Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Oba, Kyoko; Yoshizawa, Atsufumi*; Kitamura, Masaharu*
Kogaku Kyoiku, 69(3), p.3 - 10, 2021/05
The purpose of engineering ethics education is to understand the effects and impacts of technology on society and nature and the responsibilities that engineers have to fulfill for society. There are many cases used in the educational method so that the students can understand the problems surrounding the engineers. However, most of the cases correspond to event scenarios where engineers have failed to maintain safety. Resilience engineering was born from the criticism of safety measures for the purpose of preventing recurrence by seeking human error and organizational culture as the cause of accidents in the field of ergonomics. Its features are that people are considered as beings that realize safety in dangerous systems, and that they focus on good practices. This paper describes the improvement of engineering ethics education by utilizing resilience engineering concept.
Yoshizawa, Atsufumi*; Oba, Kyoko; Kitamura, Masaharu*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 18(2), p.55 - 68, 2019/06
This study aims to improve the potential of an emergency response by analyzing the workload management during the accident at the Emergency Response Center (ERC) of TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. Specifically, the research focused on the response of the ERC during the time between the discontinuation of Unit 3 core water injection and its recovery. It identified the different types of workload at the ERC had and how they had been managed based on the record of a TV conference. It also deduced the casual factors of the responses, supplementing the interview record of the director of ERC at the time by applying workload management analysis. On the basis of these findings, lessons to enhance the potential of the on-site emergency response have been obtained for ERC and outside organizations.
Yoshizawa, Atsufumi*; Oba, Kyoko; Kitamura, Masaharu*
Ningen Kogaku, 54(3), p.124 - 134, 2018/06
Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant caused a severe accident which released a large amount of radioactivity triggered by the Great East Japan Earthquake. The existing investigation reports of the accident prepared by several institutions pay attention only to the process which caused the accident but not much to the accident mitigation or the recovery process. This study focused on Unit 3 of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, including its recovery process from the accident. Based on the public data, the time sequences for the recovery process between the accident occurrence and the state of cold shutdown were classified. Then, the groups of actions were sorted out in terms of ergonomics viewpoint. The important responses in the recovery process were identified and analyzed referring to the m-SHEL model. As a result, new lessons were learned from the accident case regarding the actions required for recovering from the accident.
Yoshizawa, Atsufumi*; Oba, Kyoko; Kitamura, Masaharu*
Ningen Kogaku, 54(1), p.1 - 13, 2018/02
The two approaches as the concepts to ensure safety of the complicated socio-technical systems have been proposed by Hollnagel. They are the safety concepts called "Safety-I" to reduce risks and "Safety-II" to expand successes. The resilience engineering is suggested as the methodology to achieve Safety-II. The study analyzes the recovery of the water injection of Unit 3 based on the resilience engineering, focusing on the fact that preventing further progress of the accident case in Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant which has been evaluated for extracting risk factors. Based on those results, the study has clarified the method of learning to enhance safety which has a different view from existing accident investigation.
Yoshizawa, Atsufumi*; Oba, Kyoko; Kitamura, Masaharu*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu (Internet), 83(856), p.17-00263_1 - 17-00263_17, 2017/12
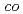 -tetrafluoroethylene) films using different media
-tetrafluoroethylene) films using different mediaNuryanthi, N.*; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Kitamura, Akane; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Yoshimura, Kimio; Sawada, Shinichi; Hasegawa, Shin; Asano, Masaharu; Maekawa, Yasunari; Suzuki, Akihiro*; et al.
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 40(4), p.359 - 362, 2015/12
The ion-track grafting of a vinylbenzyl chloride (VBC) into a poly(ethylene-co-tetrafluoroethylene) (ETFE) film is necessary for preparing nanostructured hydroxide-ion-conductive electrolyte membranes. A key for success here is to obtain as high graft levels as possible (for higher conductivity) in a smaller number of tracks (for improving the other membrane properties). To this end, therefore, the effect of the medium for the VBC grafting was investigated as part of our continuing effort to optimize the experimental conditions. A 25  m-thick ETFE film was irradiated in a vacuum chamber with 560 MeV
m-thick ETFE film was irradiated in a vacuum chamber with 560 MeV  Xe at different fluences, and then the grafting was performed by immersing the irradiated films in a 20vol% VBC monomer at 60
Xe at different fluences, and then the grafting was performed by immersing the irradiated films in a 20vol% VBC monomer at 60 C. A medium was a mixture of water (H
C. A medium was a mixture of water (H O) and isopropyl alcohol (iPrOH) at different volume ratios. The degree of grafting increased as the H
O) and isopropyl alcohol (iPrOH) at different volume ratios. The degree of grafting increased as the H O content became higher, and reached a maximum in pure H
O content became higher, and reached a maximum in pure H O. These results can be explained by considering the well-known Trommsdorff effect, in which poor solubility of the grafted polymer in polar media leads to an increased polymerization rate probably due to a lower termination rate.
O. These results can be explained by considering the well-known Trommsdorff effect, in which poor solubility of the grafted polymer in polar media leads to an increased polymerization rate probably due to a lower termination rate.
Shinohara, Yoshikuni; Kitamura, Masaharu*
JAERI-M 5664, 34 Pages, 1974/04
no abstracts in English
Yamaki, Tetsuya; Nuryanthi, N.*; Kitamura, Akane; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Yoshimura, Kimio; Sawada, Shinichi; Asano, Masaharu; Maekawa, Yasunari; Suzuki, Akihiro*; Terai, Takayuki*
no journal, ,
Heavy ions at kinetic energies typically from several hundreds of MeV to a few GeV passing through a polymer substrate induce a continuous trail of excitations and ionizations called latent tracks. We used a direct ion-track grafting method for preparation of anion exchange membranes for fuel cells. The functional anion exchange groups were introduced inside the latent tracks, thereby achieving OH -conductive channels through the thickness. These straight channels increased conductivities, while the isolated cylindrical structure of tracks restricted the water uptake.
-conductive channels through the thickness. These straight channels increased conductivities, while the isolated cylindrical structure of tracks restricted the water uptake.
Yoshizawa, Atsufumi*; Matsumoto, Atsushi*; Oba, Kyoko; Kitamura, Masaharu*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -ray-induced grafting
-ray-induced graftingNuryanthi, N.*; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Kitamura, Akane; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Yoshimura, Kimio; Sawada, Shinichi; Hasegawa, Shin; Asano, Masaharu; Maekawa, Yasunari; Suzuki, Akihiro*; et al.
no journal, ,
The ion-track grafting of a vinylbenzyl chloride (VBC) into a poly(ethylene-co-tetrafluoroethylene) (ETFE) film is necessary for preparing nanostructured hydroxide-ion conductive electrolyte membranes. A key for success here is to obtain as high graft levels as possible (for higher conductivity) in a smaller number of tracks (for improving the other membrane properties). To this end, therefore, the effect of the medium for the VBC grafting was investigated as part of our continuing effort to optimize the experimental conditions. A 25  m-thick ETFE film was irradiated in a vacuum chamber with 560 MeV
m-thick ETFE film was irradiated in a vacuum chamber with 560 MeV  Xe at different fluences, and then the grafting was performed by immersing the irradiated films in a 20vol% VBC monomer at 60
Xe at different fluences, and then the grafting was performed by immersing the irradiated films in a 20vol% VBC monomer at 60 C. A medium was a mixture of water (H
C. A medium was a mixture of water (H O) and isopropyl alcohol (iPrOH) at different volume ratios. The degree of grafting increased as the H
O) and isopropyl alcohol (iPrOH) at different volume ratios. The degree of grafting increased as the H O content became higher, and reached a maximum in pure H
O content became higher, and reached a maximum in pure H O.
O.
Kitamura, Masaharu*; Oba, Kyoko; Yoshizawa, Atsufumi*
no journal, ,
Yoshizawa, Atsufumi*; Oba, Kyoko; Kitamura, Masaharu*
no journal, ,
Oba, Kyoko; Yoshizawa, Atsufumi*; Kitamura, Masaharu*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Oba, Kyoko; Yoshizawa, Atsufumi*; Kitamura, Masaharu*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kitamura, Masaharu*; Oba, Kyoko; Yoshizawa, Atsufumi*
no journal, ,
A new framework of information provision and public dialogue concerning safety of nuclear facilities has been proposed in this paper. Basic ideas behind the framework are a novel concept of safety named Safety-II and a relevant emerging methodology of safety management called Resilience Engineering. The new ideas emphasize practices that contributed to positive outcomes in addition to failures and errors experienced during accident management. Implication of the new framework concerning the nuclear risk communication has been addressed through reflection of several field experiences.
Yamaki, Tetsuya; Nuryanthi, N.*; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Asano, Masaharu*; Sawada, Shinichi; Kitamura, Akane; Maekawa, Yasunari; Kay-Obbe, V.*; Severin, D.*; Seidl, T.*; et al.
no journal, ,
Practically, polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) has been said to be the only fluoropolymer in which ion tracks can be developed by chemical etching. We thus investigated the possibility of varying the beam parameters and applying the effect of a pre-etching treatment for PVDF ion-track membranes with the goal of achieving enhanced track etching for effective control of the pore size and shape. Our activities also cover all types of fluoropolymers including PVDF. Compared to PVDF, poly(ethylene-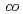 -tetrafluoroethylene) and a series of perfluoropolymers are known to be very stable in highly-concentrated acid or alkaline solutions or at higher temperatures. Although this property might make their ion-track etching very challenging, the ongoing research is expected to allow one to accumulate know-how on methods of chemical etching, which can be generalized for the chemical structures. These will give feedback to a guiding principle for effective ion-track etching in fluoropolymers.
-tetrafluoroethylene) and a series of perfluoropolymers are known to be very stable in highly-concentrated acid or alkaline solutions or at higher temperatures. Although this property might make their ion-track etching very challenging, the ongoing research is expected to allow one to accumulate know-how on methods of chemical etching, which can be generalized for the chemical structures. These will give feedback to a guiding principle for effective ion-track etching in fluoropolymers.
Oba, Kyoko; Yoshizawa, Atsufumi*; Kitamura, Masaharu*
no journal, ,
This study introduces the necessity of stepping up the concept from Safety-I, risk removal type of safety, to the Safety-II, which aims to enhance system flexibility and resilience. In order to achieve Safety-II, the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident was investigated by using Resilience Engineering, which is the methodology going toward Safety-II. Focusing on responding, which is one of the four cornerstones of Resilience Engineering, workers in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants executed flexible ideas to prevent catastrophic damage of the accident. Those responding were created by human with strong attitude in which few investigation reports mentioned. Those approaches show the importance of the Safety-II concept and Resilience Engineering methodology.
Yoshizawa, Atsufumi*; Kunito, Susumu*; Oba, Kyoko; Kitamura, Masaharu*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nuryanthi, N.*; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Kitamura, Akane; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Yoshimura, Kimio; Sawada, Shinichi; Asano, Masaharu*; Maekawa, Yasunari; Suzuki, Akihiro*; Terai, Takayuki*
no journal, ,
We have used the ion-track grafting technique for developing an anion exchange membrane for fuel cell applications. In order to obtain the membrane, a vinyl benzyl chloride (VBC) was grafted into an ion-irradiated poly(ethylene-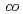 -tetrafluoroethylene) film. This study deals with investigation of the radicals remaining in each track and the VBC grafting with a variety of ion beams from the TIARA cyclotron. The accelerated ions with different masses and energies enabled us to clarify the effect of the LET and radial dose distribution in the track on the VBC grafting. Such extensive research will bring us interesting knowledge relating the track structures to the resulting membrane properties.
-tetrafluoroethylene) film. This study deals with investigation of the radicals remaining in each track and the VBC grafting with a variety of ion beams from the TIARA cyclotron. The accelerated ions with different masses and energies enabled us to clarify the effect of the LET and radial dose distribution in the track on the VBC grafting. Such extensive research will bring us interesting knowledge relating the track structures to the resulting membrane properties.