Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Soma, Yasutaka; Komatsu, Atsushi; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Yamamoto, Masahiro*; Igarashi, Takahiro
Corrosion Science, 251, p.112897_1 - 112897_15, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Experimental and modeling studies of the oxygen ingression at the crevices of stainless steels were conducted in high-temperature water (288 C). The limiting distance of oxygen ingression,
C). The limiting distance of oxygen ingression, 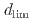 , was defined as the point beyond which the primary surface oxide changed (hematite
, was defined as the point beyond which the primary surface oxide changed (hematite  magnetite), regardless of crevice gap, oxygen concentration, and time. In situ measurements revealed increased electrical conductivity around the
magnetite), regardless of crevice gap, oxygen concentration, and time. In situ measurements revealed increased electrical conductivity around the 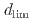 position indicating ion enrichment due to a differential oxygen concentration cell.
position indicating ion enrichment due to a differential oxygen concentration cell. 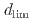 increased with increasing crevice gap, oxygen concentration, and immersion time. Modeling study suggested that oxide layer growth reduced anodic dissolution and slowed oxygen consumption, allowing oxygen ingression with time.
increased with increasing crevice gap, oxygen concentration, and immersion time. Modeling study suggested that oxide layer growth reduced anodic dissolution and slowed oxygen consumption, allowing oxygen ingression with time.
Soma, Yasutaka; Komatsu, Atsushi; Igarashi, Takahiro
Dai-71-Kai Zairyo To Kankyo Toronkai Koenshu (CD-ROM), p.253 - 256, 2024/11
In our previous study, we reported that Cl ions penetrating stainless steel crevices do not dissipate by diffusion, even in high-purity water (i.e., conductivity remains stable), likely due to electrochemical reactions inside and outside the crevice. This study further analyzes ion behavior by experimentally and computationally investigating ion concentration drivers in high-purity water. Results show that, at 50 C, the crevice conductivity of SUS316L stainless steel reached 100
C, the crevice conductivity of SUS316L stainless steel reached 100  S/cm (100-1000 times bulk water). Modeling suggests this is due to metal cations and hydroxide ions from dissolved oxygen reduction. The dissolution rate was estimated at 10nA/cm
S/cm (100-1000 times bulk water). Modeling suggests this is due to metal cations and hydroxide ions from dissolved oxygen reduction. The dissolution rate was estimated at 10nA/cm .
.
Nakashima, Shinsuke*; Moro, A.*; Komatsu, Ren*; Faragasso, A.*; Matsuhira, Nobuto*; Woo, H.*; Kawabata, Kuniaki; Yamashita, Atsushi*; Asama, Hajime*
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research 2024 (FDR2024) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2024/10
 O
O
 /U
/U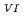 O
O
 redox equilibrium in [emim]Tf
redox equilibrium in [emim]Tf N-based liquid electrolytes towards uranium redox-flow battery
N-based liquid electrolytes towards uranium redox-flow batteryTakao, Koichiro*; Ouchi, Kazuki; Komatsu, Atsushi; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Watanabe, Masayuki
European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 27(14), p.e202300787_1 - e202300787_7, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Electrochemical behavior of U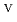 O
O
 /U
/U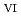 O
O
 in 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethyl)sulfonylamide ([emim]Tf
in 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethyl)sulfonylamide ([emim]Tf N) ionic liquid was studied to clarify what are required to attain its redox reversibility for utilizing depleted U as an electrode active material in a redox flow battery. As a result, reversibility of the U
N) ionic liquid was studied to clarify what are required to attain its redox reversibility for utilizing depleted U as an electrode active material in a redox flow battery. As a result, reversibility of the U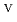 O
O
 /U
/U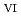 O
O
 redox reaction was successfully achieved in use of a glassy carbon working electrode under presence of Cl
redox reaction was successfully achieved in use of a glassy carbon working electrode under presence of Cl in [emim]Tf
in [emim]Tf N. To improve diffusivity of solutes, [emim]Tf
N. To improve diffusivity of solutes, [emim]Tf N diluted with an auxiliary molecular solvent, N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF). We have succeeded in demonstrating a reversible redox reaction of [U
N diluted with an auxiliary molecular solvent, N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF). We have succeeded in demonstrating a reversible redox reaction of [U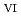 O
O Cl
Cl ]
] + e
+ e = [U
= [U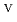 O
O Cl
Cl ]
] in the 50:50 v/v [emim]Tf
in the 50:50 v/v [emim]Tf N-DMF liquid electrolyte containing Cl
N-DMF liquid electrolyte containing Cl .
.
Soma, Yasutaka; Komatsu, Atsushi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
Corrosion, 78(6), p.503 - 515, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:7.22(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The effects of electrochemical potential (ECP) on water chemistry within a crevice are of critical importance for understanding stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of Fe-Cr-Ni alloys in high temperature water. In this study, the effects of ECP on the electrical conductivity of a solution within a Type-316L stainless steel crevice (
 ) have been studied in 288
) have been studied in 288 C and 8 MPa water containing 10 ppb Cl
C and 8 MPa water containing 10 ppb Cl as major anionic species. In situ measurements of
as major anionic species. In situ measurements of 
 in a rectangular crevice with a gap of 15
in a rectangular crevice with a gap of 15  m and a depth of 23 mm have been conducted using small sensors installed at different crevice depths. An increase in ECP from -0.49 V (vs. standard hydrogen electrode) to -0.12 V resulted in an increase in
m and a depth of 23 mm have been conducted using small sensors installed at different crevice depths. An increase in ECP from -0.49 V (vs. standard hydrogen electrode) to -0.12 V resulted in an increase in 
 from 12
from 12  Scm
Scm to 160
to 160  Scm
Scm at a distance of 21 mm from the crevice mouth. The increase in
at a distance of 21 mm from the crevice mouth. The increase in 
 reached a maximum at about 0.15 V (about 300
reached a maximum at about 0.15 V (about 300  Scm
Scm ) and then tended to decrease with increasing potential. Finite element model analysis taking into account the electrochemical reaction quantitatively reproduced this behavior. It is considered that Cl
) and then tended to decrease with increasing potential. Finite element model analysis taking into account the electrochemical reaction quantitatively reproduced this behavior. It is considered that Cl is the major anionic species transported into the crevice at relatively low potentials, and that
is the major anionic species transported into the crevice at relatively low potentials, and that 
 increases monotonically with increasing ECP. On the other hand, when ECP exceeds around 0 V, a sufficient amount of HCrO
increases monotonically with increasing ECP. On the other hand, when ECP exceeds around 0 V, a sufficient amount of HCrO
 generated by transpassive dissolution also transported into the gap. Since this chemical species is highly oxidizing, unlike Cl, it is assumed that it reacts with metal cations to oxidize and precipitate them, thereby lowering conductivity.
generated by transpassive dissolution also transported into the gap. Since this chemical species is highly oxidizing, unlike Cl, it is assumed that it reacts with metal cations to oxidize and precipitate them, thereby lowering conductivity.
Komatsu, Atsushi
JAEA-Research 2021-019, 24 Pages, 2022/05
In order to reduce the corrosion rate of materials in molten lead bismuth eutectic (LBE), it is important to adjust the oxygen concentration, and past reports show that the oxygen concentration is often adjusted to about 10 to 10
to 10 wt%. However, it is not clearly stated what concentration is optimal, and there are some reports of severe corrosion even within this concentration range. In this study, a corrosion model considering diffusion in oxide and LBE was developed for 9Cr-1Mo steel, and the corrosion control method estimated from the corrosion model were investigated. We also tried to calculate the optimum oxygen concentration to prevent the flow blockage at the low temperature of loop environment while reducing the corrosion of 9Cr-1Mo steel in molten LBE. As a result, it was expected that the corrosion mode of 9Cr-1Mo steel in LBE could be classified into three types, dense film formation, precipitation film formation, and film dissolution, depending on the ratio of oxide film thickness to diffusion layer thickness, iron concentration in LBE, and temperature. In order to inhibit corrosion, it is important to adjust the oxygen concentration so that the conditions for dense film formation can be maintained. For this purpose, it was expected that a pre-oxidized film of more than 10
wt%. However, it is not clearly stated what concentration is optimal, and there are some reports of severe corrosion even within this concentration range. In this study, a corrosion model considering diffusion in oxide and LBE was developed for 9Cr-1Mo steel, and the corrosion control method estimated from the corrosion model were investigated. We also tried to calculate the optimum oxygen concentration to prevent the flow blockage at the low temperature of loop environment while reducing the corrosion of 9Cr-1Mo steel in molten LBE. As a result, it was expected that the corrosion mode of 9Cr-1Mo steel in LBE could be classified into three types, dense film formation, precipitation film formation, and film dissolution, depending on the ratio of oxide film thickness to diffusion layer thickness, iron concentration in LBE, and temperature. In order to inhibit corrosion, it is important to adjust the oxygen concentration so that the conditions for dense film formation can be maintained. For this purpose, it was expected that a pre-oxidized film of more than 10 m should be applied before immersion in LBE. The oxygen concentration of about 10
m should be applied before immersion in LBE. The oxygen concentration of about 10 to 10
to 10 wt% is the appropriate oxygen concentration when the oxide film has grown to some extent, and a higher oxygen concentration was expected to be required when the film is thin.
wt% is the appropriate oxygen concentration when the oxide film has grown to some extent, and a higher oxygen concentration was expected to be required when the film is thin.
Igarashi, Takahiro; Otani, Kyohei; Komatsu, Atsushi; Kato, Chiaki; Sakairi, Masatoshi*
Bosei Kanri, 66(4), p.141 - 145, 2022/04
Metal corrosion is a material deterioration phenomenon based on electrochemical reactions on an atomic scale. In this paper, various methods for acquiring physical properties on metal surfaces using first-principles calculations were described. As examples of applying first-principles calculation to metal corrosion, the effect of hydrogen adsorption on the metal surface on the potential change and the effect of cation atoms in the aqueous solution on the corrosion resistance of the metal were reported.
Igarashi, Takahiro; Komatsu, Atsushi; Kato, Chiaki; Sakairi, Masatoshi*
Tetsu To Hagane, 107(12), p.998 - 1003, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.80(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)In order to clarify the effect of environmental factors on the amount of atmospheric corrosion of steel, novel model for predicting the reduction of atmospheric corrosion considering relative humidity and rain falls was developed. We conducted a one-year calculation simulation of atmospheric corrosion in Miyakojima City, Choshi City, and Tsukuba City using the developed model. Corrosion weight loss by the simulation could reproduce the measured value well. Corrosion weight loss at each point was greatly affected by the amount of flying sea salt, relative humidity, and rain falls.
Sato, Tomonori; Komatsu, Atsushi; Nakano, Junichi*; Yamamoto, Masahiro*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 70(12), p.457 - 461, 2021/12
The Primary Containment Vessel (PCV) in Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants (1F) have been exposed to a corrosive environment containing seawater components under irradiation condition. In such conditions, the hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ) is generated by water radiolysis as an oxidant in addition to dissolved oxygen. The H
) is generated by water radiolysis as an oxidant in addition to dissolved oxygen. The H O
O concentration is able to be estimated by radiolysis calculations. The corrosion tests under gamma-ray irradiation was performed. As the results, it was confirmed that the N
concentration is able to be estimated by radiolysis calculations. The corrosion tests under gamma-ray irradiation was performed. As the results, it was confirmed that the N gas purging performed in the PCV is effective in inhibiting the corrosion of carbon steel under irradiation conditions. The weight loss of carbon steel obtained in the corrosion test under gamma-ray irradiations, are evaluated using calculated O
gas purging performed in the PCV is effective in inhibiting the corrosion of carbon steel under irradiation conditions. The weight loss of carbon steel obtained in the corrosion test under gamma-ray irradiations, are evaluated using calculated O and H
and H O
O concentrations obtained by radiolysis calculations. As a results, it is confirmed that the corrosion rate of carbon steel under irradiation is determined by the sum of diffusion limiting currents of O
concentrations obtained by radiolysis calculations. As a results, it is confirmed that the corrosion rate of carbon steel under irradiation is determined by the sum of diffusion limiting currents of O and H
and H O
O as well as that of carbon steel in the O
as well as that of carbon steel in the O and H
and H O
O coexistent conditions under non-irradiation.
coexistent conditions under non-irradiation.
Igarashi, Takahiro; Komatsu, Atsushi; Kato, Chiaki; Sakairi, Masatoshi*
Bosei Kanri, 65(10), p.365 - 370, 2021/10
We have developed a new atmospheric simulation model considering important environmental factors such as airborne sea salt, temperature, relative humidity, and rainfall. The developed model was verified by comparing predicted values by the simulation and measured data for the weight loss by atmospheric corrosion. In addition, atmospheric corrosion simulations under open and sheltered exposure condition were conducted, and it was confirmed that the air corrosion weight loss was strongly suppressed by the surface cleaning effect due to rainfall.
Ouchi, Kazuki; Komatsu, Atsushi; Takao, Koichiro*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Watanabe, Masayuki
Chemistry Letters, 50(6), p.1169 - 1172, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:3.95(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The electrochemical behavior of uranium (IV) tetrachloride in ionic liquid-DMF mixture was studied for first time in order to build a redox flow battery (RFB) using U as an electrode active material. We found a quasi-reversible U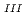 /U
/U couple that could be applied to the anode reaction of the RFB.
couple that could be applied to the anode reaction of the RFB.
Igarashi, Takahiro; Komatsu, Atsushi; Motooka, Takafumi*; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Yamamoto, Masahiro
Corrosion Science and Technology, 20(3), p.105 - 111, 2021/06
We constructed three dimensional computational model using cellular automata method to simulate the intergranular corrosion propagation of stainless steel. In the model, the computational system was constructed by three types of cells: grain (bulk), grain boundary (GB), and solution cell. Our simulations revealed that the surface roughness calculated by the model adopted distributed dissolution rates of GBs was greater than that adopted constant dissolution rates of GBs. The cross-sectional images obtained by our simulation were comparable with that obtained by corrosion tests. These results indicate that the surface roughness during corrosion relates the distribution of corrosion rate.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:60 Percentile:96.18(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
 )
)Komatsu, Kazuki*; Iwasaki, Tsugumi*; Murata, Kosuke*; Yamashiro, Hideaki*; Goh, V. S. T.*; Nakayama, Ryo*; Fujishima, Yohei*; Ono, Takumi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Shimizu, Yoshinaka*; et al.
Reproduction in Domestic Animals, 56(3), p.484 - 497, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:84.51(Agriculture, Dairy & Animal Science)We have established an archive system of livestock and wild animals from the surrounding ex-evacuation zone. Wildlife within the alert zone have been exposed to low-dose-rate (LDR) radiation for a long and continuous time. In this study, we analysed the morphological characteristics of the testes and in vitro fertilization (IVF) capacity of cryopreserved sperm of raccoons from the ex-evacuation zone of the FDNPP accident. This study revealed that the chronic and LDR radiation exposure associated with the FDNPP accident had no adverse effect on the reproductive characteristics and functions of male raccoons.
Sugawara, Takanori; Komatsu, Atsushi
JAEA-Research 2020-016, 44 Pages, 2021/01
It is required to control the oxygen concentration in lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) to prevent the corrosion of structures in LBE-cooled nuclear system. This study estimated the oxygen consumption amount in the LBE-cooled accelerator-driven system (ADS). We used the evaluation formula for the oxide layer thickness, which were derived by various experiments, to estimate the oxygen consumption amount. It was found that the maximum oxide layer thicknesses for the fuel assembly and the beam window were about 35 [ m] and 20 [
m] and 20 [ m], respectively. Based on these results, the oxygen consumption amount for the ADS plant was estimated as 30 [kg] during one cycle (one year). Through this study, it was indicated that an oxygen supply device which could supply 3-4 [g/h] oxygen in the normal operation, 150 [g/h] in the peak and about 30 [kg] during one cycle was necessary.
m], respectively. Based on these results, the oxygen consumption amount for the ADS plant was estimated as 30 [kg] during one cycle (one year). Through this study, it was indicated that an oxygen supply device which could supply 3-4 [g/h] oxygen in the normal operation, 150 [g/h] in the peak and about 30 [kg] during one cycle was necessary.
Goto, Akira; Sasaki, Akimichi*; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Miwa, Atsushi*; Terusawa, Shuji*; Kagohara, Kyoko*; Shimada, Koji
JAEA-Research 2020-013, 88 Pages, 2020/11
Improvement of the investigation techniques to identify active faults is important for the implementation of geological disposal projects from the viewpoint of avoiding locations where permeability increases due to fault displacement. Generally, the existence of active faults is confirmed by aerial photography interpretation of fault displacement topography, which is a topographical trace of fault movement, and on-site geological surveys. However, the investigation method for cases where the topographical traces are unclear is not sufficiently developed. Therefore, to improve existing topographical methods, this study deciphered lineaments up to the rank of poorly defined features, which are almost neglected in general active fault research. The investigation area is one of the geodetic strain concentration zone, called the southern Kyushu shear zone, where the seismogenic faults of the 1997 Kagoshima northwest earthquakes are concealed. We conducted aerial photography interpretation of 62 sheets of 1/25,000 topographic maps, and obtained 1,327 lineaments. Distribution density, direction and length of lineaments were also investigated with topographic and geologic information. As a result, it was clarified that the east-west lineaments in the south Kyushu shear zone predominate in the western part, and the lineaments are densely distributed in the aftershock distribution area of the Kagoshima northwest earthquake. Along with these results, we have compiled a catalog of typical 13 lineaments based on combinations of clarity, direction, length and geomorphic characters of lineaments.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Hanamuro, Takahiro; Shimada, Akiomi; Kokubu, Yoko; Asamori, Koichi; Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji; Watanabe, Takahiro; Saiga, Atsushi; et al.
JAEA-Research 2019-006, 66 Pages, 2019/11
This annual report documents the progress of research and development (R&D) in the 4th fiscal year during the JAEA 3rd Mid- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2015-2021) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the high-level radioactive waste. The planned framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques. In this report, the current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Yamamoto, Masahiro; Irisawa, Eriko; Igarashi, Takahiro; Komatsu, Atsushi; Kato, Chiaki; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
Proceedings of Annual Congress of the European Federation of Corrosion (EUROCORR 2019) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2019/09
Intergranular corrosion phenomena were analysed using modified reprocessing solution. The data indicated that corrosion rates increased with time at the initial stage, and these stayed at constant value. Intergranular corrosion propagated at grain boundary in the initial stage and then attacked whole grain boundary causing drop out of grains. Corrosion rates of steady state were sum of intergranular corrosion amounts and weight losses of dropped grains. Surface appearances and cross sections of corroded samples were analyzed. The results indicated that the initial stage of intergranular corrosion was characterized by the ratio of corrosion rates between grain boundary and matrix. These ratios differed from individual grain boundaries. Total corrosion rates were affected by the distribution of these ratios. These data were based on the numerical modelling of intergranular corrosion using cellular automata. And also, calculated results were compared with these analytical data.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Shimada, Akiomi; Asamori, Koichi; Kokubu, Yoko; Niwa, Masakazu; Watanabe, Takahiro; Saiga, Atsushi; Sueoka, Shigeru; Komatsu, Tetsuya; et al.
JAEA-Research 2018-015, 89 Pages, 2019/03
This annual report documents the progress of research and development (R&D) in the 3rd fiscal year during the JAEA 3rd Mid- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2015-2021) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the high-level radioactive waste. The planned framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques. In this report, the current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Shimada, Akiomi; Asamori, Koichi; Kokubu, Yoko; Niwa, Masakazu; Watanabe, Takahiro; Saiga, Atsushi; Sueoka, Shigeru; Komatsu, Tetsuya; et al.
JAEA-Review 2018-020, 46 Pages, 2019/01
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency, in fiscal year 2018. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2018 are described in detail based on the outline of 7 years plan (fiscal years 2015-2021). Background of this research is clarified with the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress in this report. In addition, the plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.