Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Luu, V. N.; 谷口 良徳; 宇田川 豊; 勝山 仁哉
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 442, p.114222_1 - 114222_15, 2025/10
被引用回数:0For near-term application, coated-Zr alloy claddings show potential for enhancing safety by providing better oxidation resistance and minimizing hydrogen absorption under design-basis accidents (DBA). This benefit could extend the burnup and operational cycles of fuel rods. In assessing safety, reactivity-initiated accidents (RIA) are considered as one of the DBA conditions. The current safety criteria for high-temperature oxidation failure, one of the failure modes linked to RIA, are defined by peak fuel enthalpy values that range from 205 to 270 cal/g. This wide variability presents challenges when attempting to generalize criteria for modified-Zr alloy claddings with superior oxidation resistance. Therefore, it may be more relevant to apply failure criteria based on embrittlement mechanisms, such as oxygen concentration in the  -Zr phase. This study aimed to assess the failure based on both peak fuel enthalpy and cladding embrittlement by analyzing previous NSRR experiments conducted with conventional materials using the RANNS fuel performance code. The findings suggest that the failure criteria associated with cladding embrittlement can provide a rational evaluation of failure behavior compared to the existing criterion based on peak fuel enthalpy. The local failure criterion leading to the formation of through-wall cracks during quenching is consistent with Chung's proposal (NUREG/CR-1344):
-Zr phase. This study aimed to assess the failure based on both peak fuel enthalpy and cladding embrittlement by analyzing previous NSRR experiments conducted with conventional materials using the RANNS fuel performance code. The findings suggest that the failure criteria associated with cladding embrittlement can provide a rational evaluation of failure behavior compared to the existing criterion based on peak fuel enthalpy. The local failure criterion leading to the formation of through-wall cracks during quenching is consistent with Chung's proposal (NUREG/CR-1344):  -Zr thickness of
-Zr thickness of  0.9 wt% oxygen is less than 0.1 mm, and this corresponds to approximately 35% BJ-ECR.
0.9 wt% oxygen is less than 0.1 mm, and this corresponds to approximately 35% BJ-ECR.
Li, S.; 山口 義仁; 勝山 仁哉; Li, Y.
Proceedings of ASME 2024 Pressure Vessels & Piping Conference (PVP 2024) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2024/07
Flaws due to stress corrosion cracking (SCC) were recently detected in welded joints of austenitic stainless steel piping lines in pressurized water reactors. Welding-induced high hardness and tensile residual stress are known as one of the main factors affecting SCC. In this work, thermal-elastic-plastic coupled three-dimensional finite element analyses were performed to investigate the distributions of welding residual stress and hardness in butt-welded joints of Type 316 stainless steel. Different heat inputs were applied to the pipe welds, including normal heat input, high heat input and very high heat input. Two different constraint conditions were considered for the welded joints, i.e., both ends free or clamped, the latter indicating that the welded joint is constrained by the surrounding piping system. Simulation results were compared with experimental data such as welding thermal cycle, axial shrinkage and residual stress for validation. The effects of heat input and constraint condition on the welding residual stress and hardness at different sections of the welded joints including the weld start/end location were discussed in detail.
下平 昌樹; 山口 義仁; 岩田 景子; 勝山 仁哉; 知見 康弘
Proceedings of ASME 2024 Pressure Vessels & Piping Conference (PVP 2024) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2024/07
日本電気協会規格(JEAC)4206では、加圧熱衝撃事象時の原子炉圧力容器(RPV)の非延性破壊を防止するため、材料の破壊靭性が亀裂先端に生じる応力拡大係数を上回ることが要求されている。破壊靭性は、通常板幅に対して深い亀裂を有するコンパクトテンション(C(T))試験片を用いて評価されるのに対して、応力拡大係数はRPVの板厚に対して浅いステンレスオーバーレイクラッド(クラッド)下亀裂を想定して算出される。さらに、破壊靭性試験は単軸荷重によって行われるのに対して、RPVの想定亀裂には熱応力及び内圧による二軸の荷重が負荷される。このような亀裂深さやクラッドの有無、荷重負荷条件の違いは、亀裂先端の塑性拘束状態を変化させ、破壊靭性値評価に影響を及ぼす可能性がある。本研究では、現行のRPVの構造健全性評価手法の保守性を定量的に評価するため、クラッド下亀裂を有する大型試験体を用いた多軸破壊試験を計画している。本報告では、多軸破壊試験の実施に向けた試験体形状や荷重負荷方法の検討内容及び当該試験の参照データとなる予備試験結果について報告する。予備試験では、亀裂の深さや形状を変えた試験体を用いた破壊試験を行い、浅い亀裂を有する試験体ではC(T)試験片に比べて破壊靭性値が高めに評価されることを示した。さらに、亀裂先端の拘束状態に依存せずに破壊靭性値を予測可能なローカルアプローチを用いて多軸試験体で得られる破壊靭性値の予測を行った。その結果、多軸試験体で得られる破壊靭性値は、JEAC4206に基づいて設定される破壊靭性遷移曲線に対して、十分な裕度を有することを示した。
河 侑成; 下平 昌樹; 勝山 仁哉
Transactions of the 27th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT 27) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2024/03
国内の原子炉圧力容器(RPV)の溶接継手熱影響部(継手HAZ)は監視試験対象部位である。継手HAZ内には非均質に金属組織が分布し、破壊靭性のばらつきが大きいと考えられるものの、HAZ試験片の採取位置における金属組織の違いが機械的特性及び照射脆化感受性に及ぼす影響は詳細に調べられていなかった。本研究では継手HAZの非均質な組織に着目し、まず未照射材について溶接金属と母材の境界からの距離に応じて3箇所(0.5mm, 1mm及び2mm)の継手HAZ、及び母材から採取した微小試験片(Mini-C(T)試験片)を用いて破壊靭性を評価した。その結果、HAZの破壊靭性は母材と比べてばらつきが大きく、特に溶接金属と母材の境界から0.5mmのHAZにおいて破壊靭性のばらつきが最も大きい傾向を示した。HAZに対する破壊靭性参照温度は採取した3箇所の中で有意な差が得られたものの、いずれの破壊靭性参照温度も母材より低く、破壊靭性値が高いことを確認した。本研究結果により、未照射状態では母材が継手HAZを代表して破壊靭性を保守的に評価できることを確認した。
山口 義仁; 高見澤 悠; 勝山 仁哉; Li, Y.
Proceedings of ASME 2023 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2023) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/07
原子炉圧力容器のノズル部の健全性評価において、ノズルコーナー亀裂に対する応力拡大係数が重要なパラメータである。これまで、ノズルコーナーの表面亀裂に対する様々な応力拡大係数解が提案されてきたが、その多くは亀裂の最深点にのみ着目しており、ノズルコーナーの形状寸法に関する情報は明らかになっていない。ノズルコーナー亀裂を対象とした既往の疲労試験結果によると、亀裂表面点における進展量は、最深点よりも大きいことが明らかとなっている。このことから、亀裂表面点の応力拡大係数は最深点よりも高い可能性がある。これらより、本研究では、健全性評価の信頼性を高めるため、有限要素解析を通じて、ノズルコーナーの形状寸法とき裂サイズに対応した、表面点と最深点の両方の応力拡大係数解を提案する。
下平 昌樹; 河 侑成; 高見澤 悠; 勝山 仁哉; 鬼沢 邦雄
Proceedings of ASME 2023 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2023) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2023/07
最新の原子炉圧力容器の構造健全性評価においては、マスターカーブ法に基づく正確な破壊靭性参照温度T の取得が必要である。破壊靭性参照温度T
の取得が必要である。破壊靭性参照温度T はMini-C(T)破壊靭性試験片によって取得可能であり、この試験片の寸法や初期亀裂形状に関しては、ASTM規格のE1921や日本電気協会電気技術規程JEAC4216に規定されている。最近、ASTM E1921では評価の正確性や試験を行う上での利便性を向上させるために、何度か予亀裂形状に関する規定の変更が行われてきた。このような規格の改定に伴うMini-C(T)試験片の許容予亀裂形状の変化は、予亀裂先端の塑性拘束状態を変化させ、T
はMini-C(T)破壊靭性試験片によって取得可能であり、この試験片の寸法や初期亀裂形状に関しては、ASTM規格のE1921や日本電気協会電気技術規程JEAC4216に規定されている。最近、ASTM E1921では評価の正確性や試験を行う上での利便性を向上させるために、何度か予亀裂形状に関する規定の変更が行われてきた。このような規格の改定に伴うMini-C(T)試験片の許容予亀裂形状の変化は、予亀裂先端の塑性拘束状態を変化させ、T 評価に影響を及ぼす可能性がある。本研究では、ASTM E1921やJEAC4216に規定される予亀裂形状に関する要求の妥当性について議論するため、Mini-C(T)試験片の予亀裂湾曲が破壊靭性評価に及ぼす影響について、ワイブル応力解析を含む有限要素解析によって定量的に評価した。その結果、ASTM E1921-21で定められた最大湾曲を有する亀裂形状の場合、亀裂先端の塑性拘束が弱められ、理想的な直線状亀裂を有するMini-C(T)試験片で得られる破壊靭性値に比べて高めの破壊靭性値が得られる可能性を示した。また、上述の最大湾曲を許容した場合、非保守的なT
評価に影響を及ぼす可能性がある。本研究では、ASTM E1921やJEAC4216に規定される予亀裂形状に関する要求の妥当性について議論するため、Mini-C(T)試験片の予亀裂湾曲が破壊靭性評価に及ぼす影響について、ワイブル応力解析を含む有限要素解析によって定量的に評価した。その結果、ASTM E1921-21で定められた最大湾曲を有する亀裂形状の場合、亀裂先端の塑性拘束が弱められ、理想的な直線状亀裂を有するMini-C(T)試験片で得られる破壊靭性値に比べて高めの破壊靭性値が得られる可能性を示した。また、上述の最大湾曲を許容した場合、非保守的なT が取得されることをワイブル応力解析によって示した。一方、JEAC4216で許容される最大湾曲を有する亀裂形状の場合は、理想的な直線状亀裂の場合と比べてT
が取得されることをワイブル応力解析によって示した。一方、JEAC4216で許容される最大湾曲を有する亀裂形状の場合は、理想的な直線状亀裂の場合と比べてT の有意な差は見られなかった。
の有意な差は見られなかった。
Li, S.; 山口 義仁; 勝山 仁哉; Li, Y.; Deng, D.*
Proceedings of ASME 2023 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2023) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2023/07
In this work, a framework was proposed on the comprehensive assessment of hardness and welding residual stress in Type 316 austenitic stainless steel welded joints. Firstly, an 8-pass butt-welded joint made of Type 316 stainless steel was fabricated. Finite element analysis of the welded joint was performed to investigate hardness and welding residual stress distributions. The grain growth model was developed for the hardness prediction. The Chaboche combined isotropic-kinematic strain hardening model and time-temperature dependent annealing model were adopted. The relationships between the Vickers hardness and the uniaxial plastic strain as well as grain size were collected from published literatures. The simulation results of the grain size and accumulated equivalent plastic strain were used for the hardness prediction of the welded joint. The predicted hardness was compared with the experimental data of hardness mapping. The distribution of welding residual stress on the outer surface of the welded pipe was measured by using the X-ray diffraction method and strain gauge method, respectively. The predicted welding residual stresses were compared with the measurements. The results obtained showed that the developed numerical approach can predict the hardness and welding residual stress of Type 316 stainless steel welded joints with satisfactory accuracy. The effects of structural constraint and heat input on the hardness and welding residual stress will be investigated as further works, as described in the proposed framework.
河 侑成; 飛田 徹; 高見澤 悠; 勝山 仁哉
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 145(2), p.021501_1 - 021501_9, 2023/04
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:13.27(Engineering, Mechanical)The fracture toughness in the heat-affected zone (HAZ), which is located under the weld overlay cladding on the inner surface of the reactor pressure vessel (RPV), was evaluated by considering the inhomogeneous microstructures of the HAZ. In this regard, 0.4T-C(T) specimens and Mini-C(T) specimens were manufactured to clarify the effect of the HAZ on fracture toughness. First, the fracture toughness was evaluated using 0.4T-C(T) specimens targeted on microstructural distribution due to the cladding bead location. The reference temperature (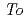 ) of HAZ at middle region of cladding bead was 12
) of HAZ at middle region of cladding bead was 12 C higher than that at overlap cladding beads. Second, the fracture toughness was evaluated using Mini-C(T) specimens focused on the microstructural difference with distance from the boundary between the cladding and the base metal. The
C higher than that at overlap cladding beads. Second, the fracture toughness was evaluated using Mini-C(T) specimens focused on the microstructural difference with distance from the boundary between the cladding and the base metal. The 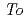 value of the central position located at 3 mm to 7 mm from the boundary between the cladding and the base metal was higher than those of the other positions in HAZ. However, the
value of the central position located at 3 mm to 7 mm from the boundary between the cladding and the base metal was higher than those of the other positions in HAZ. However, the 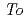 values of HAZ for both 0.4T-C(T) and Mini-C(T) specimens were significantly lower than that of the base metal at a quarter thickness by 40
values of HAZ for both 0.4T-C(T) and Mini-C(T) specimens were significantly lower than that of the base metal at a quarter thickness by 40 C
C 60
60 C. Compared with the literature data that indicated fracture toughness at the inner surface without overlay cladding and the base metal at a quarter thickness, this study concluded that the HAZ under the overlay cladding showed no detrimental effect on the conservatism of the structural integrity assessment of RPV steel.
C. Compared with the literature data that indicated fracture toughness at the inner surface without overlay cladding and the base metal at a quarter thickness, this study concluded that the HAZ under the overlay cladding showed no detrimental effect on the conservatism of the structural integrity assessment of RPV steel.
Lu, K.; 勝山 仁哉; 高見澤 悠; Li, Y.
JAEA-Research 2022-012, 39 Pages, 2023/02
供用年数の増加に伴い、発電用軽水型原子炉圧力容器(RPV)では炉心からの中性子照射により破壊靭性が低下する、いわゆる中性子照射脆化が生じる。国内では、RPVの非延性破壊を防止するため、この中性子照射脆化や、健全性評価上最も厳しい事象の1つである加圧熱衝撃事象(PTS)を考慮して、日本電気協会規程等に基づく決定論的手法により健全性評価が行われている。一方、欧米においては、近年確率論的手法の規制への導入が進んでいる。例えば米国では、PTS評価において、確率論的手法に基づく関連温度に関するスクリーニング基準が規定されており、またそのスクリーニング基準を満足しない場合には確率論的手法に基づく亀裂貫通頻度(TWCF)を指標とした評価の実施が認められている。また、供用期間中検査の試験程度や検査間隔の緩和の検討等にも確率論的手法が適用されている。ここで、確率論的手法とは具体的には確率論的破壊力学(PFM)に基づく健全性評価手法であり、長期供用に伴う機器の経年劣化に関連する様々な因子の不確実さ等を考慮して、合理的に機器の破損確率や破損頻度等を算出できる方法である。こうした背景を踏まえ、国内のRPVに対するPFMに基づく健全性評価の実施を念頭に、国内外の最新知見や専門家の意見等を反映するとともに、主として加圧水型原子炉のRPVを対象に開発が進められたPFM解析コードPASCALの整備、及びPASCALによる感度解析等により得られた知見を取りまとめて、2017年に標準的解析要領を整備し、JAEA-Research2016-022として公開した。この標準的解析要領では、破壊力学に関する知識を有する解析担当者がこれを参照することでPFM解析を実施し、TWCF等の確率論的数値指標を算出できることを目的としている。2017年以降、PFMに基づく健全性評価の更なる実用化に向けて、日本原子力研究開発機構において、沸騰水型原子炉のRPVに対するPFM解析を可能にするため、PASCALの機能を拡充するとともに、標準的解析要領の充実化を図った。本報告はその成果をまとめたものである。本報告は、以下の5つの章で構成される。まず第1章で、本報告の背景及び概要について述べる。次に第2章で、標準的解析要領の枠組みと対象範囲について述べた後、第3章にて標準的解析要領の詳細について記述する。PASCALに対する信頼性確認事例についても同章で記す。第4章では、標準的解析要領を満足し、国内の現状の代表的事例として適切と考えられる手法
高見澤 悠; Lu, K.; 勝山 仁哉; 眞崎 浩一*; 宮本 裕平*; Li, Y.
JAEA-Data/Code 2022-006, 221 Pages, 2023/02
原子炉圧力容器(RPV: Reactor Pressure Vessel)は原子炉冷却材圧力バウンダリを構成する重要機器の1つであり、中性子照射等に伴う高経年化を考慮した構造健全性確保が極めて重要である。国立研究開発法人日本原子力研究開発機構(JAEA: Japan Atomic Energy Agency)では、RPVの構造健全性評価に関する研究の一環として、確率論的破壊力学(PFM: Probabilistic Fracture Mechanics)解析コードPASCAL(PFM Analysis of Structural Components in Aging LWR)の開発を進めている。本コードは、加圧水型軽水炉(PWR: Pressurized Water Reactor)及び沸騰水型軽水炉(BWR: Boiling Water Reactor)を対象に、影響因子が持つ不確実さを考慮し、加圧熱衝撃(PTS: Pressurized Thermal Shock)事象や低温過圧事象(LTOP: Low-Temperature Over Pressure)等の過渡によるRPVの炉心領域部の破損確率や破損頻度を求めるものである。破壊力学や確率論的計算手法等に関する最新知見や国内RPVに適した評価手法・評価モデルを踏まえ、新規解析機能の導入を進めるとともに、系統的なコード検証活動を通じて信頼性向上を図ってきた。平成12年度に公開したPASCALでは、PWRのPTS事象を対象に、RPVの破損確率を解析する基本的な枠組みを整備した。平成18年度に公開したPASCAL2では、内部亀裂の評価手法や様々な非破壊検査による亀裂の検出性に関する評価モデル等を導入し、過渡事象データベースを整備した。平成22年度に公開したPASCAL3では、肉盛溶接クラッド部に着目して、亀裂の評価機能等を改良した。平成29年度に公開したPASCAL4では、応力拡大係数解や破壊靭性の不確実さを考慮した評価モデル等の改良により解析機能の高度化を図るとともに、影響因子の不確実さを認識論的不確実さと偶然的不確実さに分類し、不確実さを考慮した信頼度評価機能等を整備した。平成30年度以降は、これまでPWRのPTS事象を対象としたRPV内面側亀裂の評価機能に加えて、BWRの起動事象、LTOP事象等を想定したRPV外面側亀裂の評価機能等の整備を進めてきた。これらの機能整備を踏まえ、国内PWR及びBWRのRPVを対象とした確率論的健全性評価に資する解析コードとして、PASCAL5へとバージョンアップした。PASCAL5はPFM解析モジュールであるPASCAL-RV、PASCAL-RVの入力データの生成やRPV炉心領域部を対象とした破損頻度の算出を行うモジュールであるPASCAL-Manager、付録として附属する簡易的な熱応力解析を
真野 晃宏; 今井 隆太*; 宮本 裕平*; Lu, K.; 勝山 仁哉; Li, Y.
International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 199, p.104700_1 - 104700_13, 2022/10
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:27.08(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)有限要素法に基づく弾塑性解析は、金属材料の非線形挙動の再現に広く用いられる。この弾塑性解析を陰解法により実施する場合、応力値は通常リターンマッピングアルゴリズムを通じて時間増分ごとに更新される。一方、延性破壊等の複雑な挙動の解析では、リターンマッピングアルゴリズムに係る連立方程式の数が多くなり、収束解を得ることが困難となる場合がある。そのため、本論文では、連立方程式の数の削減を通じて陰解法による安定的な非線形解析を実現することを目的として、陰関数定理に基づき連立方程式の数を削減する一般的な手法を提案した。また、提案手法を、延性破壊解析に用いられるGurson-Tvergaard-Needleman(GTN)モデルに適用し、弾塑性解析を実施した。その結果、解析により、延性破壊に係る実験結果が再現できることを確認した。以上を踏まえ、提案手法は、金属材料の延性破壊解析に有用であると結論付けた。
Lu, K.; 高見澤 悠; 勝山 仁哉; Li, Y.
International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 199, p.104706_1 - 104706_13, 2022/10
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:53.83(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)A probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis code PASCAL was developed in Japan for probabilistic integrity assessment of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) in pressurized water reactors (PWRs) considering neutron irradiation embrittlement and pressurized thermal shock (PTS) transients. To strengthen the practical applications of PFM methodology in Japan, PASCAL has been upgraded to a new version, PASCAL5, which enables PFM analyses of RPVs in both PWRs and boiling water reactors (BWRs) subjected to a broad range of transients, including PTS and normal operational transients. In this paper, the recent improvements in PASCAL5 are described such as the incorporated stress intensity factor solutions and corresponding calculation methods for external surface cracks and embedded cracks near the RPV outer surface. In addition, the analysis conditions and evaluation models recommended for PFM analyses of Japanese RPVs in BWRs are investigated. Finally, PFM analysis examples for core region of a Japanese BWR-type model RPV subjected to two transients (i.e., low-temperature over pressure and heat-up transients) are presented using PASCAL5.
Zarazovski, M.*; Pistra, V.*; Lauerova, D.*; Obermeier, F.*; Mora, D.*; Dubyk, Y.*; Bolinder, T.*; Cueto-Felgueroso, C.*; Szavai, S.*; Dudra, J.*; et al.
Proceedings of ASME 2022 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2022) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2022/07
The APAL (Advanced Pressurized Thermal Shock (PTS) Analysis for Long-Term Operation (LTO)) project was launched in October 2020 for four years with funding from the European Union's HORIZON 2020 program. Within APAL, an extensive literature review was performed and experience with defining the state-of-the-art of the Warm Pre-Stress (WPS) effect, which has an impact on the reactor pressure vessel (RPV) brittle fracture margin in both deterministic and probabilistic terms, was collected. To gather the worldwide experience of the WPS approaches and models, a comprehensive questionnaire was developed followed by each APAL partner response. It mainly focused on the following aspects: collection of existing WPS approaches and models implemented in standards and rules for RPV brittle fracture assessment; identification of the WPS issues; collection and analysis of the existing experimental data. This work describes worldwide experience and best practice of the WPS and its application for the RPV integrity assessment. The paper's conclusions are also focused on the recommendations for dealing with WPS issues.
勝山 仁哉; 山口 義仁; 根本 義之; 古田 琢哉; 加治 芳行
Proceedings of ASME 2022 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2022) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2022/07
To assess rupture behavior of the lower head of reactor pressure vessel in boiling-water-type nuclear power plants due to severe accident like Fukushima Daiichi, we have been developing an analysis method based on coupled analysis of three-dimensional multi-physics simulations composed of radiation transport, thermal-hydraulics (TH) and thermal-elastic-plastic-creep analyses. In this simulation, Monte Carlo radiation transport calculation is firstly performed by using PHITS code to compute proton dose distribution considering molten conditions of core materials. Then the deposit energies at each location is imported into TH analysis code ANSYS Fluent with the same geometry and temperature distribution is simulated by thermal-fluid dynamics. Finally, temperature distribution obtained from TH analysis is applied to thermal-elastic-plastic-creep analyses using FINAS-STAR and then damage evaluation is carried out based on several criterions such as Kachanov, Larson-Miller-parameter, melting point. To conduct such analyses, we also have continued to obtain experimental data on creep deformation in high temperature range. In this study, to predict time and location of reactor pressure vessel (RPV) lower head rupture of boiling water reactors (BWRs) considering creep damage mechanisms, we performed creep damage evaluations based on developing analysis method by using detailed three-dimensional model of RPV lower head with control rod guide tubes, stub tubes and welds. From the detailed analysis results, it was concluded that failure regions of BWR lower head are only the control rod guide tubes or stub tubes under simulated conditions.
真野 晃宏; 山口 義仁; 勝山 仁哉; Li, Y.
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 144(1), p.011506_1 - 011506_9, 2022/02
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:17.22(Engineering, Mechanical)これまで、沸騰水型原子炉(BWR)配管系のニッケル合金異材溶接継手において応力腐食割れ(SCC)による亀裂の存在が報告されており、そのような溶接継手に対する構造健全性評価が重要となっている。現在、影響因子の固有の不確実さを確率分布として考慮することで亀裂を有する機器の破損確率を定量的に評価できる確率論的破壊力学(PFM)評価手法が、より合理的な構造健全性評価手法として注目されており、原子力機構では、溶接継手を含む原子炉配管系を対象としたPFM解析コードPASCAL-SPの開発を進めている。本研究では、PASCAL-SPにBWRのニッケル合金異材溶接継手を対象とした解析機能を新たに導入した。また、改良したPASCAL-SPを用いて、異材溶接継手を対象に、漏えいの検知及び供用期間中検査が破損確率に及ぼす影響に関する感度解析を実施した。解析結果より、改良したPASCAL-SPは、異材溶接継手の破損確率を求め、供用期間中検査等の効果を定量的に評価できることから、構造健全性評価に有用であると結論付けた。
下平 昌樹; 飛田 徹; 高見澤 悠; 勝山 仁哉; 塙 悟史
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 144(1), p.011304_1 - 011304_7, 2022/02
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:25.96(Engineering, Mechanical)JEAC4206-2016における原子炉圧力容器の構造健全性評価では、材料の破壊靭性が、想定欠陥であるクラッド下半楕円亀裂の先端における応力拡大係数よりも高いことが求められている。しかしながら、破壊靭性試験片と想定亀裂の亀裂深さやクラッドの有無といった違いにより、塑性拘束状態や破壊靭性評価に影響を及ぼす可能性がある。本研究では、クラッド下亀裂が破壊靭性評価に及ぼす影響を調べるため、3点曲げ破壊靭性試験及び有限要素解析を実施した。その結果、クラッド下亀裂の塑性拘束が表面亀裂のそれに比べて弱いことを解析によって示した。さらに、クラッド下亀裂の弱い塑性拘束の影響により、クラッド下亀裂の破壊靭性が表面亀裂よりも見かけ上高くなることを実験及びローカルアプローチによって明らかにした。
熊谷 知久*; 三浦 靖史*; 三浦 直樹*; Marie, S.*; Almahdi, R.*; 真野 晃宏; Li, Y.; 勝山 仁哉; 和田 義孝*; Hwang, J.-H.*; et al.
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 144(1), p.011509_1 - 011509_18, 2022/02
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:8.34(Engineering, Mechanical)延性材料の破壊挙動を予測するため、いくつかの延性破壊シミュレーション手法が提案されている。ただし、これらの手法には実機器への適用性に関する懸念がある。本研究では、パラメータの決定を含めたシミュレーション手法の予測能力を確認するため、実機器を想定した破壊試験に関する2つの問題を設定し、ベンチマーク解析を実施した。1つ目の問題は、周方向の表面亀裂及び貫通亀裂を有する配管に対する単調曲げ荷重負荷試験、2つ目の問題は、周方向貫通亀裂を有する配管に対する繰り返し曲げ荷重負荷試験である。ベンチマークの参加機関は、独自に選択した手法によって延性亀裂進展挙動を予測した。用いられた手法は、ボイド率基準を有するGurson-Tvergaard-Needleman(GTN)モデルに基づく有限要素法(FEM)、応力三軸度により修正される破壊ひずみ基準また破壊エネルギー基準に基づくFEM、Jまたは J基準に基づく拡張FEM及び弾塑性粒子法等である。単調曲げ荷重負荷試験に関しては、すべての手法によるシミュレーションの結果が配管の変形と亀裂進展の挙動を精度よく再現し、シミュレーション手法の実機器への適用性が確認された。一方、繰り返し曲げ荷重負荷試験におけるこれらの挙動については、ほとんどの手法で再現できなかった。今後材料の繰り返し硬化特性等を考慮したパラメータの決定手法についてさらなる検討が必要であることを確認した。
J基準に基づく拡張FEM及び弾塑性粒子法等である。単調曲げ荷重負荷試験に関しては、すべての手法によるシミュレーションの結果が配管の変形と亀裂進展の挙動を精度よく再現し、シミュレーション手法の実機器への適用性が確認された。一方、繰り返し曲げ荷重負荷試験におけるこれらの挙動については、ほとんどの手法で再現できなかった。今後材料の繰り返し硬化特性等を考慮したパラメータの決定手法についてさらなる検討が必要であることを確認した。
岩田 景子; 高見澤 悠; 河 侑成; 下平 昌樹; 岡本 芳浩; 本田 充紀; 勝山 仁哉; 西山 裕孝
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 511, p.143 - 152, 2022/01
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:31.55(Instruments & Instrumentation)The main causes of the irradiation embrittlement of RPVs are the formation of a solute cluster and the matrix defect. To investigate these embrittlement mechanisms, it is necessary to complementarily apply microstructure analyses. The extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) technique can detect changes in the atomic structure because of a vacancy-type defect or interstitial atoms introduced by irradiation around selected atoms. In this study, to investigate such microstructural changes due to irradiation, we performed an EXAFS examination for high-copper RPV steels subjected to ion irradiation. We investigated microstructures of the crystal structure around specific element such as Cu, Mn, and Ni, which are known to be the atoms included in the solute atom clusters and lattice defects such as vacancy-type defects. The results indicated that the solute atoms clusteris thought to aggregate in the Fe matrix while maintaining the bcc structure and that not only a vacancy-type defect but also a tensile configuration-type dumbbell pair could be located around both Cu and Ni atoms.
Zhang, T.; Lu, K.; 真野 晃宏; 山口 義仁; 勝山 仁哉; Li, Y.
Fatigue & Fracture of Engineering Materials & Structures, 44(12), p.3399 - 3415, 2021/12
被引用回数:20 パーセンタイル:78.33(Engineering, Mechanical)GTNモデルは、延性金属の微細組織の力学挙動を考慮するモデルであるとともに、式が明確な物理的意味を表すことから、延性金属の破壊予測のためのアプローチとして期待されている。一方、強い相関のある8つのモデルパラメータの決定が困難なため、工学的な応用はほとんど進んでいない。本研究では、GTNモデルの物理的背景に基づいて、GTNモデルのパラメータを決定するための一連の手法を提案した。具体的には、連続体損傷力学の考え方を活用し、一軸引張試験における有効ヤング率の変化からボイドの体積分率の増加を実験的に求めることで、ボイドの生成に関する3つのパラメータの値を決定した。その他のGTNモデルのパラメータに関しては、化学組成分析、ボイドが含まれる単位セルモデルを用いた解析及び有限要素逆解析により一意に決定した。また、これらのパラメータ決定手法の妥当性を、炭素鋼STPT410の亀裂付き試験片と亀裂のない試験片の両方の破壊試験の結果と決定したパラメータを用いた数値解析結果との比較を通じて確認した。
山口 義仁; 勝山 仁哉; 眞崎 浩一*; Li, Y.
Proceedings of ASME 2021 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2021) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2021/07
地震を起因とした確率論的リスク評価は、原子力発電所の耐震安全性を評価するための重要な手法の一つである。この評価では、地震ハザード,地震フラジリティ及び事故シーケンス評価から炉心損傷頻度が求められる。地震フラジリティ評価に着目すると、亀裂や減肉が発生している経年配管に対する評価には、確率論的破壊力学を適用した評価手法が有効であると考えられる。本研究では、長期間運転した原子力発電所を対象とした確率論的リスク評価手法の高度化を目的に、経年劣化事象を考慮した原子力発電所の代表的な配管系を対象とした地震フラジリティ評価に関する評価要領を整備した。本論文では、評価要領の概要と、評価要領に基づき確率論的破壊力学解析コードを用いた地震フラジリティ評価事例を紹介する。