Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kokubun, Yuji; Hosomi, Kenji; Seya, Natsumi; Nagaoka, Mika; Inoue, Kazumi; Koike, Yuko; Hasegawa, Ryo; Kubota, Tomohiro; Hirao, Moe; Iizawa, Shogo; et al.
JAEA-Review 2024-053, 116 Pages, 2025/03
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai Reprocessing Plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution prevention act, and by law of Ibaraki Prefecture), the effluent control of liquid waste discharged from the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been performed. This report describes the effluent control results of the liquid waste in the fiscal year 2023. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other nuclear fuel material usage facilities were much lower than the limits authorized by the above regulations.
Kokubun, Yuji; Nakada, Akira; Seya, Natsumi; Nagaoka, Mika; Koike, Yuko; Kubota, Tomohiro; Hirao, Moe; Yoshii, Hideki*; Otani, Kazunori*; Hiyama, Yoshinori*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2023-052, 118 Pages, 2024/03
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai Reprocessing Plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and by law of Ibaraki Prefecture), the effluent control of liquid waste discharged from the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been performed. This report describes the effluent control results of the liquid waste in the fiscal year 2022. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other nuclear fuel material usage facilities were much lower than the limits authorized by the above regulations.
Abeykoon, S.*; Howard, C.*; Dominijanni, S.*; Eberhard, L.*; Kurnosov, A.*; Frost, D. J.*; Boffa Ballaran, T.*; Terasaki, Hidenori*; Sakamaki, Tatsuya*; Suzuki, Akio*; et al.
Journal of Geophysical Research; Solid Earth, 128(9), p.e2023JB026710_1 - e2023JB026710_17, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:30.17(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Small amounts of iron sulphide minerals are found in most rocks from the Earth's mantle and as inclusions trapped in natural diamonds. Hydrogen may dissolve into iron sulphide minerals under high pressures and temperature, but is most likely lost once pressure and temperature are removed. In this study, we determined deuterium contents in iron sulphide, held under high pressure and temperature conditions, using neutron diffraction measurements with 6-ram multi-anvil press at PLANET, J-PARC. Deuterium contents in iron sulphide were measured at high-P, up to 11.4 GPa and high-T to 1300 K in in situ neutron diffraction experiments. The total deuterium content increases with both P and T. The results are used to estimate hydrogen contents of iron sulphide minerals in the deep continental lithospheric mantle, which are found to be in the range 1700-2700 ppm. This corresponds to approximately 2-3 ppm of hydrogen in the bulk mantle.
Nakada, Akira; Kanai, Katsuta; Kokubun, Yuji; Nagaoka, Mika; Koike, Yuko; Yamada, Ryohei*; Kubota, Tomohiro; Hirao, Moe; Yoshii, Hideki*; Otani, Kazunori*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2022-079, 116 Pages, 2023/03
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai Reprocessing Plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and by law of Ibaraki Prefecture), the effluent control of liquid waste discharged from the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been performed. This report describes the effluent control results of the liquid waste in the fiscal year 2021. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other nuclear fuel material usage facilities were much lower than the limits authorized by the above regulations.
Nakano, Masanao; Nakada, Akira; Kanai, Katsuta; Nagaoka, Mika; Koike, Yuko; Yamada, Ryohei; Kubota, Tomohiro; Yoshii, Hideki*; Otani, Kazunori*; Hiyama, Yoshinori*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2021-040, 118 Pages, 2021/12
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai Reprocessing Plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and by law of Ibaraki Prefecture), the effluent control of liquid waste discharged from the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been performed. This report describes the effluent control results of the liquid waste in the fiscal year 2020. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other nuclear fuel material usage facilities were much lower than the limits authorized by the above regulations.
Nakano, Masanao; Fujii, Tomoko; Nagaoka, Mika; Koike, Yuko; Yamada, Ryohei; Kubota, Tomohiro; Yoshii, Hideki*; Otani, Kazunori*; Hiyama, Yoshinori*; Kikuchi, Masaaki*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2020-070, 120 Pages, 2021/02
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai Reprocessing Plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and by law of Ibaraki Prefecture), the effluent control of liquid waste discharged from the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been performed. This report describes the effluent control results of the liquid waste in the fiscal year 2019. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other nuclear fuel material usage facilities were much lower than the limits authorized by the above regulations.
Nakano, Masanao; Fujii, Tomoko; Nagaoka, Mika; Inoue, Kazumi; Koike, Yuko; Yamada, Ryohei; Yoshii, Hideki*; Otani, Kazunori*; Hiyama, Yoshinori*; Kikuchi, Masaaki*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2019-045, 120 Pages, 2020/03
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai Reprocessing Plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and by law of Ibaraki Prefecture), the effluent control of liquid waste discharged from the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been performed. This report describes the effluent control results of the liquid waste in the fiscal year 2018. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other nuclear fuel material usage facilities were much lower than the limits authorized by the above regulations.
Ikuta, Daijo*; Otani, Eiji*; Sano, Asami; Shibazaki, Yuki*; Terasaki, Hidenori*; Yuan, L.*; Hattori, Takanori
Scientific Reports (Internet), 9, p.7108_1 - 7108_8, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:92.53(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Hydrogen is likely one of the light elements in the Earth's core. Despite its importance, no direct observation has been made of hydrogen in an iron lattice at high pressure. We made the first direct determination of site occupancy and volume of interstitial hydrogen in a face-centered cubic (fcc) iron lattice up to 12 GPa and 1200 K using the in situ neutron diffraction method. At pressures  5 GPa, the hydrogen content in the fcc iron hydride lattice (x) was small at x
5 GPa, the hydrogen content in the fcc iron hydride lattice (x) was small at x  0.3, but increased to x
0.3, but increased to x  0.8 with increasing pressure. Hydrogen atoms occupy both octahedral (O) and tetrahedral (T) sites; typically 0.870 in O-sites and 0.057 in T-sites at 12 GPa and 1200 K. The fcc lattice expanded approximately linearly at a rate of 2.22
0.8 with increasing pressure. Hydrogen atoms occupy both octahedral (O) and tetrahedral (T) sites; typically 0.870 in O-sites and 0.057 in T-sites at 12 GPa and 1200 K. The fcc lattice expanded approximately linearly at a rate of 2.22 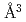 per hydrogen atom, which is higher than previously estimated (1.9
per hydrogen atom, which is higher than previously estimated (1.9 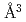 /H). The lattice expansion by hydrogen dissolution was negligibly dependent on pressure. The large lattice expansion by interstitial hydrogen reduced the estimated hydrogen content in the Earth's core that accounted for the density deficit of the core. The revised analyses indicate that whole core may contain hydrogen of 80 times of the ocean mass with 79 and 0.8 ocean mass for the outer and inner cores, respectively.
/H). The lattice expansion by hydrogen dissolution was negligibly dependent on pressure. The large lattice expansion by interstitial hydrogen reduced the estimated hydrogen content in the Earth's core that accounted for the density deficit of the core. The revised analyses indicate that whole core may contain hydrogen of 80 times of the ocean mass with 79 and 0.8 ocean mass for the outer and inner cores, respectively.
Yagmur, A.*; Karube, Shutaro*; Uchida, Kenichi*; Kondo, Kota*; Iguchi, Ryo*; Kikkawa, Takashi*; Otani, Yoshichika*; Saito, Eiji
Applied Physics Letters, 108(24), p.242409_1 - 242409_4, 2016/06
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:33.99(Physics, Applied) -bearing Mg-perovskite and its crystal chemistry at high pressure
-bearing Mg-perovskite and its crystal chemistry at high pressureMashimo, Izumi*; Otani, Eiji*; Hirao, Naohisa*; Mitsui, Takaya; Masuda, Ryo*; Seto, Makoto*; Sakai, Takeshi*; Takahashi, Suguru*; Nakano, Satoshi*
American Mineralogist, 99(8-9), p.1555 - 1561, 2014/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:22.19(Geochemistry & Geophysics) Fe
Fe O
O
Shiomi, Yuki*; Otani, Takashi*; Iguchi, Satoshi*; Sasaki, Takahiko*; Qiu, Z.*; Nakayama, Hiroyasu*; Uchida, Kenichi*; Saito, Eiji
Applied Physics Letters, 104(24), p.242406_1 - 242406_5, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:73.28(Physics, Applied)Sakamaki, Tatsuya*; Suzuki, Akio*; Otani, Eiji*; Terasaki, Hidenori*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Katayama, Yoshinori; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Wang, Y.*; Hernlund, J. W.*; Ballmer, M. D.*
Nature Geoscience, 6(12), p.1041 - 1044, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:152 Percentile:96.92(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)The bounday between Earth's rigid lighosphere and the underlying, ductile ashenosphere is marked by a distinct siseismic discontinuity. We measure the density, viscosity and structure of basaltic magmas using high-pressure and high-temperature experiments and in situ X-ray analysis under pressure of up to 5.5 GPa. We find that the magmas rapidly become denser with increasing presure and show a viscosity minimum near 4 GPa. Magma mobility determined by the density and viscosity data exhibits a peak at pressures corresponding to depths of 120-150 km, within the asthenosphere. The diminishing mobility of magma in Earth's asthenosphere as the mlets ascend could lead to excessive melt accumulation at depths of 80-100 km, at the lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary. It is concluded that the observed seismic discontinuity at the lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary records this accumulation of melt.
Watakabe, Tomoyoshi; Kaneko, Naoaki*; Aida, Shigekazu*; Otani, Akihito*; Tsukimori, Kazuyuki; Moriizumi, Makoto; Kitamura, Seiji
Dynamics and Design Conference 2013 (D&D 2013) Koen Rombunshu (USB Flash Drive), 8 Pages, 2013/08
The piping in a nuclear power plant is laid across multiple floors of a single building or two buildings, which are supported at many anchors. As the piping is excited by multiple inputs from the supporting anchors during an earthquake, seismic response analysis by multiple excitations is needed to obtain the exact seismic response of the piping. However, few tests involving such multiple excitations have been performed to verify the validity of multiple excitation analysis. To perform rational seismic design and evaluation, it is important to investigate the seismic response by multiple excitations and verify the validity of the analysis method by multiple excitation test. This paper reports on the result of the shaking test using triple uni-axial shaking tables and a 3-dimensional piping model.
Watakabe, Tomoyoshi; Kaneko, Naoaki*; Aida, Shigekazu*; Otani, Akihito*; Moriizumi, Makoto*; Tsukimori, Kazuyuki; Kitamura, Seiji
Proceedings of 2013 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2013) (DVD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2013/07
The piping in a nuclear power plant is laid across multiple floors of a single building or two buildings, which are supported at many points. As the piping is excited by multiple inputs from the supporting points during an earthquake, seismic response analysis by multiple excitations is needed to obtain the exact seismic response of the piping. However, few experiments involving such multiple excitations have been performed to verify the validity of multiple excitation analysis. To perform rational seismic design and evaluation, it is important to investigate the seismic response by multiple excitations and verify the validity of the analysis method by multiple excitation test. This paper reports on the result of the shaking test using triple uni-axial shaking tables and a 3-dimensional piping model.
Sano, Asami; Kuribayashi, Takahiro*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Yagi, Takehiko*; Otani, Eiji*
Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 189(1-2), p.56 - 62, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:53.39(Geochemistry & Geophysics)A neutron powder diffraction experiment was conducted to refine the hydrogen position of Mg-endmember deuterated wadsleyite. Preliminary refinement using the dry-structure determined by single crystal X-ray diffraction reveals a maximum peak Q1 of nuclear density in the difference Fourier map at the M3 octahedral edge, between the O1 and O4 atoms. Full Rietveld refinement was conducted assuming that the maximum peak corresponds to deuterium atom. The deuterium position was determined as (0.096, 0.289, 0.315) with occupancy of 8.2%. The structure determined by this study predicts that the hydration of wadsleyite has an anisotropic effect on diffusion properties.
Nishida, Keisuke*; Otani, Eiji*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Suzuki, Akio*; Sakamaki, Tatsuya*; Terasaki, Hidenori*; Katayama, Yoshinori
American Mineralogist, 96(5-6), p.864 - 868, 2011/05
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:68.19(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The density of liquid iron sulfide (FeS) was measured up to 3.8 GPa and 1800 K using the X-ray absorption method. The compression curve of the liquid FeS can be fitted using the Vinet equation of state. Isothermal bulk modulus and its temperature and pressure derivatives were determined by a non-linear least squares fit. Liquid FeS is more compressible than Fe-rich Fe-S liquid.
Shimada, Takahiro*; Otani, Akihito*; Iwamoto, Kosuke*; Kitamura, Seiji
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu, C, 77(777), p.1661 - 1673, 2011/05
Three dimensional seismic isolation devices have been developed for the base isolation system of the Fast Breeder Reactor that is an advanced nuclear power buildings. The developed seismic isolation system consists of the hydraulic type vertical springs with rocking suppression mechanism and the laminated rubber bearings for horizontal direction. In this paper, it is reported the frictional characteristics on high hydraulic pressure condition from the experiments on the 1/2 size of real device and the results of the seismic simulation on the real size building with isolation-device that has those characteristics.
Sakamaki, Tatsuya*; Otani, Eiji*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Terasaki, Hidenori*; Katayama, Yoshinori
American Mineralogist, 96(4), p.553 - 557, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:67.07(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The density of carbonated peridotite magma was measured up to 3.8 GPa and 2100 K using an X-ray absorption method. The bulk modulus of carbonated peridotite magma is larger than that of hydrous peridotite magma. The partial molar volume of CO in magma under high pressure and temperature conditions was calculated. Our results show that the partial molar volume of CO
in magma under high pressure and temperature conditions was calculated. Our results show that the partial molar volume of CO is less compressible than that of H
is less compressible than that of H O, suggesting that, on an equal molar basis, CO
O, suggesting that, on an equal molar basis, CO is more effective than H
is more effective than H O in reducing peridotite melt density at high pressure.
O in reducing peridotite melt density at high pressure.
Sakamaki, Tatsuya*; Otani, Eiji*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Suzuki, Akio*; Katayama, Yoshinori; Zhao, D.*
Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 299(3-4), p.285 - 289, 2010/11
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:60.20(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The density of the Apollo 14 black glass melt, which has the highest TiO content of pristine mare glasses, was measured to 4.8 GPa and 2100 K using an X-ray absorption method. A fit of the pressure-density-temperature data to the high-temperature Birch-Murnaghan equation of state yielded the isothermal bulk modulus, its pressure derivative, and the temperature derivative of the bulk modulus. Implication for heterogeneities in the lunar mantle is discussed.
content of pristine mare glasses, was measured to 4.8 GPa and 2100 K using an X-ray absorption method. A fit of the pressure-density-temperature data to the high-temperature Birch-Murnaghan equation of state yielded the isothermal bulk modulus, its pressure derivative, and the temperature derivative of the bulk modulus. Implication for heterogeneities in the lunar mantle is discussed.
Sakamaki, Tatsuya*; Otani, Eiji*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Suzuki, Akio*; Katayama, Yoshinori
American Mineralogist, 95(1), p.144 - 147, 2010/01
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:70.25(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The density of a peridotite magma was measured up to 2.5 GPa and 2300 K using an X-ray absorption method. The method allowed measurement of the density of a peridotite melt under seven different conditions and clarified the pressure and temperature dependence of the density. A fit of the pressure-density-temperature data to the high-temperature Birch-Murnaghan equation of state yielded the isothermal bulk modulus, 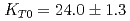 GPa, its pressure derivative,
GPa, its pressure derivative, 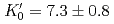 , and the derivative of bulk modulus
, and the derivative of bulk modulus  GPa/K at 2100 K. The large bulk modulus and its pressure derivative of the peridotite melt compared with that of basaltic melt is consistent with previous results from sink-float experiments.
GPa/K at 2100 K. The large bulk modulus and its pressure derivative of the peridotite melt compared with that of basaltic melt is consistent with previous results from sink-float experiments.