Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
広田 憲亮; 竹田 貴代子*; 橘 幸男; 正木 康浩*
材料と環境, 70(3), p.68 - 76, 2021/03
熱化学水素製造法(ISプロセス)の硫酸分解反応容器を想定した高温硫酸分解ガス環境下において、ステンレス鋼及びNi基合金の耐食性能評価を実施した。その結果、100時間の腐食試験ではSiを2.4%含有したNi基合金は、腐食速度が小さく、優れた耐食性能を示したほか、Alを3%含有したフェライト系ステンレス鋼(3Al-Ferrite)は、腐食速度が指標とするSiCの腐食速度(0.1mm/year)を下回る優れた耐食性能を示した。一方で3Al-Ferriteの腐食生成皮膜と同じコンセプトで、Al O
O 皮膜を材料にプレフィルミングしたNi基合金の腐食速度は、3Al-Ferriteに対して大幅に速くなった。これらの酸化皮膜/母材界面の断面でEPMA分析を行った結果、2.4Si含有Ni基合金では、Si酸化皮膜が形成されていたが、長時間の腐食試験中にSi酸化皮膜に欠陥ができ、腐食環境から酸化皮膜を介して母材粒界へのS侵入が確認された。一方で3Al-Ferriteでは、薄い均一なAl
皮膜を材料にプレフィルミングしたNi基合金の腐食速度は、3Al-Ferriteに対して大幅に速くなった。これらの酸化皮膜/母材界面の断面でEPMA分析を行った結果、2.4Si含有Ni基合金では、Si酸化皮膜が形成されていたが、長時間の腐食試験中にSi酸化皮膜に欠陥ができ、腐食環境から酸化皮膜を介して母材粒界へのS侵入が確認された。一方で3Al-Ferriteでは、薄い均一なAl O
O 皮膜が形成されており、粒界へのS侵入は確認されなかった。またAl
皮膜が形成されており、粒界へのS侵入は確認されなかった。またAl O
O 皮膜をプレフィルミングしたNi基合金では、Al
皮膜をプレフィルミングしたNi基合金では、Al O
O 皮膜に欠陥ができ、母材粒界へSが侵入していた。3Al-Ferriteに生成した腐食生成皮膜とプレフィルミングしたAl
皮膜に欠陥ができ、母材粒界へSが侵入していた。3Al-Ferriteに生成した腐食生成皮膜とプレフィルミングしたAl O
O の違いをX線回折で解析した結果、3Al-Ferriteの皮膜は、
の違いをX線回折で解析した結果、3Al-Ferriteの皮膜は、 -Al
-Al O
O のみからなるのに対し、プレフィルミングしたAl
のみからなるのに対し、プレフィルミングしたAl O
O は
は -Al
-Al O
O と
と -Al
-Al O
O が混在していることが分かった。これらの結果により、3Al-Ferriteの良好な耐食性能は、緻密な
が混在していることが分かった。これらの結果により、3Al-Ferriteの良好な耐食性能は、緻密な -Al
-Al O
O が早期に母材表面に均一形成されたことによるものと推察される。
が早期に母材表面に均一形成されたことによるものと推察される。
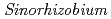 with
with 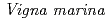 under high salt conditions using the ion beam mutation breeding
under high salt conditions using the ion beam mutation breeding丸山 雄大*; 武田 喜代子*; 友岡 憲彦*; 佐藤 勝也; 大野 豊; 横山 正*
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 99, 2016/02
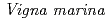 is one of wild legumes, which called as Hamaazuki, are distributed at the vicinity of the coast from tropical to sub-tropical regions and have high salt tolerance among terrestrial plants.
is one of wild legumes, which called as Hamaazuki, are distributed at the vicinity of the coast from tropical to sub-tropical regions and have high salt tolerance among terrestrial plants. 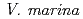 can grow at 400 mM NaCl condition. Furthermore, the root nodules on
can grow at 400 mM NaCl condition. Furthermore, the root nodules on 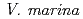 have a symbiotic relationship with rhizobia that related to the genus
have a symbiotic relationship with rhizobia that related to the genus 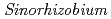 having high stress tolerance (500 mM NaCl, 45
having high stress tolerance (500 mM NaCl, 45  C, pH 10.5). Above both symbiotic partners showed extremely high salt tolerance, however,
C, pH 10.5). Above both symbiotic partners showed extremely high salt tolerance, however, 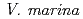 cannot develop root nodules with
cannot develop root nodules with 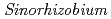 at over 80 mM NaCl conditions. To improve symbiotic performance of
at over 80 mM NaCl conditions. To improve symbiotic performance of 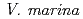 with
with 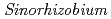 under high salt conditions,
under high salt conditions, 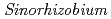 bacterial cells were irradiated by carbon ion-beam at TIARA. However, so far, we could not obtain promising mutants having good symbiotic performance with Vigna marina under high salt conditions, yet.
bacterial cells were irradiated by carbon ion-beam at TIARA. However, so far, we could not obtain promising mutants having good symbiotic performance with Vigna marina under high salt conditions, yet.
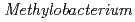 sp. ME121, isolated from soil as a mixed single colony with
sp. ME121, isolated from soil as a mixed single colony with 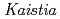 sp. 32K
sp. 32K藤浪 俊*; 武田 喜代子*; 小野寺 威文*; 佐藤 勝也; 清水 哲*; 若林 佑*; 鳴海 一成*; 中村 顕*; 伊藤 政博*
Genome Announcements (Internet), 3(5), p.e01005-15_1 - e01005-15_2, 2015/09
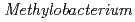 sp. ME121 was isolated from soil as a mixed single colony with
sp. ME121 was isolated from soil as a mixed single colony with 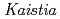 sp. 32K during our screening of L-glucose-utilizing microorganisms, and its growth was enhanced by coculture. It was expected that genomic analysis of this bacterium would provide novel information on coculture-dependent growth enhancement. The genomic information of symbiotic bacteria could be of use for studying the molecular mechanisms underlying microbial symbiosis. The draft genome sequence of
sp. 32K during our screening of L-glucose-utilizing microorganisms, and its growth was enhanced by coculture. It was expected that genomic analysis of this bacterium would provide novel information on coculture-dependent growth enhancement. The genomic information of symbiotic bacteria could be of use for studying the molecular mechanisms underlying microbial symbiosis. The draft genome sequence of 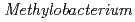 sp. ME121 is 7,096,979 bp in total length and comprises 197 large contigs (
sp. ME121 is 7,096,979 bp in total length and comprises 197 large contigs ( 500 bp) that was deposited at DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank under the accession number BBUX00000000. The draft genome sequence shows that
500 bp) that was deposited at DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank under the accession number BBUX00000000. The draft genome sequence shows that 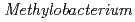 sp. ME121 has some genes that encode putative methanol/ethanol family PQQ-dependent dehydrogenases involved in methylotrophy. Some unknown factor provided by the coculture may contribute to increase the growth of
sp. ME121 has some genes that encode putative methanol/ethanol family PQQ-dependent dehydrogenases involved in methylotrophy. Some unknown factor provided by the coculture may contribute to increase the growth of 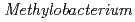 sp. ME121.
sp. ME121.
 USDA110 generated by ion-beam irradiation
USDA110 generated by ion-beam irradiation武田 喜代子*; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成*; 大野 豊; 大津 直子*; 横山 正*
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 120, 2015/03
Major constraint of biofertilizer utilization in agricultural practice is a viability loss of beneficial microorganisms in biofertilizers by high temperature stress during both storage and transportation. Therefore, we have tried to improve high temperature tolerance of  USDA110 using carbon-ion beams accelerated by an AVF cyclotron at TIARA. Consequently, we have obtained a high temperature tolerant mutant that can maintain a high survival rate at 42
USDA110 using carbon-ion beams accelerated by an AVF cyclotron at TIARA. Consequently, we have obtained a high temperature tolerant mutant that can maintain a high survival rate at 42  C for at least 7 days in yeast-mannitol broth medium, and named it as M14. The genome sequence of M14 was determined by a whole-genome shotgun strategy. The acquirement of high temperature tolerance in M14 could be attributed to 18 base mutations and/or a large-scale inversion (1.27 Mb). In the future, we will conduct further analysis on these mutations in order to decipher the molecular mechanisms of high temperature tolerance of M14.
C for at least 7 days in yeast-mannitol broth medium, and named it as M14. The genome sequence of M14 was determined by a whole-genome shotgun strategy. The acquirement of high temperature tolerance in M14 could be attributed to 18 base mutations and/or a large-scale inversion (1.27 Mb). In the future, we will conduct further analysis on these mutations in order to decipher the molecular mechanisms of high temperature tolerance of M14.
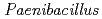 sp. strain TCA20, isolated from a hot spring containing a high concentration of calcium ions
sp. strain TCA20, isolated from a hot spring containing a high concentration of calcium ions藤浪 俊*; 武田 喜代子*; 小野寺 威文*; 佐藤 勝也; 佐野 元彦*; 高橋 優嘉*; 鳴海 一成*; 伊藤 政博*
Genome Announcements (Internet), 2(5), p.e00866-14_1 - e00866-14_2, 2014/09
Calcium-dependent 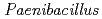 sp. strain TCA20 was isolated from a water sample of a hot spring containing a high concentration of calcium ions. Here, we report the draft genome sequence of this bacterium, which may be the basis for the research of calcium ion homeostasis. The draft genome sequence of
sp. strain TCA20 was isolated from a water sample of a hot spring containing a high concentration of calcium ions. Here, we report the draft genome sequence of this bacterium, which may be the basis for the research of calcium ion homeostasis. The draft genome sequence of 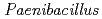 sp. strain TCA20 totals 5,631,463 bp in length and is composed of 33 large contigs (
sp. strain TCA20 totals 5,631,463 bp in length and is composed of 33 large contigs ( 500 bp) that was deposited at DDBJ/EMBL/Genbank under the accession no. BBIW00000000. The annotation of the draft genome sequence shows that
500 bp) that was deposited at DDBJ/EMBL/Genbank under the accession no. BBIW00000000. The annotation of the draft genome sequence shows that 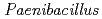 sp. strain TCA20 has a calcium-specific calcium/proton antiporter, ChaA, and a P-type calcium-transporting ATPase, YloB, was identified as calcium transporters. These transporters may also be important for the growth of
sp. strain TCA20 has a calcium-specific calcium/proton antiporter, ChaA, and a P-type calcium-transporting ATPase, YloB, was identified as calcium transporters. These transporters may also be important for the growth of 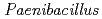 sp. strain TCA20 under the high concentration of calcium ions.
sp. strain TCA20 under the high concentration of calcium ions.
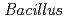 sp. strain TS-2, isolated from a jumping spider
sp. strain TS-2, isolated from a jumping spider藤浪 俊*; 武田 喜代子*; 小野寺 威文*; 佐藤 勝也; 佐野 元彦*; 鳴海 一成*; 伊藤 政博*
Genome Announcements (Internet), 2(3), p.e00458-14_1 - e00458-14_2, 2014/05
The potassium-dependent alkaliphilic 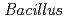 sp. strain TS-2 was isolated from the mashed extract of a jumping spider, and its draft genome sequence was obtained. Comparative genomic analysis with a previously sequenced sodium-dependent alkaliphilic
sp. strain TS-2 was isolated from the mashed extract of a jumping spider, and its draft genome sequence was obtained. Comparative genomic analysis with a previously sequenced sodium-dependent alkaliphilic 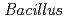 species may reveal potassium-dependent alkaline adaptation mechanisms. The draft genome sequence of
species may reveal potassium-dependent alkaline adaptation mechanisms. The draft genome sequence of 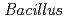 sp. strain TS-2 was 4,360,646 bp in total length, comprised 58 large contigs (
sp. strain TS-2 was 4,360,646 bp in total length, comprised 58 large contigs ( 500 bp) that was deposited at DDBJ/EMBL/Genbank under the accession number BAWL00000000. In the draft genome sequence of
500 bp) that was deposited at DDBJ/EMBL/Genbank under the accession number BAWL00000000. In the draft genome sequence of 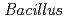 sp. strain TS-2, two sets of
sp. strain TS-2, two sets of 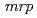 genes, which encode multisubunit secondary cation/proton antiporter-3 family proteins, were annotated. The Mrp complex acts as an Na
genes, which encode multisubunit secondary cation/proton antiporter-3 family proteins, were annotated. The Mrp complex acts as an Na /H
/H antiporter in typical alkaliphilic
antiporter in typical alkaliphilic 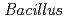 species and plays a critical role in the sodium-dependent alkaline adaptation mechanism.
species and plays a critical role in the sodium-dependent alkaline adaptation mechanism.

佐藤 勝也; 小野寺 威文*; 武田 喜代子; 鳴海 一成*
JAEA-Review 2013-059, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2012, P. 110, 2014/03
In this study, we investigated mutant frequencies of two different antibiotic-resistant mutants for carbon ion beams in  and identified the mutation sites in the streptomycin-resistant (Sm
and identified the mutation sites in the streptomycin-resistant (Sm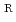 ) mutants. The Sm
) mutants. The Sm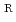 mutant frequencies increased depending on radiation dose. It seems that this dose range is the best dose to generate the mutants of interest for research and breeding purpose. Four kinds of mutation sites at the
mutant frequencies increased depending on radiation dose. It seems that this dose range is the best dose to generate the mutants of interest for research and breeding purpose. Four kinds of mutation sites at the 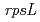 locus were determined from 8 Sm
locus were determined from 8 Sm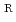 mutants. These mutations cause amino acid substitutions at position 43 (Lys to Thr or Arg) and 88 (Lys to Glu or Arg) in the S12 protein, respectively. The two hot spots at Lys43 and Lys88 in the S12 protein might be a binding target of streptomycin or adjacent to the center of streptomycin interaction with the ribosome.
mutants. These mutations cause amino acid substitutions at position 43 (Lys to Thr or Arg) and 88 (Lys to Glu or Arg) in the S12 protein, respectively. The two hot spots at Lys43 and Lys88 in the S12 protein might be a binding target of streptomycin or adjacent to the center of streptomycin interaction with the ribosome.
 USDA110 generated by ion-beam irradiation
USDA110 generated by ion-beam irradiation武田 喜代子; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成*; 大津 直子*; 横山 正*
JAEA-Review 2013-059, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2012, P. 114, 2014/03
With the aims of utilization as a biofertilizer inoculant and elucidation of high-temperature tolerance mechanism of soybean nodule bacteria, we had applied the ion beam breeding technology to a strain  (
(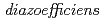 ) USDA110. Consequently, we obtained a mutant named M14 that was able to maintain high viable cell numbers under high-temperature (42
) USDA110. Consequently, we obtained a mutant named M14 that was able to maintain high viable cell numbers under high-temperature (42 C) for at least 7 days. Genome comparison with USDA110 revealed that (1) 1.27 Mbp inversion mutagenesis and (2) 84 single base mutations were occurred in M14. The acquirement of high temperature tolerance in M14 could be attributed to a large-scale inversion or small-scale mutations in the inverted region, or both.
C) for at least 7 days. Genome comparison with USDA110 revealed that (1) 1.27 Mbp inversion mutagenesis and (2) 84 single base mutations were occurred in M14. The acquirement of high temperature tolerance in M14 could be attributed to a large-scale inversion or small-scale mutations in the inverted region, or both.
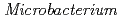 sp. strain TS-1
sp. strain TS-1藤浪 俊*; 武田 喜代子; 小野寺 威文*; 佐藤 勝也; 佐野 元彦*; 鳴海 一成*; 伊藤 政博*
Genome Announcements (Internet), 1(6), P. e01043-13, 2013/12
Alkaliphilic 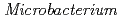 sp. strain TS-1, newly isolated from the jumping spider, showed Na
sp. strain TS-1, newly isolated from the jumping spider, showed Na -independent growth and motility. Here, we report the draft genome sequence of this bacterium, which may provide beneficial information for Na
-independent growth and motility. Here, we report the draft genome sequence of this bacterium, which may provide beneficial information for Na -independent alkaline adaptation mechanisms. The draft genome sequence of
-independent alkaline adaptation mechanisms. The draft genome sequence of 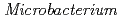 sp. strain TS-1 was 3,396,165 bp in total length and comprised 3 large contigs (2,699,404 bp, 691,278 bp, and 5,483 bp) that was deposited at DDBJ/ EMBL/GenBank under the accession number BASQ00000000. The annotation of the draft genome sequence indicated that this bacterium has 3 sets of
sp. strain TS-1 was 3,396,165 bp in total length and comprised 3 large contigs (2,699,404 bp, 691,278 bp, and 5,483 bp) that was deposited at DDBJ/ EMBL/GenBank under the accession number BASQ00000000. The annotation of the draft genome sequence indicated that this bacterium has 3 sets of 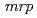 genes, which encode multisubunit secondary cation/proton antiporter-3 family proteins for pH homeostasis. The annotation also indicated that this bacterium has genes involved in chemotaxis/flagellar components, including one set of
genes, which encode multisubunit secondary cation/proton antiporter-3 family proteins for pH homeostasis. The annotation also indicated that this bacterium has genes involved in chemotaxis/flagellar components, including one set of 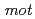 genes.
genes.
 USDA110 generated by ion-beam irradiation
USDA110 generated by ion-beam irradiation武田 喜代子; 手島 光平*; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成; 横山 正*
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 107, 2013/01
We have tried to improve high temperature tolerance of  USDA110, which is a superior inoculant to soybean in temperate area, using ion beam breeding technology. Consequently, we have obtained 20 high-temperature tolerant mutants, which can survive at 43
USDA110, which is a superior inoculant to soybean in temperate area, using ion beam breeding technology. Consequently, we have obtained 20 high-temperature tolerant mutants, which can survive at 43 C for at least 7 days. In this report, we show phenotypic characteristics of 3 mutants (strains M4, M5 and M6) that exhibit relatively higher tolerance among the mutants obtained. The colony of M4, M5 and M6 was smooth with glossy pale pink color unlike wild type. There might be a link between high temperature tolerance and these phenotypic changes. Therefore, we intend to identify factors causing these changes. The generation time of high-temperature tolerant mutants at 30
C for at least 7 days. In this report, we show phenotypic characteristics of 3 mutants (strains M4, M5 and M6) that exhibit relatively higher tolerance among the mutants obtained. The colony of M4, M5 and M6 was smooth with glossy pale pink color unlike wild type. There might be a link between high temperature tolerance and these phenotypic changes. Therefore, we intend to identify factors causing these changes. The generation time of high-temperature tolerant mutants at 30 C was about 1.5 h shorter than that of wild type.
C was about 1.5 h shorter than that of wild type.
 -sterilization of biofertilizer's carrier on bacterial inoculants survival
-sterilization of biofertilizer's carrier on bacterial inoculants survival手島 光平*; 横山 正*; 佐藤 勝也; 武田 喜代子; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 112, 2013/01
Biofertilizer is a substance that holds beneficial microorganisms for plant growth in the carrier such as peat, perlite, charcoal and soil. To use biofertilizer more efficiently, it is necessary to keep the amount of viable inoculants in the biofertilizer for a definite period of time.  -irradiation is expected to sterilize the carrier materials without changes in physical and chemical properties. In this study, to demonstrate the effectiveness of
-irradiation is expected to sterilize the carrier materials without changes in physical and chemical properties. In this study, to demonstrate the effectiveness of  -sterilization, the survivals of inoculants were monitored for the nitrogen-fixing bacteria
-sterilization, the survivals of inoculants were monitored for the nitrogen-fixing bacteria 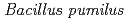 strain TUAT1 and
strain TUAT1 and 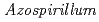 sp. strain MAFF210364.
sp. strain MAFF210364.
 -sterilization of carrier materials made with different types of soils on the shelf life of biofertilizer containing
-sterilization of carrier materials made with different types of soils on the shelf life of biofertilizer containing  strain USDA110
strain USDA110手島 光平; 佐藤 勝也; 武田 喜代子; 横山 正*; 鳴海 一成
Radioisotopes, 61(4), p.161 - 171, 2012/04
バイオ肥料とは、植物生育を促進する細菌をピートや土壌などの担体に生きたまま保持した資材であり、施肥効果の高いバイオ肥料を開発するためには、保存中の接種菌数を長期間維持する技術が必要である。そこで、土着菌を 線により滅菌した担体を用いてダイズ根粒菌のバイオ肥料を作製し、保存中の接種菌密度の変化を調べた。担体として国内の代表的な土壌5種類を供試し、
線により滅菌した担体を用いてダイズ根粒菌のバイオ肥料を作製し、保存中の接種菌密度の変化を調べた。担体として国内の代表的な土壌5種類を供試し、 線滅菌(50kGy)及びオートクレーブ滅菌(121
線滅菌(50kGy)及びオートクレーブ滅菌(121 C, 40min)処理した後、ダイズ根粒菌
C, 40min)処理した後、ダイズ根粒菌 USDA110株を接種した。バイオ肥料を4
USDA110株を接種した。バイオ肥料を4 C及び30
C及び30 Cで1年間保存し、接種菌の生菌数の経時的推移を調べた。その結果、滅菌しない担体では接種菌が減少したが、滅菌した担体では接種菌の増加が見られた。供給安定性、低線量
Cで1年間保存し、接種菌の生菌数の経時的推移を調べた。その結果、滅菌しない担体では接種菌が減少したが、滅菌した担体では接種菌の増加が見られた。供給安定性、低線量 線照射での高い滅菌効果、接種菌密度の保持性を考慮すると、被検土壌の中でケト土がバイオ肥料担体として最も適していると考えられた。
線照射での高い滅菌効果、接種菌密度の保持性を考慮すると、被検土壌の中でケト土がバイオ肥料担体として最も適していると考えられた。
 USDA 110 obtained by ion-beam microbial mutation-breeding technology
USDA 110 obtained by ion-beam microbial mutation-breeding technology武田 喜代子; 手島 光平; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成; 横山 正*
JAEA-Review 2011-043, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2010, P. 110, 2012/01
In order to prevent deterioration in viability of inoculants in biofertilizers exposed to high temperature, we are trying to improve a phenotypic character concerning high temperature tolerance in  USDA 110, which is a worldwide superior inoculant to soybean. In this study, ion-beam microbial mutation-breeding technology is used to generate high temperature tolerant mutants. We obtained 9 high temperature tolerant mutants that can survive at 45
USDA 110, which is a worldwide superior inoculant to soybean. In this study, ion-beam microbial mutation-breeding technology is used to generate high temperature tolerant mutants. We obtained 9 high temperature tolerant mutants that can survive at 45 C for 5 days. These mutants were classified into 3 groups in terms of differences in colony morphology and colony size. We will carry out further characterization of those isolates in terms of temperature tolerant and symbiotic characters.
C for 5 days. These mutants were classified into 3 groups in terms of differences in colony morphology and colony size. We will carry out further characterization of those isolates in terms of temperature tolerant and symbiotic characters.
 USDA 110 into a high temperature tolerant strain in terms of ion-beam microbial mutation-breeding technology
USDA 110 into a high temperature tolerant strain in terms of ion-beam microbial mutation-breeding technology武田 喜代子*; 手島 光平; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成; 横山 正*
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 75, 2011/01
Major constraint of biofertilizer utilization in agricultural practice is a serious deterioration of qualities in biofertilizers under both storage and transportation conditions. In order to prevent deterioration in variability of inoculants in biofertilizers exposed to high temperature, we are trying to improve a phenotypic character concerning high temperature tolerant in  USDA 110, which is a worldwide superior inoculant to soybean. In this study, ion-beam microbial mutation-breeding technology is used to generate high temperature tolerant mutants. We obtained high temperature tolerant mutants of
USDA 110, which is a worldwide superior inoculant to soybean. In this study, ion-beam microbial mutation-breeding technology is used to generate high temperature tolerant mutants. We obtained high temperature tolerant mutants of 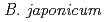 USDA 110, which can survive at 45
USDA 110, which can survive at 45 C for 5 days. Now, we are characterizing these mutants in terms of differences in several phenotypic properties.
C for 5 days. Now, we are characterizing these mutants in terms of differences in several phenotypic properties.
 USDA110 generated by ion-beam irradiation
USDA110 generated by ion-beam irradiation武田 喜代子; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成*; 大津 直子*; 横山 正*
no journal, ,
With the aims of utilization as a biofertilizer inoculant and elucidation of high-temperature tolerance mechanism of soybean nodule bacteria, we had applied the ion beam breeding technology to a strain  (
(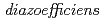 ) USDA110. Consequently, we obtained a mutant named M14 which was able to maintain high viable cell numbers under high-temperature (42 degrees) for at least 7 days. Genome comparison with USDA110 revealed that (1) 1.27 Mbp inversion mutagenesis and (2) 18 single base mutations were occurred in M14. This study was the first attempt to apply the ion beam breeding technology to a prokaryote and succeeded in proving the effectiveness of it.
) USDA110. Consequently, we obtained a mutant named M14 which was able to maintain high viable cell numbers under high-temperature (42 degrees) for at least 7 days. Genome comparison with USDA110 revealed that (1) 1.27 Mbp inversion mutagenesis and (2) 18 single base mutations were occurred in M14. This study was the first attempt to apply the ion beam breeding technology to a prokaryote and succeeded in proving the effectiveness of it.
武田 喜代子*; 手島 光平; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成; 横山 正*
no journal, ,
化学肥料からの脱却を目指し、東南アジア等では、作物生産に根粒菌等を用いたバイオ肥料の利用を奨励している。しかし、化学肥料とは異なり、輸送や保存時の高温・乾燥によるバイオ肥料の品質低下等の問題があり改良が望まれている。そこで、炭素イオンビーム照射による高温耐性ダイズ根粒菌の作出を試みた。ダイズ根粒菌 USDA110株を供試菌株とし、原子力機構高崎量子応用研究所のイオンビーム照射施設(TIARA)にて炭素イオンビームを凍結乾燥菌体に照射した。照射菌体をYM寒天培地で28
USDA110株を供試菌株とし、原子力機構高崎量子応用研究所のイオンビーム照射施設(TIARA)にて炭素イオンビームを凍結乾燥菌体に照射した。照射菌体をYM寒天培地で28 C・4日間培養した後、菌体をYM寒天培地に塗抹して45
C・4日間培養した後、菌体をYM寒天培地に塗抹して45 Cで14日間静置、又はYM液体培地に懸濁して45
Cで14日間静置、又はYM液体培地に懸濁して45 Cで5日間静置し、それぞれ28
Cで5日間静置し、それぞれ28 Cで4日間再び培養して生存する菌を高温耐性獲得変異株として選抜した。その結果、照射した菌体から、45
Cで4日間再び培養して生存する菌を高温耐性獲得変異株として選抜した。その結果、照射した菌体から、45 Cで5日間生存可能な高温耐性獲得変異株が得られた。
Cで5日間生存可能な高温耐性獲得変異株が得られた。
武田 喜代子; 手島 光平; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成; 横山 正*
no journal, ,
ダイズ根粒菌( )はバイオ肥料として世界中で利用されている。しかし、熱帯等での高温ばく露はバイオ肥料中のダイズ根粒菌の生残性を著しく低下させるため、いかにその生残性を高めるかが重要な課題になっている。突然変異育種によるダイズ根粒菌への高温耐性の付与は上記課題の解決に結びつき、農業利用上も非常に有用である。そこで、われわれはダイズ根粒菌の優良接種菌株である
)はバイオ肥料として世界中で利用されている。しかし、熱帯等での高温ばく露はバイオ肥料中のダイズ根粒菌の生残性を著しく低下させるため、いかにその生残性を高めるかが重要な課題になっている。突然変異育種によるダイズ根粒菌への高温耐性の付与は上記課題の解決に結びつき、農業利用上も非常に有用である。そこで、われわれはダイズ根粒菌の優良接種菌株である USDA110株を対象に、イオンビームを用いた微生物突然変異育種を試み、現在までに、45
USDA110株を対象に、イオンビームを用いた微生物突然変異育種を試み、現在までに、45 CのYM培地内で5日間生残可能な変異株を9株(M1
CのYM培地内で5日間生残可能な変異株を9株(M1 M9)取得した。本研究では、これら高温耐性株のコロニー形態や世代時間、共生機能等の一次的な生理・生化学的な特徴を解析し、将来の高温耐性分子機構の研究対象にする高温耐性能に関与する表現形質を探索した。
M9)取得した。本研究では、これら高温耐性株のコロニー形態や世代時間、共生機能等の一次的な生理・生化学的な特徴を解析し、将来の高温耐性分子機構の研究対象にする高温耐性能に関与する表現形質を探索した。
武田 喜代子; 手島 光平; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成; 横山 正*
no journal, ,
現在、化学肥料からの脱却を目指し、東南アジア等では根粒菌バイオ肥料の利用を奨励している。しかし、輸送や保存時の高温による接種菌の活性低下等の問題があり改良が望まれている。そこで本研究では、イオンビーム突然変異育種法を用いてダイズ根粒菌高温耐性変異株を作出するとともに、作出した変異株の高温耐性能に関与する表現形質の探索を行った。その結果、イオンビーム照射により、43 Cで7日間生存可能な高温耐性変異株を20株作出することに成功した。また、それら高温耐性株に再度イオンビーム照射を行った所、47
Cで7日間生存可能な高温耐性変異株を20株作出することに成功した。また、それら高温耐性株に再度イオンビーム照射を行った所、47 Cで3日間生存可能な高温耐性変異株を5株作出することができた。一方、高温耐性株のコロニー色がピンク色に変化することや、世代時間が野生株よりも約1.5時間短くなること等、高温耐性能とかかわりがあると推測される表現形質を幾つか発見することができた。
Cで3日間生存可能な高温耐性変異株を5株作出することができた。一方、高温耐性株のコロニー色がピンク色に変化することや、世代時間が野生株よりも約1.5時間短くなること等、高温耐性能とかかわりがあると推測される表現形質を幾つか発見することができた。
武田 喜代子; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成*; 横山 正*
no journal, ,
化学肥料からの脱却を目指し、東南アジア等では根粒菌を用いたバイオ肥料の利用を奨励している。しかし、化学肥料とは異なり、輸送や保存時の高温による接種菌の活性低下等の問題があり改良が望まれている。そこで本研究では、ダイズ根粒菌 USDA110株を対象としたイオンビーム突然変異育種を行い、42
USDA110株を対象としたイオンビーム突然変異育種を行い、42 Cで7日間生存可能なダイズ根粒菌の高温耐性変異株の作出に成功した。さらに、作出した高温耐性変異株の次世代シークエンスデータ解析を行い、野生株と比較したところ、1.27Mbpの逆位という大規模なゲノム構造変異とともに、一塩基置換・欠失及び挿入などの84か所の小規模なDNA塩基変異が存在することを明らかにした。これらの大規模な構造変異あるいは小規模な遺伝子変異が高温耐性に寄与していることが示唆された。
Cで7日間生存可能なダイズ根粒菌の高温耐性変異株の作出に成功した。さらに、作出した高温耐性変異株の次世代シークエンスデータ解析を行い、野生株と比較したところ、1.27Mbpの逆位という大規模なゲノム構造変異とともに、一塩基置換・欠失及び挿入などの84か所の小規模なDNA塩基変異が存在することを明らかにした。これらの大規模な構造変異あるいは小規模な遺伝子変異が高温耐性に寄与していることが示唆された。
佐藤 勝也; 武田 喜代子*; 鳴海 一成*; 大津 直子*; 横山 正*
no journal, ,
根粒菌はマメ科植物と共生し、窒素栄養をマメ科植物に供給する。現在、化学肥料からの脱却を目指し、東南アジア等では、この共生関係を生かした根粒菌バイオ肥料の利用が奨励されている。しかし、化学肥料とは異なり、バイオ肥料は、輸送や保存時の高温による接種菌の活性低下等の問題があり改良が望まれている。これまで我々は、ダイズ根粒菌の温帯優良接種菌株である USDA110株を対象としたイオンビーム突然変異育種を行ってきた。そして、42
USDA110株を対象としたイオンビーム突然変異育種を行ってきた。そして、42 Cの液体培地中で少なくとも1週間は高い生存率を維持することが可能な高温耐性変異株の取得に成功した。本研究では、次世代シークエンサーを用いて高温耐性変異株の全ゲノムを解読し、野生株との塩基配列の比較によってDNA変異部位を同定した。ゲノムDNA塩基配列の比較解析の結果、高温耐性変異株M14において、1.27Mbpの逆位という大規模なゲノム構造変異、及び一塩基置換・欠失及び挿入などの18ヶ所の小規模なDNA塩基変異が存在することを明らかにした。これらの大規模な構造変異あるいは小規模な遺伝子変異がM14株の高温耐性に関与している可能性が考えられた。
Cの液体培地中で少なくとも1週間は高い生存率を維持することが可能な高温耐性変異株の取得に成功した。本研究では、次世代シークエンサーを用いて高温耐性変異株の全ゲノムを解読し、野生株との塩基配列の比較によってDNA変異部位を同定した。ゲノムDNA塩基配列の比較解析の結果、高温耐性変異株M14において、1.27Mbpの逆位という大規模なゲノム構造変異、及び一塩基置換・欠失及び挿入などの18ヶ所の小規模なDNA塩基変異が存在することを明らかにした。これらの大規模な構造変異あるいは小規模な遺伝子変異がM14株の高温耐性に関与している可能性が考えられた。