Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Iwata, Keiko; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Ha, Yoosung; Shimodaira, Masaki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Honda, Mitsunori; Katsuyama, Jinya; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 511, p.143 - 152, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:31.55(Instruments & Instrumentation)Takamizawa, Hisashi; Hata, Kuniki; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Toyama, Takeshi*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 556, p.153203_1 - 153203_10, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:39.96(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Solute clusters (SCs) formed in pressurized water reactor surveillance test specimens neutron-irradiated to a fluence of 1  10
10 n/cm
n/cm were analyzed via atom probe tomography to understand the effect of silicon on solute clustering and irradiation embrittlement of reactor pressure vessel steels. In high-Cu bearing materials, Cu atoms were aggregated at the center of cluster surrounded by the Ni, Mn, and Si atoms like a core-shell structure. In low-Cu bearing materials, Ni, Mn, and Si atoms formed cluster and these solutes were not comprised core-shell structure in SCs. While the number of Cu atoms in clusters was decreased with decreasing nominal Cu content, the number of Si atoms had clearly increased. The cluster radius (
were analyzed via atom probe tomography to understand the effect of silicon on solute clustering and irradiation embrittlement of reactor pressure vessel steels. In high-Cu bearing materials, Cu atoms were aggregated at the center of cluster surrounded by the Ni, Mn, and Si atoms like a core-shell structure. In low-Cu bearing materials, Ni, Mn, and Si atoms formed cluster and these solutes were not comprised core-shell structure in SCs. While the number of Cu atoms in clusters was decreased with decreasing nominal Cu content, the number of Si atoms had clearly increased. The cluster radius ( ) and number density (
) and number density (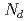 ) decreased and increased, respectively, with increasing nominal Si content. The shift in the reference temperature for nil-ductility transition (
) decreased and increased, respectively, with increasing nominal Si content. The shift in the reference temperature for nil-ductility transition ( RT
RT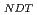 ) showed a good correlation with the square root of volume fraction (
) showed a good correlation with the square root of volume fraction (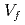 ) multiplied by r (
) multiplied by r (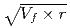 ). This suggested that the dislocation cutting through the particles mechanism dominates the precipitation hardening responsible for irradiation embrittlement. The negative relation between the nominal Si content and
). This suggested that the dislocation cutting through the particles mechanism dominates the precipitation hardening responsible for irradiation embrittlement. The negative relation between the nominal Si content and  RT
RT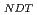 indicated that increasing of nominal Si content reduces the degree of embrittlement.
indicated that increasing of nominal Si content reduces the degree of embrittlement.
Takamizawa, Hisashi; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 143(5), p.051502_1 - 051502_8, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:25.22(Engineering, Mechanical)no abstracts in English
Iwata, Keiko; Hata, Kuniki; Tobita, Toru; Hirota, Takatoshi*; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Proceedings of ASME 2021 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2021) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2021/07
Ha, Yoosung; Shimodaira, Masaki; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Tobita, Toru; Katsuyama, Jinya; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Proceedings of ASME 2021 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2021) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2021/07
Chiba, Yusuke; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Tsubaki, Hirohiko; Iwai, Masaki; Furukawahara, Ryo; Ono, Hayato*; Hayasaka, Toshiro*
JAEA-Testing 2020-007, 42 Pages, 2021/02
Maintenance and Operation Section for Remote Control Equipment in Naraha Center for Remote Control Technology Development was the main part of the nuclear emergency response team of JAEA in full-scale operation starts on the 1st of April, 2020. In this section, we need to develop equipment for a JAEA nuclear emergency. To support full-scale operation, we have created a work robot for opening and closing doors, a work robot for opening and closing valves, and a reconnaissance robot for measuring radiation dose. This report describes how to operate a Reconnaissance robot.
Chiba, Yusuke; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Tsubaki, Hirohiko; Iwai, Masaki; Ono, Hayato*; Hayasaka, Toshiro*
JAEA-Testing 2020-006, 24 Pages, 2021/02
Maintenance and Operation Section for Remote Control Equipment in Naraha Center for Remote Control Technology Development was the main part of the nuclear emergency response team of JAEA in full-scale operation starts on the 1st of April, 2020. In this section, we need to develop equipment for a JAEA nuclear emergency. To support full- scale operation, we have created a work robot for opening and closing doors, a work robot for opening and closing valves, and a reconnaissance robot for measuring radiation dose. This report describes how to operate a work robot (opening and closing valves).
Chiba, Yusuke; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Tsubaki, Hirohiko; Iwai, Masaki; Furukawahara, Ryo; Ono, Hayato*; Hayasaka, Toshiro*
JAEA-Testing 2020-005, 29 Pages, 2021/02
Maintenance and Operation Section for Remote Control Equipment in Naraha Center for Remote Control Technology Development was the main part of the nuclear emergency response team of JAEA in full-scale operation starts on the 1st of April, 2020. In this section, we need to develop equipment for a JAEA nuclear emergency. To support full-scale operation, we have created a work robot for opening and closing doors, a work robot for opening and closing valves, and a reconnaissance robot for measuring radiation dose. This report describes how to operate the work robot (for opening and closing the door).
Hata, Kuniki; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Hojo, Tomohiro*; Ebihara, Kenichi; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 543, p.152564_1 - 152564_10, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:87.69(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Reactor pressure vessel (RPV) steels for pressurized water reactors (PWRs) with bulk P contents ranging from 0.007 to 0.012wt.% were subjected to neutron irradiation at fluences ranging from 0.3 to 1.2 10
10 n/cm
n/cm (E
(E  1 MeV) in PWRs or a materials testing reactor (MTR). Grain-boundary P segregation was analyzed using Auger electron spectroscopy (AES) on intergranular facets and found to increase with increasing neutron fluence. A rate theory model was also used to simulate the increase in grain-boundary P segregation for RPV steels with a bulk P content up to 0.020wt.%. The increase in grain-boundary P segregation in RPV steel with a bulk P content of 0.015wt.% (the maximum P concentration found in RPV steels used in Japanese nuclear power plants intended for restart) was estimated to be less than 0.1 in monolayer coverage at 1.0
1 MeV) in PWRs or a materials testing reactor (MTR). Grain-boundary P segregation was analyzed using Auger electron spectroscopy (AES) on intergranular facets and found to increase with increasing neutron fluence. A rate theory model was also used to simulate the increase in grain-boundary P segregation for RPV steels with a bulk P content up to 0.020wt.%. The increase in grain-boundary P segregation in RPV steel with a bulk P content of 0.015wt.% (the maximum P concentration found in RPV steels used in Japanese nuclear power plants intended for restart) was estimated to be less than 0.1 in monolayer coverage at 1.0 10
10 n/cm
n/cm (E
(E  1 MeV). A comparison of the PWR data with the MTR data showed that neutron flux had no effect upon grain-boundary P segregation. The effects of grain-boundary P segregation upon changes in irradiation hardening and ductile-brittle transition temperature (DBTT) shifts were also discussed. A linear relationship between irradiation hardening and the DBTT shift with a slope of 0.63 obtained for RPV steels with a bulk P content up to 0.026wt.%, which is higher than that of most U.S. A533B steels. It is concluded that the intergranular embrittlement is unlikely to occur for RPV steels irradiated in PWRs.
1 MeV). A comparison of the PWR data with the MTR data showed that neutron flux had no effect upon grain-boundary P segregation. The effects of grain-boundary P segregation upon changes in irradiation hardening and ductile-brittle transition temperature (DBTT) shifts were also discussed. A linear relationship between irradiation hardening and the DBTT shift with a slope of 0.63 obtained for RPV steels with a bulk P content up to 0.026wt.%, which is higher than that of most U.S. A533B steels. It is concluded that the intergranular embrittlement is unlikely to occur for RPV steels irradiated in PWRs.
Suzudo, Tomoaki; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Caro, A.*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 540, p.152306_1 - 152306_10, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:74.60(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Spinodal decomposition in thermally aged Fe-Cr alloys leads to significant hardening, which is the direct cause of the so-called 475C-embrittlement. To illustrate how spinodal decomposition induces hardening by atomistic interactions, we conducted a series of numerical simulations as well as reference experiments. The numerical results indicated that the hardness scales linearly with the short-range order (SRO) parameter, while the experimental result reproduced this relationship within statistical error. Both seemingly suggest that neighboring Cr-Cr atomic pairs essentially cause hardening, because SRO is by definition uniquely dependent on the appearance probability of such pairs. A further numerical investigation supported this notion, as it suggests that the dominant cause of hardening is the pinning effect of dislocations passing over such Cr-Cr pairs.
Nishiyama, Yutaka; Iwai, Masaki; Chiba, Yusuke; Tsubaki, Hirohiko; Ono, Hayato*; Hayasaka, Toshiro*; Hanyu, Toshinori*
JAEA-Technology 2020-007, 18 Pages, 2020/09
Maintenance and Operation Section for Remote Control Equipment in Naraha Center for Remote Control Technology Development is the main part of the nuclear emergency response team of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) in full-scale operation starts on the 1st of April, 2020. The section needs to develop equipment for JAEA nuclear emergency. Because of dealing the full-scale operation, the section designed and produced two sets of Multi-joint Manipulator or (for Opening Doors) against Nuclear Disaster in order to put them on two crawler robots in 2018 fiscal year. And the section also designed and produced a Crawler Robot for Opening and Closing Manual Valves in 2019 fiscal year. This report shows two sets of Multi-Joint Manipulator (for Opening Doors) and a Crawler Robot for Opening and Closing Manual Valves designed and produced by Maintenance and Operation Section for Remote Control Equipment in 2018 and 2019 fiscal year.
Nishiyama, Yutaka; Iwai, Masaki; Tsubaki, Hirohiko; Chiba, Yusuke; Hayasaka, Toshiro*; Ono, Hayato*; Hanyu, Toshinori*
JAEA-Technology 2020-006, 26 Pages, 2020/08
Maintenance and Operation Section for Remote Control Equipment in Naraha Center for Remote Control Technology Development is the main part of the nuclear emergency response team of JAEA deal with Act on Special Measures Concerning Nuclear Emergency Preparedness. The section needs to remodel crawler-type robots for tasks, crawler-type scouting robots, and so on. About two crawler-type robots for tasks, the section designed and mounted advanced wireless communication equipment on manipulators mounted on the two robots. The crawler part of the robot has been able to be controlled by way of the new equipment, and when it is broken down, it can be changed by way of an original equipment. And the new equipment makes a single relay robot controllable both the crawler part and the manipulator part of the robot, in case of wireless relay robots being needed. And after checking the ability and characteristic about 5 wireless communication equipment, the section chose and mounted the best equipment on one crawler-type scouting robot. This report shows design and mounting advanced wireless communication equipment on the two crawler-type robots for tasks and on the one crawler-type scouting robot.
Takamizawa, Hisashi; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Hirano, Takashi*
Proceedings of ASME 2020 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2020) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2020/08
no abstracts in English
Ha, Yoosung; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Katsuyama, Jinya; Hanawa, Satoshi; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 461, p.276 - 282, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:41.18(Instruments & Instrumentation)Takamizawa, Hisashi; Katsuyama, Jinya; Ha, Yoosung; Tobita, Toru; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Onizawa, Kunio
Proceedings of 2019 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2019) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2019/07
no abstracts in English
Chiba, Yusuke; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Tsubaki, Hirohiko; Iwai, Masaki
JAEA-Technology 2019-002, 29 Pages, 2019/03
Act on Special Measures Concerning Nuclear Emergency Preparedness was amended on the 30th of October in 2017. As the JAEA Emergency Assistance Organization, Maintenance and Operation Section for Remote Control Equipment in Naraha Center for Remote Control Technology Development started training for emergency response robots operation for operators in each site of JAEA in response to the new amendment. The training consists of three operations: small crawler-type mobile scouting robots, big crawler-type mobile robots with a manipulator or a long tong and small radio-controlled helicopters. The training has three classes (beginner, intermediate and advanced classes) depending on skills and experiences. This paper reports the training programs of emergency response robots operation of the beginner and intermediate classes which were used in the first half of fiscal 2018.
Tobita, Toru; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Onizawa, Kunio
JAEA-Data/Code 2018-013, 60 Pages, 2018/11
Mechanical properties of materials including fracture toughness are extremely important for evaluating the structural integrity of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs). In this report, the published data of mechanical properties of nuclear RPVs steels, including neutron irradiated materials, acquired by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), specifically tensile test data, Charpy impact test data, drop-weight test data, and fracture toughness test data, are summarized. There are five types of RPVs steels with different toughness levels equivalent to JIS SQV2A (ASTM A533B Class 1) containing impurities in the range corresponding to the early plant to the latest plant. In addition to the base material of RPVs, the mechanical property data of the two types of stainless overlay cladding materials used as the lining of the RPV are summarized as well. These mechanical property data are organized graphically for each material and listed in tabular form to facilitate easy utilization of data.
Ha, Yoosung; Tobita, Toru; Otsu, Takuyo; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 140(5), p.051402_1 - 051402_6, 2018/10
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:39.03(Engineering, Mechanical)Ha, Yoosung; Tobita, Toru; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Hanawa, Satoshi; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Proceedings of 2018 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2018), 6 Pages, 2018/07
Chimi, Yasuhiro; Iwata, Keiko; Tobita, Toru; Otsu, Takuyo; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Yoshimoto, Kentaro*; Murakami, Takeshi*; Hanawa, Satoshi; Nishiyama, Yutaka
JAEA-Research 2017-018, 122 Pages, 2018/03
Warm pre-stress (WPS) effect is a phenomenon that after applying a load at a high temperature fracture does not occur in unloading during cooling, and then the fracture toughness in reloading at a lower temperature increases effectively. Engineering evaluation models to predict an apparent fracture toughness in reloading are established using experimental data with linear elasticity. However, there is a lack of data on the WPS effect for the effects of specimen size and surface crack in elastic-plastic regime. In this study, fracture toughness tests were performed after applying load-temperature histories which simulate pressurized thermal shock transients to confirm the WPS effect. The experimental results of an apparent fracture toughness tend to be lower than the predictive results using the engineering evaluation models in the case of a high degree of plastic deformation in preloading. Considering the plastic component of preloading can refine the engineering evaluation models.