Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
岩本 ちひろ*; 高村 正人*; 上野 孝太*; 片岡 美波*; 栗原 諒*; 徐 平光; 大竹 淑恵*
ISIJ International, 62(5), p.1013 - 1022, 2022/05
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:23.47(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Neutron diffraction is a powerful non-destructive method for evaluating the microscopic structure and internal stress of metal plates as a bulk average. Precise neutron diffraction measurements with a high intensity neutron beam have already been carried out at large-scale neutron facilities. However, it is not easy to provide users with enough experimental opportunities. We are working on upgrading the neutron diffractometer with techniques of time-of-flight to enable stress measurements at RIKEN accelerator-driven compact neutron source (RANS). To improve neutron diffraction resolution, delayed neutrons, which expand neutron beam pulse width, should be suppressed. However, it is difficult to separate the delayed neutrons experimentally. In this study, a new analysis method has been proposed to deconvolute the diffraction peak from the delayed neutron component. Moreover, a new collimator system, called decoupled collimator system, has been developed to reduce the number of delayed neutrons. The diffraction patterns from a powder sample of pure body-centered cubic iron were measured with the decoupled collimator and the diffraction peak of {211} reflection was analyzed by the new analysis method using a model function of a single exponential decay function convoluted with a Gaussian function. By this method, the decoupled collimator system has been confirmed to achieve a smaller measurement limit of lattice strain 
 than a small-aperture polyethylene collimator system and a non-collimator system. The currently available
than a small-aperture polyethylene collimator system and a non-collimator system. The currently available 
 was 6.7
was 6.7 10
10 , this means that the internal stress up to 130 MPa can be well evaluated for steel materials with a Young's modulus of 200 GPa at RANS.
, this means that the internal stress up to 130 MPa can be well evaluated for steel materials with a Young's modulus of 200 GPa at RANS.
徐 平光; 高村 正人*; 岩本 ちひろ*; 箱山 智之*; 大竹 淑恵*; 鈴木 裕士
Isotope News, (774), p.7 - 10, 2021/04
近年、地球温暖化対策として、自動車などの軽量化に求められている中、高張力鋼板の成形性向上は重要な開発課題となっている。破断まで優れた伸び特性を持たせた高張力鋼板の開発には、オーステナイト組織の相分率と各構成相の集合組織を正しく制御することは極めて重要である。透過能に優れた中性子回折法は、鋼材内部の結晶情報をバルク平均で得られる特徴を持つことから、相分率と集合組織を測定する上で有力な手段である。しかし、現状では中性子回折測定が可能な中性子源は、研究用原子炉や大型加速器施設などの大型実験施設に限られ、これらは共用施設のため利用者が頻繁に測定する機会を得ることは困難である。そこで、理化学研究所では、大学や企業の研究室、工場などの現場で手軽に使える小型中性子源として「理研小型加速器中性子源RANS」を構築し、日本原子力研究開発機構と協力しながら鋼材特性の分析技術に関する一連の研究開発を進めてきた。本解説論文では、大型実験施設と比べるとビーム強度の低い小型加速器中性子源を用いて実施した、中性子回折法による相分率と集合組織測定に関する共同研究成果と、今後の展望を紹介する。
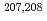 Pb
Pb近藤 壮雄*; 宇都宮 弘章*; Goriely, S.*; 岩本 ちひろ*; 秋宗 秀俊*; 山形 民穂*; 豊川 弘之*; 原田 秀郎; 北谷 文人; Lui, Y.-W.*; et al.
Nuclear Data Sheets, 119, p.310 - 313, 2014/05
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:18.15(Physics, Nuclear)Using linearly-polarized laser-Compton scattering  -rays, partial E1 and M1 photoneutron cross sections along with total cross sections were determined for
-rays, partial E1 and M1 photoneutron cross sections along with total cross sections were determined for 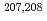 Pb at four energies near threshold by measuring anisotropies in photoneutron emission. Separately, total photoneutron cross sections were measured for
Pb at four energies near threshold by measuring anisotropies in photoneutron emission. Separately, total photoneutron cross sections were measured for 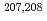 Pb with a high-efficiency 4
Pb with a high-efficiency 4 neutron detector. The partial cross section measurement provides direct evidence for the presence of pygmy dipole resonance (PDR) in
neutron detector. The partial cross section measurement provides direct evidence for the presence of pygmy dipole resonance (PDR) in 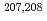 Pb near the neutron threshold. The strength of PDR amounts to 0.32% - 0.42% of the Thomas-Reiche-Kuhn sum rule. Several
Pb near the neutron threshold. The strength of PDR amounts to 0.32% - 0.42% of the Thomas-Reiche-Kuhn sum rule. Several 
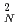 units of B(M1)
units of B(M1) strength were observed in
strength were observed in 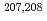 Pb just above neutron threshold, which correspond to M1 cross sections less than 10% of the total photoneutron cross sections.
Pb just above neutron threshold, which correspond to M1 cross sections less than 10% of the total photoneutron cross sections.
 ,n) and (n,
,n) and (n, )reactions
)reactions宇都宮 弘章*; Goriely, S.*; 近藤 壮雄*; 岩本 ちひろ*; 秋宗 秀俊*; 山県 民穂*; 豊川 弘之*; 原田 秀郎; 北谷 文人; Lui, Y.-W.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 88(1), p.015805_1 - 015805_6, 2013/07
被引用回数:87 パーセンタイル:96.76(Physics, Nuclear)Photoneutron cross sections were measured for  Mo,
Mo, Mo,
Mo,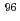 Mo,
Mo, 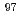 Mo,
Mo, Mo, and
Mo, and  Mo near the neutron threshold with quasi-monochromatic laser-Compton scattering
Mo near the neutron threshold with quasi-monochromatic laser-Compton scattering  -rays. The photoneutron data were analyzed with the Skyrme Hartree-Fock-Bogoliubov (HFB) plus quasiparticle random phase approximation (QRPA) model and the axially-symmetric-deformed Gogny HFB plus QRPA model of E1
-rays. The photoneutron data were analyzed with the Skyrme Hartree-Fock-Bogoliubov (HFB) plus quasiparticle random phase approximation (QRPA) model and the axially-symmetric-deformed Gogny HFB plus QRPA model of E1  -ray strength. Combining the
-ray strength. Combining the  -ray strength function constrained by the present photoneutron data with either the nuclear resonance fluorescence data or the updated Oslo data to supplement the data below the neutron threshold, a thorough analysis of the reverse (n,
-ray strength function constrained by the present photoneutron data with either the nuclear resonance fluorescence data or the updated Oslo data to supplement the data below the neutron threshold, a thorough analysis of the reverse (n, ) cross sections is made whenever measurements are available. The Oslo data and the corresponding uncertainties are updated based on the latest results of the s-wave neutron spacing and the average radiative width determined in particular for
) cross sections is made whenever measurements are available. The Oslo data and the corresponding uncertainties are updated based on the latest results of the s-wave neutron spacing and the average radiative width determined in particular for 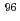 Mo.
Mo.
 -ray strength function method; A Way from photoneutron emission to radiative neutron capture
-ray strength function method; A Way from photoneutron emission to radiative neutron capture宇都宮 弘章*; 秋宗 秀俊*; 山県 民穂*; 岩本 ちひろ*; Goriely, S.*; Daoutidis, I.*; 豊川 弘之*; 原田 秀郎; 北谷 文人; 岩本 信之; et al.
Proceedings of 14th International Symposium on Capture  -Ray Spectroscopy and Related Topics, p.505 - 514, 2013/05
-Ray Spectroscopy and Related Topics, p.505 - 514, 2013/05
Radiative neutron capture cross section are of direct relevance for the synthesis of heavy elements referred to as the s-process and the r-process in nuclear astrophysics and constitute basic data in the field of nuclear engineering. The surrogate reaction technique is in active use to indirectly determine radiative neutron capture cross sections for unstable nuclei. We have devised an indirect method alternative to the surrogate reaction technique on the basis of the  -ray strength function (
-ray strength function ( -SF), a nuclear statistical quantity that interconnects photoneutron emission and radiative neutron capture in Hauser-Feshbach model calculation. The primary strength of the
-SF), a nuclear statistical quantity that interconnects photoneutron emission and radiative neutron capture in Hauser-Feshbach model calculation. The primary strength of the  -SF is low-energy E1 strength in the tail of GDR. We outline the
-SF is low-energy E1 strength in the tail of GDR. We outline the  -SF method and show application of the method to Zr, Pd and Sn isotopes. In the application of the
-SF method and show application of the method to Zr, Pd and Sn isotopes. In the application of the  -SF method, it is important to use
-SF method, it is important to use  -SF, which incorporates extra strengths of PDR and/or M1 resonance emerging around neutron threshold.
-SF, which incorporates extra strengths of PDR and/or M1 resonance emerging around neutron threshold.
近藤 壮雄*; 宇都宮 弘章*; Goriely, S.*; Daoutidis, I.*; 岩本 ちひろ*; 秋宗 秀俊*; 岡本 明之*; 山県 民穂*; 鎌田 正輝*; 伊藤 修*; et al.
Physical Review C, 86(1), p.014316_1 - 014316_7, 2012/07
被引用回数:43 パーセンタイル:87.21(Physics, Nuclear)レーザ逆コンプトン 線と高検出効率4
線と高検出効率4 型中性子検出器を用いて、
型中性子検出器を用いて、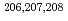 Pbの中性子閾値近傍における全光核反応断面積を測定した。また、直線偏光させた
Pbの中性子閾値近傍における全光核反応断面積を測定した。また、直線偏光させた 線と中性子放出角の非等方性を測定することにより、
線と中性子放出角の非等方性を測定することにより、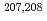 Pbに対する
Pbに対する 1及び
1及び 1励起による部分光核反応断面積を導出した。この結果、中性子閾値近傍においては
1励起による部分光核反応断面積を導出した。この結果、中性子閾値近傍においては 1励起が支配的であることなど
1励起が支配的であることなど 線強度関数に関する実験的知見を得た。
線強度関数に関する実験的知見を得た。
今泉 友見; 宮内 優; 伊藤 正泰; 綿引 俊介; 永田 寛; 花川 裕規; 那珂 通裕; 川又 一夫; 山浦 高幸; 井手 広史; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2011-031, 123 Pages, 2012/01
世界の試験研究炉は、老朽化に伴う廃炉により減少しているが、その一方でアジア諸国においては、原子力発電の導入計画が相次いでいる。このようなアジア諸国では、原子力発電所を建設した後の運転管理ができる技術者の育成が課題となっていると同時に、自国における原子力技術を高めるため、軽水炉の長期化対策,科学技術の向上,産業利用及び原子力人材育成のための試験研究炉の必要性が高まっている。このような背景から、照射試験炉センターにおいては、今後、発電用原子炉を導入する国に向け、各種照射利用や教育訓練に用いる試験研究炉の基本概念検討を開始した。設計活動を通じた本検討は、照射試験炉センターにおける試験研究炉の設計に必要な計算コードなどの環境の整備及び人材育成に貢献するとともに、本概念検討に共同研究として参加する原子力関連会社の試験研究炉にかかわる技術力の維持,向上にも貢献することが期待される。本報告は、平成22年度に設置された「照射試験炉センター汎用小型試験研究炉WG(ワーキンググループ)」と原子力関連会社が行った平成22年7月 平成23年6月までの試験研究炉の概念検討結果について取りまとめたものである。
平成23年6月までの試験研究炉の概念検討結果について取りまとめたものである。
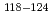 Sn and the
Sn and the  -ray strength function method
-ray strength function method宇都宮 弘章*; Goriely, S.*; 鎌田 正輝*; 秋宗 秀俊*; 近藤 壮雄*; 伊藤 修*; 岩本 ちひろ*; 山県 民穂*; 豊川 弘之*; Lui, Y.-W.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 84(5), p.055805_1 - 055805_6, 2011/11
被引用回数:46 パーセンタイル:89.64(Physics, Nuclear)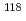 Sn,
Sn, 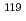 Sn,
Sn, 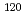 Sn,
Sn, 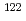 Sn、及び
Sn、及び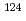 Snに対し、中性子閾値近傍の光核反応断面積を準単色レーザ逆コンプトン光を用いて測定した。得られた測定データと既存の中性子捕獲データを、ピグミー共鳴を電磁双極子励起モードに組み込んだ計算コードにより系統的に解析した。本手法、いわゆる、
Snに対し、中性子閾値近傍の光核反応断面積を準単色レーザ逆コンプトン光を用いて測定した。得られた測定データと既存の中性子捕獲データを、ピグミー共鳴を電磁双極子励起モードに組み込んだ計算コードにより系統的に解析した。本手法、いわゆる、 線強度関数法を適用することにより、放射性核種
線強度関数法を適用することにより、放射性核種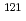 Sn及び
Sn及び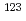 Snの中性子捕獲断面積を導出した。
Snの中性子捕獲断面積を導出した。
 SF method to palladium
SF method to palladium宇都宮 弘章*; Goriely, S.*; Arteaga, D. P.*; Daoutidis, I.*; 秋宗 秀俊*; 山県 民穂*; 近藤 壮雄*; 岩本 ちひろ*; 鎌田 正輝*; 伊藤 修*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1377, p.450 - 452, 2011/10
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Photoneutron cross sections were measured for 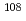 Pd,
Pd, 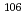 Pd, and
Pd, and 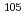 Pd with laser-Compton scattering
Pd with laser-Compton scattering  -ray beams in an application of the
-ray beams in an application of the  SF method to a radioactive nucleus
SF method to a radioactive nucleus  Pd. We present radiative neutron cross sections for
Pd. We present radiative neutron cross sections for  Pd [6.5
Pd [6.5 10
10 y] obtained with the
y] obtained with the  SF method.
SF method.
 SF method
SF method宇都宮 弘章*; Goriely, S.*; 秋宗 秀俊*; 山形 民穂*; 近藤 壮雄*; 岩本 ちひろ*; 岡本 明之*; 原田 秀郎; 北谷 文人; 後神 進史*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1377, p.255 - 259, 2011/10
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The  -ray strength function (
-ray strength function ( SF) interconnects radiative neutron capture and photoneutron emission as a common ingredient in the statistical model. Outlined here is an indirect method of determining radiative neutron-capture cross sections for unstable nuclei based on the
SF) interconnects radiative neutron capture and photoneutron emission as a common ingredient in the statistical model. Outlined here is an indirect method of determining radiative neutron-capture cross sections for unstable nuclei based on the  -ray strength function. Application examples of the
-ray strength function. Application examples of the  SF method are demonstrated.
SF method are demonstrated.
 Zr near threshold
Zr near threshold宇都宮 弘章*; Goriely, S.*; 秋宗 秀俊*; 山形 民穂*; 近藤 壮雄*; 岩本 ちひろ*; 伊藤 修*; 鎌田 正輝*; 井尾 雅則*; 楠瀬 幸一*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1377, p.447 - 449, 2010/10
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Photoneutron cross sections for  Zr near neutron threshold were examined with a photon difference technique using laser Compton scattering
Zr near neutron threshold were examined with a photon difference technique using laser Compton scattering  -ray beams. The cross section decreasing in the vicinity of neutron threshold exhibited a steep rise within 150 keV above the threshold. We draw attention to a possible relation of this striking behavior to the 3P valence neutron resonance known in neutron capture in the mass region A
-ray beams. The cross section decreasing in the vicinity of neutron threshold exhibited a steep rise within 150 keV above the threshold. We draw attention to a possible relation of this striking behavior to the 3P valence neutron resonance known in neutron capture in the mass region A  90.
90.
岩本 ちひろ*; 山本 和喜; 徐 平光; 菖蒲 敬久; 大竹 淑恵*
no journal, ,
安全性、信頼性の担保が必要不可欠である自動車や航空機、船舶、原子力発電プラントなどの様々な場面において、部材と部材とを接合する溶接をはじめとする様々な施工が原因で残留応力が発生する。この残留応力が引き起こす材料の遅れ破壊や疲労破壊、応力腐食割れによる破壊事故を防ぐために、残留応力を低減するような施工技術の開発が重要である。本研究では、このような残留応力を、現場で非破壊により部材の内部までバルク的に測定できる中性子回折手法の開発として、小型中性子源による中性子回折デバイリングの測定ならびにその形状から応力を算出する方法に取り組んでいる。本手法を利用すれば、応力変換のために直交する3方向のひずみを測定するという大変さを緩和しながら応力計測を実現することが可能である。本発表では、中性子輸送計算コードMcStasによるシミュレーションにより、小型加速器中性子源RANSからの中性子ビームを想定した角度分散型中性子回折のセットアップでの中性子回折デバイリング計測結果として得られる回折分布形状を考察する。回折分布形状は、左右非対称なピーク形状を持っているが、このようなピーク形状となる物理的な原因を、中性子ビームの角度発散やゲージボリュームからくる回折線分解能悪化に伴うものとして考察する。
徐 平光; 高村 正人*; 池田 義雅*; 角田 龍之介*; 高橋 進*; 箱山 智之*; 岩本 ちひろ*; 大竹 淑恵*; 鈴木 裕士
no journal, ,
自動車の軽量化のために使用されている高張力薄鋼板は、プレス成形による加工性が低いことから、生産不良が多い。そのため、プレス成形性を向上させる手段の一つとして、鋼材の集合組織制御に期待が寄せられている。実用に供される金属材料の微視組織は不均一な集合組織を有している。圧延板の加工性など金属材料のマクロな特性を議論する際には、金属材料のバルク平均の集合組織を考慮することが適切だと考えられる。中性子線を用いた集合組織測定は、高い透過性と大きなゲージ体積という特徴を生かして、加工性に直結する金属材料のバルク平均情報を容易に測定することができる。しかしながら、日本国内に限らず、世界中には、集合組織が測定できる中性子回折装置が極めて少ない。そこで、我々は研究用原子炉施設(JRR-3)の定常中性子源と大強度陽子加速器施設(J-PARC)のパルス中性子源を用いた集合組織測定技術を確立し、世界トップレベルの測定精度を有する集合組織測定装置を開発した。近年、中性子評価技術をより広く普及するため、理化学研究所が"いつでも、どこでも、手軽に利用できる"をキャッチフレーズとした小型中性子源(RANS)の開発を進めており、我々がこれまでに培ってきたノウハウを最大限に生かして、RANSを用いた粉末回折技術や集合組織測定技術の開発に挑戦してきた。本発表では、JRR-3, J-PARCおよびRANSで開発した鉄鋼材料の集合組織測定技術を簡単に紹介するとともに、中性子回折による集合組織測定研究に関して大型中性子施設と小型中性子源との連携案について議論する。
高村 正人*; 岩本 ちひろ*; 徐 平光; 角田 龍之介*; 栗原 諒*; 箱山 智之*; 池田 義雅*; 鈴木 裕士; 大竹 淑恵*
no journal, ,
High strength steels are becoming more and more important in automotive body structures for good weight reduction, providing further requirement in the balance between strength and formability. Numerical models in forming simulations taking into account the texture evolution may accurately analyze macroscopic plastic behavior, through referring to local surface texture measurement using Electron backscatter diffraction or X-ray diffraction. In contrast, neutron diffraction may measure the microstructure factors including bulk-averaged texture, enable to more deeply understand the mechanisms of deformation behavior. Such neutron diffraction studies usually require large-scale experimental facilities like a reactor and a large accelerator, so meet certain difficulty in the instrumental accessibility. To solve these problems, Riken Accelerator-driven Compact Neutron Source (RANS) has been developed. On-site evaluation of microstructural factors enables us to analyze metal deformation processes more efficiently. Authors have recently succeeded in accurately measuring the texture evolution of an IF steel and also in determining the retained austenite volume fraction of multi-phase steels, by optimizing the beam condition and layout of collimators, samples, detectors, etc. These results show the possibility of practical use of an in-house compact neutron source in laboratories of universities, research institutes and industrial firms.
岩本 ちひろ*; 高村 正人*; 栗原 諒*; 徐 平光; 鈴木 康介*; 高橋 進*; 山本 和喜; 菖蒲 敬久; 大竹 淑恵*
no journal, ,
中性子回折による応力測定には、回折線ピークの微小なシフトを測定するために高い回折線測定分解能が必要である。大型施設では、回折線測定分解能向上のためにチョッパー機構やポイズンモデレータなどの短パルス化デバイス導入が一般的である。しかしながら、これらのデバイスは、ビーム強度を低下させ、かつ追加遮蔽導入によるシステムの大型化にもつながる。そのため中性子ビーム強度の低い小型中性子源の現場導入を前提とした開発には不向きである。本研究では、中性子線源より下流側で中性子ビームの長パルス化を引き起こす"遅延中性子"に着目し、中性子ビーム強度と回折線測定分解能の間のトレードオフの関係を打開するための2つの開発を行なった。ひとつは、遅延中性子の発生を防ぐ非結合型コリメータシステムの開発、もうひとつは遅延中性子による長パルス化の影響を分離できる新しい回折線フィッティング関数を導入した解析法である。理化学研究所の小型加速器中性子源RANSのビームラインにおいて、これらの手法を取り入れてBCC鉄粉回折線を測定し、改善前のセットアップ時における回折線分布と比較した結果を図2に示す。(211)格子面からの回折ピークに対して、検出された回折中性子収量が非結合型コリメータシステムを使用することで2倍増加させながら、ひずみ分解能6.8 10
10 を達成した。これはヤング率が約200GPaの鉄鋼材料の応力を130MPaまで測定可能であることを示している。また、S45C試料に応力を付加させた既知応力サンプルからの回折中性子トライアル測定を行った。その結果500MPa
を達成した。これはヤング率が約200GPaの鉄鋼材料の応力を130MPaまで測定可能であることを示している。また、S45C試料に応力を付加させた既知応力サンプルからの回折中性子トライアル測定を行った。その結果500MPa 200MPaの圧縮応力を格子ひずみから同定することに成功した。
200MPaの圧縮応力を格子ひずみから同定することに成功した。
山本 和喜; 徐 平光; 岩本 ちひろ*; 樹神 克明; 大竹 淑恵*; 菖蒲 敬久
no journal, ,
理化学研究所のRANSをベースとした中性子回折装置の開発を進めている。これまでの先行実験研究からRANSの現在の装置分解能は応力測定に対し十分な信頼性があるとは言えず、中性子輸送シミュレーション及び回折光学系に関連する解析を用いて、分解能の向上のための改善策を調査してきた。装置分解能を低下させる要因はいくつかあるが、そのうちの2つが検出器の配置に関係していることが分かった。1つは検出器の位置分解能(
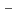
 )によるもので、もう1つはモデレータ固有の時間減衰特性(
)によるもので、もう1つはモデレータ固有の時間減衰特性(
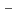
 )によるものである。また、中性子パルスは陽子パルスより遅れるため、中性子輸送計算によりその遅れ時間を評価し、測定した飛行時間から遅延時間分を控除することで正確に補正する方法を考案した。さらに、大面積検出器を高回折角側(2
)によるものである。また、中性子パルスは陽子パルスより遅れるため、中性子輸送計算によりその遅れ時間を評価し、測定した飛行時間から遅延時間分を控除することで正確に補正する方法を考案した。さらに、大面積検出器を高回折角側(2
 90
90 )に配置した場合及び中性子ビーム軸と平行(2
)に配置した場合及び中性子ビーム軸と平行(2 = 90
= 90 )に配置した場合の回折スペクトルを、McStasを用いて計算した。定量的な比較から、検出器を高回折角側に配置することにより、装置分解能が明らかに向上することが分かった。今後、今回提案する機器配置で実証実験を行い改善の効果を評価する。
)に配置した場合の回折スペクトルを、McStasを用いて計算した。定量的な比較から、検出器を高回折角側に配置することにより、装置分解能が明らかに向上することが分かった。今後、今回提案する機器配置で実証実験を行い改善の効果を評価する。
岩本 ちひろ*; 高村 正人*; 上野 孝太*; 栗原 諒*; 徐 平光; 鈴木 裕士; 大竹 淑恵*
no journal, ,
理化学研究所小型中性子源RANSでは、これまでに飛行時間法による中性子回折測定の開発を行っており、集合組織や体積率の測定を成功させてきた。さらに、残留応力測定への高度化として回折線分解能を向上するために、大型施設で利用されている非結合型中性子減速材の導入によって、結合型中性子減速材の場合と比較してBCC鉄粉の211結晶面からの回折線分解能が若干改善された。本研究では、回折線強度を増やし、かつバックグラウンドを低減するためのビームライン開発を行った。まず、空間的・時間的に広がった中性子ビームがサンプルへ照射されることを防ぐため、また広がった中性子ビームが実験室内床面などから散乱されることで発生するバックグランドを抑えるため、減速材から中性子取り出し口までの開口部内壁に、熱中性子遮蔽材であるB Cゴムシートを貼りつけた。さらに、サンプルへのビーム強度を増加させるため、これまで中性子取り出し口からサンプルまでの間に設置していた長さ3m、開口50
Cゴムシートを貼りつけた。さらに、サンプルへのビーム強度を増加させるため、これまで中性子取り出し口からサンプルまでの間に設置していた長さ3m、開口50 50mm
50mm のポリエチレンコリメータを外し、長さ3m、開口250
のポリエチレンコリメータを外し、長さ3m、開口250 250mm
250mm のボロン含有ポリエチレン(BPE)導管を設置した。この導管の下流側開口部には、上流からのビーム由来のバックグラウンドを低減するために、BPE導管の最下流に開口50mm角、厚さ15mmのB
のボロン含有ポリエチレン(BPE)導管を設置した。この導管の下流側開口部には、上流からのビーム由来のバックグラウンドを低減するために、BPE導管の最下流に開口50mm角、厚さ15mmのB Cゴムシートで作成したコリメータを設置した。この改善後のセットアップを用いてBCC鉄粉回折線を測定し、改善前のセットアップ時における回折線分布と比較した。200結晶面以外の回折線ピークにおいて、セットアップ改善後の回折線強度が増加し、また回折線ピークの形状も鋭い形状をしている結果が得られている。この改善により、RANSにおける残留応力測定のS/N向上及び測定時間短縮化が可能となることが示された。
Cゴムシートで作成したコリメータを設置した。この改善後のセットアップを用いてBCC鉄粉回折線を測定し、改善前のセットアップ時における回折線分布と比較した。200結晶面以外の回折線ピークにおいて、セットアップ改善後の回折線強度が増加し、また回折線ピークの形状も鋭い形状をしている結果が得られている。この改善により、RANSにおける残留応力測定のS/N向上及び測定時間短縮化が可能となることが示された。
岩本 ちひろ*; 高村 正人*; 上野 孝太*; 片岡 美波*; 栗原 諒*; 徐 平光; 大竹 淑恵*
no journal, ,
Neutron diffraction is a powerful non-destructive method for evaluating the microscopic structure and internal stress of metallic materials and related semi-finished parts as a bulk average. To implement on-site stress measurements via the neutron diffraction at laboratories and factories frequently and even daily, we are establishing and upgrading the novel measurement and analysis methodology of time-of-flight neutron diffraction at RIKEN accelerator-driven compact neutron source (RANS). In this study, we have proposed two methods to improve the determination resolution of the diffraction peak position by focusing on delayed neutrons due to background scattering from devices such as reflector surrounding the neutron moderator and the polyethylene collimator. First, an analysis method has been proposed to deconvolute original diffraction peak from the delayed neutron component by defining a new model function to well describe the profile shape of delayed neutron diffraction. Second, a new decoupled collimator system has been developed to reduce the number of delayed neutrons. The diffraction patterns from a powder sample of pure body-centered cubic iron were measured with the decoupled collimator and the diffraction peak of {211} reflection was analyzed by the new analysis method using the neutron diffraction profile model function,  , a single exponential decay function convoluted with a Gaussian function. By this method, the decoupled collimator system has been confirmed to achieve a smaller measurement limit of lattice strain
, a single exponential decay function convoluted with a Gaussian function. By this method, the decoupled collimator system has been confirmed to achieve a smaller measurement limit of lattice strain 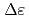 than a small-aperture polyethylene collimator system and a non-collimator system. The currently available
than a small-aperture polyethylene collimator system and a non-collimator system. The currently available 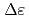 was 6.7
was 6.7 10
10 , which means that the internal stress up to 130 MPa can be well evaluated at RANS for steel materials with a Young's modulus of 200 GPa.
, which means that the internal stress up to 130 MPa can be well evaluated at RANS for steel materials with a Young's modulus of 200 GPa.
徐 平光; 山本 和喜; 岩本 ちひろ*; 高村 正人*
no journal, ,
While the bulk crystallographic textures are usually evaluated through the relative difference in neutron diffraction intensities of polycrystal materials from various sample orientations, an irregular sample geometric shape (different from a sphere and a cube) has an evident effect on the stereographic orientation distribution of neutron diffraction intensities due to the change in locally diffracted gauge volume and the neutron penetration path, which disturbs the quantitative calculation of real preferred orientation of materials and leads to clear uncertainty in nondestructive bulk texture measurements of finished or semi-finished products. Here, the stereographic diffraction intensity distributions of several high strength low alloy steel samples with same microstructure and texture but in various shapes and sizes were measured using RESA angle dispersive neutron diffraction. By referring to the classic neutron attenuation correction theory, the absorption correction reliability was examined to enable that the relevant intensity ratios among the rolling direction, the normal direction, the transverse direction, etc. are almost consistent with the corresponding data from a referred cubic sample. In the poster session, the recalculated bulk textures using the intensity-corrected diffraction profiles of different shaped samples will be given out to make a further comparison and discussion.
山本 和喜; 徐 平光; 岩本 ちひろ*; 高村 正人*; 大竹 淑恵*; 菖蒲 敬久
no journal, ,
構造材の材料開発においては、材料の遅れ破壊,疲労破壊及び腐食の原因となる残留応力の低減並びに損傷破断の防止が求められており、これらのオンサイト評価が極めて重要とされている。こうしたことから、理研では小型加速器中性子源(RANS)を用いた回折計を開発しており、オンサイト評価を想定した中性子回折実験の材料開発及び工法開発の適用性を調査している。小型中性子源には測定精度の向上、測定時間の短縮等さまざまな課題があり、これまで実験的に最適な条件を模索してきたが、2021年度より中性子輸送シミュレーションによる評価を開始したところである。PHITS及びMVPを用いてMcStas用の線源コンポーネントを開発した。このコンポーネントを用いて2019年に実施したFe材の回折実験の再現を試みたところ、そのシミュレーション結果は実験で得られた回折線の特徴をよく捉えたものであった。今後、本手法を向上させ、小型加速器中性子源のオンサイト評価に係る課題解決のツールとして利用したい。