Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 84(1), p.012006_1 - 012006_18, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:72.31(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We report on the event structure and double helicity asymmetry ( ) of jet production in longitudinally polarized
) of jet production in longitudinally polarized  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured
= 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured  = -0.0014
= -0.0014  0.0037 at the lowest
0.0037 at the lowest  bin and -0.0181
bin and -0.0181  0.0282 at the highest
0.0282 at the highest  bin. The measured
bin. The measured  is compared with the predictions that assume various
is compared with the predictions that assume various 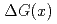 distributions.
distributions.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV
= 200 and 62.4 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(6), p.064903_1 - 064903_29, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:184 Percentile:99.44(Physics, Nuclear)Transverse momentum distributions and yields for  , and
, and  in
in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different
= 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different  collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as
collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as  and
and  scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in
scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in  collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
 and Au+Au collisions at
and Au+Au collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Aramaki, Y.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(4), p.044912_1 - 044912_16, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:49.7(Physics, Nuclear)Measurements of electrons from the decay of open-heavy-flavor mesons have shown that the yields are suppressed in Au+Au collisions compared to expectations from binary-scaled  collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to
collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to  collisions.
collisions.
 +
+  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV and scaling properties of hadron production
= 200 GeV and scaling properties of hadron productionAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 83(5), p.052004_1 - 052004_26, 2011/03
Times Cited Count:177 Percentile:98.48(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The PHENIX experiment at RHIC has measured the invariant differential cross section for production of 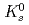 ,
,  ,
,  and
and  mesons in
mesons in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. The spectral shapes of all hadron transverse momentum distributions are well described by a Tsallis distribution functional form with only two parameters,
= 200 GeV. The spectral shapes of all hadron transverse momentum distributions are well described by a Tsallis distribution functional form with only two parameters,  and
and  , determining the high
, determining the high  and characterizing the low
and characterizing the low  regions for the spectra, respectively. The integrated invariant cross sections calculated from the fitted distributions are found to be consistent with existing measurements and with statistical model predictions.
regions for the spectra, respectively. The integrated invariant cross sections calculated from the fitted distributions are found to be consistent with existing measurements and with statistical model predictions.
; ; Iwanaga, Masayuki; Todokoro, Akio; ; Masui, Jinichi; Miura, Nobuyuki*; Lovett, J. E.*
PNC TN8410 86-52, 66 Pages, 1987/01
None
Russo, P. A.*; Asakura, Yoshiro*; Hsue, S. T.*; Kondo, Isao*; Sprinkle, J. K. Jr.*; Masui, J.*; Johnson, S. S.*; Shoji, J.*
PNC TN841 82-10, 76 Pages, 1982/08
An instrument based upon high-resolution  -ray measurements has beentested for more than 1 year at the TokaiReprocessing Facility for determinationof plutonium concentration by K-edge absorption densitometry and for determination of plutonium isotopic fractions bytransmission-corrected passive
-ray measurements has beentested for more than 1 year at the TokaiReprocessing Facility for determinationof plutonium concentration by K-edge absorption densitometry and for determination of plutonium isotopic fractions bytransmission-corrected passive  -ray spectrometry. The nondestructive assay instrument was designed and built atLos Alamos National Laboratory for theTokai Advanced Safeguards Technology Exercise (TASTEX). It was used at Tokai forthe timely assay of more than 100 productsolution samples daring the TASTEX evaluations The results were compared tosolution samples during the TASTEXaluations. The results were compared toreference values obtained by conventionaldestructive analysis of these samples. The precision and accuracy of plutoniumconcentrations measured by the K-edgetechnique are shown to be with in 0.6% (1
-ray spectrometry. The nondestructive assay instrument was designed and built atLos Alamos National Laboratory for theTokai Advanced Safeguards Technology Exercise (TASTEX). It was used at Tokai forthe timely assay of more than 100 productsolution samples daring the TASTEX evaluations The results were compared tosolution samples during the TASTEXaluations. The results were compared toreference values obtained by conventionaldestructive analysis of these samples. The precision and accuracy of plutoniumconcentrations measured by the K-edgetechnique are shown to be with in 0.6% (1 ) in these applications. The precisionsand accuracies of the isotopic fractions. determined by these passive
) in these applications. The precisionsand accuracies of the isotopic fractions. determined by these passive
Asakura, Yoshiro*; Miyahara, Kenji; *; Masui, J.*; Kondo, Isao*; *; *; Kamata, Masayuki
PNC TN852 81-18, 266 Pages, 1981/05
None
Miyahara, Kenji; Asakura, Yoshiro*; *; Masui, J.*; Kondo, Isao*; *; Kamata, Masayuki; *
PNC TN852 81-15, 46 Pages, 1981/04
None
Tsuboya, Takao*; Kamata, Masayuki; Wada, Yukio; Masui, J.*; *; Wada, Tsutomu*; ; *
PNC TN851 76-01, 42 Pages, 1976/01
None
Masui, Tomomi; Koizumi, Satoshi; Hashimoto, Takeji; Iwase, Hiroki; Shikinaka, Kazuhiro*; Kwon, H.*; Kakugo, Akira*; Gong, J.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Masui, Tomomi; Shikinaka, Kazuhiro*; Kwon, H.*; Koizumi, Satoshi; Hashimoto, Takeji; Iwase, Hiroki; Kakugo, Akira*; Gong, J.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Masui, Tomomi; Shikinaka, Kazuhiro*; Kwon, H.*; Koizumi, Satoshi; Hashimoto, Takeji; Iwase, Hiroki; Kakugo, Akira*; Gong, J.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Masui, Tomomi; Shikinaka, Kazuhiro*; Kwon, H.*; Koizumi, Satoshi; Hashimoto, Takeji; Iwase, Hiroki; Kakugo, Akira*; Gong, J.*
no journal, ,
Actin is one of the most abundant cytoskeleton proteins in eucaryotic cell. They play a crucialrole in cell motility by polymerizing monomeric globular G-actin into polymeric filamentous actin (F-actin). With actin-binding proteins (ABPs), they form higher order structures such as linear bundles, two-dimensional networks and three-dimensional gels. It has been considered that these structures are controlled by ABPs. However recent study have shown that the only one kind of artificial cationic polymer can form variety of structures depending its concentration and salt concentration. This system is a good model to elucidate the mechanism of regulation of actin and ABPs complex structure. Based on these backgrounds, we have investigated the effects of salt concentration on the stability and structure of actin-polycation complexes by using small angle neutron scattering (SANS) technique.
Masui, Tomomi; Shikinaka, Kazuhiro*; Kwon, H.*; Koizumi, Satoshi; Hashimoto, Takeji; Iwase, Hiroki; Kakugo, Akira*; Gong, J.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Masui, Tomomi; Shikinaka, Kazuhiro*; Kwon, H.*; Koizumi, Satoshi; Hashimoto, Takeji; Iwase, Hiroki; Kakugo, Akira*; Gong, J.*
no journal, ,
Actin is one of the cytoskeleton proteins and it is most abundant proteins in eucaryotic cell. They play a crucial role in cell motility by polymerization of monomeric globular G-actin into polymeric filamentous actin (F-actin). With actin binding proteins, they form various structures such as linear bundles, two-dimensional networks, and three-dimensional gels. It has been considered that these structures are controlled by the specific interaction between actin and binding protein. However from the physicochemical point of view, actin has negative charge and actin-binding protein has positive charge. Thus, the electrostatic interaction might play important role to determinein the structure. Based on this idea, we have investigated the effects of salt concentration on the stability and structure of actin-polymer complexes by using small angle neutron scattering (SANS) technique.
Masui, Tomomi; Shikinaka, Kazuhiro*; Kwon, H.*; Koizumi, Satoshi; Hashimoto, Takeji; Iwase, Hiroki; Kakugo, Akira*; Gong, J.*
no journal, ,
Actin is one of the cytoskeleton proteins and it is most abundant proteins in eucaryotic cell. They play a crucial role in cell motility by polymerization of monomeric globular G-actin into polymeric filamentous actin (F-actin). With actin binding proteins, they form various structures such as linear bundles, two-dimensional networks, and three-dimensional gels. It has been considered that these structures are controlled by the specific interaction between actin and binding protein. However from the physicochemical point of view, actin has negative charge and actin-binding protein has positive charge. Thus, the electrostatic interaction might play important role to determine in the structure. Based on this idea, we have investigated the effects of salt concentration on the stability and structure of actin-polymer complexes by using small angle neutron scattering (SANS) technique.
Masui, Tomomi; Shikinaka, Kazuhiro*; Kwon, H.*; Koizumi, Satoshi; Hashimoto, Takeji; Iwase, Hiroki; Kakugo, Akira*; Gong, J.*
no journal, ,
Actin is one of the most abundant cytoskeleton proteins in eucaryotic cell. They play a crucial role in cell motility by polymerizing monomeric globular G-actin into polymeric filamentous actin (F-actin). Withactin-binding proteins (ABPs), they form higher order structures such as linear bundles, two-dimensional networks and three-dimensional gels. In this study we have constructed model cytoskeleton system composed of F-actin, cationic polymer and salt. To investigate salt induced hierarchical structure change we employed fluorescence microscopy and small angle neutron scattering (SANS) technique.
Masui, Tomomi; Shikinaka, Kazuhiro*; Koizumi, Satoshi; Hashimoto, Takeji; Kakugo, Akira*; Gong, J.*; Kwon, H.*
no journal, ,
We reconstituted in vitro model cytoskeleton using F-actin and polycation. We have investigated hierarchical structural change of F-actin/polycation complexes induced by salt quantitatively by fluorescence microscopy and small angle neutron scattering. Based on the obtained structural parameters, we will discuss dominant interactions which determine the structure.
Masui, Tomomi; Shikinaka, Kazuhiro*; Koizumi, Satoshi; Kakugo, Akira*; Hashimoto, Takeji; Gong, J.*
no journal, ,
Hierarchical structures of F-actin, an anionic polyelectrolyte, and PDMAPAA-Q, a synthetic linear cationic polyelectrolyte (polycation), complexes in KCl salt solutions have been examined over a wide range of length scales from nanometer to micrometer using a combination of ultra-small-angle neutron scattering technique and fluorescence microscopy. We found hierarchical condensation of actin/polycation complex composed of a superbundle of 10 micrometer, protobundle of 100 nanometer, and protofilament (F-actin) of nanometer. These structures are largely influenced by salt concentrations. With increase of salt concentration superbundle structure changes from globular to extended states, simultaneously, the regularity of F-actin inside the protobundle increased and protobundle size increased about ten times larger. Further increase of salt concentration brings the protobundle disassemble to single F-actin.