Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tanaka, Kazuya; Yamaji, Keiko*; Masuya, Hayato*; Tomita, Jumpei; Ozawa, Mayumi*; Yamasaki, Shinya*; Tokunaga, Kohei; Fukuyama, Kenjin*; Ohara, Yoshiyuki*; Maamoun, I.*; et al.
Chemosphere, 355, p.141837_1 - 141837_11, 2024/05
In this study, biogenic Mn(IV) oxide was applied to remove Ra from mine water collected from a U mill tailings pond in the Ningyo-toge center. Just 7.6 mg of biogenic Mn(IV) oxide removed more than 98% of the  Ra from 3 L of mine water, corresponding to a distribution coefficient of 10
Ra from 3 L of mine water, corresponding to a distribution coefficient of 10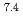 mL/g for Ra at pH 7. The obtained value was convincingly high for practical application of biogenic Mn(IV) oxide in water treatment.
mL/g for Ra at pH 7. The obtained value was convincingly high for practical application of biogenic Mn(IV) oxide in water treatment.
Yamaguchi, Akiko; Kurihara, Yuichi*; Nagata, Kojiro*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Higaki, Shogo*; Kobayashi, Toru; Tanida, Hajime; Ohara, Yoshiyuki*; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; et al.
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 661, p.317 - 332, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:79.28(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
 Ra in natural water samples by ICP-MS
Ra in natural water samples by ICP-MSTomita, Jumpei; Ozawa, Mayumi; Ohara, Yoshiyuki; Miyamoto, Yutaka
KEK Proceedings 2021-2, p.130 - 134, 2021/12
no abstracts in English
 U accumulations in
U accumulations in 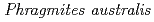 naturally growing at the mill tailings pond; Iron plaque formation possibly related to root-endophytic bacteria producing siderophores
naturally growing at the mill tailings pond; Iron plaque formation possibly related to root-endophytic bacteria producing siderophoresNakamoto, Yukihiro*; Doyama, Kohei*; Haruma, Toshikatsu*; Lu, X.*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Kozai, Naofumi; Fukuyama, Kenjin; Fukushima, Shigeru; Ohara, Yoshiyuki; Yamaji, Keiko*
Minerals (Internet), 11(12), p.1337_1 - 1337_17, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:35.78(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Mine drainage is a vital water problem in the mining industry worldwide because of the heavy metal elements and low pH. Rhizofiltration using wetland plants is an appropriate method to remove heavy metals from the water via accumulation in the rhizosphere. 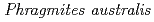 is one of the candidate plants for this method because of metal accumulation, forming iron plaque around the roots. At the study site, which was the mill tailings pond in the Ningyo-toge uranium mine,
is one of the candidate plants for this method because of metal accumulation, forming iron plaque around the roots. At the study site, which was the mill tailings pond in the Ningyo-toge uranium mine,  has been naturally growing since 1998. The results showed that
has been naturally growing since 1998. The results showed that  accumulated Fe, Mn, and
accumulated Fe, Mn, and  U in the nodal roots without/with iron plaque compared with other plant tissues. Among the 837 bacterial colonies isolated from nodal roots, 88.6% showed siderophore production activities. Considering iron plaque formation around
U in the nodal roots without/with iron plaque compared with other plant tissues. Among the 837 bacterial colonies isolated from nodal roots, 88.6% showed siderophore production activities. Considering iron plaque formation around  roots, we hypothesized that microbial siderophores might influence iron plaque formation because bacterial siderophores have catechol-like functional groups. The complex of catechol or other phenolics with Fe was precipitated due to the networks between Fe and phenolic derivatives. The experiment using bacterial products of root endophytes, such as
roots, we hypothesized that microbial siderophores might influence iron plaque formation because bacterial siderophores have catechol-like functional groups. The complex of catechol or other phenolics with Fe was precipitated due to the networks between Fe and phenolic derivatives. The experiment using bacterial products of root endophytes, such as 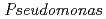 spp. and
spp. and 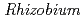 spp., showed precipitation with Fe ions, and we confirmed that several
spp., showed precipitation with Fe ions, and we confirmed that several 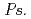 spp. and
spp. and 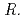 spp. produced unidentified phenolic compounds. In conclusion, root-endophytic bacteria such as
spp. produced unidentified phenolic compounds. In conclusion, root-endophytic bacteria such as 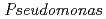 spp. and
spp. and 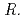 spp., isolated from metal-accumulating roots of
spp., isolated from metal-accumulating roots of  , might influence iron plaque formation as the metal accumulation site. Iron plaque formation is related to tolerance in
, might influence iron plaque formation as the metal accumulation site. Iron plaque formation is related to tolerance in  , and
, and 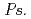 spp. and
spp. and 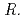 spp. might indirectly contribute to tolerance.
spp. might indirectly contribute to tolerance.
Miura, Daisuke*; Kumada, Takayuki; Sekine, Yurina; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Oba, Yojiro; Ohara, Takashi; Takata, Shinichi; Hiroi, Kosuke; Morikawa, Toshiaki*; et al.
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 54(2), p.454 - 460, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:13.05(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We developed a spin-contrast-variation neutron powder diffractometry technique that extracts the structure factor of hydrogen atoms, namely, the contribution of hydrogen atoms to a crystal structure factor. Crystals of L-glutamic acid were dispersed in a dpolystyrene matrix containing 4-methacryloyloxy-2,2,6,6,-tetramethyl-1-piperidinyloxy (TEMPO methacrylate) to polarize their proton spins dynamically. The intensities of the diffraction peaks of the sample changed according to the proton polarization, and the structure factor of the hydrogen atoms was extracted from the proton-polarization dependent intensities. This technique is expected to enable analyses of the structures of hydrogen-containing materials that are difficult to determine with conventional powder diffractometry.
 He
He
 excimer cluster tracers in superfluid helium-4 via neutron-
excimer cluster tracers in superfluid helium-4 via neutron- He absorption reaction
He absorption reactionSonnenschein, V.*; Tsuji, Yoshiyuki*; Kokuryu, Shoma*; Kubo, Wataru*; Suzuki, So*; Tomita, Hideki*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*; Matsushita, Taku*; Wada, Nobuo*; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 91(3), p.033318_1 - 033318_12, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation) He
He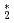 clusters via neutron-
clusters via neutron- He absorption reaction toward visualization of full velocity field in quantum turbulence
He absorption reaction toward visualization of full velocity field in quantum turbulenceMatsushita, Taku*; Sonnenschein, V.*; Guo, W.*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Hiroi, Kosuke; Hirota, Katsuya*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*; Ito, Daisuke*; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; et al.
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 196(1-2), p.275 - 282, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:3.89(Physics, Applied)Fukushima, Shigeru; Sakao, Ryota; Nagayasu, Takaaki; Ohara, Yoshiyuki
Heisei-29-Nendo Zenkoku Kozan, Seirenjo Gemba Tantosha Kaigi Shigen/Shinzozai Koenshu, p.61 - 66, 2017/06
no abstracts in English
Nishida, Nobuho; Ohara, Yoshiyuki; Kawamoto, Tsutomu
Heisei-28-Nendo Zenkoku Kozan, Seirenjo Gemba Tantosha Kaigi Shigen/Shinzozai Koenshu, p.69 - 74, 2016/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center, has been conducting environmental remediation of the Ningyo-toge mine and Togo mine, after decades of mine-related activities including uranium exploration, mining and test milling were terminated, with doing safety measure, under Mining Safety law. As the one, culvert installation and multi-layered capping were performed at Upstream of Yotsugi Mill Tailings Pond to inspect about stability of multi-layered capping with checking rainwater infiltration restraint and radon dissipation inhibiting effect, from FY 2011 to FY 2012. And it was presumed possibility of amount of underground water is increased, as result of fluctuation numerical analysis for Upstream of Yotsugi Mill Tailings Pond before and after the multi-layered capping, and the water level of bowling holes around the Pond and spring water which flows from lower place of the Pond. But a culvert possesses enough drainage function and groundwater does not rise to the multi-layered capping part. Therefore, it is considered that there isn't problem to the stability of the current state of the multi-layered capping, but we will continue the monitoring of the water level of the bowling hole around the Pond, and the spring water which flows from lower place of the Pond.
Yokoyama, Kaoru; Hata, Haruhi; Naganuma, Masaki; Ohara, Yoshiyuki; Ishimori, Yuu
Radioisotopes, 64(11), p.687 - 696, 2015/11
Authors developed the new analysis technique (hereinafter referred to as the equivalent model) which calculates the amount of uranium by correcting the influence of uneven distribution of the uranium. Two  rays different in the shelter effect are used in the equivalent model. The
rays different in the shelter effect are used in the equivalent model. The  rays (766 keV, 1001 keV) released from
rays (766 keV, 1001 keV) released from 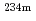 Pa are used for uranium quantitative determination. The quantity error is decided by the
Pa are used for uranium quantitative determination. The quantity error is decided by the  ray with the small calculation rate. The way to get the high calculation rate is considered to reduce the quantity error. Many
ray with the small calculation rate. The way to get the high calculation rate is considered to reduce the quantity error. Many  rays are scattered by the Compton effect in radioactive waste, and scattered photons occur. We applied the scattered photon with the big count rate to equivalent model. It was effective to apply the count rate of the scattered photon by the Compton effect to equivalent model.
rays are scattered by the Compton effect in radioactive waste, and scattered photons occur. We applied the scattered photon with the big count rate to equivalent model. It was effective to apply the count rate of the scattered photon by the Compton effect to equivalent model.
 -ray spectra
-ray spectraHata, Haruhi; Yokoyama, Kaoru; Ishimori, Yuu; Ohara, Yoshiyuki; Tanaka, Yoshio; Sugitsue, Noritake
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 104, p.143 - 146, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:71.70(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)We investigated the feasibility of using support vector machine (SVM), a computer learning method, to classify uranium waste drums as natural uranium or reprocessed uranium based on their origins. The method was trained using 12 training datasets were used and tested on 955 datasets of  -ray spectra obtained with NaI(Tl) scintillation detectors. The results showed that only 4 out of 955 test datasets were different from the original labels-one of them was mislabeled and the other three were misclassified by SVM. These findings suggest that SVM is an effective method to classify a large quantity of data within a short period of time. Consequently, SVM is a feasible method for supporting the scaling factor method and as a supplemental tool to check original labels.
-ray spectra obtained with NaI(Tl) scintillation detectors. The results showed that only 4 out of 955 test datasets were different from the original labels-one of them was mislabeled and the other three were misclassified by SVM. These findings suggest that SVM is an effective method to classify a large quantity of data within a short period of time. Consequently, SVM is a feasible method for supporting the scaling factor method and as a supplemental tool to check original labels.
Nagayasu, Takaaki; Torikai, Kazuyoshi; Ohara, Yoshiyuki; Uechi, Yasufumi
Journal of MMIJ, 131(6), p.357 - 358, 2015/06
no abstracts in English
Yokoyama, Kaoru; Hata, Haruhi; Ohara, Yoshiyuki; Naganuma, Masaki; Sugitsue, Noritake
Radioisotopes, 63(12), p.559 - 566, 2014/12
The amount of  U in uranium-contaminated waste drums generated in the decommissioning of nuclear facilities is evaluated using
U in uranium-contaminated waste drums generated in the decommissioning of nuclear facilities is evaluated using  ray measurement. We used the
ray measurement. We used the  -ray measurement system made from CANBERRA: Qualitative and Quantitative (Q
-ray measurement system made from CANBERRA: Qualitative and Quantitative (Q ) Low Level Waste Assay Systems and measured the waste drum. This equipment assumes uniform distribution of the uranium radiation source. But, homogeneity is not checked with a real waste drum. Authors developed the new analysis technique which calculates the amount of uranium by correcting the influence of uneven distribution of the uranium radiation source. As a result of evaluating using the new analysis technique, the error which the radiation source uneven distribution in a drum gives to
) Low Level Waste Assay Systems and measured the waste drum. This equipment assumes uniform distribution of the uranium radiation source. But, homogeneity is not checked with a real waste drum. Authors developed the new analysis technique which calculates the amount of uranium by correcting the influence of uneven distribution of the uranium radiation source. As a result of evaluating using the new analysis technique, the error which the radiation source uneven distribution in a drum gives to  U quantitative value of this equipment has been evaluated.
U quantitative value of this equipment has been evaluated.
Yokoyama, Kaoru; Rong, D.*; Ohara, Yoshiyuki
Kagaku Kogaku, 78(11), p.818 - 821, 2014/11
By the thermal disposal of the city garbage polluted with radioactive cesium, Cs adheres to incineration ashes and remains in municipal waste incineration facility. In order to acquire the distribution information in the waste incineration plant of the incineration ashes to which Cs adhered from viewpoints of radiation protection, burning analysis is conducted with the existing incinerator and the action of incineration ashes is evaluated. This approach is introduced by this report.
Naganuma, Masaki; Ohara, Yoshiyuki; Miyamoto, Yasunori*; Murashita, Tatsuya*; Makita, Akinori*; Nohiro, Tetsuya*
JAEA-Technology 2014-012, 11 Pages, 2014/06
In Japan Atomic Energy Agency Ningyo-toge environmental engineering center, exploration for uranium and technical development of uranium refining, conversion and enrichment which are the front end of a nuclear fuel cycle have been performed since 1955. In 2002, we introduced Q2 low-level-waste drum measuring system which is a bulk measuring method of the passive  ray. In 2007, OS2 analyzing operation system which was used in Q2, was replaced with windows system. This replacement improved the performance of the analysis of Q2. But quantified values of uranium obtained from win system did not correspond exactly to OS2 system. We considered whether the drum which was measured by OS2 system, was measured again by windows system. But it was difficult to measure these drum by win system. So in this study, we studied a calculation method for adjusting quantified values of uranium obtained by each system.
ray. In 2007, OS2 analyzing operation system which was used in Q2, was replaced with windows system. This replacement improved the performance of the analysis of Q2. But quantified values of uranium obtained from win system did not correspond exactly to OS2 system. We considered whether the drum which was measured by OS2 system, was measured again by windows system. But it was difficult to measure these drum by win system. So in this study, we studied a calculation method for adjusting quantified values of uranium obtained by each system.
 low level waste assay systems
low level waste assay systemsYokoyama, Kaoru; Hata, Haruhi; Ohara, Yoshiyuki; Sugitsue, Noritake
Radioisotopes, 62(11), p.833 - 840, 2013/11
We have proposed a new theory on passive  assay for
assay for  U determination of uranium-contaminated waste drums. According to this theory, regardless of the inhomogeneity of waste matrix density or uranium source distribution, we can accurately determine the amount of
U determination of uranium-contaminated waste drums. According to this theory, regardless of the inhomogeneity of waste matrix density or uranium source distribution, we can accurately determine the amount of  U contained in drums nondestructively using count rates of rays of two energies (1001 keV and 766 keV) emitted from
U contained in drums nondestructively using count rates of rays of two energies (1001 keV and 766 keV) emitted from  U progeny nuclide
U progeny nuclide 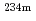 Pa. This technique is aimed final at introducing into the existing
Pa. This technique is aimed final at introducing into the existing  ray measuring device. In this paper, we have verified the theory using the existing
ray measuring device. In this paper, we have verified the theory using the existing  ray measuring device by tests under various simulated waste drums conditions. We used the
ray measuring device by tests under various simulated waste drums conditions. We used the  -ray measurement system made from CANBERRA: Qualitative and Quantitative (Q
-ray measurement system made from CANBERRA: Qualitative and Quantitative (Q ) Low Level Waste Assay Systems. The application validity of this evaluation technique was shown.
) Low Level Waste Assay Systems. The application validity of this evaluation technique was shown.
Ohara, Yoshiyuki; Naganuma, Masaki; Nohiro, Tetsuya*; Yoshida, Kimikazu*; Makita, Akinori*; Sakate, Mitsuo*; Irisawa, Takumi*; Murashita, Tatsuya*
JAEA-Technology 2012-048, 39 Pages, 2013/03
In Japan Atomic Energy Agency Ningyo-Toge Environmental Engineering Center, exploration for uranium and technical development of uranium refining, conversion and enrichment which are the front end of a nuclear fuel cycle have been performed since 1955. By these research and development, about 15000 radioactive waste (200 liter drum) has occurred by now. The analytical and measurement technique of the amount of uranium which are included in radioactive waste drum were very an inexperienced in those days. Therefore, measurement strict till 2002 was not able to be started. Such a situation as this, we introduced "Q2 low-level-waste drum measuring system" which is a bulk measuring method of the passive  ray using a NaI scintillation detector in 2002. As a result, the total amount of uranium in a waste drum was estimated as about 20 tons.
ray using a NaI scintillation detector in 2002. As a result, the total amount of uranium in a waste drum was estimated as about 20 tons.
 1 pathway on human umbilical vein endothelial cells; Comparison between X-ray and carbon-ion beam irradiation
1 pathway on human umbilical vein endothelial cells; Comparison between X-ray and carbon-ion beam irradiationKiyohara, Hiroki*; Ishizaki, Yasuki*; Suzuki, Yoshiyuki*; Kato, Hiroyuki*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Ono, Tatsuya*; Takahashi, Takeo*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Nakano, Takashi*
Journal of Radiation Research, 52(3), p.287 - 292, 2011/03
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:51.68(Biology)Yamasaki, Chisato*; Murakami, Katsuhiko*; Fujii, Yasuyuki*; Sato, Yoshiharu*; Harada, Erimi*; Takeda, Junichi*; Taniya, Takayuki*; Sakate, Ryuichi*; Kikugawa, Shingo*; Shimada, Makoto*; et al.
Nucleic Acids Research, 36(Database), p.D793 - D799, 2008/01
Times Cited Count:52 Percentile:70.47(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Here we report the new features and improvements in our latest release of the H-Invitational Database, a comprehensive annotation resource for human genes and transcripts. H-InvDB, originally developed as an integrated database of the human transcriptome based on extensive annotation of large sets of fulllength cDNA (FLcDNA) clones, now provides annotation for 120 558 human mRNAs extracted from the International Nucleotide Sequence Databases (INSD), in addition to 54 978 human FLcDNAs, in the latest release H-InvDB. We mapped those human transcripts onto the human genome sequences (NCBI build 36.1) and determined 34 699 human gene clusters, which could define 34 057 protein-coding and 642 non-protein-coding loci; 858 transcribed loci overlapped with predicted pseudogenes.
Enoeda, Mikio; Ohara, Yoshihiro; Akiba, Masato; Sato, Satoshi; Hatano, Toshihisa; Kosaku, Yasuo; Kuroda, Toshimasa*; Kikuchi, Shigeto*; Yanagi, Yoshihiko*; Konishi, Satoshi; et al.
JAERI-Tech 2001-078, 120 Pages, 2001/12
This report is a summary of the design works, which was discussed in the design workshop held in 2000 for the demonstration (DEMO) blanket aimed to strengthen the commercial competitiveness and technical feasibility simultaneously. The DEMO blanket must supply the feasibility and experience of the total design of the power plant and the materials. This conceptual design study was performed to determine the updated strategy and goal of the R&D of the DEMO blanket which applies the supercritical water cooling proposed in A-SSTR, taking into account the recent progress of the plasma research and reactor engineering technology.