus of this research is to propose and trial investigate the new approach which identify influencing factors for uncertainty in a systematic manner for High Temperature Gas -cooled Reactor (HTGR). As a trial investigation, this approach is tested to evaluation of maximum fuel temperature in a depressurized loss-of-forced circulation (DLOFC) accident and failure of mitigation systems such as control rod systems from the view point of reactor dynamics and thermal hydraulic characteristics. As a result, 16 influencing factors are successfully selected in accordance with the suggested procedure. In the future, the selected influencing factors will be used as input parameter for uncertainty propagation analysis.
Nakajima, Kenji; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Ito, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Endo, Hitoshi*; Fujita, Masaki*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Gong, W.*; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(3), p.9_1 - 9_59, 2017/12
The neutron instruments suite, installed at the spallation neutron source of the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), is reviewed. MLF has 23 neutron beam ports and 21 instruments are in operation for user programs or are under commissioning. A unique and challenging instrumental suite in MLF has been realized via combination of a high-performance neutron source, optimized for neutron scattering, and unique instruments using cutting-edge technologies. All instruments are/will serve in world-leading investigations in a broad range of fields, from fundamental physics to industrial applications. In this review, overviews, characteristic features, and typical applications of the individual instruments are mentioned.
 Li
Li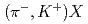 reaction to search for
reaction to search for 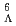 H
HHonda, Ryotaro*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hayakawa, Shuhei; Hosomi, Kenji; Ichikawa, Yudai; Imai, Kenichi; Nagamiya, Shoji; Sako, Hiroyuki; Sato, Susumu; Sugimura, Hitoshi; et al.
Physical Review C, 96(1), p.014005_1 - 014005_23, 2017/07
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:73.79(Physics, Nuclear)Honda, Yuki; Sato, Hiroyuki; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Ohashi, Hirofumi
Proceedings of 25th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-25) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2017/07
There is growing interest in uncertainty analysis for probabilistic risk assessment (PRA). Our target is the uncertainty analysis method development for depressurized loss-of-forced circulation (DLOFC) accident with failure of control rod systems (CRS). As one of key elements, this paper focuses on the quantification of uncertainty for the fuel temperature which is dominant for a source term analysis. As an initial step, this paper aims to suggest a procedure to identify influencing factors which is input parameter for uncertainty analysis, and shows the results of derivation of variable parameters by expansion of dynamic equation and extraction of uncertainties in variable factors.
Ono, Masato; Fujiwara, Yusuke; Honda, Yuki; Sato, Hiroyuki; Shimazaki, Yosuke; Tochio, Daisuke; Homma, Fumitaka; Sawahata, Hiroaki; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Takada, Shoji
Proceedings of 2017 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2017) (CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2017/04
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has carried out research and developments towards nuclear heat utilization of High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) using High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR). The nuclear heat utilization systems connected to HTGR will be designed on the basis of non-nuclear-grade standards in terms of easier entry for the chemical plant companies and the construction economics of the systems. Therefore, it is necessary that the reactor operations continue even if abnormal events occur in the systems. Heat application system abnormal simulating test with HTTR was carried out in non-nuclear heating operation to focus on the thermal effect in order to obtain data of the transient temperature behavior of the metallic components in the Intermediate Heat Exchanger (IHX). The IHX is the key components to connect the HTTR with the heat application system. In the test, the coolant helium gas temperature was heated up to 120 C by the compression heat of the gas circulators in the HTTR under the ideal condition to focus on the heat transfer. The tests were conducted by decreasing the helium gas temperature stepwise by increasing the mass flow rate to the air cooler. The temperature responses of the IHX were investigated. For the components such as the heat transfer tubes and heat transfer enhancement plates of IHX, the temperature response was slower in the lower position in comparison with the higher position. The reason is considered that thermal load fluctuation is imposed in the secondary helium gas which flows from the top to the bottom in the heat transfer tubes of the IHX. The test data are useful to verify the numerical model of the safety evaluation code.
C by the compression heat of the gas circulators in the HTTR under the ideal condition to focus on the heat transfer. The tests were conducted by decreasing the helium gas temperature stepwise by increasing the mass flow rate to the air cooler. The temperature responses of the IHX were investigated. For the components such as the heat transfer tubes and heat transfer enhancement plates of IHX, the temperature response was slower in the lower position in comparison with the higher position. The reason is considered that thermal load fluctuation is imposed in the secondary helium gas which flows from the top to the bottom in the heat transfer tubes of the IHX. The test data are useful to verify the numerical model of the safety evaluation code.
Honda, Yuki; Sato, Hiroyuki; Ohashi, Hirofumi
Proceedings of 2017 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2017) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2017/04
We have been conducting a source term evaluation method development for high temperature gas-cooled reactors considering structural failures in the major components. This paper present the results of transient analysis for depressurized loss-of-forced cooling accident with ruptures of the cross cut ducts and standpipe, which may be initiated by earthquake. The sequences accounts failures of mitigation systems such as core heat removal by Vessel Cooling System (VCS) and reactor shut down by control rod systems. We will show the effect of mitigation system failure to depressurized loss-of-forced cooling accident in the view point of fuel temperature and natural circulation flow rate which is important for source term evaluation. The major findings obtained in this study showed that multiple failures in mitigation systems for a representative HTGR plant do not aggravate the accident. The result demonstrated that a simplification of event sequence analysis and source term analysis can be achieved with a design fully utilizing the safety characteristics of HTGR.
Tochio, Daisuke; Honda, Yuki; Sato, Hiroyuki; Sekita, Kenji; Homma, Fumitaka; Sawahata, Hiroaki; Takada, Shoji; Nakagawa, Shigeaki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 54(1), p.13 - 21, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.62(Nuclear Science & Technology)GTHTR300C is designed and developed in JAEA. The reactor system is required to continue a stable and safety operation as well as a stable power supply in the case that thermal-load is fluctuated by the occurrence of abnormal event in the heat utilization system. Then, it is necessary to demonstrate that the thermal-load fluctuation should be absorbed by the reactor system so as to continue the stable and safety operation could be continued. The thermal-load fluctuation absorption tests without nuclear heating were planned and conducted in JAEA to clarify the absorption characteristic of thermal-load fluctuation mainly by the reactor and by the IHX. As the result it was revealed that the reactor has the larger absorption capacity of thermal-load fluctuation than expected one, and the IHX can be contributed to the absorption of the thermal-load fluctuation generated in the heat utilization system in the reactor system. It was confirmed from there result that the reactor and the IHX has effective absorption capacity of the thermal-load fluctuation generated in the heat utilization system. Moreover it was confirmed that the safety estimation code based on RELAP5/MOD3 can represents the thermal-load fluctuation absorption behavior conservatively.
Honda, Yuki; Fukaya, Yuji; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Baker, R. I.*; Sato, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 8th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2016) (CD-ROM), p.704 - 713, 2016/11
A high-temperature gas-cooled reactor (HTGR) has superior safety characteristics. A loss of forced cooling (LOFC) test using a high-temperature engineering test reactor (HTTR) has been carried out to verify the inherent safety of an HTGR when forced cooling is diminished without reactor scram. In the test, an all-gas circulator was tripped with an initial reactor power of 9 MW and re-criticality was shown. This study focuses on developing a point kinetics method with RELAP5-3D code for an LOFC accident. There is a large temperature difference between the inlet and outlet of the core in an HTGR, and the temperature fluctuation range has been large in several accidents. We analyze the temperature dependency of xenon-135 reactivity and show that the temperature dependency of xenon-135 microscopic absorption cross-section affected the re-criticality time of the LOFC test.