Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakashio, Nobuyuki*; Osugi, Takeshi; Kurosawa, Shigenobu; Ishikawa, Joji; Hemmi, Ko; Iketani, Shotaro; Yokobori, Tomohiko
JAEA-Technology 2022-016, 47 Pages, 2022/08
The Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI) of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) started operation of the Advanced Volume Reduction Facilities (AVWF) for production of waste packages for disposal of low-level radioactive solid wastes (LLW). To clarify the operating conditions for homogenization of non-metallic LLW, preliminary tests were carried out using the plasma melting furnace of the non-metal melting unit. The fluidity of molten waste influences homogenization conditions of solidified products. It was clarified that the viscosity, which is determined by the chemical composition and the melting temperature, influence the fluidity of molten waste greatly through previous literature review and the small-scale melting tests. In the preliminary tests, the simulated waste with a cold tracer loaded in 200 L drums were melted. Using the waste chemical components (basicity, iron oxide concentration) as an experimental parameter, the homogeneity of the chemical components of the solidified product was investigated and the homogenization conditions of melting tests were examined. The retention ratio of the tracer in the molten bath was also confirmed. The viscosity of the molten wastes was measured and the correlation with homogeneity was examined. In addition, the technical requirements that should be concerned in advance for future actual operation were discussed.
Matsuya, Yusuke; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Yachi, Yoshie*; Satou, Yukihiko; Ishikawa, Masayori*; Date, Hiroyuki*; Sato, Tatsuhiko
Cancers (Internet), 14(4), p.1045_1 - 1045_15, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:78.82(Oncology)An insoluble cesium-bearing microparticle (Cs-BMP) was discovered after the incident at the Fukushima nuclear power plant. Radiation risk by intake of internal exposure to radioactive cesium is conventionally estimated from organ dose, assuming that soluble cesium is uniformly distributed throughout human body. Meanwhile, such Cs-BMPs are assumed to adhere in the long term to normal tissue, leading to chronic non-uniform exposure. In this study, to clarify the normal tissue effects for Cs-BMP exposure, we investigated the relationship between the inflammatory responses and DNA damage induction. From experiments focusing on the inflammatory signaling pathways such as NF- B p65 and COX-2, compared to the uniform exposure to
B p65 and COX-2, compared to the uniform exposure to  -rays, NF-
-rays, NF- B p65 tended to be more activated in the cells proximal to the Cs-BMP, while both NF-
B p65 tended to be more activated in the cells proximal to the Cs-BMP, while both NF- B p65 and COX-2 were significantly activated in the distal cells. Experiments with inhibitors for NF-
B p65 and COX-2 were significantly activated in the distal cells. Experiments with inhibitors for NF- B p65 and COX-2 suggested involvement of such inflammatory responses both in the reduced radiosensitivity of the cells proximal to Cs-BMP and the enhanced radiosensitivity of the cells distal from Cs-BMP. These results suggested that radiation effects for Cs-BMP exposure can differ from that estimated based on conventional uniform exposure to normal tissues.
B p65 and COX-2 suggested involvement of such inflammatory responses both in the reduced radiosensitivity of the cells proximal to Cs-BMP and the enhanced radiosensitivity of the cells distal from Cs-BMP. These results suggested that radiation effects for Cs-BMP exposure can differ from that estimated based on conventional uniform exposure to normal tissues.
Rodriguez, G.*; Varaine, F.*; Costes, L.*; Venard, C.*; Serre, F.*; Chanteclair, F.*; Chenaud, M.-S.*; Dechelette, F.*; Hourcade, E.*; Plancq, D.*; et al.
EPJ Nuclear Sciences & Technologies (Internet), 7, p.15_1 - 15_8, 2021/00
France (CEA and FRAMATOME) and Japan (JAEA, MHI and MFBR) have carried out studies to establish a common technical view regarding sodium-cooled fast reactor concept. Japan and France performed a common work to examine ways to develop a feasible common design concept, which could be built both in France and/or in Japan. This paper is providing a review of this joint synthesis on Sodium Fast Reactor design concept.
Matsuya, Yusuke; Satou, Yukihiko; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Date, Hiroyuki*; Ishikawa, Masayori*; Sato, Tatsuhiko
Scientific Reports (Internet), 9(1), p.10365_1 - 10365_9, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:57.85(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Insoluble radioactive microparticles (so called Cs-bearing particles) have been assumed to adhere in the long term to trachea after aspirated into respiratory system, leading to heterogeneous dose distribution within healthy tissue around the particles. The biological effects posed by such a particle remain unclear. Here, we show cumulative DNA damage in cultured cells proximal and distal to the particle under localized chronic exposure in comparison with uniform exposure. We placed the particle-contained microcapillary onto a glass-base dish containing normal human lung cells in vitro, and observed a significant change in nuclear  -H2AX foci after 24 h or 48 h exposure to the particle. The dose calculation by a Monte Carlo simulation and the comparison with nuclear foci under uniform exposure suggested that the localized exposure to a Cs-bearing particle leads to not only signal-induced DNA damage to distal cells but also the reduction of DNA damage induction yield to proximal cells (protective effects). Considering the small organ dose, the conventional radiation risk assessment is adequate. This study is the first to quantify the spatial distribution of cumulative DNA lesions under heterogeneous exposure by insoluble Cs-bearing particles.
-H2AX foci after 24 h or 48 h exposure to the particle. The dose calculation by a Monte Carlo simulation and the comparison with nuclear foci under uniform exposure suggested that the localized exposure to a Cs-bearing particle leads to not only signal-induced DNA damage to distal cells but also the reduction of DNA damage induction yield to proximal cells (protective effects). Considering the small organ dose, the conventional radiation risk assessment is adequate. This study is the first to quantify the spatial distribution of cumulative DNA lesions under heterogeneous exposure by insoluble Cs-bearing particles.
Kudo, Hideyuki*; Otani, Yuichi*; Hara, Masahide*; Kato, Atsushi; Ishikawa, Nobuyuki; Otaka, Masahiko; Nagai, Keiichi; Saito, Junichi; Ara, Kuniaki; Ide, Akihiro*
Proceedings of 2019 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2019) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2019/05
A next generation SFR in Japan has adopted an advanced dry cleaning system which consists of the argon gas blowing process to reduce the amount of metallic residual sodium remaining on spent fuel assemblies. This paper describes experimental and analytical work focusing on the amount of residual sodium remaining on a fuel pin bundle before and after the argon gas blowing process. The experiments were conducted using a sodium test loop and a short specimen consisting of a 7 pin bundle. The effects of the blowing gas velocity and the blowing time were quantitatively analyzed in the experiments. On the basis of these experimental results, evaluation models predicting the amount of the residual sodium were constructed.
Ide, Akihiro*; Kudo, Hideyuki*; Inuzuka, Taisuke*; Hara, Masahide*; Kato, Atsushi; Ishikawa, Nobuyuki; Otaka, Masahiko; Nagai, Keiichi; Saito, Junichi; Ara, Kuniaki
Proceedings of 2019 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2019) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2019/05
A next generation SFR in Japan has adopted an advanced dry cleaning system which consists of the following process of argon gas blowing to reduce the amount of metallic sodium, moist argon gas blowing to deactivate the residual sodium, and direct storage in the SFP without using storage containers. This three-step process increases economic competitiveness and reduces waste products. In this Research and Development work, the amount of residual sodium and performance of the dry cleaning process were investigated. This paper describes experimental and analytical work for all parts of a fuel assembly except for a fuel pin bundle.
Chadwick, M. B.*; Capote, R.*; Trkov, A.*; Herman, M. W.*; Brown, D. A.*; Hale, G. M.*; Kahler, A. C.*; Talou, P.*; Plompen, A. J.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*; et al.
Nuclear Data Sheets, 148, p.189 - 213, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:78 Percentile:97.87(Physics, Nuclear)The CIELO collaboration has studied neutron cross sections on nuclides that significantly impact criticality in nuclear facilities -  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Fe,
Fe,  O and
O and  H - with the aim of improving the accuracy of the data and resolving previous discrepancies in our understanding. This multi-laboratory pilot project, coordinated via the OECD/NEA Working Party on Evaluation Cooperation (WPEC) Subgroup 40 with support also from the IAEA, has motivated experimental and theoretical work and led to suites of new evaluated libraries that accurately reflect measured data and also perform well in integral simulations of criticality. This report summarizes our results and outlines plans for the next phase of this collaboration.
H - with the aim of improving the accuracy of the data and resolving previous discrepancies in our understanding. This multi-laboratory pilot project, coordinated via the OECD/NEA Working Party on Evaluation Cooperation (WPEC) Subgroup 40 with support also from the IAEA, has motivated experimental and theoretical work and led to suites of new evaluated libraries that accurately reflect measured data and also perform well in integral simulations of criticality. This report summarizes our results and outlines plans for the next phase of this collaboration.
Chadwick, M. B.*; Capote, R.*; Trkov, A.*; Kahler, A. C.*; Herman, M. W.*; Brown, D. A.*; Hale, G. M.*; Pigni, M.*; Dunn, M.*; Leal, L.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.02001_1 - 02001_9, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:96.53(Nuclear Science & Technology)The CIELO collaboration has studied neutron cross sections on nuclides ( O,
O,  Fe,
Fe, 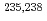 U and
U and  Pu) that significantly impact criticality in nuclear technologies with the aim of improving the accuracy of the data and resolving previous discrepancies in our understanding. This multi-laboratory pilot project, coordinated via the OECD/NEA Working Party on Evaluation Cooperation (WPEC) Subgroup 40 with support also from the IAEA, has motivated experimental and theoretical work and led to suites of new evaluated libraries that accurately reflect measured data and also perform well in integral simulations of criticality.
Pu) that significantly impact criticality in nuclear technologies with the aim of improving the accuracy of the data and resolving previous discrepancies in our understanding. This multi-laboratory pilot project, coordinated via the OECD/NEA Working Party on Evaluation Cooperation (WPEC) Subgroup 40 with support also from the IAEA, has motivated experimental and theoretical work and led to suites of new evaluated libraries that accurately reflect measured data and also perform well in integral simulations of criticality.
Nakashio, Nobuyuki; Osugi, Takeshi; Iseda, Hirokatsu; Tohei, Toshio; Sudo, Tomoyuki; Ishikawa, Joji; Mitsuda, Motoyuki; Yokobori, Tomohiko; Kozawa, Kazushige; Momma, Toshiyuki; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(1), p.139 - 145, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.56(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
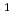 H,
H,  O,
O,  Fe,
Fe, 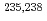 U, and
U, and  Pu
PuChadwick, M. B.*; Dupont, E.*; Bauge, E.*; Blokhin, A.*; Bouland, O.*; Brown, D. A.*; Capote, R.*; Carlson, A. D.*; Danon, Y.*; De Saint Jean, C.*; et al.
Nuclear Data Sheets, 118, p.1 - 25, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:112 Percentile:98.39(Physics, Nuclear)CIELO (Collaborative International Evaluated Library Organization) provides a new working paradigm to facilitate evaluated nuclear reaction data advances. It brings together experts from across the international nuclear reaction data community to identify and document discrepancies among existing evaluated data libraries, measured data, and model calculation interpretations, and aims to make progress in reconciling these discrepancies to create more accurate ENDF-formatted files. The focus will initially be on a small number of the highest-priority isotopes, namely  H,
H,  O,
O,  Fe,
Fe, 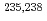 U, and
U, and  Pu. This paper identifies discrepancies between various evaluations of the highest priority isotopes. The evaluated data for these materials in the existing nuclear data libraries are reviewed, and some integral properties are given. The paper summarizes a program of nuclear science and computational work needed to create the new CIELO nuclear data evaluations.
Pu. This paper identifies discrepancies between various evaluations of the highest priority isotopes. The evaluated data for these materials in the existing nuclear data libraries are reviewed, and some integral properties are given. The paper summarizes a program of nuclear science and computational work needed to create the new CIELO nuclear data evaluations.
Ito, Chikara; Ito, Keisuke; Ishikawa, Takashi; Yoshida, Akihiro; Sanada, Yukihisa; Torii, Tatsuo; Notomi, Akihiro*; Wakabayashi, Genichiro*; Miyazaki, Nobuyuki*
Hoshasen, 39(1), p.7 - 11, 2013/09
no abstracts in English
Bierwage, A.; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Shinohara, Koji; Todo, Yasushi*; Deng, W.*; Ishikawa, Masao; Matsunaga, Go; Yagi, Masatoshi
Proceedings of 24th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2012) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2012/10
Bierwage, A.; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Todo, Yasushi*; Deng, W.*; Ishikawa, Masao; Matsunaga, Go; Shinohara, Koji; Yagi, Masatoshi
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 7(Sp.1), p.2403081_1 - 2403081_4, 2012/07
Ishikawa, Nobuyuki; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Fujita, Kaoru; Yamada, Yumi*; Okazaki, Hitoshi*; Suzuki, Shinichi*
Proceedings of 2012 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP '12) (CD-ROM), p.483 - 489, 2012/06
The development of safety protection system for JSFR is progressed in terms of logic circuits, selection of trip signals and its setting values for reactor trip. In addition, it is necessitated to evaluate the satisfaction for requirements of the safety protection system by safety analyses considering comprehensive parameter ranges. For this purpose, we will report the current status of the development focusing on the evaluation results for satisfaction of safety protection system based on safety standard.
Aizawa, Kosuke; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Ishikawa, Nobuyuki; Kubo, Shigenobu; Okazaki, Hitoshi*; Mito, Makoto*; Tozawa, Katsuhiro*; Hayashi, Masateru*
Proceedings of 2012 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP '12) (CD-ROM), p.465 - 474, 2012/06
A conceptual design study of an advanced sodium-cooled fast reactor JSFR has progressed in the "Fast Reactor Cycle Technology Development (FaCT)" project in Japan. JSFR has two failed fuel detection systems in the core. One is a failed fuel detection (FFD) system which continuously monitors a fission product from failed fuel subassembly. The other is a failed fuel detection and location (FFDL) system which locates when it receives signals from FFD. In this study, requirements to the FFD-DN and the FFD-DN design to meet the requirements were investigated for the commercial and demonstration JSFR. For the FFDL systems, experiences in the previous fast reactors and the research and development of FFDL system for JSFR were investigated. Operation experiences of the Selector-valve FFDL system were accumulated in PFR and Phenix. Tagging-gas system experiences were accumulated in EBR-II and FFTF.
Ishikawa, Nobuyuki; Okubo, Tsutomu
Proceedings of International Conference on Toward and Over the Fukushima Daiichi Accident (GLOBAL 2011) (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2011/12
It is necessary to consider the transition from LWR to FBR cycle in terms of reactor introduction point of view since the FBR necessitate LWR originated plutonium in its introduction stage. The plutonium necessary for introduction of FBR is supplied from reprocessing of spent fuel of LWR, not only in the form of UOX fuel but also MOX one. In this sense, the MOX spent fuel from LWR plays a role of plutonium supply source for FBR so that it may require effective use of plutonium in LWR in advance for introduction of FBR. The high conversion type LWR (HC-LWR) may be a preferable option for plutonium utilization in LWR especially taking into account the transition to FBR cycle, since it can preserve much amount of plutonium with good isotopic composition for FBR. Considering these points, in this study, the characteristics of HC-LWR are evaluated in terms of effective plutonium utilization for transition to FBR cycle.
Bierwage, A.; Todo, Yasushi*; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Shinohara, Koji; Ishikawa, Masao; Yagi, Masatoshi
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 6, p.2403109_1 - 2403109_5, 2011/08
Ishikawa, Nobuyuki*; Sueyoshi, Hitoshi*; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Akita, Koichi
Yosetsu Gakkai Rombunshu (Internet), 29(3), p.218 - 224, 2011/08
Cold cracking test was conducted using Y-grooved constraint weld joint by intentionally introducing hydrogen gas, and critical hydrogen content in the weld metal to cold cracking was determined. Residual stress distribution in the weld meal was measured by neutron diffraction technique. The root portion showed highest tensile stress of over 1110 MPa in the transverse direction, which is the same as the crack opening direction.
Tohei, Toshio; Nakashio, Nobuyuki; Osugi, Takeshi; Ishikawa, Joji; Mizoguchi, Takafumi; Hanawa, Ritsu; Someya, Keita*; Takahashi, Kenji*; Iseda, Hirokatsu; Kozawa, Kazushige; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2010-008, 28 Pages, 2010/06
The Waste Volume Reduction Facility (WVRF) was constructed for volume reduction and the chemical stabilization of the low level radioactive waste in the Nuclear Science Research Institute of JAEA. The metal melting system in the WVRF treats radioactive metal waste. From the experience of trial operations, the improvement has conducted on the casting process in the metal melting system. The performance of the improved casting process was verified through the trial operations from Oct. 2008. In this report, we describe the reduction of the processing time, of the utilities consumption, of the load of maintenance on the improved casting process.
Nakano, Yoshihiro; Fukaya, Yuji; Akie, Hiroshi; Ishikawa, Nobuyuki; Okubo, Tsutomu; Uchikawa, Sadao
JAEA-Research 2009-061, 92 Pages, 2010/03
A series of research on a high conversion type innovative water reactor for flexible fuel cycle (FLWR) has been conducted. This FLWR is a boiling water reactor (BWR) with a tight triangular fuel rod lattice and the uranium plutonium mixed oxide (MOX) fuel. FLWR is designed for two types of cores to be developed in succession. The preceding core is a high conversion type FLWR (HC-FLWR) and the other core is Reduced Moderation Water Reactor (RMWR) of which the conversion ratio is more than 1.0. Three design studies and a senario study on HC-FLWR are presented in this report. The first design study is for a representative core. The second one is for a transition core from HC-FLWR to RMWR. In the transition core, both assemblies for HC-FLWR and RMWR exist. The third one is for a core to recycle minor actinides (MAs). Regarding to the scenario study, based on design results of the representative core, effective plutonium utilization in future LWR was considered within general framework.