Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Wakai, Eiichi; Nogami, Shuhei*; Kasada, Ryuta*; Ito, Yuzuru*; Takada, Fumiki; 6 of others*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 417, p.1325 - 1330, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:86.52(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Kondo, Keietsu; Aoyagi, Yoshiteru; Kato, Yoshiaki; Taguchi, Taketoshi; Takada, Fumiki; Nakano, Junichi; Ugachi, Hirokazu; Tsukada, Takashi; Takakura, Kenichi*; et al.
Proceedings of 15th International Conference on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems - Water Reactors (CD-ROM), p.1203 - 1216, 2011/08
In order to investigate the effect of neutron dose rate on tensile property and irradiation assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) growth behavior, the crack growth rate (CGR) test, tensile test and microstructure observation have been conducted with type 304 stainless steel specimens. The specimens were irradiated in high temperature water simulating the temperature of boiling water reactor (BWR) up to about 1dpa with two different dose rates at the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR). The radiation hardening increased with the dose rate, but there was little effect on CGR. Increase of the yield strength of specimens irradiated with the low dose rate condition was caused by the increase of number density of frank loops. Little difference of radiation-induced segregation at grain boundaries was observed in specimens irradiated by different dose rates. Furthermore, there was little effect on local plastic deformation behavior near crack tip in the crystal plasticity simulation.
Suzuki, Kazuhiko; Jitsukawa, Shiro; Okubo, Nariaki; Takada, Fumiki
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 240(6), p.1290 - 1305, 2010/06
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:70.25(Nuclear Science & Technology)Kato, Yoshiaki; Takada, Fumiki; Sozawa, Shizuo; Nakagawa, Tetsuya
JAEA-Testing 2009-008, 29 Pages, 2010/03
This report summarizes about the new equipment for the microstructural observation on the nuclear materials such as the structural material of light water reactor, which was installed in the JMTR Hot Laboratory. This experimental device, one of the PIE apparatuses, is useful to obtain the technical knowledge on the material degradation behavior by neutron irradiation damage and accumulate the data base for the integrity evaluation of nuclear power plant.
Taguchi, Taketoshi; Kato, Yoshiaki; Takada, Fumiki; Omi, Masao; Nakagawa, Tetsuya
UTNL-R-0471, p.5_7_1 - 5_7_8, 2009/03
no abstracts in English
Kato, Yoshiaki; Miwa, Yukio; Takada, Fumiki; Omi, Masao; Nakagawa, Tetsuya
JAEA-Testing 2008-005, 48 Pages, 2008/06
This report is concerned with the EBSD-OIM analyzer for irradiated reactor materials, which was installed in the JMTR Hot Laboratory. As the first time in the world, it was installed in a hot cell as one of the examination facilities for irradiated nuclear materials and contributes to studies on IASCC (irradiation aided stress corrosion cracking) and IGSCC (irradiation grain boundary stress corrosion cracking). Its maintenance and operating experiences were described.
Kato, Yoshiaki; Yamamoto, Toshio; Takada, Fumiki; Omi, Masao; Nakagawa, Tetsuya
JAEA-Testing 2008-004, 22 Pages, 2008/06
This report is concerned with replacement of the radiation monitors in the lead cells of JMTR Hot Laboratory in the 2007 fiscal year. It was carried out on two of seven systems of the radiation monitors. The designing, producing, installing, adjusting and inspecting were described.
Hayashi, Koji; Shibata, Akira; Iwamatsu, Shigemi; Sozawa, Shizuo; Takada, Fumiki; Omi, Masao; Nakagawa, Tetsuya
JAEA-Technology 2008-016, 51 Pages, 2008/03
The irradiation capsule 74M-52J was irradiated during total 136 cycles at reactor core of JMTR and the maximum neutron dose reached on 3.9 10
10 n/m
n/m at the capsule outer-tube made of a type 304 stainless steel. In order to produce mechanical test specimens from the outer tube, a punching technique was developed as a simple remote-handling method in a hot-cell. From comparison between the punching and the mechanical cutting methods, it was clarified that the punching technique was applicable to practical use. Moreover, an evaluation test of mechanical properties using specimens sampled from the 74M-52 was performed in-water high temperature condition, less than 288
at the capsule outer-tube made of a type 304 stainless steel. In order to produce mechanical test specimens from the outer tube, a punching technique was developed as a simple remote-handling method in a hot-cell. From comparison between the punching and the mechanical cutting methods, it was clarified that the punching technique was applicable to practical use. Moreover, an evaluation test of mechanical properties using specimens sampled from the 74M-52 was performed in-water high temperature condition, less than 288 C. The result shows that the residual elongation is 18% at 150
C. The result shows that the residual elongation is 18% at 150 C and 13% at 288
C and 13% at 288 C. It was confirmed that the type 304 stainless steel irradiated up to such high dose shows enough ductility.
C. It was confirmed that the type 304 stainless steel irradiated up to such high dose shows enough ductility.
Wakai, Eiichi; Ando, Masami; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Taguchi, Tomitsugu; Stroller, R. E.*; Yamamoto, Toshio; Kato, Yoshiaki; Takada, Fumiki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 367-370(1), p.74 - 80, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:56.84(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Shibata, Akira; Takada, Fumiki
JAEA-Technology 2007-031, 24 Pages, 2007/03
The fracture toughness which represents resistance for brittle or ductile fracture is one of the most important material property concerning linear and non-linear fracture mechanics analyses. In order to respond to needs of collecting data relating to fracture toughness of pressure vessel and austenitic stainless steels, fracture toughness test for irradiated materials has been performed in JMTR Hot Laboratory. On the other hand, there has been no computer program for analysis of fracture toughness using the test data obtained from the test apparatus installed in the hot cell. Therefore, only load-displacement data have been provided to users to calculate fracture toughness of irradiated materials. Recently, request of analysis of fracture toughness have been increased. Thus a computer program, which calculates the amount of the crack extension, the compliance and the fracture toughness from the data acquired from the test apparatus installed in the hot cell, has been developed. In the program unloading elastic compliance method is applied based on ASTM E1820-01. Through the above development, the request for the fracture toughness analysis can be satisfied and the fracture toughness of irradiated test specimens can be provided to users.
Yamada, Hirokazu*; Kawamura, Hiroshi; Nagao, Yoshiharu; Takada, Fumiki; Kono, Wataru*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 355(1-3), p.119 - 123, 2006/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:35.34(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In this study, the bending properties of welding joint of irradiated material and un-irradiated material (irradiated/un-irradiated joints) were investigated using SS316LN-IG, which is the candidate material for the cooling pipe of ITER. The results of this study showed that the bending position of joints using un-irradiated material was un-irradiated part and that the bending position of irradiated/irradiated joints was fusion area or HAZ (heat affected zone). Although the bending position of joints was different bor the combination pattern between irradiated and un-irradiated materials, the bending strength of joint was almost same. Additionally, it is confirmed that bending strength did not depend on the combination pattern between the irradiated and un-irradiated materials, nor on the relationship between the heat input direction and the bending load direction.
Wakai, Eiichi; Otsuka, Hideo*; Matsukawa, Shingo; Furuya, Kazuyuki*; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Oka, Keiichiro*; Onuki, Somei*; Yamamoto, Toshio*; Takada, Fumiki; Jitsukawa, Shiro
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.1077 - 1084, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:58.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Yamada, Hirokazu*; Sato, Satoshi; Mori, Kensuke*; Nagao, Yoshiharu; Takada, Fumiki; Kawamura, Hiroshi
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(1-7), p.631 - 637, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.58(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study estimated the neutron irradiation effect with 1.5 dpa on the mechanical properties of the SS/SS HIP joint materials jointed in the standard HIP joint condition. Results of this study showed that the HIP process in the standard HIP condition could make SS/SS HIP joint material of which tensile properties was equivalent to that of the SS base material. In addition, the effect of surface roughness at the HIP joint material on the mechanical properties of SS/SS HIP joint material was estimated.
 C in JMTR
C in JMTRWakai, Eiichi; Jitsukawa, Shiro; Tomita, Hideki*; Furuya, Kazuyuki; Sato, Michitaka*; Oka, Keiichiro*; Tanaka, Teruyuki*; Takada, Fumiki; Yamamoto, Toshio*; Kato, Yoshiaki; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 343(1-3), p.285 - 296, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:93.97(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The dependence of helium production on radiation-hardening and -embrittlement has been examined in a reduced-activation martensitic F82H steel doped with  B,
B,  B and
B and  B+
B+ B irradiated at 250
B irradiated at 250 C to 2.2 dpa. The total amounts of doping boron were about 60 massppm. The range of He concentration produced in the specimens was from about 5 to about 300 appm. Tensile and fracture toughness tests were performed after neutron irradiation. 50 MeV-He
C to 2.2 dpa. The total amounts of doping boron were about 60 massppm. The range of He concentration produced in the specimens was from about 5 to about 300 appm. Tensile and fracture toughness tests were performed after neutron irradiation. 50 MeV-He irradiation was also performed to implant about 85 appm He atoms at 120
irradiation was also performed to implant about 85 appm He atoms at 120 C by AVF cyclotron to 0.03 dpa, and small punch testing was performed to obtain DBTT. Radiation-hardening of the neutron-irradiated specimens increased slightly with increasing He production. The 100 MPam
C by AVF cyclotron to 0.03 dpa, and small punch testing was performed to obtain DBTT. Radiation-hardening of the neutron-irradiated specimens increased slightly with increasing He production. The 100 MPam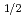 DBTT for the F82H+
DBTT for the F82H+ B, F82H+
B, F82H+ B+
B+ B, and F82H+
B, and F82H+ B were 40, 110, and 155
B were 40, 110, and 155 C, respectively. The shifts of DBTT due to He production were evaluated as about 70
C, respectively. The shifts of DBTT due to He production were evaluated as about 70 C by 150 appmHe and 115
C by 150 appmHe and 115 C by 300 appmHe. The DBTT shift in the small punch testing was evaluated as 50
C by 300 appmHe. The DBTT shift in the small punch testing was evaluated as 50 C.
C.
Yamada, Hirokazu*; Kawamura, Hiroshi; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Kalinin, G.*; Nagao, Yoshiharu; Takada, Fumiki; Nishikawa, Masahiro*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 340(1), p.57 - 63, 2005/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:34.88(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)This study was performed to clear the effect of neutron re-irradiation on mechanical properties to welding material un-irradiated and irradiated stainless steel. The effect of re-irradiation to these weldaments were evaluated by tensile tests, metallographical observation and hardness test. The result of tensile tests shows that ultimate tensile strength of all joints specimen were almost similar, 0.2% yield strength and total elongation were depend on the irradiation damage and weldaments or not. Therefore, fracture mechanism was not change by re-irradiation. However, brittlement of material was depend on irradiation damage and the property of deformation was sensitive by the effect of irradiation damage or the effect of welding heat.
Wakai, Eiichi; Taguchi, Tomitsugu; Yamamoto, Toshio*; Tomita, Hideki*; Takada, Fumiki; Jitsukawa, Shiro
Materials Transactions, 46(3), p.481 - 486, 2005/03
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:60.52(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Wakai, Eiichi; Taguchi, Tomitsugu; Yamamoto, Toshio*; Kato, Yoshiaki; Takada, Fumiki
Materials Transactions, 45(8), p.2638 - 2640, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.14(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Wakai, Eiichi; Matsukawa, Shingo; Yamamoto, Toshio*; Kato, Yoshiaki; Takada, Fumiki; Sugimoto, Masayoshi; Jitsukawa, Shiro
Materials Transactions, 45(8), p.2641 - 2643, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:40.24(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Saito, Shigeru; Fukaya, Kiyoshi*; Ishiyama, Shintaro; Amezawa, Hiroo; Yonekawa, Minoru; Takada, Fumiki; Kato, Yoshiaki; Takeda, Takashi; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; Nakahira, Masataka
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 307-311(Part2), p.1573 - 1577, 2002/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:22.58(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Ioka, Ikuo; Miwa, Yukio; Tsuji, Hirokazu; Yonekawa, Minoru; Takada, Fumiki; Hoshiya, Taiji
JSME International Journal, Series A, 45(1), p.51 - 56, 2002/01
The low cycle creep-fatigue test with tensile strain hold of the austenitic stainless steel irradiated to 2dpa was carried out at 823K in vacuum. The applicability of creep-fatigue life prediction methods to the irradiated specimen was examined. The fatigue life on the irradiated specimen without tensile strain hold time was reduced by a factor of 2-5 in comparison with the unirradiated specimen. The fraction of intergranular fracture increased with increasing strain hold time. The decline in fatigue life of the irradiated specimen with tensile strain hold was almost equal to that of the unirradiated specimen. For the irradiated specimen, the time fraction damage rule trends to yield unsafe estimated lives and the ductility exhaustion damage rule trends to yield generous results. However, all of data were predicted within a factor of three on life by the linear damage rule.