Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
藤本 純治*; 船木 博志*; 小椎八重 航*; 松尾 衛; 前川 禎通*
IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 58(8), p.1500407_1 - 1500407_7, 2022/08
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:27.91(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Motivated by the recent experiment done by Yu et al. [X. Z. Yu, et. al., Sci. Adv., 6, 25, eaaz9744 (2020)] on magnetic skyrmion creation and annihilation by electric currents in FeGe devices with a notch structure, we examine the interaction between the electric current vorticity near the notch and localized spins, and obtain three effects of the current vorticity on the localized spins. The first one is an effective Zeeman field induced by the current vorticity. This effective Zeeman field is responsible for skyrmion creation. The second effect is a vorticity-induced Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya (DM) interaction with the direction of the DM vector being parallel to the vorticity direction and is different from the vector of the intrinsic DM interaction. This vorticity-induced DM interaction makes the skyrmions distorted. The third effect is a spin current due to the gradient of the vorticity and the spin current drives the magnetic skyrmions far from the notch. Our theory opens a new path to design the magnetic textures by using structural settings.
藤本 純治*; 小椎八重 航*; 松尾 衛; 前川 禎通
Physical Review B, 103(22), p.L220402_1 - L220402_5, 2021/06
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:46.19(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction, i.e., antisymmetric exchange interaction, combined with a Zeeman magnetic field gives rise to various magnetic states such as chiral, helical, and skyrmionic states. This interaction conventionally originates from spin-orbit coupling and thus needs somewhat heavy elements. In contrast, we here show a Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction which is driven by electric current vorticity. We also find that the vorticity acts on localized spins as a Zeeman field, which may explain a recent experiment on current-driven magnetic skyrmion creation and annihilation without an external magnetic field in a device with a notch structure in FeGe. The theory explains the control of skyrmion creation and annihilation by current direction and opens different possibilities for studies of magnetic textures by using structural settings.
関野 まり*; 岡本 聡*; 小椎八重 航*; 森 道康; 前川 禎通
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 3, p.017014_1 - 017014_5, 2014/06
Temperature dependence of thermopower in the multiorbital Hubbard model is studied by using the dynamical mean-field theory with the non-crossing approximation impurity solver. It is found that the Coulomb interaction, the Hund coupling, and the crystal filed splitting bring about non-monotonic temperature dependence of the thermopower, including its sign reversal. The implication of our theoretical results to some materials is discussed.
森 道康; 小椎八重 航*; 挽野 真一*; 前川 禎通
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 26(25), p.255702_1 - 255702_5, 2014/06
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:13.77(Physics, Condensed Matter)A magnetic domain wall (DW) behaves as a massive particle with elasticity. Sliding and oscillation of the DW have been observed experimentally, whereas vibration of a width in the DW, "breathing mode", has not been measured so far. We theoretically propose how to observe the breathing mode by the Josephson junction having a ferromagnetic layer between superconducting electrodes. The current-voltage ( -
- ) curve is calculated by an equivalent circuit of the resistively shunted junction model. The breathing mode is identified by stepwise structures in the
) curve is calculated by an equivalent circuit of the resistively shunted junction model. The breathing mode is identified by stepwise structures in the  -
- curve, which appear at the voltages
curve, which appear at the voltages  =
=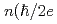 )
) with the fundamental constant
with the fundamental constant 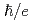 , integer number
, integer number  , and the frequency of the breathing mode
, and the frequency of the breathing mode  .
.
筒井 健二; 遠山 貴己*; 小椎八重 航*; 前川 禎通
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 400(3), p.032105_1 - 032105_4, 2012/12
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:45.30(Physics, Applied)La Sr
Sr NiO
NiO はホール・ドープしたS=1の二次元反強磁性絶縁体であり、銅酸化物高温超伝導体の参照物質として調べられてきている、この物質において、光学伝導度では
はホール・ドープしたS=1の二次元反強磁性絶縁体であり、銅酸化物高温超伝導体の参照物質として調べられてきている、この物質において、光学伝導度では =0の時電荷移動型ギャップが観測され、ホール・ドープによってギャップ内にエネルギー的に広がった吸収スペクトルが現れる。われわれは以前に光学伝導度のギャップ内に現れるスペクトルが、Niサイトにおける高スピン状態から低スピン状態への励起であることを示したが、共鳴非弾性X線散乱においても光学伝導度と同様な励起が現れるかどうかが興味深い。そこで本研究では、光学伝導度の計算と同じく、
=0の時電荷移動型ギャップが観測され、ホール・ドープによってギャップ内にエネルギー的に広がった吸収スペクトルが現れる。われわれは以前に光学伝導度のギャップ内に現れるスペクトルが、Niサイトにおける高スピン状態から低スピン状態への励起であることを示したが、共鳴非弾性X線散乱においても光学伝導度と同様な励起が現れるかどうかが興味深い。そこで本研究では、光学伝導度の計算と同じく、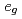 軌道の2バンド・ハバード模型に対する数値的厳密対角化法によって、共鳴非弾性X線散乱スペクトルを計算し、その励起の起源を議論する。
軌道の2バンド・ハバード模型に対する数値的厳密対角化法によって、共鳴非弾性X線散乱スペクトルを計算し、その励起の起源を議論する。
挽野 真一*; 森 道康; 小椎八重 航*; 前川 禎通
Applied Physics Letters, 100(15), p.152402_1 - 152402_3, 2012/04
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:21.56(Physics, Applied)We theoretically propose a principle for precise measurement of oscillatory domain wall (DW) by a ferromagnetic Josephson junction, which is composed of a ferromagnetic wire with DW and two superconducting electrodes. The current-voltage curve exhibits stepwise structures, only when DW oscillates in the ferromagnetic wire. The voltage step appears at 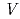 =
=  (
( /2
/2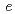 )
) 
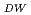 with the fundamental constant
with the fundamental constant  /
/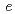 , integer number
, integer number  , and the DW frequency
, and the DW frequency 
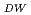 . Since
. Since 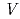 can be determined in the order of 10
can be determined in the order of 10 accuracy, the oscillatory DW will be measured more precisely than present status by conventional method.
accuracy, the oscillatory DW will be measured more precisely than present status by conventional method.
松尾 まり; 岡本 敏史*; 小椎八重 航*; 森 道康; 前川 禎通
Physical Review B, 84(15), p.153107_1 - 153107_4, 2011/10
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:37.58(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We examine the temperature dependence of thermopower in the single band Hubbard model using dynamical mean-field theory. The strong Coulomb interaction brings about the coherent-to-incoherent crossover as temperature increases. As a result, the thermopower exhibits non-monotonic temperature dependence and asymptotically approaches values given by the Mott-Heikes formula. In the light of our theoretical result, we discuss the thermopower in some transition metal oxides. The magnetic field dependence of the thermopower is also discussed.
 Sr
Sr VO
VO
打田 正輝*; 大石 晃史*; 松尾 まり; 小椎八重 航*; 小野瀬 佳文*; 森 道康; 藤岡 淳*; 宮坂 茂樹*; 前川 禎通; 十倉 好紀*
Physical Review B, 83(16), p.165127_1 - 165127_5, 2011/04
被引用回数:32 パーセンタイル:74.73(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We report a systematic investigation on the high-temperature thermoelectric response in a typical filling-control Mott transition system La Sr
Sr VO
VO . In the vicinity of the Mott transition, incoherent charge transport appears with increasing temperature and the thermopower undergoes two essential crossovers, asymptotically approaching the limit values expected from the entropy consideration, as known as Heikes formula. By comparison with the results of the dynamical mean field theory, we show that the thermopower in the Mott critical state mainly measures the entropy per charge carrier that depends on electronic degrees of freedom available at the measurement temperature. Our findings verify that the Heikes formula is indeed applicable to the real correlated electron systems at practical temperatures (T
. In the vicinity of the Mott transition, incoherent charge transport appears with increasing temperature and the thermopower undergoes two essential crossovers, asymptotically approaching the limit values expected from the entropy consideration, as known as Heikes formula. By comparison with the results of the dynamical mean field theory, we show that the thermopower in the Mott critical state mainly measures the entropy per charge carrier that depends on electronic degrees of freedom available at the measurement temperature. Our findings verify that the Heikes formula is indeed applicable to the real correlated electron systems at practical temperatures (T 200K).
200K).
森 道康; 小椎八重 航*; 挽野 真一*; 前川 禎通
no journal, ,
We theoretically propose how to observe the breathing mode by the Josephson junction having a ferromagnetic layer between superconducting electrodes. The current-voltage (I-V) curve is calculated by an equivalent circuit of the resistively shunted junction model. The breathing mode is identified by stepwise structures in the I-V curve, which appear at the voltages V=n( /2e)w with the fundamental constant
/2e)w with the fundamental constant  /2e, integer number n, and the frequency of the breathing mode w. This is the most feasible method to observe the breathing mode of the DW due to the sensitivity of the Josephson junction. In principle, magnetic resonance methods are also possible to measure the breathing mode. However, owing to their low sensitivity, theresonance measurements would be limited to a sample containing huge numbers of DWs or a specific structure of a ferromagnet. Although such ameasurement is realized in the Skyrmion lattice, in which the rotational and the breathing modes are observed, it has not been done on the breathing mode of the DW so far. Our method is accessible to the breathing mode of a single DW due to the sensitivity of the Josephson junction.
/2e, integer number n, and the frequency of the breathing mode w. This is the most feasible method to observe the breathing mode of the DW due to the sensitivity of the Josephson junction. In principle, magnetic resonance methods are also possible to measure the breathing mode. However, owing to their low sensitivity, theresonance measurements would be limited to a sample containing huge numbers of DWs or a specific structure of a ferromagnet. Although such ameasurement is realized in the Skyrmion lattice, in which the rotational and the breathing modes are observed, it has not been done on the breathing mode of the DW so far. Our method is accessible to the breathing mode of a single DW due to the sensitivity of the Josephson junction.
松尾 まり; 岡本 敏史*; 小椎八重 航*; 森 道康; 前川 禎通
no journal, ,
電子相関の強い系では、電子の運ぶスピン・軌道自由度によるエントロピー輸送が熱起電力に寄与し大きな熱起電力を生み出すことが示されている。このような中、大きな熱起電力を持つことで知られるコバルト酸化物において、低温で熱起電力の大きな磁場依存性が観測された。本研究では、強い電子相関が、熱起電力の磁場効果において、どのような影響をもたらすかに着目し、ハバード模型を用いて熱電応答係数の磁場依存性を調べてきた。計算には動的平均場理論(DMFT)を用いた。これまで1サイト不純物問題のソルバーとして、Iterative perturbation theory(IPT)を用いて、熱電応答の磁場依存性を調べてきた。この近似理論は、電子相関を過小に評価する傾向があるため、強相関領域における精度の低下が著しい。そこで今回、強結合極限からの展開であるNon-crossing approximation(NCA)をソルバーとして用い、より強い相関を含む系における熱電応答の計算を行った。これまでの結果との比較を通して、熱電応答の磁場依存性において強い電子間相関がもたらす効果について議論をする。
森 道康; 挽野 真一*; 小椎八重 航*; 前川 禎通
no journal, ,
Nano-scale magnetic materials for spintronics devices are extensively studied due to many advantages such as enhanced operationspeed, low power consumption, and high integration of memory cell. Non-volatile memory using a magnetic domain wall (DW) is one example of such devices, and many studies are devoted to control DW. Among those studies, the oscillatory DW is experimentally observed and is examined toward applications, e.g. high sensitive magnetic sensor, nano-scale telecommunication, rf-assisted writing of magnetic bit, and microwave generator. Once such devices are realized in a microscopic circuit, one needs to measure the DW frequency more precisely. We theoretically propose a principle for precise measurement of oscillatory domain wall (DW) by a ferromagnetic Josephson junction,which is composed of a ferromagnetic wire with DW and two superconducting electrodes. The current-voltage curve exhibits stepwisestructures, only when DW oscillates in the ferromagnetic wire. The voltage step appears at V=n(h/2e)f with the fundamental constant h/e,integer number n, and the DW frequency f. Since V can be determined in the order of 10 accuracy, the oscillatory DW will be measured more precisely than present status by conventional method.
accuracy, the oscillatory DW will be measured more precisely than present status by conventional method.
森 道康; 挽野 真一*; 小椎八重 航*; 前川 禎通
no journal, ,
強磁性体で隔てられた超伝導体の接合を考え、その強磁性体中で磁壁が振動運動している場合の電流電圧特性を理論的に導いた。その結果、磁壁の振動数の整数倍に比例定数をかけた電圧のところで、電流電圧特性が階段状に変化しうることを見いだした。比例係数がプランク定数と素電荷で与えられ、電圧はジョセフソン接合を用いて極めて高い精度で規定されているので、磁壁の振動数の高精度な観測が可能になると期待される。
森 道康; 小椎八重 航*; 挽野 真一*; 前川 禎通
no journal, ,
強磁性体で隔てられた超伝導体の接合を考え、その強磁性体中に磁壁が含まれている場合の電流電圧特性を理論的に導いた。振動運動している場合の電流電圧特性を理論的に導いた。その結果、磁壁の振動数の整数倍に比例定数をかけた電圧のところで、電流電圧特性が階段状に変化しうることを見出した。比例係数がプランク定数と素電荷で与えられ、電圧はジョセフソン接合を用いて極めて高い精度で規定されているので、磁壁の振動数の高精度な観測が可能になると期待される。
森 道康; 小椎八重 航*; 前川 禎通*
no journal, ,
Josephson diode effect between two singlet superconductors separated by a Rashba system is studied theoretically. The coupling energy of two superconductors is analytically calculated using a tunneling Hamiltonian with a one-dimensional model. By applying a magnetic field perpendicular to a current bias, we obtain a coupling energy proportional to the current bias and the magnetic field. This makes the critical current asymmetric with respect to the current bias or the magnetic field, i.e., Josephson diode effect. In addition, depending on a distance between the superconducting electrodes  , the Josephson diode effect changes its sign and magnitude. The magnitude is inversely proportional to a band split caused by the spin-orbit interaction. Since
, the Josephson diode effect changes its sign and magnitude. The magnitude is inversely proportional to a band split caused by the spin-orbit interaction. Since  is experimentally controllable, the Josephson diode effect can be optimized by tuning of
is experimentally controllable, the Josephson diode effect can be optimized by tuning of  .
.
松尾 まり; 岡本 敏史*; 小椎八重 航*; 森 道康; 前川 禎通
no journal, ,
The cobalt oxides, Na CoO
CoO have a large thermopower due to an entropy transport by the degrees of freedom of electron's spin and orbital as characteristics of strongly correlated electron systems. Wang et al. observed much larger magnetic field response of thermopower of Na
have a large thermopower due to an entropy transport by the degrees of freedom of electron's spin and orbital as characteristics of strongly correlated electron systems. Wang et al. observed much larger magnetic field response of thermopower of Na CoO
CoO at low temperatures than usual metals. Motivated by their observation of the huge magnetic field response of thermopower, we investigate theoretically effects of strong correlation between electrons on the field response of thermopower at low temperatures. We study magnetic field dependence of the Seebeck coefficient of the single band Hubbard model using Dynamical Mean Field Theory and non-crossing approximation as one-site Anderson impurity solver. Our results show that the strong Coulomb interaction derives a narrow quasi-particle band structure and a large response of the Seebeck coefficient to magnetic field.
at low temperatures than usual metals. Motivated by their observation of the huge magnetic field response of thermopower, we investigate theoretically effects of strong correlation between electrons on the field response of thermopower at low temperatures. We study magnetic field dependence of the Seebeck coefficient of the single band Hubbard model using Dynamical Mean Field Theory and non-crossing approximation as one-site Anderson impurity solver. Our results show that the strong Coulomb interaction derives a narrow quasi-particle band structure and a large response of the Seebeck coefficient to magnetic field.
森 道康; 小椎八重 航*; 前川 禎通*
no journal, ,
本研究では、面内磁場下のラシュバ系を介した超伝導体間の結合エネルギーを、トンネルハミルトニアンを用いて解析的に調べた。導出された結合エネルギーの表式は、電流バイアス下の条件で、バイアス電流と磁場の積に比例する項を含み、これがジョセフソンダイオード効果となることが分かった。得られた解析的結果では、接合間距離によってジョセフソンダイオード効果は振動減衰し、その振動周期はスピン軌道相互作用によるバンド乖離エネルギーで決まる。このことから、ジョセフソンダイオード効果は、接合間距離によって最適化される。
松尾 まり; 岡本 敏史*; 小椎八重 航*; 森 道康; 前川 禎通
no journal, ,
We theoretically investigate the temperature  and the magnetic field dependences of thermopower. To focus on the strong electron correlation, the Hubbard model is solved in the dynamical mean field theory with the non-crossing approximation impurity solver. The thermopower shows a non-monotonic behavior as a function of
and the magnetic field dependences of thermopower. To focus on the strong electron correlation, the Hubbard model is solved in the dynamical mean field theory with the non-crossing approximation impurity solver. The thermopower shows a non-monotonic behavior as a function of  and asymptotes to the high-
and asymptotes to the high- values given by the Heikes formula, depending on the ratio of Coulomb repulsion and
values given by the Heikes formula, depending on the ratio of Coulomb repulsion and  . The large response to the magnetic-field, which is observed in the cobalt oxides, can be associated with the sharp quasiparticle peak intrinsic to the strongly correlated electron system. We discuss the effect of orbital degeneracy, which is another key factor to enhance the thermopower in the correlated system.
. The large response to the magnetic-field, which is observed in the cobalt oxides, can be associated with the sharp quasiparticle peak intrinsic to the strongly correlated electron system. We discuss the effect of orbital degeneracy, which is another key factor to enhance the thermopower in the correlated system.
森 道康; 小椎八重 航*; 前川 禎通*
no journal, ,
面内磁場下のラシュバ系を介した超伝導体間の結合エネルギーを、トンネルハミルトニアンを用いて解析的に導出した。電流バイアスにより、電流と磁場の各々に線形な項が現れ、ダイオード効果を示すことが分かった。接合間距離によって結合エネルギーは振動減衰し、その振動周期はフェルミ面のトポロジーを反映することも明らかとなった。
松尾 まり; 岡本 敏史*; 小椎八重 航*; 森 道康; 前川 禎通
no journal, ,
コバルト酸化物NaCoO は大きな熱起電力を持つことで知られる物質である。その巨大な熱起電力の起源として、電子相関の強い系では、電子の運ぶスピン・軌道自由度によるエントロピー輸送の熱起電力への寄与が提案されており、2つの高温極限においてドーピングとスピン・軌道自由度に依存した熱起電力の式が示されている。本研究では、強い電子相関に着目し、ハバード模型をもちいて熱電応答係数の温度依存性を広い温度領域にわたって調べてきた。計算には動的平均場理論(DMFT)を用いた。DMFTは電子相関を非摂動的に取り込みながら、コヒーレントとインコヒーレントの両部分を扱うことができる手法である。1サイト不純物問題のソルバーとしては、強結合極限からの展開であるNon-crossing approximation(NCA)を用いている。前回の学会では、1軌道ハバード模型における熱起電力が温度とともに非単調に振る舞うことを示し、2つの高温極限の式によって与えられる値にそれぞれ漸近する様子を示した。今回は、ハバード模型に軌道自由度を取り込み、軌道の効果が与える熱電応答の温度依存性への寄与について議論を行う。
は大きな熱起電力を持つことで知られる物質である。その巨大な熱起電力の起源として、電子相関の強い系では、電子の運ぶスピン・軌道自由度によるエントロピー輸送の熱起電力への寄与が提案されており、2つの高温極限においてドーピングとスピン・軌道自由度に依存した熱起電力の式が示されている。本研究では、強い電子相関に着目し、ハバード模型をもちいて熱電応答係数の温度依存性を広い温度領域にわたって調べてきた。計算には動的平均場理論(DMFT)を用いた。DMFTは電子相関を非摂動的に取り込みながら、コヒーレントとインコヒーレントの両部分を扱うことができる手法である。1サイト不純物問題のソルバーとしては、強結合極限からの展開であるNon-crossing approximation(NCA)を用いている。前回の学会では、1軌道ハバード模型における熱起電力が温度とともに非単調に振る舞うことを示し、2つの高温極限の式によって与えられる値にそれぞれ漸近する様子を示した。今回は、ハバード模型に軌道自由度を取り込み、軌道の効果が与える熱電応答の温度依存性への寄与について議論を行う。
松尾 まり; 岡本 敏史*; 小椎八重 航*; 森 道康; 前川 禎通
no journal, ,
遷移金属酸化物に代表される強相関電子系は、高効率熱電材料の探索に新たな可能性を与えるものとして、注目を集めている。強相関電子系が示す巨大な熱起電力の起源として、電荷・スピン・軌道自由度が与えるエントロピー輸送への寄与が提案されている。この理論は、La Sr
Sr VO
VO に観測される熱起電力の非単調な温度依存性に見られる高温側の漸近的な振る舞いをよく説明する。本研究では、これまでの計算を拡張し、多軌道ハバード模型における熱電応答係数の温度依存性を広い温度領域にわたって調べた。解析手法として動的平均場理論を用いた。この手法は電子相関を非摂動的に取り込みながら、コヒーレントそしてインコヒーレントな電子状態の両部分を同時に取り扱うことができる手法である。また1サイト不純物問題のソルバーとして、強結合極限からの展開であり複雑な相互作用に対応することが可能な非交差近似を用いた。講演では、熱電応答の温度依存性にみる、軌道間の交換相互作用並びに結晶場分裂の役割について議論する。
に観測される熱起電力の非単調な温度依存性に見られる高温側の漸近的な振る舞いをよく説明する。本研究では、これまでの計算を拡張し、多軌道ハバード模型における熱電応答係数の温度依存性を広い温度領域にわたって調べた。解析手法として動的平均場理論を用いた。この手法は電子相関を非摂動的に取り込みながら、コヒーレントそしてインコヒーレントな電子状態の両部分を同時に取り扱うことができる手法である。また1サイト不純物問題のソルバーとして、強結合極限からの展開であり複雑な相互作用に対応することが可能な非交差近似を用いた。講演では、熱電応答の温度依存性にみる、軌道間の交換相互作用並びに結晶場分裂の役割について議論する。