Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -ray discrimination based on the property and thickness controls of scintillators using Li glass and LiCAF(Ce) in a
-ray discrimination based on the property and thickness controls of scintillators using Li glass and LiCAF(Ce) in a  -ray field
-ray field冠城 雅晃; 島添 健次*; 寺阪 祐太; 富田 英生*; 吉橋 幸子*; 山崎 淳*; 瓜谷 章*; 高橋 浩之*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1046, p.167636_1 - 167636_8, 2023/01
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:92.52(Instruments & Instrumentation)波形分別手法を実施せず、強い 線場において熱中性子検出器をするための無機シンチレーターの厚さと性質の制御に焦点を当てた。測定では、0.5mmならびに1.0mm厚のGS20
線場において熱中性子検出器をするための無機シンチレーターの厚さと性質の制御に焦点を当てた。測定では、0.5mmならびに1.0mm厚のGS20 (Liガラス)ならびにLiCaAlF
(Liガラス)ならびにLiCaAlF 結晶(LiCAF:Ce)を採用し、上記のシンチレーターを結合させた光電子増倍管からのパルス信号を1Gspsのデジタル信号処理に入力し、360ns間の波形面積を積分した。
結晶(LiCAF:Ce)を採用し、上記のシンチレーターを結合させた光電子増倍管からのパルス信号を1Gspsのデジタル信号処理に入力し、360ns間の波形面積を積分した。 Coの
Coの 線場において、0.5mm厚のGS20
線場において、0.5mm厚のGS20 では0.919Gy/hまで中性子検出器が可能であった。一方で、0.5mm厚のLiCAF:Ceは、0.473Gy/hまで中性子検出が可能であったが、0.709Gy/hで中性子検出器が不可能であり、中性子/
では0.919Gy/hまで中性子検出器が可能であった。一方で、0.5mm厚のLiCAF:Ceは、0.473Gy/hまで中性子検出が可能であったが、0.709Gy/hで中性子検出器が不可能であり、中性子/ 線分別において、GS20
線分別において、GS20 は、より良いエネルギー分解能と高中性子検出効率により、LiCAF:Ceよりも優れている結果であった。
は、より良いエネルギー分解能と高中性子検出効率により、LiCAF:Ceよりも優れている結果であった。
芝 知宙; 冠城 雅晃; 能見 貴佳; 鈴木 梨沙; 小菅 義広*; 名内 泰志*; 高田 映*; 長谷 竹晃; 奥村 啓介
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research (FDR2022) (Internet), 3 Pages, 2022/10
A technique that can easily determine the presence of nuclear material in removed object from Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant site is important from the viewpoint of sorting fuel debris from radioactive waste. In the case of fresh uranium, the amount of nuclear material in the waste generated from nuclear facilities can be determined by measuring 1001 keV gamma-rays emitted by 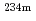 Pa, which is a daughter nuclide of
Pa, which is a daughter nuclide of  U. However, it has been pointed out that such gamma-ray measurement cannot be used for fuel debris that contains a large portion of fission products (FPs) emitting various energies of gamma-rays. In this study, we focus on prompt fission gamma-rays that are directly emitted from nuclear materials and those energy exists in a higher energy region than those of FPs, and aim to measure them in simple manners.
U. However, it has been pointed out that such gamma-ray measurement cannot be used for fuel debris that contains a large portion of fission products (FPs) emitting various energies of gamma-rays. In this study, we focus on prompt fission gamma-rays that are directly emitted from nuclear materials and those energy exists in a higher energy region than those of FPs, and aim to measure them in simple manners.
名内 泰志*; 能見 貴佳; 鈴木 梨沙; 小菅 義広*; 芝 知宙; 高田 映*; 冠城 雅晃; 奥村 啓介
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research (FDR2022) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2022/10
As one of the identification techniques for materials in fuel debris, the neutron induced gamma ray spectroscopy (NIGS) is focused on since the gamma ray spectrum is intrinsic to isotopes. The energy of the target gamma ray in NIGS is often higher than that of most of fission products. To demonstrate feasibility of NIGS for the identification, we have measured and analyzed the HPGe response of isotopes for Cf-252 neutron irradiation for plutonium samples and several structural materials. As a result, we confirmed the possibility to identify light water, boron, concrete, sea water, structural material, signal lines and coils, fuel cladding, gadolinium, uranium, and plutonium contained in the retrieved materials from Fukushima Daiichi NPPs.
 Co radiation source under an intense
Co radiation source under an intense  Cs radiation field using an application-specific CeBr
Cs radiation field using an application-specific CeBr spectrometer suited for use in intense radiation fields
spectrometer suited for use in intense radiation fields冠城 雅晃; 島添 健次*; 加藤 昌弘*; 黒澤 忠弘*; 高橋 浩之*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(8), p.983 - 992, 2022/08
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Passive  -ray spectroscopy is a useful technique for surveying the radioactive wastes and spent nuclear fuels under nuclear decommissioning. However, this method depends on material properties such as the activity, density, element, scale, and (especially) low-energy
-ray spectroscopy is a useful technique for surveying the radioactive wastes and spent nuclear fuels under nuclear decommissioning. However, this method depends on material properties such as the activity, density, element, scale, and (especially) low-energy  rays from
rays from  U and
U and  Pu. The
Pu. The  -decay lines of
-decay lines of  Cs,
Cs,  Cs,
Cs,  Co, and
Co, and  Eu occur at greater energies (than those of
Eu occur at greater energies (than those of  U and
U and  Pu), and these nuclides provide significant information on spent nuclear fuel and radioactive wastes. A CeBr
Pu), and these nuclides provide significant information on spent nuclear fuel and radioactive wastes. A CeBr spectrometer with a small-volume crystal has been previously developed for use in intense radiation measurements. We exposed the spectrometer to radiation dose rates of 0.025, 0.151, 0.342, 0.700, and 0.954 Sv/h under a standard
spectrometer with a small-volume crystal has been previously developed for use in intense radiation measurements. We exposed the spectrometer to radiation dose rates of 0.025, 0.151, 0.342, 0.700, and 0.954 Sv/h under a standard  Cs radiation field. A 6.38 MBq
Cs radiation field. A 6.38 MBq  Co calibration source was placed in front of the detector surface. Identification of the full energy peak at 1173 keV was impossible at dose rates higher than 0.700 Sv/h. However, subtraction of the
Co calibration source was placed in front of the detector surface. Identification of the full energy peak at 1173 keV was impossible at dose rates higher than 0.700 Sv/h. However, subtraction of the  Cs radiation spectra from the
Cs radiation spectra from the  -ray spectra enabled the identification of the full energy peaks at 1173 and 1333 keV at dose rates of up to 0.954 Sv/h; the relative energy resolution at 1173 and 1333 keV was only slightly degraded at this dose rate.
-ray spectra enabled the identification of the full energy peaks at 1173 and 1333 keV at dose rates of up to 0.954 Sv/h; the relative energy resolution at 1173 and 1333 keV was only slightly degraded at this dose rate.
 -ray spectrometer and its performance under intense
-ray spectrometer and its performance under intense  Cs and
Cs and  Co radiation fields
Co radiation fields冠城 雅晃; 島添 健次*; 加藤 昌弘*; 黒澤 忠弘*; 鎌田 圭*; Kim, K. J.*; 吉野 将生*; 庄司 育宏*; 吉川 彰*; 高橋 浩之*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1010, p.165544_1 - 165544_9, 2021/09
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)2011年の東京電力ホールディングス福島第一原子力発電所の事故以来、世界各地で廃止措置措置に入る原子力施設が増加している。これらの原子力施設では、放射性物質の適切な管理が要求されている。そこで、ガンマ線スペクトル測定技術は、放射性物質の重要な情報を得ることができるため、有益なツールである。さらに、放射性物質の空間情報も重要であるため、ガンマ線イメージングについて求められている。しかしながら、これらの施設には、強度放射線場が広がるため、ガンマ線スペクトル測定やガンマ線イメージングが困難になる。そのため、寸法が5mm  5mm
5mm  5mmの小さなCeBr
5mmの小さなCeBr シンチレーター4個で分割した
シンチレーター4個で分割した 線スペクトロメーターを開発した。上記の4個のシンチレーターは、強度放射場に特化したマルチアノード光電子増倍管と組合わせた。私たちは、
線スペクトロメーターを開発した。上記の4個のシンチレーターは、強度放射場に特化したマルチアノード光電子増倍管と組合わせた。私たちは、 Csと
Csと Coの放射線場で照射試験を実施した。
Coの放射線場で照射試験を実施した。 Cs照射場の線量率1375mSv/hにおいて、相対エネルギー分解能が、それぞれのチャンネルで、9.2
Cs照射場の線量率1375mSv/hにおいて、相対エネルギー分解能が、それぞれのチャンネルで、9.2 0.05%, 8.0
0.05%, 8.0 0.08%, 8.0
0.08%, 8.0 0.03%, 9.0
0.03%, 9.0  0.04%であった。
0.04%であった。
 scintillator under intense
scintillator under intense  -ray fields for nuclear decommissioning
-ray fields for nuclear decommissioning冠城 雅晃; 島添 健次*; 加藤 昌弘*; 黒澤 忠弘*; 鎌田 圭*; Kim, K. J.*; 吉野 将生*; 庄司 育宏*; 吉川 彰*; 高橋 浩之*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 988, p.164900_1 - 164900_8, 2021/02
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:87.80(Instruments & Instrumentation)近年、2011年の東京電力ホールディングス福島第一原子力発電所事故より、世界各地で、廃止措置になる原子力施設が増加している。一方、原子力施設の廃止措置工程においては、放射性廃棄物や使用済み核燃料を適切な管理下で回収しなければならないため。そこで、本研究は、高線量率下でのガンマ線スペクトロメトリを実現するため、5mm 5mm
5mm 5mmの微小CeBr
5mmの微小CeBr スペクトロメーターを構築した。さらに、(1)毎秒ギガサンプリング率のデジタル信号処理、(2)後段3段ダイノード電圧印加機能付光電子増倍管により、1Sv/hを超える線量率でのガンマ線スペクトル測定に成功した。
スペクトロメーターを構築した。さらに、(1)毎秒ギガサンプリング率のデジタル信号処理、(2)後段3段ダイノード電圧印加機能付光電子増倍管により、1Sv/hを超える線量率でのガンマ線スペクトル測定に成功した。 Cs放射線場で、662keVのエネルギー分解能(半値幅)が、22mSv/hで4.4%であり、それが1407mSv/hでは5.2%である。対して、
Cs放射線場で、662keVのエネルギー分解能(半値幅)が、22mSv/hで4.4%であり、それが1407mSv/hでは5.2%である。対して、 Co放射線場では、1333keVのエネルギー分解能(半値幅)が、26mSv/hで3.1%であり、それが2221mSv/hでは4.2%である。これらは、
Co放射線場では、1333keVのエネルギー分解能(半値幅)が、26mSv/hで3.1%であり、それが2221mSv/hでは4.2%である。これらは、 Cs,
Cs,  Cs,
Cs,  Co,
Co,  Euのガンマ線を分解できる要求を満たており、同時に1Sv/h以上で上記核種のガンマ線分析が可能なことを示唆するものである。
Euのガンマ線を分解できる要求を満たており、同時に1Sv/h以上で上記核種のガンマ線分析が可能なことを示唆するものである。
 gamma-ray spectrometer suitable for the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station
gamma-ray spectrometer suitable for the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station冠城 雅晃; 島添 健次*; 大鷹 豊*; 上ノ町 水紀*; 鎌田 圭*; Kim, K. J.*; 吉野 将生*; 庄子 育宏*; 吉川 彰*; 高橋 浩之*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 971, p.164118_1 - 164118_8, 2020/08
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:64.73(Instruments & Instrumentation)Our work focused on the passive gamma-ray analysis (PGA) of the nuclear fuel debris based on measuring gamma rays with an energy greater than 1 MeV for the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS). The PGA requires gamma-ray spectrometers to be used under the high dose rates in the FDNPS, then we fabricated a small cubic CeBr spectrometer with dimensions of 5 mm
spectrometer with dimensions of 5 mm  5 mm
5 mm  5 mm, coupled to a Hamamatsu R7600U-200 photomultiplier tube (PMT). The performance at dose rates of 4.4 to 750 mSv/h in a
5 mm, coupled to a Hamamatsu R7600U-200 photomultiplier tube (PMT). The performance at dose rates of 4.4 to 750 mSv/h in a  Co field was investigated. The energy resolution (FWHM) at 1333 keV ranged from 3.79% to 4.01%, with a standard deviation of 6.9%, which met the narrow gamma decay spectral lines between
Co field was investigated. The energy resolution (FWHM) at 1333 keV ranged from 3.79% to 4.01%, with a standard deviation of 6.9%, which met the narrow gamma decay spectral lines between  Eu (1274 keV) and
Eu (1274 keV) and  Co (1333 keV). However, the spectra shifted to a higher energy level as the dose rate increase, there was a 51% increase at the dose rates of 4.4 to 750 mSv/h, which was caused by the PMT gain increase.
Co (1333 keV). However, the spectra shifted to a higher energy level as the dose rate increase, there was a 51% increase at the dose rates of 4.4 to 750 mSv/h, which was caused by the PMT gain increase.
冠城 雅晃; 鳥居 建男; 小川 徹
JAEA-Review 2019-031, 251 Pages, 2020/01
福島第一原子力発電所の廃炉をはじめとした過酷な放射線環境下で、現場作業者の被ばく線量を低減するため、遠隔技術やロボティクスの高度化に大きな期待が集まっている。しかし、ロボットの遠隔制御のための最先端の要素技術やセンサー, 電子機器の耐放射線性にも厳しい限界がある。原子力へのロボット技術の応用拡大に向けて、機器の耐放射線性の向上(Radiation hardness)や運用における放射線環境への適応力(Radiation smartness)が求められる。さらに、将来の核燃料デブリの探査と取り出しに向けては、福島第一原子力発電所内の高線量率現場での放射線イメージングや核燃料デブリの検出といった、放射線計測(Radiation measurement)および位置認識・周辺環境の把握のための技術の開発が必要である。今回の福島リサーチカンファレンスでは、遠隔技術のさらなる進展のため、さまざまな分野の専門化を交えて将来のビジョンを共有することを目指している。
佐藤 優樹; 寺阪 祐太; 宮村 浩子; 冠城 雅晃; 谷藤 祐太; 川端 邦明; 鳥居 建男
Reactor Dosimetry; 16th International Symposium on Reactor Dosimetry (ISRD-16) (ASTM STP 1608), p.428 - 436, 2018/11
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.05(Nuclear Science & Technology)We developed a lightweight compact Compton camera to measure the distribution of radioactive contamination inside the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. We conducted performance evaluation tests in the coastal area of Fukushima, Japan, using the camera, which employs a cerium (Ce)-doped GAGG (Gd Al
Al Ga
Ga O
O ) scintillator coupled with a multipixel photon counter. The camera can clearly visualize spreading of radioactivity along the ground surface. In addition, we performed three-dimensional image reconstruction of the distribution of radioactive contamination using the multi-angle data obtained with the Compton camera. We succeeded in obtaining a three-dimensional image of radioactive contamination in the outdoor area.
) scintillator coupled with a multipixel photon counter. The camera can clearly visualize spreading of radioactivity along the ground surface. In addition, we performed three-dimensional image reconstruction of the distribution of radioactive contamination using the multi-angle data obtained with the Compton camera. We succeeded in obtaining a three-dimensional image of radioactive contamination in the outdoor area.
冠城 雅晃; 佐藤 優樹; 吉原 有里*; 島添 健次*; 高橋 浩之*; 鳥居 建男
Reactor Dosimetry; 16th International Symposium on Reactor Dosimetry (ISRD-16) (ASTM STP 1608), p.405 - 414, 2018/11
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.05(Nuclear Science & Technology)On March 11, 2011, a massive earthquake occurred in the Tohoku region of Japan, and a large tsunami hit the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F), resulting in a nuclear accident. Despite the years that have passed since the accident, decommissioning remains a concern. Radiation measurement techniques are very important for accelerating the decommissioning and ensuring low radiation exposure to workers. Our gamma-ray imaging system is the detection device for determining the three dimensional radioactive distributions of nuclear fuel debris, measuring high-energy gamma rays (greater than 1 MeV). Silicon semiconductor detectors are among the candidate detectors for radiation measurements in our system because of their radiation-hardness and high counting rate capability. We have been developing a stacked amorphous-silicon (Si)/crystal-Si heterojunction Si strip detector, which has 1-mm-pitch striped electrodes (0.5 mm wide) and 1.2-mm-pitch stacked technology. The detector consists of an Si strip mounted on a thin printed circuit board, front-end readout electronics with a complementary metal oxide semiconductor application specific integrated circuit, and a field programmable gate array. The threshold level of energy deposition of each pulse signal in each channel can be set from the application-specific integrated circuit, and gamma-ray images with energy discrimination can be obtained. The energy threshold level for discrimination of  Co gamma rays from
Co gamma rays from  Cs gamma rays was investigated experimentally and by means of simulation, and it was found to be about 500 keV. Therefore, our Si strip detector has the required position sensitivity and energy discrimination ability for identifying high-energy gamma-ray source distributions.
Cs gamma rays was investigated experimentally and by means of simulation, and it was found to be about 500 keV. Therefore, our Si strip detector has the required position sensitivity and energy discrimination ability for identifying high-energy gamma-ray source distributions.
佐藤 優樹; 谷藤 祐太; 寺阪 祐太; 宇佐美 博士; 冠城 雅晃; 川端 邦明; 宇津木 弥*; 菊地 弘幸*; 高平 史郎*; 鳥居 建男
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(9), p.965 - 970, 2018/09
被引用回数:33 パーセンタイル:96.48(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), operated by Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc., went into meltdown after the occurrence of a large tsunami caused by the Great East Japan Earthquake of March 11, 2011. The radiation distribution measurements inside the FDNPS buildings are indispensable to execute decommissioning tasks in the reactor buildings. We conducted the radiation imaging experiment inside the turbine building of Unit 3 of the FDNPS using a compact Compton camera, and succeeded in visualizing the high-dose contamination (up to 3.5 mSv/h). We also drew a three-dimensional radiation distribution map inside the turbine building by integrating the radiation image resulting from the Compton camera into the point cloud data of the experimental environment acquired using the scanning laser range finder. The radiation distribution map shows the position of these contaminations on the real space image of the turbine building. The radiation distribution map helps workers to easily recognize the radioactive contamination and to decrease the radiation exposure; the contamination cannot be observed with the naked eye, naturally.
 -ray imager mounted on a multicopter drone
-ray imager mounted on a multicopter drone佐藤 優樹; 小澤 慎吾*; 寺阪 祐太; 冠城 雅晃; 谷藤 祐太; 川端 邦明; 宮村 浩子; 和泉 良*; 鈴木 敏和*; 鳥居 建男
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(1), p.90 - 96, 2018/01
被引用回数:43 パーセンタイル:98.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)A remote radiation imaging system comprising a lightweight Compton camera and a multicopter drone was developed to remotely and quickly measure radioactive contamination inside the buildings of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS). The drone system is used for measuring detailed radiation distributions in narrow areas, which have been difficult to gauge with conventional aircraft monitoring using helicopters. A measurement of radiation distributions in outdoor environments in the coastal areas of Fukushima, Japan, was performed. The drone system with the Compton camera succeeded in remote observations of dense hotspots from the sky over a contaminated area near the FDNPS. The time required for image reconstruction is approximately 550 s in the case of a 9-m flight altitude for the hotspots with a surface dose rate of several tens of  Sv/h. This drone system will be used inside the buildings of the FDNPS for remote measurement of radioactive contamination.
Sv/h. This drone system will be used inside the buildings of the FDNPS for remote measurement of radioactive contamination.
佐藤 優樹; 寺阪 祐太; 小澤 慎吾*; 宮村 浩子; 冠城 雅晃; 谷藤 祐太; 川端 邦明; 鳥居 建男
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 12(11), p.C11007_1 - C11007_8, 2017/11
被引用回数:19 パーセンタイル:66.46(Instruments & Instrumentation)The Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), operated by Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc., went into meltdown after the large tsunami caused by the Great East Japan Earthquake of March 11, 2011. Very large amounts of radionuclides were released from the damaged plant. Radiation distribution measurements inside the building of FDNPS are indispensable to execute the decommission tasks in the reactor buildings. We have developed a light-weight compact Compton camera to three-dimensionally measure the distribution of radioactive contamination inside FDNPS. The total weight of the Compton camera is lower than 1.0 kg. The  -ray sensor of the Compton camera employs the Ce-doped GAGG scintillators coupled with a multi-pixel photon counter (MPPC: Hamamatsu Photonics K.K.,). We performed the 3D image reconstruction of the
-ray sensor of the Compton camera employs the Ce-doped GAGG scintillators coupled with a multi-pixel photon counter (MPPC: Hamamatsu Photonics K.K.,). We performed the 3D image reconstruction of the  Cs-radioactive sources as shown in Fig. 1; the 3D radiation image is reconstructed using the multi-angle data measured with the Compton camera. Here, we introduce the development status of the 3D radiation imaging system consisting of the Compton camera. Moreover, we present the results of a performance evaluation test for 3D image reconstruction of radioactive contaminations in details.
Cs-radioactive sources as shown in Fig. 1; the 3D radiation image is reconstructed using the multi-angle data measured with the Compton camera. Here, we introduce the development status of the 3D radiation imaging system consisting of the Compton camera. Moreover, we present the results of a performance evaluation test for 3D image reconstruction of radioactive contaminations in details.
 -ray imager mounted on a remotely operated machine
-ray imager mounted on a remotely operated machine佐藤 優樹; 川端 邦明; 小澤 慎吾*; 和泉 良*; 冠城 雅晃; 谷藤 祐太; 寺阪 祐太; 宮村 浩子; 河村 拓馬; 鈴木 敏和*; et al.
IFAC-PapersOnLine, 50(1), p.1062 - 1066, 2017/07
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:65.78(Automation & Control Systems)The development of remote and quick radiation imaging methods in the high dose-rate environment is requested to accelerate implementation of decommissioning of the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP). We developed the remote radiation imaging system consisting of a Compton camera and a multicopter drone to remotely measure the radioactive contamination on the several radioactive fields in the environment and inside the building of nuclear facilities such as the FDNPP. The drone system succeeded in the observation of several hotspots from the sky at the outdoor environments in coastal areas of Fukushima, Japan. In addition, we are now developing the SLAM technology for remotely operated machines such as the drone to complete the remote radiation imaging system, which can autonomous flight.
冠城 雅晃; 山田 寛尚*; 宮川 毅*; 森河 良太*; 高須 昌子*; 加藤 宝光*; 上坂 充*
Polymer Journal, 48(2), p.189 - 195, 2016/02
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:18.57(Polymer Science)本研究は、テロメア一本鎖DNAとPOT1について分子動力学シミュレーションを100ns行った。テロメアDNAとPOT1の結合状態を確認するため、POT1の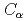 原子とテロメアDNAのO5'原子の距離を計算した。そして、単独状態と結合状態において、テロメア一本鎖DNAの両端塩基間距離、根平均二乗距離(RMSD)、慣性半径を計算した。さらに、単独状態と結合状態の根平均二乗揺らぎ(RMSF)を比較し、POT1とテロメアDNAの間の水素結合の平均数も計算した。グリニシン94(Gln94)と一本鎖テロメアDNAでPOT1と最近接なTTAGGGの一番目(G')のグアニンの間に水素結合が最頻度で現れる。そして、Gln94とG'が単独状態と結合状態でのRMSF値の差が最大になる。本研究では、Gln94とG'は、結合系において重要な部分で、結合状態の安定性に関係していると結論づけている。
原子とテロメアDNAのO5'原子の距離を計算した。そして、単独状態と結合状態において、テロメア一本鎖DNAの両端塩基間距離、根平均二乗距離(RMSD)、慣性半径を計算した。さらに、単独状態と結合状態の根平均二乗揺らぎ(RMSF)を比較し、POT1とテロメアDNAの間の水素結合の平均数も計算した。グリニシン94(Gln94)と一本鎖テロメアDNAでPOT1と最近接なTTAGGGの一番目(G')のグアニンの間に水素結合が最頻度で現れる。そして、Gln94とG'が単独状態と結合状態でのRMSF値の差が最大になる。本研究では、Gln94とG'は、結合系において重要な部分で、結合状態の安定性に関係していると結論づけている。
冠城 雅晃
島添 健次*
The present invention carries out highly accurate assay of a sample, even under high-dose radiation, by analyzing an energy spectrum obtained by a radiation detector. In this radiation analysis method, first, the spectrum (actual spectrum) of a sample is measured by a radiation detector (sample measurement step: S1). In this step, two or more types of scintillators having different sizes are used and two or more types of shielding substances having different thicknesses are used to obtain an actual spectrum for each condition (setting condition). Next, measurement similar to that described above is carried out with respect to a reference radiation source (reference radiation source measurement step: S2). Next, a background nuclide-derived component, which is a component derived from a background nuclide (137Cs) in the actual spectrum, is inferred from the reference spectrum obtained in the reference radiation source measurement step (S2) (background nuclide-derived component inference step: S3). ・・・
冠城 雅晃
島添 健次*
The present invention carries out highly accurate assay of a sample, even under high-dose radiation, by analyzing an energy spectrum obtained by a radiation detector. In this radiation analysis method, first, the spectrum (actual spectrum) of a sample is measured by a radiation detector (sample measurement step: S1). In this step, two or more types of scintillators having different sizes are used and two or more types of shielding substances having different thicknesses are used to obtain an actual spectrum for each condition (setting condition). Next, measurement similar to that described above is carried out with respect to a reference radiation source (reference radiation source measurement step: S2). Next, a background nuclide-derived component, which is a component derived from a background nuclide (137Cs) in the actual spectrum, is inferred from the reference spectrum obtained in the reference radiation source measurement step (S2) (background nuclide-derived component inference step: S3). ・・・
冠城 雅晃
島添 健次*
The present invention carries out highly accurate assay of a sample, even under high-dose radiation, by analyzing an energy spectrum obtained by a radiation detector. In this radiation analysis method, first, the spectrum (actual spectrum) of a sample is measured by a radiation detector (sample measurement step: S1). In this step, two or more types of scintillators having different sizes are used and two or more types of shielding substances having different thicknesses are used to obtain an actual spectrum for each condition (setting condition). Next, measurement similar to that described above is carried out with respect to a reference radiation source (reference radiation source measurement step: S2). Next, a background nuclide-derived component, which is a component derived from a background nuclide (137Cs) in the actual spectrum, is inferred from the reference spectrum obtained in the reference radiation source measurement step (S2) (background nuclide-derived component inference step: S3). ・・・
冠城 雅晃
島添 健次*
高線量下においても放射線検出器で得られたエネルギースペクトルの解析によって試料の分析を高精度で行う。 この放射線分析方法においては、まず、試料のスペクトル(実測スペクトル)が放射線検出器によって測定される(試料測定工程:S1)。ここではシンチレータとして異なる大きさのものが複数種類、遮蔽体として異なる厚さのものが複数種類用いられ、各条件(設定条件)毎に実測スペクトルが得られる。次に、参照用線源に対して、前記同様の測定が行われる(参照用線源測定工程:S2)。次に、参照用線源測定工程(S2)で得られた参照スペクトルから、前記のように実測スペクトル中における背景核種(137CS)に起因する成分である背景核種起因成分を推定する(背景核種起因成分推定工程:S3)。次に、実測スペクトルと背景核種起因成分との差分となる補正後スペクトルが算出される(補正後スペクトル算出工程:S4)。
佐藤 優樹; 谷藤 祐太; 寺阪 祐太; 宇佐美 博士; 冠城 雅晃; 宮村 浩子; 川端 邦明; 鳥居 建男
no journal, ,
福島第一原子力発電所(以下、1F)の事故により1F建屋内外に放出された放射性物質について、詳細な除染計画の立案や作業員の被ばく線量の低減のために、飛散した放射性物質を可視化するための技術開発が求められている。原子力機構廃炉国際共同研究センターは放射性物質を可視化するための装置として、小型・軽量なコンプトンカメラを開発し、放射性物質の分布を3次元的に可視化するための技術開発を進めている。加えて、レーザー等による光測量技術を用いて建屋構造物の3次元モデルを構築し、これを放射線イメージと重ね合わせることによって、より視認しやすい放射性物質分布図の構築を目指している。これまでに福島第一原子力発電所建屋内部において、開発したコンプトンカメラを用いて放射性物質のイメージング試験を実施し、建屋内部に存在するホットスポットの3次元的な可視化に成功した。加えて、測域センサーを用いて建屋内部の3次元モデルを構築し、放射線イメージと重ね合わせることによる放射線分布マップの構築を試みた。発表では試験結果の詳細と今後の予定を紹介する。