Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakamura, Satoshi; Ishii, Sho*; Kato, Hitoshi*; Ban, Yasutoshi; Hiruta, Kenta; Yoshida, Takuya; Uehara, Hiroyuki; Obata, Hiroki; Kimura, Yasuhiko; Takano, Masahide
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(1), p.56 - 64, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.66(Nuclear Science & Technology)A dissolution method for analyzing the elemental composition of fuel debris using the sodium peroxide (Na O
O ) fusion technique has been developed. Herein, two different types of simulated debris materials (such as solid solution of (Zr,RE)O
) fusion technique has been developed. Herein, two different types of simulated debris materials (such as solid solution of (Zr,RE)O and molten core-concrete interaction products (MCCI)) were taken. At various temperatures, these debris materials were subsequently fused with Na
and molten core-concrete interaction products (MCCI)) were taken. At various temperatures, these debris materials were subsequently fused with Na O
O in crucibles, which are made of different materials, such as Ni, Al
in crucibles, which are made of different materials, such as Ni, Al O
O , Fe, and Zr. Then, the fused samples are dissolved in nitric acid. Furthermore, the effects of the experimental conditions on the elemental composition analysis were evaluated using inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES), which suggested the use of a Ni crucible at 923 K as an optimum testing condition. The optimum testing condition was then applied to the demonstration tests with Three Mile Island unit-2 (TMI-2) debris in a shielded concrete cell, thereby achieving complete dissolution of the debris. The elemental composition of TMI-2 debris revealed by the proposed dissolution method has good reproducibility and has an insignificant contradiction in the mass balance of the sample. Therefore, this newly developed reproducible dissolution method can be effectively utilized in practical applications by dissolving fuel debris and estimating its elemental composition.
, Fe, and Zr. Then, the fused samples are dissolved in nitric acid. Furthermore, the effects of the experimental conditions on the elemental composition analysis were evaluated using inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES), which suggested the use of a Ni crucible at 923 K as an optimum testing condition. The optimum testing condition was then applied to the demonstration tests with Three Mile Island unit-2 (TMI-2) debris in a shielded concrete cell, thereby achieving complete dissolution of the debris. The elemental composition of TMI-2 debris revealed by the proposed dissolution method has good reproducibility and has an insignificant contradiction in the mass balance of the sample. Therefore, this newly developed reproducible dissolution method can be effectively utilized in practical applications by dissolving fuel debris and estimating its elemental composition.
Kato, Hiroyuki S.*; Muroyama, Mizuho*; Kobayakawa, Nano*; Muneyasu, Riku*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Murase, Natsumi*; Watanabe, Seiya*; Yamada, Takashi*; Kanematsu, Yusuke*; Tachikawa, Masanori*; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 15(43), p.10769 - 10776, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:37.13(Chemistry, Physical)Kageyama, Tomio; Denuma, Akio; Koizumi, Jin*; Odakura, Manabu*; Haginoya, Masahiro*; Isaka, Shinichi*; Kadowaki, Hiroyuki*; Kobayashi, Shingo*; Morimoto, Taisei*; Kato, Yoshiaki*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2022-033, 130 Pages, 2023/03
Uranium handling facility for development of nuclear fuel manufacturing equipment (Mockup room) was constructed in 1972. The Mockup room has a weak seismic resistance and is deteriorating with age. Also, the original purpose with this facility have been achieved and there are no new development plans using this facility. Therefore, interior equipment installed in this facility had been dismantled and removed since March 2019. After that, the Mockup room was inspected for contamination, and then controlled area in the Mockup room was cancelled on March 29th 2022. A total of 6,549 workers (not including security witnesses) were required for this work. The amount of non-radioactive waste generated by this work was 31,300 kg. The amount of radioactive waste generated by this work was 3,734 kg of combustible waste (103 drums), 4,393 kg of flame resistance waste (61 drums), 37,790 kg of non-combustible waste (124 drums, 19 containers). This report describes about the dismantling and removing the interior equipment in the Mockup room, the amount of waste generated by this work, and procedure for cancellation the controlled area in the facility.
Tajima, Hiroyuki*; Oue, Daigo*; Matsuo, Mamoru; Kato, Takeo*
PNAS NEXUS (Internet), 2(3), p.pgad045_1 - pgad045_6, 2023/03
Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu; Hayashi, Naoki; Saha, P. K.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Tani, Norio; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(9), p.1174 - 1205, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:73.20(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, the purpose of the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) is to accelerate a 1 MW, high-intensity proton beam. To achieve beam operation at a repetition rate of 25 Hz at high intensities, the RCS was elaborately designed. After starting the RCS operation, we carefully verified the validity of its design and made certain improvements to establish a reliable operation at higher power as possible. Consequently, we demonstrated beam operation at a high power, namely, 1 MW. We then summarized the design, actual performance, and improvements of the RCS to achieve a 1 MW beam.
 Co radiation source under an intense
Co radiation source under an intense  Cs radiation field using an application-specific CeBr
Cs radiation field using an application-specific CeBr spectrometer suited for use in intense radiation fields
spectrometer suited for use in intense radiation fieldsKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(8), p.983 - 992, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:28.39(Nuclear Science & Technology)Kobayashi, Daisuke; Yamamoto, Masahiko; Nishida, Naoki; Miyoshi, Ryuta; Nemoto, Ryo*; Hayashi, Hiroyuki*; Kato, Keisuke; Nishino, Saki; Kuno, Takehiko; Kitao, Takahiko; et al.
Nihon Hozen Gakkai Dai-18-Kai Gakujutsu Koenkai Yoshishu, p.237 - 240, 2022/07
All gloves attached to glove-box in Tokai Reprocessing Plant have a fixed expiration date and have to be replaced every 4-year. However, degrees of glove deterioration are different depending on its usage environment (frequency, chemicals, radiation, etc.), because of rubber products. Therefore, physical properties such as tensile strength, elongation, hardness of gloves are measured, and the life-time of gloves are estimated. As a result, gloves without any defects in its appearance have enough physical property for acceptance criteria of new glove. The extrapolated physical property of glove is sufficiently larger than the reported values of damaged glove. No deterioration in physical properties of gloves, that are periodically replaced without any defects in its appearance, is observed and the usable life-time of the glove is estimated to be 8 years.
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Morishita, Masaki*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ando, Masanori; Ashida, Takashi; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Doda, Norihiro; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Ezure, Toshiki; Fukano, Yoshitaka; et al.
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.3, 631 Pages, 2022/07
This book is a collection of the past experience of design, construction, and operation of two reactors, the latest knowledge and technology for SFR designs, and the future prospects of SFR development in Japan. It is intended to provide the perspective and the relevant knowledge to enable readers to become more familiar with SFR technology.
Kusano, Kanya*; Ichimoto, Kiyoshi*; Ishii, Mamoru*; Miyoshi, Yoshizumi*; Yoden, Shigeo*; Akiyoshi, Hideharu*; Asai, Ayumi*; Ebihara, Yusuke*; Fujiwara, Hitoshi*; Goto, Tadanori*; et al.
Earth, Planets and Space (Internet), 73(1), p.159_1 - 159_29, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:38.33(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)The PSTEP is a nationwide research collaboration in Japan and was conducted from April 2015 to March 2020, supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan. It has made a significant progress in space weather research and operational forecasts, publishing over 500 refereed journal papers and organizing four international symposiums, various workshops and seminars, and summer school for graduate students at Rikubetsu in 2017. This paper is a summary report of the PSTEP and describes the major research achievements it produced.
Asakura, Kazuki; Shimomura, Yusuke; Donomae, Yasushi; Abe, Kazuyuki; Kitamura, Ryoichi; Miyakoshi, Hiroyuki; Takamatsu, Misao; Sakamoto, Naoki; Isozaki, Ryosuke; Onishi, Takashi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2021-020, 42 Pages, 2021/10
The disposal of radioactive waste from the research facility need to calculate from the radioactivity concentration that based on variously nuclear fuels and materials. In Japan Atomic Energy Agency Oarai Research and Development Institute, the study on considering disposal is being advanced among the facilities which generate radioactive waste as well as the facilities which process radioactive waste. This report summarizes a study result in FY2020 about the evaluation method to determine the radioactivity concentration in radioactive waste on Oarai Research and Development Institute.
 -ray spectrometer and its performance under intense
-ray spectrometer and its performance under intense  Cs and
Cs and  Co radiation fields
Co radiation fieldsKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Kamada, Kei*; Kim, K. J.*; Yoshino, Masao*; Shoji, Yasuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1010, p.165544_1 - 165544_9, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)The number of nuclear facilities being decommissioned has been increasing worldwide, in particular following the accident of the Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings' Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station in 2011. In these nuclear facilities, proper management of radioactive materials is required. Then, A  -ray spectrometer with four segmentations using small volume CeBr
-ray spectrometer with four segmentations using small volume CeBr scintillators with a dimension of
scintillators with a dimension of 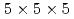
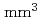 was developed. The four scintillators were coupled to a multi-anode photomultiplier tube specific to intense radiation fields. We performed the
was developed. The four scintillators were coupled to a multi-anode photomultiplier tube specific to intense radiation fields. We performed the  -ray exposure study under
-ray exposure study under  Cs and
Cs and  Co radiation fields. Under the
Co radiation fields. Under the  Cs radiation field, the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was 9.2
Cs radiation field, the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was the relative energy resolution at 1375 mSv/h was 9.2 0.05%, 8.0
0.05%, 8.0 0.08%, 8.0
0.08%, 8.0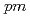 0.03%, and 9.0
0.03%, and 9.0 0.04% for the four channels, respectively.
0.04% for the four channels, respectively.
 scintillator under intense
scintillator under intense  -ray fields for nuclear decommissioning
-ray fields for nuclear decommissioningKaburagi, Masaaki; Shimazoe, Kenji*; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Kamada, Kei*; Kim, K. J.*; Yoshino, Masao*; Shoji, Yasuhiro*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 988, p.164900_1 - 164900_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:84.25(Instruments & Instrumentation)An increasing number of nuclear facilities have been decommissioned worldwide following the 2011 accident of the TEPCO' Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. During the decommissioning, radioactive materials have to be retrieved under proper management. In this study, a small cubic CeBr spectrometer with dimensions of 5 mm
spectrometer with dimensions of 5 mm  5 mm
5 mm  5 mm was manufactured to perform
5 mm was manufactured to perform  -ray spectroscopy under intense
-ray spectroscopy under intense  -ray fields. Furthermore, thanks to a fast digital process unit and a customized photomultiplier, the device could perform
-ray fields. Furthermore, thanks to a fast digital process unit and a customized photomultiplier, the device could perform  -ray spectroscopy at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h. The energy resolution (FWHM) at 662 keV ranged from 4.4% at 22 mSv/h to 5.2% at 1407 mSv/h for a
-ray spectroscopy at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h. The energy resolution (FWHM) at 662 keV ranged from 4.4% at 22 mSv/h to 5.2% at 1407 mSv/h for a  Cs radiation field. Correspondingly, at 1333 keV, it ranged from 3.1% at 26 mSv/h to 4.2% at 2221 mSv/h for a
Cs radiation field. Correspondingly, at 1333 keV, it ranged from 3.1% at 26 mSv/h to 4.2% at 2221 mSv/h for a  Co radiation field, which suggested to realize
Co radiation field, which suggested to realize  -ray assessment of
-ray assessment of  Cs,
Cs,  Cs,
Cs,  Co, and
Co, and  Eu at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h.
Eu at dose rates of over 1 Sv/h.
Yamamoto, Tomohiko; Kato, Atsushi; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Hara, Hiroyuki*
Nuclear Technology, 206(12), p.1875 - 1890, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)This paper gives a detailed evaluation of the countermeasures for the external hazards and severe accidents that could impact the 2010 JSFR design building by lessons learned from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (Fukushima I NPP) accident.
Akagi, Yosuke*; Kato, Hiroyasu*; Tachi, Yukio; Sakamoto, Hiroyuki*
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 5, p.233 - 236, 2018/11
A large amount of radioactive contaminated concrete will be generated from the decommissioning in the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant (NPP). For developing the plans of decommissioning and waste management including decontamination and disposal, it is important to estimate radionuclides inventory and concentration distribution in the concrete materials. In this study, effective diffusivities (De) and distribution coefficients (Kd) of HTO, Cs, I and U in OPC mortar were measured by through-diffusion and batch sorption experiments. De values derived were in the sequence of HTO, I, Cs, U, implying that cation exclusion effects may be important mechanisms in OPC mortar. Kd values derived by batch tests were higher by more than one order of magnitude than the diffusion-derived Kd values, indicating that crushing of samples had a strong influence on sorption. Diffusion and sorption mechanisms in OPC mortar were evaluated to predict the penetration behavior of these radionuclides.
Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Harada, Hiroyuki; Kato, Shinichi; Kinsho, Michikazu; Okabe, Kota
Proceedings of 6th International Beam Instrumentation Conference (IBIC 2017) (Internet), p.461 - 465, 2018/03
In the J-PARC RCS, a large fraction of our effort has been concentrated on reducing and managing beam losses to achieve 1MW high power proton beam operation. Standard beam loss monitor (BLM), which is installed outside of the magnet in every cell of beam optics and detect the beam loss at wide area in each cell, is insufficient to investigate finer beam loss mechanism in the ring. Thus we developed new scintillation type BLM to detect the beam loss at spot area on the vacuum chamber inside the magnet. The new BLM has separating structure a photomultiplier (PMT) from a plastic scintillator and connecting with optical fibres. Because small plastic scintillator is installed on the vacuum chamber directly, it has capability to have high sensitivity for localized spot area beam loss. On the other hand, the PMT can precisely be operated without being affected by magnetic field by keeping the PMT from the magnet. The new BLM leads the RCS to achieve the stable high power beam operation. In this presentation, we report the detail of the performance of the new BLM.
Harada, Hiroyuki; Yamane, Isao*; Saha, P. K.; Suganuma, Kazuaki; Kinsho, Michikazu; Irie, Yoshiro*; Kato, Shinichi
Proceedings of 14th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.684 - 688, 2017/12
The high-intensity proton accelerator adopts a charge exchange injection scheme, which injects with exchanging from negative Hydrogen ion to proton by using carbon foil. This scheme can realize high intensity proton beam but the uncontrolled beam losses are caused by scattering between beams and the foil. Additionally, the collision may occur the foil beak. Therefore, a new injection scheme for higher intensity is needed as an alternative to the foil. In the J-PARC 3GeV RCS, we newly propose and develop a laser stripping injection scheme. However, it is necessary that laser power is two order higher than latest laser one. To realize this big issue, we develop the laser storage ring, which can provide laser pulse of high repetition rate by recycling one. In this presentation, we will introduce the laser stripping injection scheme and describe the concept of the laser storage ring with high repetition rate and report the current status.
 stripping to protons by using only lasers in the 3-GeV RCS of J-PARC
stripping to protons by using only lasers in the 3-GeV RCS of J-PARCSaha, P. K.; Harada, Hiroyuki; Yamane, Isao*; Kinsho, Michikazu; Miura, Akihiko; Okabe, Kota; Liu, Y.*; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Kato, Shinichi; Irie, Yoshiro*
Proceedings of 14th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.866 - 870, 2017/12
Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Kato, Shinichi; Okabe, Kota; Harada, Hiroyuki; Kinsho, Michikazu
Proceedings of 14th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.877 - 881, 2017/12
It is key issue to reduce the level of the radio-activation of the devices in high power proton accelerator, to achieve MW class high power beam operation. The 3 GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) adopted a beam collimation system which aims to localize the beam loss at the collimators and to reduce the level of residual doses at the other devices. However, relatively high residual doses are detected in not only the beam collimator area but also a vicinity of the stripper foil. The results of previous work, measurements of the detailed residual dose distribution and simulations of the radio-activation by the PHITS, indicate that the high level residual dose around the stripper foil is caused by secondary particles due to nuclear reaction at the foil. In order to suppress the secondary particles from foil, we try hard to reduce the number of foil hitting particles during the beam injection period. As a result, the level of the radio-activation around the foil can be decreased. At the same time, new beam loss monitor to detect the secondary particles from the foil is developed. In this presentation, we report the secondary particles detections and estimations of number of the foil hitting particles. In addition, we discuss the reduction of the radio-activation.
Hotchi, Hideaki; Harada, Hiroyuki; Kato, Shinichi; Okabe, Kota; Saha, P. K.; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; Tamura, Fumihiko; Tani, Norio; Watanabe, Yasuhiro; Yoshimoto, Masahiro
Proceedings of 14th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.95 - 99, 2017/12
no abstracts in English
Hotchi, Hideaki; Harada, Hiroyuki; Hayashi, Naoki; Kato, Shinichi; Kinsho, Michikazu; Okabe, Kota; Saha, P. K.; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; Tamura, Fumihiko; Tani, Norio; et al.
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 20(6), p.060402_1 - 060402_25, 2017/06
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:88.67(Physics, Nuclear)The 3-GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) is the world's highest class of high-power pulsed proton driver, aiming for an output beam power of 1 MW. The most important issues in realizing such a high-power beam operation are to control and minimize beam loss for maintaining machine activations within permissible levels. In RCS, numerical simulation was successfully utilized along with experimental approaches to isolate the mechanism of beam loss and find its solution. By iteratively performing actual beam experiments and numerical simulations, and also by several hardware improvements, we have recently established a 1-MW beam operation with very low fractional beam loss of a couple of 10 . In this paper, our recent efforts toward realizing such a low-loss high-intensity beam acceleration are presented.
. In this paper, our recent efforts toward realizing such a low-loss high-intensity beam acceleration are presented.