Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Komuro, Michiyasu; Kanazawa, Hiroyuki; Kokusen, Junya; Shimizu, Osamu; Honda, Junichi; Harada, Katsuya; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Nakada, Masami; Inagawa, Jun
JAEA-Technology 2021-042, 197 Pages, 2022/03
Plutonium Research Building No.1 was constructed in 1960 for the purpose of establishing plutonium handling technology and studying its basic physical properties. Radiochemical research, physicochemical research and analytical chemistry regarding solutions and solid plutonium compounds had been doing for the research program in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). In 1964, the laboratory building was expanded and started the researching plutonium-uranium mixed fuel and reprocessing of plutonium-based fuel, playing an advanced role in plutonium-related research in Japan. Since then, the research target has been expanded to include transplutonium elements, and it has functioned as a basic research facility for actinides. The laboratory is constructed by concrete structure and it has the second floor, equipped with 15 glove boxes and 4 chemical hoods. Plutonium Research Building No.1 was decided as one of the facilities to be decommissioned by Japan Atomic Energy Agency Reform Plan in September 2014. So far, the contamination survey of the radioactive materials in the controlled area, the decontamination of glove boxes, and the consideration of the equipment dismantling procedure have been performed as planned. The radioisotope and nuclear fuel materials used in the facility have been transfer to the other facilities in JAEA. The decommissioning of the facility is proceeding with the goal of completing by decommissioning the radiation controlled area in 2026. In this report, the details of the decommissioning plan and the past achievements are reported with the several data.
Otsuka, Yusuke*; Kanazawa, Naoya*; Hirayama, Motoaki*; Matsui, Akira*; Nomoto, Takuya*; Arita, Ryotaro*; Nakajima, Taro*; Hanashima, Takayasu*; Ukleev, V.*; Aoki, Hiroyuki; et al.
Science Advances (Internet), 7(47), p.eabj0498_1 - eabj0498_9, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:63.29(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Kokusen, Junya; Akasaka, Shingo*; Shimizu, Osamu; Kanazawa, Hiroyuki; Honda, Junichi; Harada, Katsuya; Okamoto, Hisato
JAEA-Technology 2020-011, 70 Pages, 2020/10
The Uranium Enrichment Laboratory in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) was constructed in 1972 for the purpose of uranium enrichment research. The smoke emitting accident on 1989 and the fire accident on 1997 had been happened in this facility. The research on uranium enrichment was completed in JFY1998. The decommissioning work was started including the transfer of the nuclear fuel material to the other facility in JFY2012. The decommissioning work was completed in JFY2019 which are consisting of removing the hood, dismantlement of wall and ceiling with contamination caused by fire accident. The releasing the controlled area was performed after the confirmation of any contamination is not remained in the target area. The radioactive waste was generated while decommissioning, burnable and non-flammable are 1.7t and 69.5t respectively. The Laboratory will be used as a general facility for cold experiments.
Shiina, Hidenori; Ono, Katsuto; Nishi, Masahiro; Uno, Kiryu; Kanazawa, Hiroyuki; Oi, Ryuichi; Nihei, Yasuo
Dekomisshoningu Giho, (61), p.29 - 38, 2020/03
The Research Hot Laboratory (RHL) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) was constructed in 1961, as the first one in Japan, to perform the examinations of irradiated fuels and materials. RHL consists of 10 heavy concrete cells and 38 lead cells. RHL contributed to research and development program in or out of JAEA for the investigation of irradiation behavior for fuels and nuclear materials. However, RHL is the one of target as the rationalization program for decrepit facilities in former Tokai institute. Therefore the decommissioning works of RHL started on April 2003. The dismantling of 12 lead cells has been progressing since 2010. The dismantling procedure of lead cells was performed in the following order. The peripheral equipment in lead cells were removed and contamination survey of the inner surface of the cells. Then, the backside shield doors were extracted. The lifting frame for the isolation tent was set on the cells. After that, the ceiling plates, isolation walls and lead blocks were removed. The strippable paint was used to remove permeable contamination on the inner surface of structural steel of the cells. The dismantling work will be continued to mention the efficiency of decommissioning works and reduction of radioactive waste with ensuring safety.
Miyai, Hiromitsu; Suzuki, Miho; Kanazawa, Hiroyuki
JAEA-Technology 2016-041, 46 Pages, 2017/03
In the Reactor Fuel Examination Facility (RFEF) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), Post Irradiation Examinations (PIEs) have been carried out for a long time in order to verify the reliability and the safety of the nuclear fuels irradiated in nuclear power plants. Samples for the PIEs are small and have various shapes. In order to facilitate the handling of the samples using a manipulator, the several kinds of jigs have been used for PIEs at RFEF those jigs are usually manufactured by machining process. We tried to make the jigs, which is PLA resin, with 3D printer and instead of machining process for the reduction of the manufacturing time and the improvement of the dimensional accuracy of the jig this time. It became clear that the actual dimensions of the jigs manufactured with 3D printer were roughly smaller at the concave section and larger at the convex section compared with the dimensions of the plan. So it is necessary to make a plan for the jigs after consideration of the characteristic of the 3D printer. The jigs can be applied to SEM observation, because the deposition of carbon film onto the jigs was well. And the jigs can be used to for the metallography, because the jigs were applicable without any harmful effects on polishing and etching processes.
Miyai, Hiromitsu; Suzuki, Miho; Kanazawa, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 54th Annual Meeting of Hot Laboratories and Remote Handling (HOTLAB 2017) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2017/00
In the Reactor Fuel Examination Facility (RFEF) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), Post Irradiation Examinations (PIEs) have been carried out for a long time in order to verify the reliability and the safety of the nuclear fuels irradiated in nuclear power plants. Samples for the PIEs are small and have various shapes. In order to facilitate the handling of the samples using a manipulator, the several kinds of jigs have been used for PIEs at RFEF. Those jigs are usually manufactured by machining process. We tried to make the jigs, which is PLA resin, with 3D printer and instead of machining process for the reduction of the manufacturing time and the improvement of the dimensional accuracy of the jig this time. It became clear that the actual dimensions of the jigs manufactured with 3D printer were roughly smaller at the concave section and larger at the convex section compared with the dimensions of the plan. So it is necessary to make a plan for the jigs after consideration of the characteristic of the 3D printer. The jigs can be applied to SEM observation, because the deposition of carbon film onto the jigs was well. And the jigs can be used to for the metallography, because the jigs were applicable without any harmful effects on polishing and etching processes.
Matsui, Hiroki; Suzuki, Miho; Obata, Hiroki; Kanazawa, Hiroyuki
JAEA-Technology 2014-017, 57 Pages, 2014/06
The Reactor Fuel Examination Facility in JAEA has been used for Post Irradiation Examinations to verify the reliability and safety of the nuclear fuels irradiated in commercial reactors. EPMA (Electron Probe Micro Analyzer) has been utilized for the qualitative analysis of the fission product in the fuel pellet and the detailed observation of the oxide layers formed at the inner and outer surfaces of fuel cladding. Commercial EPMAs were remodeled so that the EPMAs can be applied for radioactive samples. Several shields was set in the EPMA to avoid the  -rays which radiate from a radioactive sample to the proportional counter in the EPMA. It is important to calculate this shielding performance adequately to maintain the precision of analysis. This report describes the results of re-evaluation of the performance of the shields in the EPMAs in the RFEF by using the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport Code System and the examination results of
-rays which radiate from a radioactive sample to the proportional counter in the EPMA. It is important to calculate this shielding performance adequately to maintain the precision of analysis. This report describes the results of re-evaluation of the performance of the shields in the EPMAs in the RFEF by using the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport Code System and the examination results of  -ray effect to the X-ray spectrum data by using a radioactive sample.
-ray effect to the X-ray spectrum data by using a radioactive sample.
Sagisaka, Akito; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Ogura, Koichi; Sakaki, Hironao; Yogo, Akifumi; Mori, Michiaki; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Okada, Hajime; Kanazawa, Shuhei; et al.
Reza Kenkyu, 42(2), p.160 - 162, 2014/02
High-intensity laser and thin-foil interactions produce high-energy particles, hard X-ray, high-order harmonics, and terahertz radiation. A proton beam driven by a high-intensity laser has received attention as a compact ion source for medical and other applications. We have measured the proton yield from thin-foil targets irradiated with a high-intensity Ti:sapphire laser (J-KAREN) at JAEA. The longitudinal extent of the preformed plasma protruding from the front surface of the target is reduced by decreasing the duration of the amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) before the main pulse. The maximum proton energy in the target normal direction increases when the size of the preformed plasma is controlled.
Ogura, Koichi; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Yogo, Akifumi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Orimo, Satoshi; Sagisaka, Akito; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Mori, Michiaki; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 51(4), p.048003_1 - 048003_2, 2012/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:8.46(Physics, Applied)A proton beam driven by a repetitive high-intensity-laser is utilized to induce a  Li(p,n)
Li(p,n) Be nuclear reaction. The total activity of
Be nuclear reaction. The total activity of  Be are evaluated by two different methods. The activity obtained measuring the decay
Be are evaluated by two different methods. The activity obtained measuring the decay  -rays after 1912 shots at 1 Hz is 1.7
-rays after 1912 shots at 1 Hz is 1.7 0.2 Bq. This is in good agreement with 1.6
0.2 Bq. This is in good agreement with 1.6 0.3 Bq evaluated from the proton energy distribution measured using a time-of-flight detector and the nuclear reaction cross-sections. We conclude that the production of activity can be monitored in real time using the time-of-flight-detector placed inside a diverging proton beam coupled with a high-speed signal processing system.
0.3 Bq evaluated from the proton energy distribution measured using a time-of-flight detector and the nuclear reaction cross-sections. We conclude that the production of activity can be monitored in real time using the time-of-flight-detector placed inside a diverging proton beam coupled with a high-speed signal processing system.
Sagisaka, Akito; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Ma, J.*; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Kanazawa, Shuhei; et al.
NIFS-PROC-85, p.30 - 33, 2011/02
The experiment of proton generation is performed for developing the laser-driven ion source. We observe proton signals in the laser-plasma interaction by using a thin-foil target. To get higher energy protons the size of the preformed plasma is reduced by changing the laser contrast level. In the high-contrast laser pulse case the maximum energy of the protons generated at rear side of the target increases.
Koya, Toshio; Nozawa, Yukio; Hanada, Yasushi; Ono, Katsuto; Kanazawa, Hiroyuki; Nihei, Yasuo; Owada, Isao
Dekomisshoningu Giho, (42), p.41 - 48, 2010/09
The Research Hot Laboratory (RHL) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) had been contributed to R&D program for fuels and nuclear materials in or out of JAEA. However, the decommissioning work of RHL has been started on April 2003 as the rationalization program for decrepit facilities in former Tokai institute. This work will be progressing, dismantling the lead cells and decontamination of concrete caves then release in the regulation of controlled area. The partial area of RHL will be used for the central storage of un- irradiated fuel and for temporary storage of radioactive device generated by J-PARC. The 18 lead cells had been dismantled and the preparing work for remained 20 lead cells has been finished including the removal of the applause from the cells, survey of the contamination revel in the lead cells and prediction of radio active waste. The future plan of decommissioning work has been prepared to incarnate the basic vision and dismantling procedure.
Sagisaka, Akito; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Ma, J.*; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Kanazawa, Shuhei; et al.
Reza Kenkyu, 38(9), p.702 - 705, 2010/09
High-intensity laser and thin-foil interactions produce high-energy particles, hard X-ray, high-order harmonics, and terahertz (THz) radiation. A proton beam driven by a high-intensity laser has received attention as a compact ion source for medical applications. In this study we have tested simultaneous generation of protons and THz radiation from a thin-foil target. We use a Ti:sapphire laser system (J-KAREN) at JAEA. A laser beam is focused by an off-axis parabolic mirror at the thin-foil target. We observed the high-energy proton in the rear side of the target and THz radiation in the reflected direction. Next, high energy protons are observed by reducing the size of preformed plasma.
Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Mori, Michiaki; Nakai, Yoshiki*; Shimomura, Takuya; Sasao, Hajime*; Tanaka, Momoko; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Tanoue, Manabu*; Kondo, Shuji; Kanazawa, Shuhei; et al.
Reza Kenkyu, 38(9), p.669 - 675, 2010/09
This paper reviews the temporal contrast and spatial beam quality improvement techniques in a high intensity Ti:sapphire laser system that is based on chirped-pulse amplification (CPA). We describe a low gain optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification (OPCPA) preamplifier that uses high energy, clean pulse seeding and is shown to significantly improve the contrast to better than 10 -10
-10 relative to the peak of the main femtosecond pulse. We also report the use of a diffractive optical element for beam homogenization of a 100 J level Nd:glass green pump laser, achieving a flat-topped spatial profile with a filling factor near 80 %.
relative to the peak of the main femtosecond pulse. We also report the use of a diffractive optical element for beam homogenization of a 100 J level Nd:glass green pump laser, achieving a flat-topped spatial profile with a filling factor near 80 %.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Sakaki, Hironao; Hori, Toshihiko; Bolton, P.; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Yogo, Akifumi; Mori, Michiaki; Orimo, Satoshi; Pirozhkov, A. S.; et al.
Physical Review Special Topics; Accelerators and Beams, 13(7), p.071304_1 - 071304_7, 2010/07
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:78.98(Physics, Nuclear)A laser-driven repetition-rated 1.9 MeV proton beam line composed of permanent quadrupole magnets (PMQs), a radio frequency (rf) phase rotation cavity, and a tunable monochromator is developed to evaluate and to test the simulation of laser-accelerated proton beam transport through an integrated system for the first time. In addition, the proton spectral modulation and focusing behavior of the rf phase rotationcavity device is monitored with input from a PMQ triplet. In the 1.9 MeV region we observe very weakproton defocusing by the phase rotation cavity. The final transmitted bunch duration and transverse profile are well predicted by the PARMILA particle transport code. The transmitted proton beam duration of 6 ns corresponds to an energy spread near 5% for which the transport efficiency is simulated to be 10%. The predictive capability of PARMILA suggests that it can be useful in the design of future higher energy transport beam lines as part of an integrated laser-driven ion accelerator system.
 ), high-intensity (500 TW) J-KAREN laser system
), high-intensity (500 TW) J-KAREN laser systemKiriyama, Hiromitsu; Mori, Michiaki; Nakai, Yoshiki; Shimomura, Takuya; Sasao, Hajime; Tanaka, Momoko; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Tanoue, Manabu*; Okada, Hajime; Kondo, Shuji; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2010-002, p.18 - 21, 2010/06
We have developed a femtosecond high intensity laser system, which combines both Ti:sapphire chirped-pulse amplification (CPA) and optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification (OPCPA) techniques, that produces more than 30 J broadband output energy, indicating the potential for achieving peak powers in excess of 500 TW. With a cleaned high-energy seeded OPCPA preamplifier as a front-end in the system, for the final compressed pulse (without pumping the booster amplifier) we found that the temporal contrast in this system exceeds 10 on the sub-nanosecond timescale, and is near 10
on the sub-nanosecond timescale, and is near 10 on the nanosecond timescale before the main femtosecond pulse. Using diffractive optical elements for beam homogenization of 100-J level high-energy Nd:glass green pump laser in a Ti:sapphire final amplifier, we have successfully generated broadband high-energy output with near-perfect top-hat intensity distributions.
on the nanosecond timescale before the main femtosecond pulse. Using diffractive optical elements for beam homogenization of 100-J level high-energy Nd:glass green pump laser in a Ti:sapphire final amplifier, we have successfully generated broadband high-energy output with near-perfect top-hat intensity distributions.
Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Mori, Michiaki; Nakai, Yoshiki; Shimomura, Takuya; Sasao, Hajime; Tanoue, Manabu*; Kanazawa, Shuhei; Wakai, Daisuke*; Sasao, Fumitaka*; Okada, Hajime; et al.
Optics Letters, 35(10), p.1497 - 1499, 2010/05
Times Cited Count:86 Percentile:94.79(Optics)OPCPA (Optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification) operation with low gain by seeding with high energy, clean pulses is shown to significantly improve the contrast to better than 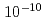 -
-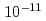 in a high intensity Ti:sapphire laser system that is based on chirped pulse amplification. In addition to the high contrast broadband high energy output from the final amplifier is achieved with a flat-topped spatial profile of filling factor near 77%. This is the result of pump beam spatial profile homogenization with diffractive optical elements. Final pulse energies exceed 30-Joules indicating capability for reaching peak powers in excess of 500-TW.
in a high intensity Ti:sapphire laser system that is based on chirped pulse amplification. In addition to the high contrast broadband high energy output from the final amplifier is achieved with a flat-topped spatial profile of filling factor near 77%. This is the result of pump beam spatial profile homogenization with diffractive optical elements. Final pulse energies exceed 30-Joules indicating capability for reaching peak powers in excess of 500-TW.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Sakaki, Hironao; Hori, Toshihiko; Bolton, P.; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Yogo, Akifumi; Mori, Michiaki; Orimo, Satoshi; Pirozhkov, A. S.; et al.
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.88 - 90, 2010/05
The concept of a compact ion particle accelerator has become attractive in view of recent progress in laser-driven ion acceleration. We report here the recent progress in the laser-driven proton beam transport at the Photo Medical Research Center (PMRC) at JAEA, which is established to address the challenge of laser-driven ion accelerator development for ion beam cancer therapy.
Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Mori, Michiaki; Nakai, Yoshiki; Shimomura, Takuya; Sasao, Hajime; Tanaka, Momoko; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Tanoue, Manabu*; Okada, Hajime; Kondo, Shuji; et al.
Applied Optics, 49(11), p.2105 - 2115, 2010/04
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:82.71(Optics)We have developed a femtosecond high intensity laser system, which combines both Ti:sapphire chirped-pulse amplification (CPA) and optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification (OPCPA) techniques, that produces more than 30-J broadband output energy, indicating the potential for achieving peak powers in excess of 500-TW. With a cleaned high-energy seeded OPCPA preamplifier as a front-end in the system, for the compressed pulse without pumping the final amplifier we found that the temporal contrast in this system exceeds 10 on the sub-nanosecond timescales, and is near 10
on the sub-nanosecond timescales, and is near 10 on the nanosecond timescale prior to the peak of the main femtosecond pulse. Using diffractive optical elements for beam homogenization of 100-J level high-energy Nd:glass green pump laser in a Ti:sapphire final amplifier, we have successfully generated broadband high-energy output with a near-perfect top-hat-like intensity distribution.
on the nanosecond timescale prior to the peak of the main femtosecond pulse. Using diffractive optical elements for beam homogenization of 100-J level high-energy Nd:glass green pump laser in a Ti:sapphire final amplifier, we have successfully generated broadband high-energy output with a near-perfect top-hat-like intensity distribution.
Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Mori, Michiaki; Nakai, Yoshiki; Shimomura, Takuya*; Tanoue, Manabu*; Okada, Hajime; Sasao, Hajime; Wakai, Daisuke*; Kondo, Shuji; Kanazawa, Shuhei; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2009-007, p.97 - 100, 2010/03
no abstracts in English
Yogo, Akifumi; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Mori, Michiaki; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Orimo, Satoshi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Nagatomo, Hideo*; et al.
European Physical Journal D, 55(2), p.421 - 425, 2009/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:19.84(Optics)We demonstrate the laser-ion acceleration from a near-critical density plasma, when amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) was used to convert a solid foil target into the lower-density target. In this work, a direct comparison is made by changing the ASE intensity by factor 3 in order to investigate the target density-dependency of the laser-ion acceleration. The beam direction of high-energy component is successfully controlled by modifying the target density. The near-critical density plasma can be a favorable target to control the beam direction to be dependent on its energy.