Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ohashi, Yusuke; Shimaike, Masamitsu; Matsumoto, Takashi; Takahashi, Nobuo; Yokoyama, Kaoru; Morimoto, Yasuyuki
Nuclear Technology, 209(5), p.777 - 786, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)At the Ningyo-Toge Center, technical development related to uranium refining conversion and enrichment has been completed, and decommissioning of these facilities has begun. The error between the quantity of dismantled materials estimated from the facility design drawings and the actual quantity of dismantled materials was minimal when averaging over the entire Uranium Refining and Conversion Plant and Uranium Enrichment Engineering Facility, which results indicated that the preliminary estimate of the quantity of dismantled materials for decommissioning was reasonable. Most of the dismantled materials, which have no contamination history and are properly managed were able to be carried out to recyclers as non-radioactive waste (NR). In addition, the possibility of evaluating the uranium concentration of clearance level in dismantled objects was confirmed through gamma-ray measurement tests using mock-up waste.
Okazaki, Yasuyuki*; Hayashi, Hisashi*; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Morimoto, Shingo*; Shinji, Masato*
Proceedings of 5th ISRM Young Scholars' Symposium on Rock Mechanics and International Symposium on Rock Engineering for Innovative Future (YSRM 2019 and REIF 2019) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2019/12
In the design of tunnel support, the behavior of the rock mass around a tunnel and the stress acting on the tunnel support may be predicted using a numerical analysis. However, in such a numerical analysis, it is common to assume that each stratum comprises a homogeneous material, ignoring the heterogeneity of the geomechanical properties inherent to the rock mass. For this reason, it is not unusual for the results of the numerical analysis to differ from the actual behavior. We performed a tunnel excavation analysis considering the heterogeneity of the geomechanical properties in the rock mass to investigate the local increase in the tunnel support stress obtained in the 350 m gallery at the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory. The results revealed that, in order to predict the locally increased support stress in advance, it is necessary to carry out a tunneling excavation analysis considering the heterogeneity of the geomechanical properties. It was also revealed that the scale at which the geomechanical properties fluctuate is an important factor.
Umezawa, Katsuhiro; Morimoto, Yasuyuki; Nakayama, Takuya; Nakagiri, Toshio
Proceedings of 27th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-27) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2019/05
In December 2016, the Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA Ningyo-toge) announced new concept of "Uranium and Environmental Research Platform". As part of the concept, uranium waste engineering research are now undergoing. The objective of the research is to establish the processing technology for safely and reasonable disposal of uranium waste. In particular, estimation of the amount of uranium and harmful substances and development of technologies to reduce their concentration in the waste to the permissive level for the disposal in shallow ground disposal are needed. We are now developing the technologies to reduce the concentration of uranium and harmful substances shown below. (1) Survey on uranium inventory. Uranium waste is now stored in 10-odd thousands of 200 L drums. We are surveying amount and chemical form of uranium in the drums. (2) Development of decontamination technology of metal and concrete waste. We are investigating decontamination methods for metals and concrete contaminated with uranium. (3) Development of technologies to remove, detoxify and fix the harmful substances. We are surveying the types and amounts of harmful substances in waste. In addition, we are investigating the method to remove, detoxify, and fix harmful substances. (4) Measurement technology of uranium radioactivity. We are investigating and examining ways to improve the quantitative accuracy of measurement and shorten the measurement time. (5) Development of uranium removal technology from sludge. We are investigating new processing method to remove uranium from sludge which is applicable for several kind of sludge. The results of these technological developments and environmental research will be reflected to "small-scale field test" and "disposal demonstration test" which are planned for demonstration of the uranium waste disposal technology.
Nakayama, Takuya; Yagi, Naoto; Sato, Kazuhiko; Hinoda, Shingo; Nakagiri, Toshio; Morimoto, Yasuyuki; Umezawa, Katsuhiro; Sugitsue, Noritake
JAEA-Review 2018-005, 163 Pages, 2018/03
The Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center of JAEA has been working together with local communities for more than 60 years. Through our R&D projects on from uranium exploration to uranium enrichment as a part of the nuclear fuel cycle (i.e., front-end), we have accumulated experiences in the fields of management of uranium related technology. Taking advantage of such our potential, we will start new R&D program on "Research on Uranium and the Environment". In December 2016 we announced our new concept of the "Uranium and Environmental Research Platform" as a framework aimed at contributing to regional and international society through R&D programs (environmental research and uranium waste engineering research) that are needed to steadily carry out decommissioning of uranium handling facilities.
Terunuma, Akihiro; Mimura, Ryuji; Nagashima, Hisao; Aoyagi, Yoshitaka; Hirokawa, Katsunori*; Uta, Masato; Ishimori, Yuu; Kuwabara, Jun; Okamoto, Hisato; Kimura, Yasuhisa; et al.
JAEA-Review 2016-008, 98 Pages, 2016/07
Japan Atomic Energy Agency formulated the plan to achieve the medium-term target in the period of April 2010 to March 2015(hereinafter referred to as "the second medium-term plan"). JAEA determined the plan for the business operations of each year (hereinafter referred to as "the year plan"). This report is that the Sector of Decommissioning and Radioactive Waste Management has summarized the results of the decommissioning technology development and decommissioning of nuclear facilities which were carried out in the second medium-term plan.
Matsumoto, Takashi; Morimoto, Yasuyuki; Takahashi, Nobuo; Takata, Masaharu; Yoshida, Hideaki; Nakashima, Shinichi; Ishimori, Yuu
JAEA-Technology 2015-036, 60 Pages, 2016/01
The Enrichment Engineering Facilities of the Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center was constructed in order to establish the technical basis of the uranium enrichment plant in Japan. Uranium enrichment tests, using natural and reprocessed uranium, were carried out from 1979 to 1990 at two types of plants in the facilities. UF handling equipment and Supplemental equipment in these plants are intended to be dismantled by 2019 in order to make places for future projects, for example, inventory investigation, precipitation treatment, etc. This report shows the basic plan of this decommissioning project and presents the current state of dismantling in the first-half of the fiscal year of 2014, with indicating its schedule, procedure, situation, results, and so on. The dismantled materials generated amounted to 37 mesh containers and 199 drums, and the secondary waste generated amounted to 271.4 kg.
handling equipment and Supplemental equipment in these plants are intended to be dismantled by 2019 in order to make places for future projects, for example, inventory investigation, precipitation treatment, etc. This report shows the basic plan of this decommissioning project and presents the current state of dismantling in the first-half of the fiscal year of 2014, with indicating its schedule, procedure, situation, results, and so on. The dismantled materials generated amounted to 37 mesh containers and 199 drums, and the secondary waste generated amounted to 271.4 kg.
Izumo, Sari; Usui, Hideo; Kubota, Shintaro; Tachibana, Mitsuo; Kawagoshi, Hiroshi; Takahashi, Nobuo; Morimoto, Yasuyuki; Tokuyasu, Takashi; Tanaka, Yoshio; Sugitsue, Noritake
JAEA-Technology 2014-021, 79 Pages, 2014/07
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has developed PROject management data evaluation code for DIsmantling Activities (PRODIA) to make an efficient decommissioning for nuclear facilities. PRODIA is a source code which provides estimated value such as manpower needs, costs, etc., for dismantling by evaluation formulas according to the type of nuclear facility. Evaluation formulas of manpower needs for dismantling of equipments about reprocessed uranium conversion in Uranium Refining and Conversion Plant are developed in this report. In the result, 7 formulas for prepare process, 24 formulas for dismantling process and 8 formulas for clean-up process are derived. It is confirmed that an unified evaluation formula can be used instead of 8 formulas about dismantling process of steel equipment for uranium conversion process, and 3 types of simplified formula can be used for preparation process and clean-up process respectively.
Sugitsue, Noritake; Morimoto, Yasuyuki; Tokuyasu, Takashi; Tanaka, Yoshio
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 12(3), p.242 - 256, 2013/09
This technical report showed the situation of the dismantling of the main equipment in the radiation controlled area of a uranium refining and conversion plant. And, the dismantling which we did is the work of the beginning of a uranium refining and conversion plant decommissioning project. We started dismantling in April 2008, and finished dismantling of the main equipment in a radiation controlled area in 29 September 2011. The dismantling waste and equipment was stored in the 200 little drum. All the contamination equipment can be sealed and kept in this stage. The radioactivity inventory of a uranium refining and conversion plant does not change in this stage. However, the risk of contamination by aged deterioration of this facility became remarkable small. Moreover, we were able to get many information and experience about dismantling.
Izumo, Sari; Usui, Hideo; Tachibana, Mitsuo; Morimoto, Yasuyuki; Takahashi, Nobuo; Tokuyasu, Takashi; Tanaka, Yoshio; Sugitsue, Noritake
Proceedings of 15th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2013) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2013/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Environmental)Usui, Hideo; Izumo, Sari; Shibahara, Yuji; Morimoto, Yasuyuki; Tokuyasu, Takashi; Takahashi, Nobuo; Tanaka, Yoshio; Sugitsue, Noritake; Tachibana, Mitsuo
Proceedings of International Waste Management Symposia 2012 (WM2012) (CD-ROM), 13 Pages, 2012/02
Dismantling of dry conversion facility in the uranium refining and conversion plant at Ningyo-toge began in 2008. During dismantling activities, project management data have been collected. Establishment of the calculation formula for dismantling of each kind of equipment makes it possible to evaluate manpower for dismantling the whole facility. However, it is not easy to prepare calculation formula for all kinds of equipment in the facility. Therefore, a simpler evaluation method was considered to calculate manpower based on facility characteristics. The results showed promise for evaluating dismantling manpower with respect to each chemical process. To create an effective dismantling plan, it is necessary to carefully consider use of a GH preliminarily. Thus, an evaluation method of project management data such as manpower and secondary waste generation was considered. The results showed promise for evaluating project management data of GH by using established calculation formula.
Zaima, Naoki; Morimoto, Yasuyuki; Sugitsue, Noritake; Kado, Kazumi
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2010) (CD-ROM), p.311 - 320, 2010/10
Takahashi, Nobuo; Yokoyama, Kaoru; Morimoto, Yasuyuki; Shimaike, Masamitsu; Ikegami, Sohei; Sugitsue, Noritake
JAEA-Technology 2010-003, 92 Pages, 2010/06
At the reprocessed uranium conversion facilities, Hydration and Conversion room-1,2,3, Dehydration and Conversion room-1,2, Dry process filter room have been dismantled according to the schedule, in 2009 fiscal year. The  -ray measurement had been carried out before dismantlement to evaluate the radioactivity inventory. As a result, the uranium recovery work was forecasted for reasonable dismantlement. In addition, the feature nuclide affecting the results of the measurement on the air dose was evaluated. Additionally, as the waste data,
-ray measurement had been carried out before dismantlement to evaluate the radioactivity inventory. As a result, the uranium recovery work was forecasted for reasonable dismantlement. In addition, the feature nuclide affecting the results of the measurement on the air dose was evaluated. Additionally, as the waste data,  -ray analysis results are shown.
-ray analysis results are shown.
 Bh and
Bh and  Db produced in the
Db produced in the  Cm +
Cm +  Na reaction
Na reactionMorita, Kosuke*; Morimoto, Koji*; Kaji, Daiya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; Kudo, Yuki*; Sato, Nozomi*; Sumita, Takayuki*; Yoneda, Akira*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 78(6), p.064201_1 - 064201_6, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:77.51(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Decay properties of an isotope  Bh and its daughter nucleus
Bh and its daughter nucleus  Db produced by the
Db produced by the  Cm(
Cm( Na,5
Na,5 ) reaction were studied by using a gas-filled recoil separator coupled with a position-sensitive semiconductor detector.
) reaction were studied by using a gas-filled recoil separator coupled with a position-sensitive semiconductor detector.  Bh was clearly identified from the correlation of the known nuclide,
Bh was clearly identified from the correlation of the known nuclide,  Db. The obtained decay properties of
Db. The obtained decay properties of  Bh and
Bh and  Db are consistent with those observed in the
Db are consistent with those observed in the  113 chain, which provided further confirmation of the discovery of
113 chain, which provided further confirmation of the discovery of  113.
113.
 113 produced by the
113 produced by the  Bi(
Bi( Zn,n)
Zn,n) 113 reaction
113 reactionMorimoto, Koji*; Morita, Kosuke*; Kaji, Daiya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; Kudo, Yuki*; Sato, Nozomi; Sumita, Takayuki*; Yoneda, Akira*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
We performed the experiment to synthesize an isotope of the element 113 produced by a  Bi(
Bi( Zn,n)
Zn,n) 113 reaction using a gas-filled recoil ion separator (GARIS) at RIKEN. Two decay chains were observed, and assigned to those originating from an isotope
113 reaction using a gas-filled recoil ion separator (GARIS) at RIKEN. Two decay chains were observed, and assigned to those originating from an isotope  113. Both chains were connected into the previously known decays of
113. Both chains were connected into the previously known decays of  Bh and
Bh and  Db via previously unknown decays of
Db via previously unknown decays of  113,
113, 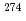 Rg, and
Rg, and 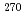 Mt. Although the
Mt. Although the  Bh was known nuclide, a number of atoms reported so far was limited. In order to study more precise decay property of the
Bh was known nuclide, a number of atoms reported so far was limited. In order to study more precise decay property of the  Bh, we performed the direct production of
Bh, we performed the direct production of  Bh by the
Bh by the  Cm(
Cm( Na,5n)
Na,5n) Bh reaction. In this experiment, the
Bh reaction. In this experiment, the  Bh was clearly identified from the correlation of the nuclide,
Bh was clearly identified from the correlation of the nuclide,  Db. The obtained decay properties of
Db. The obtained decay properties of  Bh and
Bh and  Db are consistent with those observed in the
Db are consistent with those observed in the  113 chain, which provided further confirmation of the discovery of
113 chain, which provided further confirmation of the discovery of  113.
113.
Tanaka, Yoshio; Morimoto, Yasuyuki; Tokuyasu, Takashi; Takahashi, Nobuo; Sugitsue, Noritake
no journal, ,
In the decommissioning of the atomic energy plant, the secondary waste is generated by the equipment dismantlement. In the decommissioning of the uranium conversion plant in fiscal 2008, a lot of secondary waste was generated due to the dismantlement of the "greenhouse (GH)" (GH stands for the temporary construction where workers cut off the equipments to prevent the pollution expansion.). Therefore, there is a possibility that the size reduction of GH leads to the secondary waste reduction. In fiscal 2009, the size reduction of GH was tried by the cutting area setup. In this report, the effect of the cutting area was examined with a view toward the secondary waste reduction. As a result, the cutting area is effective in the workers number reduction and the secondary waste reduction at the complicated plant such as the uranium conversion plant.
Tokuyasu, Takashi; Morimoto, Yasuyuki; Ikegami, Sohei; Sugitsue, Noritake; Tachibana, Mitsuo; Tanimoto, Masataka; Ishigami, Tsutomu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Bh and its daughter nuclei
Bh and its daughter nucleiMorimoto, Koji*; Morita, Kosuke*; Kaji, Daiya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; Kudo, Yuki*; Sato, Nozomi; Sumita, Takayuki*; Yoneda, Akira*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
A nuclide,  Bh, is the great-grand-daughter of
Bh, is the great-grand-daughter of  113 that is produced in the
113 that is produced in the  Bi +
Bi +  Zn reaction. The identification was based on a genetic link to the known daughter nucleus
Zn reaction. The identification was based on a genetic link to the known daughter nucleus  Db by alpha-decays. The main purpose of this work is to provide further confirmation of the production and identification of the isotope
Db by alpha-decays. The main purpose of this work is to provide further confirmation of the production and identification of the isotope  113. As a present result, a state in
113. As a present result, a state in  Bh, which decays by an alpha emission with the energies ranging from 9.05 to 9.23 MeV, feeds a state in
Bh, which decays by an alpha emission with the energies ranging from 9.05 to 9.23 MeV, feeds a state in  Db, which decays by alpha emission and by SF with a previously known half-life. The result provided a further confirmation of the production and identification of the isotope of the 113th element,
Db, which decays by alpha emission and by SF with a previously known half-life. The result provided a further confirmation of the production and identification of the isotope of the 113th element,  113, studied by a research group at RIKEN.
113, studied by a research group at RIKEN.
Ikegami, Sohei; Tanaka, Yoshio; Tokuyasu, Takashi; Takahashi, Nobuo; Sugitsue, Noritake; Morimoto, Yasuyuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shimaike, Masamitsu; Takahashi, Nobuo; Morimoto, Yasuyuki; Ikegami, Sohei; Sugitsue, Noritake
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kawatsuma, Shinji; Ishibashi, Makoto*; Morimoto, Yasuyuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English