Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -ray fields
-ray fields冠城 雅晃; 鎌田 圭*; 石井 隼也*; 松本 哲郎*; 真鍋 征也*; 増田 明彦*; 原野 英樹*; 加藤 昌弘*; 島添 健次*
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 19(11), p.P11019_1 - P11019_16, 2024/11
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)A new LiCAF:Ce detector with an ultra-thick (99  m) crystal and optimized readout was developed. The LiCAF:Ce and KG2 detectors were used to detect a sealed Cf-252 neutron source (neutron emission rate of ~
m) crystal and optimized readout was developed. The LiCAF:Ce and KG2 detectors were used to detect a sealed Cf-252 neutron source (neutron emission rate of ~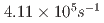 ) using a 5 cm thick high-density polyethylene (HDPE) block located at the front of the detector. At the air kerma rates at the front surface of the HDPE block (
) using a 5 cm thick high-density polyethylene (HDPE) block located at the front of the detector. At the air kerma rates at the front surface of the HDPE block (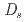 ) of up to 1.07 Gy/h, the effective neutron count rate (
) of up to 1.07 Gy/h, the effective neutron count rate (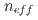 ) for the LiCAF:Ce detector was the same within margins of errors, but it decreased by 5.7
) for the LiCAF:Ce detector was the same within margins of errors, but it decreased by 5.7  0.8% at 2.97 Gy/h. In contrast, for the KG2 detector, with
0.8% at 2.97 Gy/h. In contrast, for the KG2 detector, with 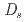 increased up to 1.07 Gy/h,
increased up to 1.07 Gy/h, 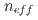 for KG2 increased up to 20
for KG2 increased up to 20  1.0 % at 1.07 Gy/h. Then,
1.0 % at 1.07 Gy/h. Then, 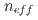 decreased by 20
decreased by 20  1.0% at 2.97 Gy/h. Therefore, the LiCAF:Ce detector exhibited a smaller influence on neutron count rates by
1.0% at 2.97 Gy/h. Therefore, the LiCAF:Ce detector exhibited a smaller influence on neutron count rates by  -rays compared to the KG2 detector because of the faster decay time and optimization of digital pulse processing.
-rays compared to the KG2 detector because of the faster decay time and optimization of digital pulse processing.
石井 隼也*; 清水 森人*; 加藤 昌弘*; 黒澤 忠弘*; 辻 智也; 吉富 寛; 谷村 嘉彦; 渡部 浩司*
Journal of Radiological Protection, 44(3), p.031516_1 - 031516_8, 2024/09
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Environmental Sciences)The dosimeter response should be calibrated in a reference field near the user's radiation environment. Environments around nuclear reactors and radiation therapy facilities have high-energy photons with energies exceeding that of  Co gamma rays, and controlling exposure to these photons is important. The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) and National Metrology Institute of Japan (NMIJ) have high-energy reference fields with energies above several MeV for different types of accelerators. Their reference fields have different fluence-energy distributions. In this study, the energy dependencies of the two-cavity ionization chambers, which are often used by secondary laboratories, were experimentally and computationally evaluated for each high-energy field. These results agreed well with relative expanded uncertainties (
Co gamma rays, and controlling exposure to these photons is important. The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) and National Metrology Institute of Japan (NMIJ) have high-energy reference fields with energies above several MeV for different types of accelerators. Their reference fields have different fluence-energy distributions. In this study, the energy dependencies of the two-cavity ionization chambers, which are often used by secondary laboratories, were experimentally and computationally evaluated for each high-energy field. These results agreed well with relative expanded uncertainties ( = 2), and their capabilities for air kerma measurements in each high-energy reference field were confirmed. Therefore, the capabilities of the air-kerma measurements can be verified in the two high-energy reference fields.
= 2), and their capabilities for air kerma measurements in each high-energy reference field were confirmed. Therefore, the capabilities of the air-kerma measurements can be verified in the two high-energy reference fields.
Martin, P. G.*; Jones, C. P.*; Bartlett, S.*; Ignatyev, K.*; Megson-Smith, D.*; 佐藤 志彦; Cipiccia, S.*; Batey, D. J.*; Rau, C.*; 末木 啓介*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 10, p.22056_1 - 22056_17, 2020/12
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:10.06(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The structural form and elemental distribution of material originating from different Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant reactors (Units 1 and 3) is hereby examined to elucidate their contrasting release dynamics and the current in-reactor conditions to influence future decommissioning challenges. Complimentary computed X-ray absorption tomography and X-ray fluorescence data show that the two suites of Si-based material sourced from the different reactor Units have contrasting internal structure and compositional distribution. The known event and condition chronology correlate with the observed internal and external structures of the particulates examined, which suggest that Unit 1 ejecta material sustained a greater degree of melting than that likely derived from reactor Unit 3. In particular, we attribute the near-spherical shape of Unit 1 ejecta and their internal voids to there being sufficient time for surface tension to round these objects before the hot (and so relatively low viscosity) silicate melt cooled to form glass. In contrast, a more complex internal form associated with the sub-mm particulates invoked to originate from Unit 3 suggest a lower peak temperature, over a longer duration. Using volcanic analogues, we consider the structural form of this material and how it relates to its environmental particulate stability and the bulk removal of residual materials from the damaged reactors. We conclude that the brittle and angular Unit 3 particulate are more susceptible to further fragmentation and particulate generation hazard than the round, higher-strength, more homogenous Unit 1 material.
川崎 将亜; 中嶌 純也; 吉田 圭佑; 加藤 小織; 西野 翔; 野崎 天生; 中川 雅博; 角田 潤一; 菅谷 雄基; 長谷川 里絵; et al.
JAEA-Data/Code 2017-004, 57 Pages, 2017/03
原子力施設の事故発生時においては、事故による影響及びその範囲を迅速に把握するために、放出された放射性物質による一般公衆への影響や事故による作業者の個人被ばく線量を早期に評価し報告することが求められる。そのため、原子力科学研究所放射線管理部においては、事故発生時の迅速な対応に資するために、一般公衆及び作業者の被ばく線量評価について、評価方法及び必要となる各種パラメータ等を想定される事故事例ごとにまとめ、事例集を整備した。本事例集では、原子力科学研究所で想定される各種事故に加え、過去の原子力事故で放出された放射性物質による被ばく評価について扱っており、これらは緊急時における被ばく評価についての知見・技術の継承にも用いることができる。
 20年度
20年度石仙 順也; 住谷 正人; 関 真和; 小林 冬実; 石井 淳一; 梅田 幹
JAEA-Technology 2012-041, 32 Pages, 2013/02
定常臨界実験装置(STACY)及び過渡臨界実験装置(TRACY)の燃料調製施設においては、臨界実験で使用する硝酸ウラニル溶液を準備するため、実験目的に応じてウラン濃度,硝酸濃度,可溶性中性子毒物濃度等の調整を行っている。平成16年度から平成20年度にかけては、STACY及びTRACYで使用する燃料の調整のため、硝酸ウラニル溶液のU濃縮缶による濃縮及び脱硝を行った。並行して、平成17年度及び平成18年度には、核分裂生成物等の中性子吸収効果を定量するためのSTACY実験のために、可溶性中性子毒物を添加した溶液燃料の調整を行った。この実験が終了した後、平成18年度及び平成19年度にかけて可溶性中性子毒物添加燃料の一部について、ミキサセトラを用いた溶媒抽出法により、中性子毒物の除去を行った。本報告書は、これらの平成16年度から平成20年度に実施した燃料調製施設の運転データについてまとめたものである。
相羽 信行; 石井 康友; Bierwage, A.; 廣田 真; 白石 淳也; 矢木 雅敏
no journal, ,
プラズマ理論シミュレーショングループにおける近年のMHD安定性に関する研究では、特に"プラズマ流"及び"高エネルギー粒子"の効果について着目し、それぞれ成果を上げている。これらはそれぞれ現存の実験装置において観測されているMHDモードの安定性に大きな影響を与えていることが知られているのみならず、ITERにおいて発生が懸念されているMHDモードの駆動源・安定化機構としてその理解が求められている重要な課題である。今回のワークショップでは、プラズマ理論シミュレーショングループがこれらのテーマにかかわるこれまでに上げてきた研究成果、特に出張者の専門分野であるELMに関連した周辺MHD安定性に対するプラズマ回転の影響の解析結果とその結果に基づいたJT-60Uの実験解析について発表する。
 -ray spectroscopy study in intense
-ray spectroscopy study in intense  -ray fields using a small LBC scintillator for an in situ nuclear fuel debris assay
-ray fields using a small LBC scintillator for an in situ nuclear fuel debris assay冠城 雅晃; 石井 隼也*; 加藤 昌弘*
no journal, ,
A  -ray spectroscopy system using a small cubic LaBr
-ray spectroscopy system using a small cubic LaBr Cl
Cl
 scintillator measuring the crystal dimensions of 5
scintillator measuring the crystal dimensions of 5  5
5  5 mm
5 mm was developed for an in situ nuclear fuel debris assay. In an intense
was developed for an in situ nuclear fuel debris assay. In an intense  Cs radiation field, this study showed that the system had good energy resolution (
Cs radiation field, this study showed that the system had good energy resolution ( 4%) at dose rates up to 0.407 Gy/h. The full energy peak at 662 keV can be identified at dose rates of up to 2.97 Gy/h.
4%) at dose rates up to 0.407 Gy/h. The full energy peak at 662 keV can be identified at dose rates of up to 2.97 Gy/h.
佐藤 志彦; 末木 啓介*; 石井 達也*; 五十嵐 淳哉*; Martin, P.*; Jones, C.*; Scott, T.*
no journal, ,
2011年に発生した福島第一原子力発電所(1F)事故では、放出したセシウムの一部がケイ酸化合物に取り込まれた不溶性Cs粒子として放出したことが判明している。このうち3月12日の1号機由来と15日早朝の2あるいは3号機からの放出が確認されているが、それ以外の事故イベントによる粒子の放出はまだ確認されていない。本研究では不溶性Cs粒子が報告されている1F北西地域以外で採取した土壌試料に探索対象を拡大することで、他の粒子放出のイベント有無、および新たな種類の放射性粒子の存在を調査した。
 -ray nuclide in an intense
-ray nuclide in an intense  -ray field for nuclear decommissioning
-ray field for nuclear decommissioning冠城 雅晃; 石井 隼也*; 加藤 昌弘*
no journal, ,
 -ray spectroscopy assay is a supporting technique for managing and disposing radioactive waste and spent nuclear fuel. A
-ray spectroscopy assay is a supporting technique for managing and disposing radioactive waste and spent nuclear fuel. A  -ray-spectroscopy system for intense
-ray-spectroscopy system for intense  -ray fields without radiation shields was developed using a small LaBr
-ray fields without radiation shields was developed using a small LaBr Cl
Cl (1
(1  x
x  3) scintillator with dimensions of 5 mm
3) scintillator with dimensions of 5 mm  5 mm
5 mm  5 mm. The scintillator has suitable properties of fast decay time (
5 mm. The scintillator has suitable properties of fast decay time ( 25 ns) and high energy resolution (2.8% - 3.5%). The scintillator was coupled to a photomultiplier tube covered with an aluminum case for shading and shielding electromagnetic noise. The anode pulse signals were digitized with 10
25 ns) and high energy resolution (2.8% - 3.5%). The scintillator was coupled to a photomultiplier tube covered with an aluminum case for shading and shielding electromagnetic noise. The anode pulse signals were digitized with 10 samplings per second and 14-bit quantum resolution. The digital values were averaged over 8 ns and applied to a 10 ns digital low-pass filter integrated for 136 ns.
samplings per second and 14-bit quantum resolution. The digital values were averaged over 8 ns and applied to a 10 ns digital low-pass filter integrated for 136 ns.  -ray nuclide identification of
-ray nuclide identification of  Ba (6.45 MBq) was investigated in a
Ba (6.45 MBq) was investigated in a  Cs radiation field at varying dose rates. In the measured
Cs radiation field at varying dose rates. In the measured  -ray spectra, full energy peaks (peak) of
-ray spectra, full energy peaks (peak) of  Ba with primary emission ratios (emission ratio
Ba with primary emission ratios (emission ratio  5%) were detected at 0.0658 Gy/h. As the irradiation dose rate increases, peaks with low emission rates were not detected initially. This
5%) were detected at 0.0658 Gy/h. As the irradiation dose rate increases, peaks with low emission rates were not detected initially. This  -ray spectroscopy system detected a low energy peak at 81 keV at 0.474 Gy/h and
-ray spectroscopy system detected a low energy peak at 81 keV at 0.474 Gy/h and  Ba at dose rates up to 1.07 Gy/h using the peak with the highest emission ratio (356 keV).
Ba at dose rates up to 1.07 Gy/h using the peak with the highest emission ratio (356 keV).