Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Oki, Shigeo; Maruyama, Shuhei; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Ohtaki, Akira; Kubo, Shigenobu; Hibi, Koki*; Kan, Taro*
Proceedings of 2017 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2017) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2017/04
Ono, Kiyoshi; Shiotani, Hiroki; Ohtaki, Akira; Mukaida, Kyoko; Abe, Tomoyuki
Proceedings of International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles; Safe Technologies and Sustainable Scenarios (FR-13) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2013/03
In parallel to the mid-term analyses by the AEC after the Fukushima-accident, JAEA implemented the long-term scenario analyses for the nuclear fuel cycle options including FR cycle deployment. As a result, it was revealed that FR cycle deployment brings great benefits to reduction of uranium demand, spent fuel storage, radioactive waste generation, and Pu stockpiles in addition to potential hazard of HLW in "20 GWe constant after 2030" case. Meanwhile, it was also revealed the benefits of reduction of radioactive waste generation and Pu stockpiles in "Gradual decrease from 20 GWe after 2030" case.
Koma, Yoshikazu; Yano, Kimihiko; Ohtaki, Akira; Sato, Koji
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2005/10
On the course of changing the fuel cycle of thermal reactors into that based on fast reactors, those reactors share the capacity of electricity generation. The first commercial aqueous reprocessing plant for the fuels from a sodium cooled fast reactor was investigated in having a function of thermal reactor fuel treatment. After summarizing the differences in reprocessing fast and thermal reactor "FATHER" fuels, a process considering the change of head end and addition of secondary crystallization was proposed. Arrangement of the additional equipments was made and the resulted increase of the plant volume seems only a slight difference. For reprocessing the FATHER fuels at a throughput of 200 t/y, a plant for fast reactor fuels is appropriate for the design basis.
Shiotani, Hiroki; Ohtaki, Akira; Ono, Kiyoshi; Hirao, Kazunori; Kato, Atsushi; Yasumatsu, Naoto*; Kubota, Sadae*
JNC TN9400 2004-052, 514 Pages, 2004/09
This report presents the outline of the development and the results of characteristic evaluation on the candidate Fast Reactor (FR) cycle system concepts, scenario study on FR cycle deployment and cost-benefit analysis on the candidate FR cycle system concepts in the interim evaluation (FY2001 through FY2003) of the second phase of the Japanese "Feasibility Study on Commercialization of Fast Breeder Reactor Cycle System (FS)".
Ono, Kiyoshi; Ohtaki, Akira; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Nakagiri, Toshio; ; Sekine, Takashi;
JNC TN9410 2004-013, 76 Pages, 2004/06
This report describes the features of technology, the schedule and the organization for the research and development regarding the hydrogen production technology using FBR thermal energy. Now, the hydrogen production system is proposed as one of new business models for FBR deployment. This system is the production of hydrogen either thermal energy at approximately 500deg-C or electricity produced by a sodium cooled FBR. Hydrogen is expected to be one of the future dean secondary energies without carbon-dioxide emission. Meanwhile the global energy demand will increase, especially in Asian countries, and the energy supply by fossil fuels is not the best choice considering the green house effect and the stability of energy supply. The development of the hydrogen technology using FBR that satisfies "sustainable energy development" and "utilization of energies free from environmental pollution" will be one of the promising options. Based on the above mentioned recognition, we propose the direction of the development, the issues to be solved, the time schedule, the budget, and the organization for R&D of three hydrogen production technologies, the thermochemical hybrid process, the low temperature steam reforming process, and the high temperature steam electrolysis process in JNC.
; Ohtaki, Akira;
JNC TN9410 2003-002, 84 Pages, 2003/05
In the "Feasibility Study on Commercialized FBR Cycle Systems (F/S)", scenario evaluations, cost-benefit evaluations and system charactelistic evaluations to show the significance of the FBR cycle system introduction concretely are performed while design studies for FBR Plants, reprocessing systems and fabrication systems are conducted. In these evaluations, future society of various conditions and situation is assumed, and investigation and analysis about needs and social effect of FBR cycle are carried out. In this study, promising FBR cycle concepts are suggested by taking information such as domestic and foreign policies and bills, an economic prediction, a supply and demand prediction of resources, a project of technology development into consideration in addition to system design information. The development of the FBR Cycle Database which this report introduced started in 1999 fiscal year to enable managed unitarily and searched reference information to use for the above scenario evaluations, cost-benefit evaluations and system characteristic evaluations. In 2000 fiscal year, its prototype was made and used tentatively, and we extracted the problems in operation and functions from that, and, in 2001 fiscal year, the entry system and the search system using the Web page were made in order to solve problems of the prototype, and started use in our group. Moreover, in 2002 fiscal year, we expanded and improved the search system and promoted the efficiency of management work, and use in JNC through intranet of the database was started. In addition, as a result of having made the entry of about 350 data in 2002 fiscal year, the collected number of the database reaches about 7,250 by the end of March, 2003. We are to continue the entry of related information of various evaluations in F/S Phase 2 from now on. In addition, we are to examine improvement of convenience of the search system and cooperation with the economy database.
Ohtaki, Akira; ; ;
JNC TN9400 2002-035, 43 Pages, 2002/06
This report provides the results of our investigation about the new harmonized concept of hard energy path and soft energy path in the future hydrogen society, as a part of FBR cycle introduction scenario study in the JNC's "Feasibility Study on Commercialized Fast Reactor Cycle System". First, we considered that an environmental preservation policy and hydrogen utilization might be the current in the 21st century, then, investigated the supply-and-demand status of resources and energy in hydrogen society. Furthermore, the harmonized image of a nuclear fuel cycle and soft energy paths (distributed power supplies, fuel cell vehicle, chemical plant, etc.) was investigated. Nuclear fuel cycle is considered to contribute to the supply of the platinum group metals whose the increase in demand will be expected in hydrogen society in addition to production of the CO free energies (electric power, hydrogen, etc.) by nuclear energy. And the range of the supply-and-demand balance of the platinum group metals recovered from the reprocessed waste was calculated. Fufthermore, its radioactivity characteristics and the problem on the utilization of the recovered elements was evaluated. In order to propose the supply system of the resource and energy preserving the environment. We are going to study the infrastructure for the supply of recovered elements and CO
free energies (electric power, hydrogen, etc.) by nuclear energy. And the range of the supply-and-demand balance of the platinum group metals recovered from the reprocessed waste was calculated. Fufthermore, its radioactivity characteristics and the problem on the utilization of the recovered elements was evaluated. In order to propose the supply system of the resource and energy preserving the environment. We are going to study the infrastructure for the supply of recovered elements and CO free energy.
free energy.
; Ohtaki, Akira;
JNC TN9400 2002-034, 41 Pages, 2002/06
In the "Feasibility Study on Commercialized Fast Reactor Cycle System (F/S)", scenario evaluations, cost-benefit evaluations and system characteristic evaluations to show significance of the Fast Breeder Reactor (FBR) cycle system introduction concretely are performed in parallel with a design study for FBR plants, reprocessing systems and fabrication systems. In these evaluations, informations such as economic prospects, prospects for supply and demand of resources and a progress of engineering development are used in addition to design information. This report explains a FBR Cycle Database in order to carry out management and search of various design information and the relating information. The prototype system of the database was completed in the 2000 fiscal year, and the problem of the user number restriction of the prototype system has been improved by Web-ization in the 2001 fiscal year, About 7,000 data are stored in this data base (as of the end of March, 2002). The expansion of user etc., and the continuation of input work of various evaluation information will be carried out, in the phase 2 of F/S.
Ohtaki, Akira; ;
JNC TN9400 2002-033, 97 Pages, 2002/03
This report concerns it self with the results of an investigation about the possibility of future nuclear utilization in the part of FBR cycle introduction scenario study in the JNC's "Feasibility Study on Commercialized Fast Reactor Cycle System (theF/S)". We have investigated about the problems that confront energy industries and electric power companies, the capacities of distributed generation, the coexistence method of a distlibuted generation and large-scale power supply generation, and the development status of a small-scale nuclear reactor from a wide viewpoint. Especially the spread of distributed generation causes the decrease of the electlicity demand which the electric power companies supplies. Since introduction scale of a distributed power supply is also expeceted to increase in the future, it will give some influences to a future nuclear plan and a power supply plan. The hydrogen utilization with out greenhouse gas mission is expected to spread with distributed generation, such as a fuel cell and a micro-gas turbine. Therefore,we proposed the new business model that the hydrogen produced by using uclear surplus electricity is consumed distributed generation, such as a fuel cell and a micro-gas turbine. We plan to evaluate quantitatively the best power supply composition based on this load stability business model, FBR introduction capacities, the load factor, and the amount of CO reduction.
reduction.
; Ohtaki, Akira; Kofuji, Hirohide; Ono, Kiyoshi; Hirao, Kazunori
Saikuru Kiko Giho, (12), p.105 - 115, 2001/09
None
; Ohtaki, Akira; Kofuji, Hirohide; ;
JNC TN9400 2001-061, 335 Pages, 2001/03
This report is intended to explain the outline of the characteristic evaluation work on various FR cycle system concepts, following the design work, in the 1st phase of the JNC's "Feasibility Study on Commercialized Fast Reactor Cycle System (the F/S)" (from 1999 to March 2001). The purpose of this characteristic evaluation is to reveal the performance of candidate FR cycle systems. For this synthetic estimation, six viewpoints, such as Economics, Effective utilization of uranium resource, Reduction of environmental impact, Safety, Proliferation resistance, and Technological feasibility, are selected. In addition, aiming at the practical use in phase 2, we examined an application to FBR research and development of cost benefit analysis method used for the policy evaluation. Furthermore, long-term nuclear material mass flow was analyzed and the scenario of "FBR application for the hydrogen production" is proposed, considering how FBR would be utilized for the 21st century. And, a database including the various documents & data used for evaluation was constructed.
Ono, Kiyoshi; Kofuji, Hirohide; Ohtaki, Akira; Yonezawa, Shigeaki; ; ;
JNC TN9400 2001-036, 151 Pages, 2000/12
This study on success scenarios for the Fast Breeder Reactor (FBR) deployment was performed taking account of future situation of fossil, renewable and nuclear energies in Japan as well as the world from the viewpoints of the following four items; economics, environment, energy security and restriction of natural uranium resources. In the economics scenario, if carbon tax is added to generating cost of LNG, coal and oil and the economics of FBR cycle is competitive with LWR cycle in the future, FBR cycle will be expected to introduce as the middle and base load power plant. In the environment scenario, there is also any possibility that FBR cycle which can burn and transmute minor actinide and fission product elements will be introduced in order to reduce the burden of deposit facility and the toxicity of high-level waste. In the uranium resources restriction scenario, FBR cycle needs to be deployed at the latest in the middle of 21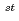 century from the viewpoint of the restriction of natural uranium resources. This study was carried out in a part of JNC's feasibility study on commercialized FBR cycle system.
century from the viewpoint of the restriction of natural uranium resources. This study was carried out in a part of JNC's feasibility study on commercialized FBR cycle system.
; Ohtaki, Akira; ; ;
JNC TN9400 2001-028, 51 Pages, 2000/12
This scenario study on the global nuclear energy was performed from the viewpoints of the maximum utilization of natural uranium resources, in order to clarify the role of nuclear energy in the future global primary energy supply. Social conditions, such as site issue and financial issue, aren't taken into consideration. Main three scenarios set up in this study are as follows, (1)LWR once-through (2)LWR with plutonium recycling (3)LWR+FBR From preliminary estimation, the following results were obtained. In the LWR once-through scenario and the LWR with plutonium recycling scenario, the nuclear energy can't support energy supply in the reference case B estimated by IIASA/WEC in the Global Energy Perspectives 1998. The nuclear energy decreases gradually after the middle of 21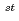 century and exhausts uranium resource to phase out till the beginning of 22
century and exhausts uranium resource to phase out till the beginning of 22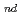 century. On the other hand, if the FBR cycle is introduced in the future for Plutonium utilization, the nuclear energy is expected to be one of the most important sustainable energy options beyond the next century.
century. On the other hand, if the FBR cycle is introduced in the future for Plutonium utilization, the nuclear energy is expected to be one of the most important sustainable energy options beyond the next century.
Ohtaki, Akira; ; ; ; ;
JNC TN9410 2000-006, 74 Pages, 2000/04
To evaluate materials balance in nuclear fuel cycle quickly and quantitatively the fuel cycle requirement code "FAMILY" was improved. And an accumulated TRU&LLFP quantity analysis code was developed. The contents are as follows: (1)A calculation ability of minor actinide production and expenditure was added to the "FAMILY" code. (2)An output program for the "FAMILY" calculation results was developed. (3)A simple version of "FAMILY" code was developed. (4)An analysis code for accumulated TRU&LLFP quantity in nuclear fuel cycle was developed.
; Ohtaki, Akira
PNC TN9460 96-005, 66 Pages, 1996/05
In order to facilitate plant dynamic analysis by Super-COPD, the pre- and post-processor programs of the code were developed. The pre-processor program converts the measured data into the input data as boundary conditions of Super-COPD. The post-processor program converts the measured data into the output format of Super-COPD. This data conversion enables direct comparisons between measured and calculated data through the plotting utility programs. The pre- and post-processor programs developed in this report are very useful to set the input data and the post process data in short time.
Ohtaki, Akira;
PNC TN9410 96-142, 102 Pages, 1996/04
In order to evaluate the pressure history at the leaked position and the amount of sodium leakage regarding the sodium leak accident of MONJU, the plant system dynamics were calculated by Super-COPD. It was estimated from the calculated results that the sodium leakage was halted around 23:28, which was 3 hours and 41 minutes after the initiation. The pressure loss coefficient of the leaked position was evaluated to be 2.16 in two kinds of the water experiments of PNC and of Toshiba-IHI. Using cofficient to the calculated pressure history, the minimum and the maximum leakage rates were evaluated to be 35.5 and 51.9g/sec respectively, and the average rate was 48.9g/sec. Therefore, the total amount of sodium leakage was estimated to be 650 38kg.
38kg.
Ohtaki, Akira
PNC TN9410 96-054, 170 Pages, 1995/12
In this paper analyses of natural circulation simulation tests in Monju were conducted to study the applicability of a plant dynamics analysis code (Super-COPD) to the evaluation of decay heat removal by natural circulation. At first basic characteristics of both primary and secondary heat transport systems were examined by separate analyses and then integral system analyses with primary and secondary systems were conducted to confirm the whole system behavior. A modeling of the reactor core and pressure loss characteristics were selected as analysis parameters in the primary system analyses. The effect of the overflow line on natural circulation characteristics were examined in the secondary system analyses. By the separate analyses it was indicated that a precise modeling of core flow channels and input data of axial height for calculating natural circulation head were important for the evaluation of natural circulation characteristics. In addition in the case of low flow condition (about 1-2% of rated flow), the effect of thermal stratification in the horizontal pipe on natural circulation head was observed during the transition to natural circulation condition. Therefore, the need of modeling for thermal stratification in the piping system was pointed out. The switching of flow direction from forward flow to back flow observed at the evaporator side in the secondary system was successfully simulated by the consideration of the overflow line. The results of synthesis analyses with primary and secondary systems were agreed with the measured data in Monju within the accuracy of 10%. Thus it was confirmed that Super-COPD is applicable to the evaluation of decay heat removal by natural circulation.
; ; ; ; Ohtaki, Akira; ; Hayashi, Kenji
PNC TN9410 95-187, 194 Pages, 1995/07
The Large Scale Thermal Hydraulic Test has been examined by Large Scale Thermal Hydraulic Test Working Group consisted of specialists in O-arai Engineering Center. The examination in the Japanese fiscal year 1995 was advanced the main subjects from the fundamental technology for the commercial FBR to that for the demon-stration FBR. The procedure in this year was as follows. (1)Review the technical subjects deduced last year and re-select to the commercial FBR design, (2)To make clear the role of the analysis and experiments for the future design, (3)To fix the theme of this test, and (4)To narrow down the fundamental ideas for the test facility. The test themes for these subjects were focused on and the fundamental ideas for the test facility were narrowed down to 3. The cost of these three kinds of facilities were also roughly compared. Finally the plan for each test was examined and the necessary specification for the facility were selected. This report describes these results and the test plans for the Large Scale Thermal Hydraulic Test. These results will be advanced in the study for the Large Scale Thermal Hydraulic Test Plan next year.
Ohtaki, Akira; Miyakawa, Akira; Nakai, Satoru
PNC TN9410 95-060, 204 Pages, 1995/02
The modular integrated plant dynamics analysis code "Super-COPD" is being developed. The validation of the code by using the MONJU functional test data was carried out to evaluate the accuracy of the calculation models and the validation results that had been carried out by using scale model test data. The procedure of the validation was as follows: (1)Setting up of the MONJU system data. The plant system data were set up by the tests data. (2)Refinement of the I/O. An input/output program for the MONJU test data was added to the code. (3)Evaluation of the test data. The test data to be used for the validation and program module to be validated were identified. The intermediate heat exchanger (IHX), steam generator (SG) and auxiliary cooling system (ACS) were selected as validation components. (4)Validation. The performance of some components was evaluated. The calculation and modification of the code were carried out. The following results were obtained. (1)IHX. The recommended calculation mesh number and plenum heat capacity and the items to be validated by the start up test were obtained. (2)SG. The recommended heat loss, validity of plenum model and the effectiveness of the flow rate to the thermal calculation were confirmed. A new model for the change of effective flow area in the SG may be needed at very low flow rate. (3)ACS. The ACS thermal/hydraulics were evaluated. The accuracy of air cooler thermal/hydraulics models, interlock/control system models, vane/blower models were validated. The accuracy of the calculation models and the validation results by using scale models was confirmed. Validation of the code using the start up test results under power operation is scheduled.
Ohtaki, Akira; ; Tanabe, Hiromi
PNC TN9410 93-137, 142 Pages, 1993/04
A plant thermal transient analysis on 600MWe class plant in FY1992 was carried out. A module integrated plant dynamics analysis code Super-COPD was used for the analysis and five analysis cases were chosen to evaluate the plant dynamics characteristics. Four of cases were from Monju operation mode III and one was water/steam re-circulation system failure. A plant system to mitigate thermal transient were examined and evaluated. Followings are summary of each case: (1)[Primary main pump stick] A temperature drop of 145 deg occurred in intermediate heat transfer system (IHTS) cold leg. By decreasing the safety system operation time, secondary pump flow coast down time and secondary loop pony motor flow, the temperature drop was decreased to 60 deg that is smaller than that of Monju. (2)[Secondary main pump stick] There were no significant differences between this plant and Monju. (3)[Main steam and feed water pipe rupture] Twenty minutes after the rupture, a temperature rise to 435 deg in IHTS cold leg. This was caused by large sodium flow rate in steam generator so that hot leg temperature flew down through steam generator to the cold leg without heat exchange. This temperature raise was cleared by decreasing the sodium flow rate in the steam generator. (4)[water/steam re-circulation system failure] The objective of this system is to mitigate the thermal transient and shorten the plant restart. On the contrary, in case of failure, steam generator exit sodium temperature dropped rapidly to feed water temperature and also whole plant temperature decreased rapidly. The new interlock which cuts the feed water with a low signal of steam generator exit sodium temperature, can mitigate this temperature drop.