Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yomogida, Takumi; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Okumura, Takuma*; Yamada, Shinya*; Tatsuno, Hideyuki*; Noda, Hirofumi*; Hayakawa, Ryota*; Okada, Shinji*; Takatori, Sayuri*; Isobe, Tadaaki*; et al.
Analyst, 149(10), p.2932 - 2941, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:40.01(Chemistry, Analytical)In this study, we successfully applied a transition-edge sensor (TES) spectrometer as a detector for microbeam X-ray measurements from a synchrotron X-ray light source to determine uranium (U) distribution at the micro-scale and its chemical species in biotite obtained from the U mine. It is difficult to separate the fluorescent X-ray of the U L
 line at 13.615 keV from that of the Rb K
line at 13.615 keV from that of the Rb K line at 13.395 keV in the X-ray fluorescence spectrum with an energy resolution of approximately 220 eV of the conventional silicon drift detector (SDD). Meanwhile, the fluorescent X-rays of U L
line at 13.395 keV in the X-ray fluorescence spectrum with an energy resolution of approximately 220 eV of the conventional silicon drift detector (SDD). Meanwhile, the fluorescent X-rays of U L
 and Rb K
and Rb K were fully separated by TES with 50 eV energy resolution at the energy of around 13 keV. The successful peak separation by TES led to an accurate mapping analysis of trace U in micro-X-ray fluorescence measurements and a decrease in the signal-to-background ratio in micro-X-ray absorption near edge structure spectroscopy.
were fully separated by TES with 50 eV energy resolution at the energy of around 13 keV. The successful peak separation by TES led to an accurate mapping analysis of trace U in micro-X-ray fluorescence measurements and a decrease in the signal-to-background ratio in micro-X-ray absorption near edge structure spectroscopy.
 -edge for Ce in bauxites using transition-edge sensors; Implications for Ti-rich geological samples
-edge for Ce in bauxites using transition-edge sensors; Implications for Ti-rich geological samplesLi, W.*; Yamada, Shinya*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Okumura, Takuma*; Hayakawa, Ryota*; Nitta, Kiyofumi*; Sekizawa, Oki*; Suga, Hiroki*; Uruga, Tomoya*; Ichinohe, Yuto*; et al.
Analytica Chimica Acta, 1240, p.340755_1 - 340755_9, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:66.73(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
Okutsu, Kenichi*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Kino, Yasushi*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Oka, Toshitaka; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*
JJAP Conference Proceedings (Internet), 9, p.011003_1 - 011003_7, 2023/00
Muon catalyzed fusion ( CF) is a cyclic reaction where a negatively charged muon itself acts like a catalyst of nuclear fusion between hydrogen isotopes. In the
CF) is a cyclic reaction where a negatively charged muon itself acts like a catalyst of nuclear fusion between hydrogen isotopes. In the  CF reaction, muon transfer from deuteron to triton and muonic molecular formation are rate-limiting processes. In this work, we have investigated the role of resonance states of muonic molecule in the
CF reaction, muon transfer from deuteron to triton and muonic molecular formation are rate-limiting processes. In this work, we have investigated the role of resonance states of muonic molecule in the  CF which affects the muonic deuterium atom population. Solving simultaneous rate equations numerically by the fourth-order Runge-Kutta method, we determined the muonic molecular formation rate so that the number of fusion events reproduces a latest experimental result. It is revealed that the resonance states play a role to enhance the fusion rate by accelerating the de-excitation of the muonic atoms.
CF which affects the muonic deuterium atom population. Solving simultaneous rate equations numerically by the fourth-order Runge-Kutta method, we determined the muonic molecular formation rate so that the number of fusion events reproduces a latest experimental result. It is revealed that the resonance states play a role to enhance the fusion rate by accelerating the de-excitation of the muonic atoms.
Okutsu, Kenichi*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 170, p.112712_1 - 112712_4, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:31.52(Nuclear Science & Technology)A muonic molecule which consists of two hydrogen isotope nuclei (deuteron (d) or tritium (t)) and a muon decays immediately via nuclear fusion and the muon will be released as a recycling muon, and start to find another hydrogen isotope nucleus. The reaction cycle continues until the muon ends up its lifetime of 2.2  s. Since the muon does not participate in the nuclear reaction, the reaction is so called a muon catalyzed fusion (
s. Since the muon does not participate in the nuclear reaction, the reaction is so called a muon catalyzed fusion ( CF). The recycling muon has a particular kinetic energy (KE) of the muon molecular orbital when the nuclear reaction occurs. Since the KE is based on the unified atom limit where distance between two nuclei is zero. A precise few-body calculation estimating KE distribution (KED) is also in progress, which could be compared with the experimental results. In the present work, we observed recycling muons after
CF). The recycling muon has a particular kinetic energy (KE) of the muon molecular orbital when the nuclear reaction occurs. Since the KE is based on the unified atom limit where distance between two nuclei is zero. A precise few-body calculation estimating KE distribution (KED) is also in progress, which could be compared with the experimental results. In the present work, we observed recycling muons after  CF reaction.
CF reaction.
Yamashita, Takuma*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 169, p.112580_1 - 112580_5, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:31.52(Nuclear Science & Technology)A muon ( ) having 207 times larger mass of electron and the same charge as the electron has been known to catalyze a nuclear fusion between deuteron (d) and triton (t). These two nuclei are bound by
) having 207 times larger mass of electron and the same charge as the electron has been known to catalyze a nuclear fusion between deuteron (d) and triton (t). These two nuclei are bound by  and form a muonic hydrogen molecular ion, dt
and form a muonic hydrogen molecular ion, dt . Due to the short inter-nuclear distance of dt
. Due to the short inter-nuclear distance of dt , the nuclear fusion, d +t
, the nuclear fusion, d +t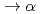 + n + 17.6 MeV, occurs inside the molecule. This reaction is called muon catalyzed fusion (
+ n + 17.6 MeV, occurs inside the molecule. This reaction is called muon catalyzed fusion ( CF). Recently, the interest on
CF). Recently, the interest on  CF is renewed from the viewpoint of applications, such as a source of high-resolution muon beam and mono-energetic neutron beam. In this work, we report a time evolution calculation of
CF is renewed from the viewpoint of applications, such as a source of high-resolution muon beam and mono-energetic neutron beam. In this work, we report a time evolution calculation of  CF in a two-layered hydrogen isotope target.
CF in a two-layered hydrogen isotope target.
Okumura, Takuma*; Azuma, Toshiyuki*; Bennet, D. A.*; Caradonna, P.*; Chiu, I.-H.*; Doriese, W. B.*; Durkin, M. S.*; Fowler, J. W.*; Gard, J. D.*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 31(5), p.2101704_1 - 2101704_4, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:14.18(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)A superconducting transition-edge sensor (TES) microcalorimeter is an ideal X-ray detector for experiments at accelerator facilities because of good energy resolution and high efficiency. To study the performance of the TES detector with a high-intensity pulsed charged-particle beam, we measured X-ray spectra with a pulsed muon beam at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) in Japan. We found substantial temporal shifts of the X-ray energy correlated with the arrival time of the pulsed muon beam, which was reasonably explained by pulse pileup due to the incidence of energetic particles from the initial pulsed beam.
 X rays
X raysOkumura, Takuma*; Azuma, Toshiyuki*; Bennet, D. A.*; Caradonna, P.*; Chiu, I. H.*; Doriese, W. B.*; Durkin, M. S.*; Fowler, J. W.*; Gard, J. D.*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 127(5), p.053001_1 - 053001_7, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:76.61(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We observed electronic  X rays emitted from muonic iron atoms using a superconducting transition-edge-type sensor microcalorimeter. The energy resolution of 5.2 eV in FWHM allowed us to observe the asymmetric broad profile of the electronic characteristic
X rays emitted from muonic iron atoms using a superconducting transition-edge-type sensor microcalorimeter. The energy resolution of 5.2 eV in FWHM allowed us to observe the asymmetric broad profile of the electronic characteristic 
 and
and 
 X rays together with the hypersatellite
X rays together with the hypersatellite 
 X rays around 6 keV. This signature reflects the time-dependent screening of the nuclear charge by the negative muon and the
X rays around 6 keV. This signature reflects the time-dependent screening of the nuclear charge by the negative muon and the  -shell electrons, accompanied by electron side-feeding. Assisted by a simulation, this data clearly reveals the electronic
-shell electrons, accompanied by electron side-feeding. Assisted by a simulation, this data clearly reveals the electronic  - and
- and  -shell hole production and their temporal evolution during the muon cascade process.
-shell hole production and their temporal evolution during the muon cascade process.
Nagae, Daisuke*; Abe, Yasushi*; Okada, Shunsuke*; Omika, Shuichiro*; Wakayama, Kiyoshi*; Hosoi, Shun*; Suzuki, Shinji*; Moriguchi, Tetsuro*; Amano, Masamichi*; Kamioka, Daiki*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 986, p.164713_1 - 164713_7, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:72.28(Instruments & Instrumentation)Abe, Mitsushi*; Bae, S.*; Beer, G.*; Bunce, G.*; Choi, H.*; Choi, S.*; Chung, M.*; da Silva, W.*; Eidelman, S.*; Finger, M.*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(5), p.053C02_1 - 053C02_22, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:156 Percentile:99.31(Physics, Multidisciplinary)This paper introduces a new approach to measure the muon magnetic moment anomaly  and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)
and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)  at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure
at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure  and
and  using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for
using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for  is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of
is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of  e
e cm.
cm.
Nakano, Masanao; Fujita, Hiroki; Kono, Takahiko; Nagaoka, Mika; Inoue, Kazumi; Yoshii, Hideki*; Otani, Kazunori*; Hiyama, Yoshinori*; Kikuchi, Masaaki*; Sakauchi, Nobuyuki*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2017-001, 115 Pages, 2017/03
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai reprocessing plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and bylaw of Ibaraki prefecture), the effluent control of liquid waste discharged from the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been performed. This report describes the effluent control results of the liquid waste in the fiscal year 2015. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other nuclear fuel material usage facilities were much lower than the limits authorized by the above regulations.
Fukushima, Mineo; Kawatsuma, Shinji; Okada, Takashi
Proceedings of American Nuclear Society Embedded Topical on Decommissioning, Decontamination and Reutilization and Technology Expo (DD&R 2012) (DVD-ROM), p.67 - 68, 2012/06
The accident on Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant has been occurred by the TSUNAMI that generated form Great East Japan Earthquake happened in 11th March 2011. Just after the earthquake, JAEA is assisting activities concerning the accident of the Fukushima No.1 Nuclear Power Station including teleoperation, decontamination and radiation monitoring in the site. JAEA had already developed some robotics, RESQ series, for radiological emergency response in 2001, after JCO criticality accidents occurred. However, they could not work for the NPP because of lack of maintenance. According to the situation and condition of the FUKUSHIMA-DAIICHI accident, JAEA has modified above mentioned robotics and prepared supporting equipments like as Robotics control vehicles. JAEA has provided Robotics and Robotics Control vehicles to TEPCO and is continuously supporting Tokyo Electric Company for plant restoration.
Kawatsuma, Shinji; Fukushima, Mineo; Okada, Takashi
Industrial Robot; An International Journal, 39(5), p.428 - 435, 2012/00
Times Cited Count:130 Percentile:95.79(Engineering, Industrial) molecular beams
molecular beamsTeraoka, Yuden; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Moritani, Kosuke; Takakuwa, Yuji*; Ogawa, Shuichi*; Ishizuka, Shinji*; Okada, Michio*; Fukuyama, Tetsuya*; Kasai, Toshio*
Hoshako, 18(5), p.298 - 309, 2005/09
Representative research results in surface reaction dynamics, performed at a surface chemistry experimental station installed in the JAEA soft X-ray beamline in the SPring-8, were reviewed. As a research result in JAEA, SiO desorption mechanisms in the Si(001) oxidation at high temperature were introduced. As a collaboration with Osaka University on oxidation reaction dynamics of Cu, collision-induced atom absorption process was introduced. As a collaboration with Tohoku University on Ti(0001) oxidation reaction dynamics, it was introduced that two peaks, found in an incident energy dependence of initial sticking probability, were corresponding to potential energy barriers of dissociative adsorption of O molecules.
molecules.
Okawa, Yoshinao; Kashimura, Shinji*; Murano, Yoshihiro*; Ito, Michio*; Okada, Kenichi*; Izumi, Keisuke*; Tsuchida, Takashi*
Dai-19-Kai Denki Setsubi Gakkai Zenkoku Taikai Koen Rombunshu, p.415 - 416, 2001/00
no abstracts in English
三村 竜二; 川妻 伸二; 岡田 尚
斉藤 義彦*
【課題】地表付近の線量率と、人体に影響を及ぼす高さ付近での線量率を同時に測定できると共に、測定地点が変更されても実質的に同一の高さにおける空間の線量率を測定することができる装置及び方法を提供すること。 【解決手段】機器支持ロッド、機器支持ロッドを把持するためのグリップ、機器支持ロッドの一端部に取り付けられたGPS受信機、グリップに関してGPS受信機と反対側の位置において、機器支持ロッドに取り付けられた、第1放射線検出器、第1放射線検出器と一定の間隔を隔てて、機器支持ロッドの一端部と反対側の他端部に取り付けられた、第2放射線検出器、第1及び/又は第2放射線検出器の測定値信号を切替えてその場で表示できると共に、それらの同時測定値信号と測定時のGPS受信機からの位置信号とを外部に送信するための装置であって、グリップよりもGPS受信機側に取り付けられた通信制御装置を備えている。
三村 竜二; 川妻 伸二; 岡田 尚
斉藤 義彦*
【課題】立木や建物の側壁など、垂直面におけるγ線の線量率マップを精確に作成するための装置を提供すること。 【解決手段】伸縮可能なロッドの先端にガイガーミューラ管を取り付け、高所におけるγ線の線量率を測定すると共に、その位置を把握するために、そのGM管と実質的に同位置のロッド上に赤外線発光部を設け、かつロッドの位置から離れた個所に赤外線カメラと可視光カメラを設置して、両者のカメラで撮像された映像を画像処理することで、赤外線発光部の位置とその位置での線量率を、可視光カメラで捉えた測定対象物上に重ねて表示するようにしている。この操作を順次位置を変えながら繰り返すことにより、例えば、建物側壁面などの線量率の分布を建物側壁の可視光写真上に表示する。
Kawatsuma, Shinji; Okada, Takashi; Fukushima, Mineo
no journal, ,
Japan Atomic Energy Agency developed Nuclear Disaster Response Robotics in 2001 after JCO criticality accidents occurred. It is very sorry that Nuclear Disaster Response Robotics could not work when the Fukushima-Daiichi accident occurred by a big earthquake and a huge Tsunami on March 11th 2011. According to the situation and condition of the Fukushima-Daiichi accident, JAEA has modified above mentioned Nuclear Disaster Response Robotics and prepared supporting equipments like as Robotics Control vehicles. JAEA has provided Robotics and Robotics Control vehicle to TEPCO and is continuously supporting TEPCO for plant restoration. This paper summarize JAEA ROBOTICS Emergency Response to Fukushima-Daiichi accident and describe lessons learned.
Yamashita, Takuma*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
A muon ( ) having 207 times larger mass of electron and the same charge as the electron has been known to catalyze a nuclear fusion (
) having 207 times larger mass of electron and the same charge as the electron has been known to catalyze a nuclear fusion ( CF) between deuteron (d) and triton (t). In this work, we have solved simultaneous reaction rate equations by the 4th-order Runge-Kutta method for the jointed
CF) between deuteron (d) and triton (t). In this work, we have solved simultaneous reaction rate equations by the 4th-order Runge-Kutta method for the jointed  CF cycles in the two layers (H
CF cycles in the two layers (H /D
/D and D
and D /T
/T ). The T
). The T concentration to maximize the intensities of fusion neutrons and muons emitted to the vacuum will be discussed.
concentration to maximize the intensities of fusion neutrons and muons emitted to the vacuum will be discussed.
 CF experiment at J-PARC MLF
CF experiment at J-PARC MLFNatori, Hiroaki*; Doiuchi, Shogo*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Kino, Yasushi*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Miyashita, Konan*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Nagatani, Yukinori*; Nishimura, Shoichiro*; Oka, Toshitaka; et al.
no journal, ,
A muonic molecule which consists of muon and two hydrogen isotope nuclei (deuteron (d) or tritium (t)) decays immediately via nuclear fusion (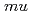 CF) and the muon will be released as a recycling muon. We attempted to use these muons to develop the scanning muon microscope. In this work, we will report the detection of neutron which emits during the
CF) and the muon will be released as a recycling muon. We attempted to use these muons to develop the scanning muon microscope. In this work, we will report the detection of neutron which emits during the  CF reaction.
CF reaction.
Miyashita, Konan*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
Muon catalyzed fusion ( CF) is a cyclic reaction where a negatively charged muon itself acts like a catalyst of nuclear fusion between hydrogen isotopes. In this work, we have designed the shape of the thermal shield to reduce the background noise.
CF) is a cyclic reaction where a negatively charged muon itself acts like a catalyst of nuclear fusion between hydrogen isotopes. In this work, we have designed the shape of the thermal shield to reduce the background noise.