Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yasuda, Hiroshi*; Saito, Tatsuo; Fumoto, Hiromichi*; Sugawara, Shinetsu*; Tsuchida, Shoji*; Kasai, Atsushi*; Furuta, Sadaaki*
Hoken Butsuri (Internet), 58(3), p.120 - 134, 2023/11
This paper is a summary of the activity report of the specialized study group of the Japan Health Physics Society on handling of naturally occurring radioactive wastes from humanities and social sciences perspective. To ensure the reliability of the long-term assessment, this special committee first reviews options for disposal of uranium waste depending on its concentration, especially those adopted or considered in Japan and overseas (U.S.A., U.K.) for uranium concentrations exceeding a sufficiently small amount of uranium (an average of 1 Bq/g of the sum of  U,
U,  U, and
U, and  U).
U).
Davies, S. J. C.*; Bolea-Alamanac, B.*; Endo, Kaori*; Yamamoto, Yu*; Yamasaki, Shudo*; Malins, A.; Evans, J.*; Sullivan, S.*; Ando, Shuntaro*; Nishida, Atsushi*; et al.
Journal of Transport & Health, 28, p.101564_1 - 101564_11, 2023/01
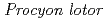 )
)Komatsu, Kazuki*; Iwasaki, Tsugumi*; Murata, Kosuke*; Yamashiro, Hideaki*; Goh, V. S. T.*; Nakayama, Ryo*; Fujishima, Yohei*; Ono, Takumi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Shimizu, Yoshinaka*; et al.
Reproduction in Domestic Animals, 56(3), p.484 - 497, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:83.05(Agriculture, Dairy & Animal Science)We have established an archive system of livestock and wild animals from the surrounding ex-evacuation zone. Wildlife within the alert zone have been exposed to low-dose-rate (LDR) radiation for a long and continuous time. In this study, we analysed the morphological characteristics of the testes and in vitro fertilization (IVF) capacity of cryopreserved sperm of raccoons from the ex-evacuation zone of the FDNPP accident. This study revealed that the chronic and LDR radiation exposure associated with the FDNPP accident had no adverse effect on the reproductive characteristics and functions of male raccoons.
Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Ebine, Masumi; Birumachi, Atsushi; Sakasai, Kaoru
Proceedings of 2019 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC 2019), Vol.1, p.735 - 736, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)A large area, position-sensitive scintillation neutron detector was developed for upgrading the SENJU, time-of-flight Laue single crystal neutron diffractometer, in J-PARC MLF. The detector has a neutron-sensitive area of 512  512 mm with a pixel size of 4
512 mm with a pixel size of 4  4 mm. The detector was developed for upgrading of the SENJU instrument. The large area detector is to be installed below the vacuum tank to enlarge a covering solid angle. A
4 mm. The detector was developed for upgrading of the SENJU instrument. The large area detector is to be installed below the vacuum tank to enlarge a covering solid angle. A  Li:ZnS (Ag) scintillator and wavelength-shifting fiber technologies are employed. Each fiber channel is read out individually with photon counting mode. The electronics boards are implemented at the backside of the detector, enabling the detector depth as short as 20 cm. The detector exhibited a detection efficiency of 45% for thermal neutron. No degradation in fiber position and in neutron sensitivity has been observed over one year after production. In this paper, detector design and detector performances are presented.
Li:ZnS (Ag) scintillator and wavelength-shifting fiber technologies are employed. Each fiber channel is read out individually with photon counting mode. The electronics boards are implemented at the backside of the detector, enabling the detector depth as short as 20 cm. The detector exhibited a detection efficiency of 45% for thermal neutron. No degradation in fiber position and in neutron sensitivity has been observed over one year after production. In this paper, detector design and detector performances are presented.
Nakamura, Tatsuya; Kawasaki, Takuro; To, Kentaro; Tsutsui, Noriaki; Ebine, Masumi; Birumachi, Atsushi; Sakasai, Kaoru
Proceedings of 2018 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC 2018) (Internet), 3 Pages, 2019/10
A two-dimensional scintillation neutron detector with a submillimeter spatial resolution was developed for pulsed neutron diffraction imaging at the J-PARC MLF. The detector comprised the thin, single ZnS/ LiF scintillator screen coupled with the crossed wavelength-shifting fiber array for light collection. For a high spatial resolution, the wavelength shifting fibers with diameter of 0.1 mm were used them for assembling the detector. The prototype detector that has a neutron-sensitive area of 24
LiF scintillator screen coupled with the crossed wavelength-shifting fiber array for light collection. For a high spatial resolution, the wavelength shifting fibers with diameter of 0.1 mm were used them for assembling the detector. The prototype detector that has a neutron-sensitive area of 24  24 mm
24 mm exhibited a spatial resolution of 0.20
exhibited a spatial resolution of 0.20 0.06 mm and 0.16
0.06 mm and 0.16 0.06 mm for x and y directions, respectively. The detector had a detection efficiency of 7
0.06 mm for x and y directions, respectively. The detector had a detection efficiency of 7 for thermal neutrons with a
for thermal neutrons with a  Co
Co  -ray sensitivity in the order of 10
-ray sensitivity in the order of 10 . In this paper detailed detector design is presented together with experimental results using the pulsed neutron beam.
. In this paper detailed detector design is presented together with experimental results using the pulsed neutron beam.
Suekuni, Koichiro*; Lee, C. H.*; Tanaka, Hiromi*; Nishibori, Eiji*; Nakamura, Atsushi*; Kasai, Hidetaka*; Mori, Hitoshi*; Usui, Hidetomo*; Ochi, Masayuki*; Hasegawa, Takumi*; et al.
Advanced Materials, 30(13), p.1706230_1 - 1706230_6, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:62 Percentile:89.45(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Thermoelectric materials for highly efficient devices must satisfy conflicting requirements of high electrical conductivity and low thermal conductivity. In this paper, we studied the crystal structure and phonon dynamics of tetrahedrites (Cu,Zn) (Sb,As)
(Sb,As) S
S . The results revealed that the Cu atoms in a planar coordination are rattling, which effectively scatter phonons. These findings provide a new strategy for the development of highly efficient thermoelectric materials with planar coordination.
. The results revealed that the Cu atoms in a planar coordination are rattling, which effectively scatter phonons. These findings provide a new strategy for the development of highly efficient thermoelectric materials with planar coordination.
Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Tsutsui, Noriaki; Ebine, Masumi; Birumachi, Atsushi; Sakasai, Kaoru
Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC 2016), Vol.2, p.1506 - 1508, 2018/01
Position-dependent neutron sensitivity within an element of the scintillator / wavelength-shifting fiber coil (SFC) was evaluated by using a collimated pulsed neutron beam at the J-PARC/MLF. The collimated beam that has a size of 1  1 mm
1 mm was scanned over the SFC element. The neutron counts were recorded and plotted in each incident position. The scanning results showed less neutron sensitivity at the juncture of the rolled scintillator, suggesting less light collection efficiency or a lack of scintillator materials due to imperfect manufacturing process.
was scanned over the SFC element. The neutron counts were recorded and plotted in each incident position. The scanning results showed less neutron sensitivity at the juncture of the rolled scintillator, suggesting less light collection efficiency or a lack of scintillator materials due to imperfect manufacturing process.
Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Tsutsui, Noriaki; Ebine, Masumi; Birumachi, Atsushi; Sakasai, Kaoru
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 12(12), p.C12025_1 - C12025_9, 2017/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:18.79(Instruments & Instrumentation)A high-spatial-resolution, large-area position-sensitive scintillation-based neutron detector module has been developed for a new time-of-flight Laue single-crystal diffractometer to be constructed at J-PARC MLF. A first prototype detector implementing commercial  Li:ZnS screens was produced based on a scintillator/wavelength-shifting fibre technology. The detector exhibited a spatial resolution of 2.5 mm with a neutron-sensitive area of 320
Li:ZnS screens was produced based on a scintillator/wavelength-shifting fibre technology. The detector exhibited a spatial resolution of 2.5 mm with a neutron-sensitive area of 320  320 mm
320 mm . We report on an initial evaluation of the detector performance, including its spatial resolution, detection efficiency and long-term background measurement, and also provide a brief description of a new neutron instrument.
. We report on an initial evaluation of the detector performance, including its spatial resolution, detection efficiency and long-term background measurement, and also provide a brief description of a new neutron instrument.
 64 cm
64 cm area position-sensitive scintillation neutron detector as an alternative to helium-3 gas based detector
area position-sensitive scintillation neutron detector as an alternative to helium-3 gas based detectorNakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Honda, Katsunori; Ebine, Masumi; Birumachi, Atsushi; Sakasai, Kaoru
Proceedings of 2015 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC 2015), Vol.1, p.680 - 683, 2016/11
A two-dimensional scintillation neutron detector that has neutron-sensitive area of 64  64 cm
64 cm was developed for neutron scattering instruments by using wavelength shifting fibers technology. We designed the detector to have a pixel size of 20
was developed for neutron scattering instruments by using wavelength shifting fibers technology. We designed the detector to have a pixel size of 20  20 mm
20 mm . In order to compensate light attenuation occurred travelling along the wavelength-shifting fiber the scintillation light was read out from both sides of the fiber. The prototype detector exhibited a detection efficiency of 40% for 1.8
. In order to compensate light attenuation occurred travelling along the wavelength-shifting fiber the scintillation light was read out from both sides of the fiber. The prototype detector exhibited a detection efficiency of 40% for 1.8 neutrons, which was similar to previously developed detector with a smaller size of 32
neutrons, which was similar to previously developed detector with a smaller size of 32  32 cm
32 cm . The detailed detector design and experimental results measured by using the pulsed neutrons at the J-PARC/MLF are presented.
. The detailed detector design and experimental results measured by using the pulsed neutrons at the J-PARC/MLF are presented.
Shibama, Yusuke; Okano, Fuminori; Yagyu, Junichi; Kaminaga, Atsushi; Miyo, Yasuhiko; Hayakawa, Atsuro*; Sagawa, Keiich*; Mochida, Tsutomu*; Morimoto, Tamotsu*; Hamada, Takashi*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 98-99, p.1614 - 1619, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.44(Nuclear Science & Technology)The JT-60SA vacuum vessel (150 tons) is a double wall torus structure and the maximum major radius of 5.0 m and height of 6.6 m. The manufacturing design concept is that the vessel is split in the 10 toroidal sectors manufactured at factory, and assembled on-site; seven of the 40-degree sectors, two of the 30-degree beside final one, and the final of the 20-degree. The final sector is assembled with the VV thermal shield and toroidal field magnets into the 340-degree as prepared in one sector. Sectors are temporally fitted on-site and adjusted one over the other before the assembly. After measurement of the dimensions and the reference, these sectors are transferred onto the cryostat base. First, three 80-degree sectors are manufactured with mating each 40-degree sector by direct joint welding. The rest sectors including the final sector are jointed with splice plates. Welding manipulator and its guide rails are used for these welding. In this paper, the detail of the VV sectors assembly including the final sector is explained. Welding technologies to joint the two of 40-degree sectors are reported with the present manufacturing status and the welding trial on the vertical stub with the partial mock-up of the final sector are discussed with the assembly process.
Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Kawasaki, Takuro; Ebine, Masumi; Birumachi, Atsushi; Sakasai, Kaoru; Soyama, Kazuhiko
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 784, p.202 - 207, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:23.54(Instruments & Instrumentation)A two-dimensional scintillation neutron detector incorporating an interpolation method readout by wavelength-shifting (WLS) fiber was developed to make an effective pixel size smaller than the physical pitch of the WLS fibre array. The detector that was made with the crossed arranged WLS fiber arrays where the fibers were placed in a regular pitch of 2.5 mm in  and
and  directions. The dedicated signal processing algorithms that calculated an incident position of neutron with a base length of the same, half and quarter of the physical WLS fiber pitch were developed for the detector operated in a photon-counting method. The paper demonstrated the feasibility of the developed interpolation method using a collimated neutron beam.
directions. The dedicated signal processing algorithms that calculated an incident position of neutron with a base length of the same, half and quarter of the physical WLS fiber pitch were developed for the detector operated in a photon-counting method. The paper demonstrated the feasibility of the developed interpolation method using a collimated neutron beam.
Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Okano, Fuminori; Sakasai, Akira; Hanada, Masaya; Akino, Noboru; Ichige, Hisashi; Kaminaga, Atsushi; Kiyono, Kimihiro; Kubo, Hirotaka; Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; et al.
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 13(4), p.167 - 178, 2014/12
The JT-60U torus was disassembled so as to newly install the superconducting tokamak JT-60SA torus. The JT-60U used the deuterium for 18 years, so the disassembly project of the JT-60U was the first disassembly experience of a fusion device with radioactivation in Japan. All disassembly components were stored with recording the data such as dose rate, weight and kind of material, so as to apply the clearance level regulation in future. The lessons learned from the disassembly project indicated that the cutting technologies and storage management of disassembly components were the key factors to conduct the disassembly project in an efficient way. After completing the disassembly project, efforts have been made to analyze the data for characterizing disassembly activities, so as to contribute the estimation of manpower needs and the radioactivation of the disassembly components on other fusion devices.
Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Okano, Fuminori; Hanada, Masaya; Sakasai, Akira; Kubo, Hirotaka; Akino, Noboru; Chiba, Shinichi; Ichige, Hisashi; Kaminaga, Atsushi; Kiyono, Kimihiro; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 89(9-10), p.2018 - 2023, 2014/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:15.22(Nuclear Science & Technology)Disassembly of the JT-60U torus was started in 2009 after 18-years D operations, and was completed in October 2012. The JT-60U torus was featured by the complicated and welded structure against the strong electromagnetic force, and by the radioactivation due to D-D reactions. Since this work is the first experience of disassembling a large radioactive fusion device in Japan, careful disassembly activities have been made. About 13,000 components cut into pieces with measuring the dose rates were removed from the torus hall and stored safely in storage facilities by using a total wokers of 41,000 person-days during 3 years. The total weight of the disassembly components reached up to 5,400 tons. Most of the disassembly components will be treated as non-radioactive ones after the clearance verification under the Japanese regulation in future. The assembly of JT-60SA has started in January 2013 after this disassembly of JT-60U torus.
operations, and was completed in October 2012. The JT-60U torus was featured by the complicated and welded structure against the strong electromagnetic force, and by the radioactivation due to D-D reactions. Since this work is the first experience of disassembling a large radioactive fusion device in Japan, careful disassembly activities have been made. About 13,000 components cut into pieces with measuring the dose rates were removed from the torus hall and stored safely in storage facilities by using a total wokers of 41,000 person-days during 3 years. The total weight of the disassembly components reached up to 5,400 tons. Most of the disassembly components will be treated as non-radioactive ones after the clearance verification under the Japanese regulation in future. The assembly of JT-60SA has started in January 2013 after this disassembly of JT-60U torus.
 He at J-PARC/MLF
He at J-PARC/MLFNakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Honda, Katsunori; Birumachi, Atsushi; Ebine, Masumi; Sakasai, Kaoru; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Katagiri, Masaki*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 528, p.012042_1 - 012042_7, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:86.61(Optics)A wavelength-shifting fiber based scintillator detector has been developed as a helium-3 alternative detector in J-PARC/MLF. The detector is aimed at using for an inelastic neutron scattering instrument in a pulsed neutron source. The detector should have a capability to have a large-area coverage with a moderate pixel size as well as high detector efficiency, low  sensitivity, and a low background rate. We have developed a detector that has a larger neutron-sensitive area with a moderate pixel size based on the detector implemented in the SENJU instrument in the J-PARC/MLF. The prototype detector has a pixel size of 20
sensitivity, and a low background rate. We have developed a detector that has a larger neutron-sensitive area with a moderate pixel size based on the detector implemented in the SENJU instrument in the J-PARC/MLF. The prototype detector has a pixel size of 20  20 mm with a neutron-sensitive area of 320
20 mm with a neutron-sensitive area of 320  320 mm. In the presentation detailed detector performances are presented in comparison to those measured by an original SENJU detector.
320 mm. In the presentation detailed detector performances are presented in comparison to those measured by an original SENJU detector.
 B
B O
O ceramic scintillator detector as an alternative to a
ceramic scintillator detector as an alternative to a  He-gas-based detector for a plutonium canister assay system
He-gas-based detector for a plutonium canister assay systemNakamura, Tatsuya; Ozu, Akira; To, Kentaro; Sakasai, Kaoru; Suzuki, Hiroyuki; Honda, Katsunori; Birumachi, Atsushi; Ebine, Masumi; Yamagishi, Hideshi*; Takase, Misao; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 763, p.340 - 346, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.66(Instruments & Instrumentation)A neutron-sensitive ZnS/ B
B O
O ceramic scintillator detector was developed as an alternative to a
ceramic scintillator detector was developed as an alternative to a  He-gas-based detector for use in a plutonium canister assay system. The detector has a modular structure, with a flat ZnS/
He-gas-based detector for use in a plutonium canister assay system. The detector has a modular structure, with a flat ZnS/ B
B O
O ceramic scintillator strip that is installed diagonally inside a light-reflecting aluminium case with a square cross section. The prototype detectors, which have a neutron-sensitive area of 30 mm
ceramic scintillator strip that is installed diagonally inside a light-reflecting aluminium case with a square cross section. The prototype detectors, which have a neutron-sensitive area of 30 mm  250 mm, exhibited a sensitivity of 21.7-23.4
250 mm, exhibited a sensitivity of 21.7-23.4  0.1 cps
0.1 cps nv for thermal neutrons, a
nv for thermal neutrons, a  Cs
Cs  -ray sensitivity of 1.1-1.9
-ray sensitivity of 1.1-1.9 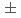 0.2
0.2  10
10 and a count variation of less than 6% over the detector length. A trial experiment revealed a temperature coefficient of less than -0.24
and a count variation of less than 6% over the detector length. A trial experiment revealed a temperature coefficient of less than -0.24 0.05% /
0.05% /  C over the temperature range of 20-50
C over the temperature range of 20-50 C.
C.
Nishiyama, Tomokazu; Miyo, Yasuhiko; Okano, Fuminori; Sasajima, Tadayuki; Ichige, Hisashi; Kaminaga, Atsushi; Miya, Naoyuki; Sukegawa, Atsuhiko; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Sakasai, Akira
JAEA-Technology 2014-006, 30 Pages, 2014/03
JT-60 tokamak device and the peripheral equipment were disassembled so as to be upgraded to the superconducting tokamak JT-60SA. The disassembled components were stored into storage and airtight containers at the radioactive control area. The total weight and the total number of those components are about 1,100 tons and about 11,500 except for large components. Radiation measurements and records of the radioactive components were required one by one under the law of Act on Prevention of Radiation Disease Due to Radioisotopes, etc. for the control of transport and storage from the radioactive control area to the other area. The storage management of the radioactive components was implemented by establishing the work procedure and the component management system by barcode tags. The radioactive components as many as 11,500 were surely and effectively stored under the law. The report gives the outline of the storage of JT-60 radioactive components by the storage containers.
Okano, Fuminori; Ichige, Hisashi; Miyo, Yasuhiko; Kaminaga, Atsushi; Sasajima, Tadayuki; Nishiyama, Tomokazu; Yagyu, Junichi; Ishige, Yoichi; Suzuki, Hiroaki; Komuro, Kenichi; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2014-003, 125 Pages, 2014/03
The disassembly of JT-60 tokamak device and its peripheral equipments, where the total weight was about 5400 tons, started in 2009 and accomplished in October 2012. This disassembly was required process for JT-60SA project, which is the Satellite Tokamak project under Japan-EU international corroboration to modify the JT-60 to the superconducting tokamak. This work was the first experience of disassembling a large radioactive fusion device based on Radiation Hazard Prevention Act in Japan. The cutting was one of the main problems in this disassembly, such as to cut the wielded parts together with toroidal field coils, and to cut the vacuum vessel into two. After solving these problems, the disassembly completed without disaster and accident. This report presents the outline of the JT-60 disassembly, especially tokamak device and ancillary facilities for tokamak device.
 He-gas-based detector for neutron-scattering instruments
He-gas-based detector for neutron-scattering instrumentsNakamura, Tatsuya; Katagiri, Masaki*; To, Kentaro; Honda, Katsunori; Suzuki, Hiroyuki; Ebine, Masumi; Birumachi, Atsushi; Sakasai, Kaoru; Soyama, Kazuhiko
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 741, p.42 - 46, 2014/03
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:45.30(Instruments & Instrumentation)A position-sensitive tubular scintillator-based neutron detector is proposed as an alternative to a  He-gas-based detector. The detector has a neutron-detecting element constructed from rolled ZnS/
He-gas-based detector. The detector has a neutron-detecting element constructed from rolled ZnS/ LiF scintillator screens that sandwich wavelength-shifting (WLS) fibre coils (SFC element). Multiple SFC elements are enclosed in an aluminium tube in a row to form a one-dimensional position-sensitive neutron detector. The design of the WLS fibre coil, which was determined by performing basic experiments, comprised two 0.75-mm-diameter WLS fibres wound in parallel at a pitch of 1.5 mm. A 64-element detector with a pixel size of 22 mm
LiF scintillator screens that sandwich wavelength-shifting (WLS) fibre coils (SFC element). Multiple SFC elements are enclosed in an aluminium tube in a row to form a one-dimensional position-sensitive neutron detector. The design of the WLS fibre coil, which was determined by performing basic experiments, comprised two 0.75-mm-diameter WLS fibres wound in parallel at a pitch of 1.5 mm. A 64-element detector with a pixel size of 22 mm  20 mm (width
20 mm (width  length) successfully demonstrated the detection principle. The tubular shape of the new detector is similar to the usual 25-mm-diameter
length) successfully demonstrated the detection principle. The tubular shape of the new detector is similar to the usual 25-mm-diameter  He tube, making this an alternative detector with the potential to be installed in a vacuum tank for inelastic-neutron-scattering instruments.
He tube, making this an alternative detector with the potential to be installed in a vacuum tank for inelastic-neutron-scattering instruments.
 m spatial resolution comprising a fibre-optic taper with wavelength-shifting fibre readout for time-of-flight neutron imaging
m spatial resolution comprising a fibre-optic taper with wavelength-shifting fibre readout for time-of-flight neutron imagingNakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Kawasaki, Takuro; Honda, Katsunori; Suzuki, Hiroyuki; Ebine, Masumi; Birumachi, Atsushi; Sakasai, Kaoru; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Katagiri, Masaki*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 737, p.176 - 183, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:66.74(Instruments & Instrumentation)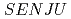 single-crystal time-of-flight neutron diffractometer at J-PARC/MLF
single-crystal time-of-flight neutron diffractometer at J-PARC/MLFKawasaki, Takuro; Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Hosoya, Takaaki*; Oikawa, Kenichi; Ohara, Takashi; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Ebine, Masumi; Birumachi, Atsushi; Sakasai, Kaoru; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 735, p.444 - 451, 2014/01
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:78.95(Instruments & Instrumentation)