Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nawa, Kazuhiro*; Tanaka, Kimihito*; Kurita, Nubuyuki*; Sato, Taku*; Sugiyama, Haruki*; Uekusa, Hidehiro*; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Tanaka, Hidekazu*
Nature Communications (Internet), 10, p.2096_1 - 2096_8, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:72.39(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Search for topological materials has been actively promoted in the field of condensed matter physics for their potential application in energy-efficient information transmission and processing. Recent studies have revealed that topologically invariant states, such as edge states in topological insulators, can emerge not only in a fermionic electron system but also in a bosonic system, enabling nondissipative propagation of quasiparticles. Here we report the topologically nontrivial triplon bands measured by inelastic neutron scattering on the spin-1/2 two-dimensional dimerized antiferromagnet Ba CuSi
CuSi O
O Cl
Cl . The excitation spectrum exhibits two triplon bands that are clearly separated by a band gap due to a small alternation in interdimer exchange interaction, consistent with a refined crystal structure. By analytically modeling the triplon dispersion, we show that Ba
. The excitation spectrum exhibits two triplon bands that are clearly separated by a band gap due to a small alternation in interdimer exchange interaction, consistent with a refined crystal structure. By analytically modeling the triplon dispersion, we show that Ba CuSi
CuSi O
O Cl
Cl is the first bosonic realization of the coupled Su-Schrieffer-Heeger model, where the presence of topologically protected edge states is prompted by a bipartite nature of the lattice.
is the first bosonic realization of the coupled Su-Schrieffer-Heeger model, where the presence of topologically protected edge states is prompted by a bipartite nature of the lattice.
Yonezawa, Rika; Gunji, Ikuko; Sugiyama, Kenji; Ayame, Junko; Takashita, Hirofumi
JAEA-Review 2015-020, 80 Pages, 2016/02
At the request of the government of Japan and Fukushima prefecture, the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories and the Nuclear Science Research Institute of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) conducted the internal dosimetry examination program for the residents of Fukushima prefecture (Fukushima residents) affected by the Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO) Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident by whole-body counting (WBC) starting in July 2011, the year of Great East Japan Earthquake and Tsunami. At the internal dosimetry examination, almost Fukushima residents worried about effects of radiation and suffered from various serious situations, which were caused by not only the nuclear accident but also the earthquake and tsunami. Therefore, JAEA had direct dialogue focused on active listening, as risk communication with Fukushima residents in order to mitigate Fukushima residents' anxiety and stress. This report evaluates the effects of the activities and shows the ways of our communication with Fukushima residents during WBC to mitigate Fukushima residents' anxiety and stress.
Ayame, Junko; Sugiyama, Kenji; Takashita, Hirofumi; Yamamoto, Ryuichi
JAEA-Review 2015-016, 182 Pages, 2016/02
Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories (NCL) of JAEA has held the explanatory meetings in Ibaraki prefecture since May 2011 in order to transmit factual information and reduce the excessive anxiety about radiation risk. Applying to our past risk communication process to the explanatory meetings, we built a process of interactivity between participants and our staff for the meetings. We incorporated the participants' needs into the meetings, and, as far as possible, we had interactive two-way communication so that the meetings were not one-way and persuasive but promote mutual understanding. According to the opinions and the results of questionnaire survey that were received from the participants, it became evident that the interactive explanatory meetings were effective in reducing participants' anxiety. This report explains the risk communication process for carrying out the explanatory meeting, and shows the activities of the meetings, questions and opinions from the participants, and questionnaire results that NCL implemented.
Sugiyama, Kenji; Ayame, Junko; Takashita, Hirofumi; Yamamoto, Ryuichi
JAEA-Review 2015-013, 75 Pages, 2016/02
JAEA has held public meetings on radiation and its health effects mainly for parents of students in kindergartens, elementary schools, and junior high schools in Fukushima prefecture after the Fukushima nuclear accident. These meetings are held based on our experience of practicing risk communication activities for a decade in JAEA with local residents. Questionnaires were collected after the meetings. By analyzing questionnaires, we confirmed that interactive communication is effective in increasing participants' understanding and in decreasing their anxiety. Risk communication study office supported the staff members of the meetings providing information such as participants' questions in the past meetings. To provide information, we made a homepage and held the orientation for the staff members Questionnaires of the staff members were also collected and analyzed after the public meetings.
Sugiyama, Kenji; Takashita, Hirofumi; Yamamoto, Ryuichi; Itabashi, Kiyoshi
JAEA-Review 2014-018, 110 Pages, 2014/07
JAEA has held public meetings on radiation and its health effects mainly for parents of students in kindergartens, elementary schools, and junior high schools in Fukushima Prefecture after the Fukushima nuclear accident. These meetings are held based on our experience of practicing risk communication activities for a decade in JAEA with local residents. Questionnaires were collected after the meetings. By analyzing questionnaires, we confirmed that interactive communication is effective in increasing participants' understanding and in decreasing their anxiety. Most of the participants answered that they understood the contents and that it eased their mind.
Ayame, Junko; Yonezawa, Rika; Sugiyama, Kenji; Takashita, Hirofumi; Yamamoto, Ryuichi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 54(8), p.543 - 548, 2012/08
, 54(8), p.543 - 548, 2012/08
no abstracts in English
Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Hayashi, Takumi; Iwai, Yasunori; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Hara, Masanori*; Sugiyama, Takahiko*; Okuno, Kenji*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 86(9-11), p.2152 - 2155, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)It is quite significant subject how to confine the tritium in a fusion reactor. Especially, it is strongly desired to get the data for tritiated water. This is because tritiated water is much hazardous than the hydrogen form of tritium. As for the behavior of high concentration tritium water, we could get a series of valuable data for the corrosion of the tritiated water against metal materials. In the case where a metal material is in water, an oxidized layer is formed at the surface of the metal. The oxidized layer functions as a passive layer for the corrosion. However, it has been observed that the formation of the oxidized layer was prevented by the presence of tritium in water (0.23 GBq/cc). The chemical exchange column has been applied in ITER as the tritium recovery system from tritiated water. A set of data for an advanced chemical exchange column has been obtained.
 -Alkyl-2-pyrrolidone derivatives (Alkyl =
-Alkyl-2-pyrrolidone derivatives (Alkyl =  -propyl,
-propyl,  -butyl,
-butyl, 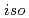 -butyl, and cyclohexyl)
-butyl, and cyclohexyl)Takao, Koichiro*; Noda, Kyoko*; Nogami, Masanobu*; Sugiyama, Yuichi*; Harada, Masayuki*; Morita, Yasuji; Nishimura, Kenji*; Ikeda, Yasuhisa*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 46(10), p.995 - 999, 2009/10
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:65.50(Nuclear Science & Technology)We have been developing an advanced reprocessing system for spent FBR fuels based on precipitation method using pyrrolidone derivatives. In the present study, the solubility of UO (NO
(NO )
) (NRP)
(NRP) (NRP =
(NRP =  -alkyl-2-pyrrolidone, alkyl =
-alkyl-2-pyrrolidone, alkyl =  -propyl,
-propyl,  -butyl,
-butyl, 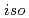 -butyl and cyclohexyl) in aqueous solutions with HNO
-butyl and cyclohexyl) in aqueous solutions with HNO has been examined. As a result, the solubility of each species of UO
has been examined. As a result, the solubility of each species of UO (NO
(NO )
) (NRP)
(NRP) generally decreases with increasing concentrations of HNO
generally decreases with increasing concentrations of HNO and NRP (
and NRP (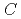 (HNO
(HNO ) and
) and 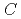 (NRP), respectively). The solubility of UO
(NRP), respectively). The solubility of UO (NO
(NO )
) (NRP)
(NRP) also depends on the type of NRP; a higher hydrophobicity of NRP generally leads to a lower solubility of UO
also depends on the type of NRP; a higher hydrophobicity of NRP generally leads to a lower solubility of UO (NO
(NO )
) (NRP)
(NRP) . The logarithms of effective solubility products (
. The logarithms of effective solubility products (
 ) of UO
) of UO (NO
(NO )
) (NRP)
(NRP) at different
at different 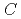 (HNO
(HNO ) values and 293 K were evaluated.
) values and 293 K were evaluated.
Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Hayashi, Takumi; Iwai, Yasunori; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Hara, Masanori*; Sugiyama, Takahiko*; Okuno, Kenji*
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 85(10), p.716 - 725, 2009/10
In a fusion reactor, tritium must be handled in a vacuum vessel, a fuel cycle, and other systems. It is quite significant subject how to confine the tritium in these systems. ITER is the first machine in the world where the tritium confinement would be demonstrated. It is essential to establish a series of database for tritium handling technology to analyze the data obtained at ITER. Especially, it is strongly desired to get the data for tritium water. This is because tritium water is much hazardous than the hydrogen form of tritium. For these reasons, our attention is focused on the study on the behavior of tritium water in the fuel cycle system and structural materials of the system. As for the behavior of high concentration tritium water, we could get the first series of valuable data for the corrosion of the tritium water against metal materials in the world. The behavior of tritium in a surface area of metal and organic compounds was also discussed. As for tritium recovery from tritium water, we could get the data on an advanced chemical exchange column. The chemical exchange column has been applied in ITER as the tritium recovery system from tritium water. Our data showed that the column performance could be remarkably improved. Tritium durability and catalyst tests have also been carried out for the chemical exchange column. Some other possible method for the tritium recovery has also been studied such as an advance adsorption method.
Masaki, Kei; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Hirohata, Yuko*; Oya, Yasuhisa*; Shibahara, Takahiro*; Hayashi, Takao; Sugiyama, Kazuyoshi*; Arai, Takashi; Okuno, Kenji*; Miya, Naoyuki
Nuclear Fusion, 47(11), p.1577 - 1582, 2007/11
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:43.93(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)In JT-60U, erosion/deposition analyses for the plasma facing wall have shown that deposition was dominant at the inner-middle first wall and the inner divertor, whereas erosion dominant at the upper first wall and the outer divertor. Assuming toroidal symmetry in the erosion and deposition patterns, the net carbon erosion and deposition in the divertor area were estimated to be 0.34 kg and 0.55 kg, respectively. In a whole, the increment of carbon in the divertor region was 0.21 kg, which should be originated from the first wall. The hydrogen concentration in the thick deposition layer of the inner divertor was 0.02 in (H+D)/C. In the plasma-shadowed area underneath the divertor region at around 420 K, re-deposited layers of 2  m-thick were found with high hydrogen concentration of 0.8 in (H+D)/C. The carbon deposition rate in the plasma-shadowed area, however, was 8
m-thick were found with high hydrogen concentration of 0.8 in (H+D)/C. The carbon deposition rate in the plasma-shadowed area, however, was 8 10
10 atoms/s, which was one order smaller than that (6
atoms/s, which was one order smaller than that (6 10
10 atoms/s) on the wall surface.
atoms/s) on the wall surface.
Masaki, Kei; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Hirohata, Yuko*; Oya, Yasuhisa*; Shibahara, Takahiro*; Hayashi, Takao; Sugiyama, Kazuyoshi*; Arai, Takashi; Okuno, Kenji*; Miya, Naoyuki
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
Evaluation of fuel inventory and its retention process are critical issues for a next-step fusion device, especially with carbon-based wall. In order to resolve the issues, the hydrogen retention and carbon deposition analyses for the plasma facing surfaces and plasma-shadowed area of JT-60U have been performed. In JT-60U, erosion/deposition analyses for the plasma facing wall have shown that deposition was dominant at the inner-middle first wall and the inner divertor, whereas erosion dominant at the upper first wall and the outer divertor. Assuming toroidal symmetry in the erosion and deposition patterns, the net carbon erosion and deposition in the divertor area were estimated to be 0.34 kg and 0.55 kg, respectively. In a whole, the increment of carbon in the divertor region was 0.21 kg, which should be originated from the first wall. The hydrogen concentration in the thick deposition layer of the inner divertor was  0.02 in (H+D)/C. In the plasma-shadowed area underneath the divertor region at around 420 K, re-deposited layers of
0.02 in (H+D)/C. In the plasma-shadowed area underneath the divertor region at around 420 K, re-deposited layers of  2
2 m-thick were found with high hydrogen concentration of
m-thick were found with high hydrogen concentration of  0.8 in (H+D)/C. The carbon deposition rate in the plasma-shadowed area, however, was 8
0.8 in (H+D)/C. The carbon deposition rate in the plasma-shadowed area, however, was 8 10
10 atoms/s, which was one order smaller than that (6
atoms/s, which was one order smaller than that (6 10
10 atoms/s) on the wall surface.
atoms/s) on the wall surface.
Kanamori, Masashi; Kawata, Tomio; Hitoshi, Watanabe,; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Sugiyama, Toshihide; Miyabe, Kenjiro; Kobayashi, Hirohide
JNC TN8450 2003-009, 506 Pages, 2004/03
This paper describes all the activities that were executed by JNC related to JCO criticality accident on September 30,1999. During the JCO accident, the activities of radiation monitoring, environmental monitoring, criticality termination operation, computer simulation of criticality accident, whole body exposure measurements by WBC about 24-Na, back up of local government like consultation of residents near by were performed by JNC. After the accident Japanese government and Nuclear Safety Commission establishes the investigation committee of JCO accident. JNC has also back up this activity. For example, investigation of the causes, accident scenario, estimation of the doses of the workers and personnel for deserter, counter measure operation. This paper summarizes all the important activity executed by JNC in the meantime.
Oya, Yasuhisa*; Morimoto, Yasutomi*; Oyaizu, Makoto*; Hirohata, Yuko*; Yagyu, Junichi; Miyo, Yasuhiko; Goto, Yoshitaka*; Sugiyama, Kazuyoshi*; Okuno, Kenji*; Miya, Naoyuki; et al.
Physica Scripta, T108, p.57 - 62, 2004/00
no abstracts in English
Masaki, Kei; Sugiyama, Kazuyoshi*; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Goto, Yoshitaka*; Tobita, Kenji; Miyo, Yasuhiko; Kaminaga, Atsushi; Kodama, Kozo; Arai, Takashi; Miya, Naoyuki
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 2(2), p.130 - 139, 2003/06
no abstracts in English
Masaki, Kei; Sugiyama, Kazuyoshi*; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Goto, Yoshitaka*; Miyasaka, Kazutaka*; Tobita, Kenji; Miyo, Yasuhiko; Kaminaga, Atsushi; Kodama, Kozo; Arai, Takashi; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 313-316, p.514 - 518, 2003/03
Times Cited Count:56 Percentile:94.64(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Detailed tritium profiles on the JT-60U W-shaped divertor and first wall tiles were examined by Tritium Imaging Plate Technique (TIPT) and full combustion method. The tritium deposition image obtained by TIPT was consistent with the distribution measured by combustion method. The highest tritium concentration was 60 kBq/cm at the dome top tile. However, deposition layer was not obviously observed on the dome top tile. The tritium concentration in the inner divertor target tile was lower (2 kBq/cm
at the dome top tile. However, deposition layer was not obviously observed on the dome top tile. The tritium concentration in the inner divertor target tile was lower (2 kBq/cm ) even with the thick deposition layer of
) even with the thick deposition layer of  60
60  m. This tritium distribution can be explained by energetic triton particle loss due to ripple loss. According to the simulation using the OFMC code, 31% of the triton particles produced by D-D nuclear reaction is implanted deeply to the wall without fully losing the initial energy of 1 MeV.
m. This tritium distribution can be explained by energetic triton particle loss due to ripple loss. According to the simulation using the OFMC code, 31% of the triton particles produced by D-D nuclear reaction is implanted deeply to the wall without fully losing the initial energy of 1 MeV.
Sugiyama, Kazuyoshi*; Miyasaka, Kazutaka*; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Masaki, Kei; Goto, Yoshitaka*; Tobita, Kenji; Kodama, Kozo; Miya, Naoyuki
Physica Scripta, T103, p.56 - 58, 2003/00
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:62.16(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Sugiyama, Kazuyoshi*; Masaki, Kei; Goto, Yoshitaka*; Tobita, Kenji; Miya, Naoyuki
IAEA-CN-94/EX/P2-11 (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2002/00
no abstracts in English
; Sugiyama, Kenji; ; ; ; Ojima, Hisao;
PNC TN1430 97-005, 229 Pages, 1997/11
no abstracts in English
 C
C
Funasaka, Hideyuki; Sugiyama, Kenji; Yamamoto, Kazunori; Takahashi, Takeshi
Chemical Physics Letters, 241(3), p.154 - 160, 1995/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:13.99(Chemistry, Physical)None
Funasaka, Hideyuki; Sugiyama, Kenji; Yamamoto, Kazunori; Takahashi, Takeshi
Chemical Physics Letters, 236(3), p.277 - 284, 1995/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:25.19(Chemistry, Physical)None