Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Akiomi; Asamori, Koichi; Sueoka, Shigeru; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Nakajima, Toru; Ogata, Manabu; Uchida, Mao; Nishiyama, Nariaki; Tanaka, Kiriha; et al.
JAEA-Review 2024-035, 29 Pages, 2024/09
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), in fiscal year 2024. The objectives and contents of this research are described in detail based on the JAEA 4th Medium- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2022-2028). In addition, the background of this research is described from the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress. The plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Ogata, Manabu; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Nakanishi, Toshimichi*
Earth, Planets and Space (Internet), 76, p.123_1 - 123_11, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)Marine terraces developed along the southeastern coast of Kii Peninsula, southwestern Japan, face a seismogenic region along the Nankai Trough. We determined the emergence age of one of these marine terraces by using feldspar OSL dating of the marine terrace sediments. The target marine terrace has previously been correlated with MIS 5e on the basis of morphostratigraphy. Samples for pIRIR dating were obtained from foreshore deposits of the marine terrace. pIRIR signals were measured at 150  C (pIRIR
C (pIRIR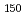 ) and 225
) and 225  C (pIRIR
C (pIRIR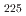 ). These results show that the surface of the marine terrace corresponds to MIS 5e rather than MIS 5c or 7, which is consistent with the chronological framework based on the morphological features of the terraces in this study area.
). These results show that the surface of the marine terrace corresponds to MIS 5e rather than MIS 5c or 7, which is consistent with the chronological framework based on the morphological features of the terraces in this study area.
Nakanishi, Toshimichi*; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Ogata, Manabu; Kawamura, Makoto; Yasue, Kenichi*
Gekkan Chikyu "Kiso deta Kara Kangaeru Dai Yonkigaku No Shintenkai-I" Gogai No.71, p.148 - 155, 2022/02
The formation process of terrace topography was investigated by observing and analyzing boring core samples collected in the middle reaches of the Kumano River. It was assumed that the older terrace topography was distributed higher than the current riverbed surface. However, since tributary debris flow deposits may be thickly distributed beneath the old gyre river valley, care must be taken when using the surface of the ground as an index of uplift and erosion.
Ogata, Manabu; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Nakanishi, Toshimichi
Dai Yonki Kenkyu, 60(2), p.27 - 41, 2021/06
no abstracts in English
Goto, Akira; Sasaki, Akimichi*; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Miwa, Atsushi*; Terusawa, Shuji*; Kagohara, Kyoko*; Shimada, Koji
JAEA-Research 2020-013, 88 Pages, 2020/11
Improvement of the investigation techniques to identify active faults is important for the implementation of geological disposal projects from the viewpoint of avoiding locations where permeability increases due to fault displacement. Generally, the existence of active faults is confirmed by aerial photography interpretation of fault displacement topography, which is a topographical trace of fault movement, and on-site geological surveys. However, the investigation method for cases where the topographical traces are unclear is not sufficiently developed. Therefore, to improve existing topographical methods, this study deciphered lineaments up to the rank of poorly defined features, which are almost neglected in general active fault research. The investigation area is one of the geodetic strain concentration zone, called the southern Kyushu shear zone, where the seismogenic faults of the 1997 Kagoshima northwest earthquakes are concealed. We conducted aerial photography interpretation of 62 sheets of 1/25,000 topographic maps, and obtained 1,327 lineaments. Distribution density, direction and length of lineaments were also investigated with topographic and geologic information. As a result, it was clarified that the east-west lineaments in the south Kyushu shear zone predominate in the western part, and the lineaments are densely distributed in the aftershock distribution area of the Kagoshima northwest earthquake. Along with these results, we have compiled a catalog of typical 13 lineaments based on combinations of clarity, direction, length and geomorphic characters of lineaments.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Kokubu, Yoko; Shimada, Koji; Hanamuro, Takahiro; Shimada, Akiomi; Niwa, Masakazu; Asamori, Koichi; Watanabe, Takahiro; Sueoka, Shigeru; et al.
JAEA-Research 2020-011, 67 Pages, 2020/10
This annual report documents the progress of research and development (R&D) in the 5th fiscal year during the JAEA 3rd Mid- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2015-2021) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the high-level radioactive waste. The planned framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques. The current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Shimada, Koji; Kokubu, Yoko; Niwa, Masakazu; Asamori, Koichi; Watanabe, Takahiro; Sueoka, Shigeru; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; et al.
JAEA-Review 2020-010, 46 Pages, 2020/07
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), in fiscal year 2020. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2020 are described in detail based on the JAEA 3rd Medium- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2015-2021). In addition, the background of this research is described from the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress. The plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Hanamuro, Takahiro; Shimada, Akiomi; Kokubu, Yoko; Asamori, Koichi; Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji; Watanabe, Takahiro; Saiga, Atsushi; et al.
JAEA-Research 2019-006, 66 Pages, 2019/11
This annual report documents the progress of research and development (R&D) in the 4th fiscal year during the JAEA 3rd Mid- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2015-2021) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the high-level radioactive waste. The planned framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques. In this report, the current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Hanamuro, Takahiro; Shimada, Akiomi; Kokubu, Yoko; Asamori, Koichi; Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji; Watanabe, Takahiro; Sueoka, Shigeru; et al.
JAEA-Review 2019-010, 46 Pages, 2019/09
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency, in fiscal year 2019. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2019 are described in detail based on the outline of 7 years plan (fiscal years 2015-2021). Background of this research is clarified with the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress in this report. In addition, the plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Onoe, Hironori; Kosaka, Hiroshi*; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Yasue, Kenichi
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 26(1), p.3 - 14, 2019/06
In this study, it is focused on topographic changes due to uplift and denudation, also climate perturbations, a method which is able to assess the long-term variability of groundwater flow conditions using the coefficient variation based on some steady-state groundwater flow simulation results was developed. Spatial distribution of long residence time area which is not much influenced due to long-term topographic change and recharge rate change during the past one million years was able to estimate through the case study of the Tono area, Central Japan. By applying this evaluation method, it is possible to identify the local area that has low variability of groundwater flow conditions due to topographic changes and climate perturbations from the regional area quantitatively and spatially.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Shimada, Akiomi; Asamori, Koichi; Kokubu, Yoko; Niwa, Masakazu; Watanabe, Takahiro; Saiga, Atsushi; Sueoka, Shigeru; Komatsu, Tetsuya; et al.
JAEA-Research 2018-015, 89 Pages, 2019/03
This annual report documents the progress of research and development (R&D) in the 3rd fiscal year during the JAEA 3rd Mid- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2015-2021) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the high-level radioactive waste. The planned framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques. In this report, the current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Shimizu, Mayuko; Sano, Naomi; Ueki, Tadamasa; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Yasue, Kenichi*; Niwa, Masakazu
Island Arc, 28(2), p.e12295_1 - e12295_13, 2019/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:16.50(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Shimada, Akiomi; Asamori, Koichi; Kokubu, Yoko; Niwa, Masakazu; Watanabe, Takahiro; Saiga, Atsushi; Sueoka, Shigeru; Komatsu, Tetsuya; et al.
JAEA-Review 2018-020, 46 Pages, 2019/01
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency, in fiscal year 2018. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2018 are described in detail based on the outline of 7 years plan (fiscal years 2015-2021). Background of this research is clarified with the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress in this report. In addition, the plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Komatsu, Tetsuya
Jissen Togo Shizen Chirigaku, p.105 - 121, 2018/07
no abstracts in English
Tokuyasu, Kayoko; Yasue, Kenichi; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Tamura, Itoko; Horiuchi, Yasuharu
QST-M-2; QST Takasaki Annual Report 2015, P. 189, 2017/03
Understanding the stage of mountain building is crucial to the stability assessment of geological environments in geological disposal system. In this context, we have carried out the research and development of provenance analysis techniques to elucidate the mountain-building stage. Here we present the results focusing on the R&D using the Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) signals from quartz in sediments and their basement rocks.
Komatsu, Tetsuya
Chigaku Zasshi, 125(5), p.661 - 698, 2016/10
The Pamir is a mountain region of the westernmost part of the Himalayan-Tibetan orogen and extends  300 km from north to south and 300-400 km from west to east. The Pamir lies on a double subduction zone, where two buoyant continental lithospheric plates have subducted several hundred kilometers deep into the asthenosphere. The southern plate is the northward-dipping Hindu Kush slab, and the northern plate is the southward-dipping Pamir slab. This paper reviews recent studies on the Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the Pamir in this unique tectonic setting.
300 km from north to south and 300-400 km from west to east. The Pamir lies on a double subduction zone, where two buoyant continental lithospheric plates have subducted several hundred kilometers deep into the asthenosphere. The southern plate is the northward-dipping Hindu Kush slab, and the northern plate is the southward-dipping Pamir slab. This paper reviews recent studies on the Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the Pamir in this unique tectonic setting.
Katori, Takuma*; Kobayashi, Kenta*; Yasue, Kenichi; Niwa, Masakazu; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Hosoya, Takashi*; Sasao, Eiji
no journal, ,
Understanding fault zone evolution is important for constructing the topographical and geological model for a time scale more than one million year. We analyzed fault rocks of the Byobuyama fault in Tono area by several methods including structural analysis in the field and using optical microscope, determination of mineral composition based on X-ray diffraction analysis, and chemical composition analysis using an X-ray fluorescence instrument. Based on these analyses, studied fault rocks could record several stages of fault activity under different depths and stress regimes.
Tokuyasu, Kayoko; Yasue, Kenichi; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Tamura, Itoko; Horiuchi, Yasuharu
no journal, ,
We have carried out the research and development of provenance analysis techniques to elucidate the mountain-building stage using quartz ESR signals in sediments. The R&D was conducted using the Tokai Formation including Toki Sand and Gravel Formation distributed over the Tono area. In the northern part of the area, bedrocks consist of sedimentary rocks, Nohi Rhyolite and Sanyo Granite, whereas consist of Ryoke Granites in the southern part. Samples of sediments were taken from the quarry located between the Tsukechi River and Atera fault. Basement rock samples were also taken in and around the quarry. Outcrop observation indicates that the provenance of sediments changed between the lower and upper parts. Quartz grains for ESR measurements were extracted from all samples. As a result, granitic rocks of Sanyo belt were not exposed to the drainage basin during the deposition of the lower part between 3.9 and 2.0 Ma, then the granitic rocks were exposed during the deposition of upper part after about 2.0 Ma. We conclude that it is possible to estimate the sediment provenance using ESR properties.
Onoe, Hironori; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Yasue, Kenichi*; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Kato, Tomoko; Sasao, Eiji
no journal, ,
JAEA have been developing the Geological-Evolutionary Models (GEMs) taking into account of long-term change of the geological environment in order to evaluate the geosphere stability. This paper summarized the current status of Research and development activities with analysis on effects of uncertainties of GEMs for evaluation of long-term variability of groundwater flow conditions.
Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Onoe, Hironori; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Yasue, Kenichi*; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Kato, Tomoko; Sasao, Eiji
no journal, ,
JAEA have been developing the Geological-Evolutionary Models (GEMs) taking into account of long-term change of the geological environment in order to evaluate the geosphere stability. This paper summarized the current status of R&D activities with analysis of uncertainties included in the geological model that is a base model of the GEMs.