Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Abe, Hiroshi; Tokuhira, Shinnosuke*; Uchida, Hirohisa*; Oshima, Takeshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 365(Part A), p.214 - 217, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:52.11(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Abe, Hiroshi; Shimomura, Takuya; Tokuhira, Shinnosuke*; Shimada, Yukihiro*; Takenaka, Yusuke*; Furuyama, Yuta*; Nishimura, Akihiko; Uchida, Hirohisa*; Daido, Hiroyuki; Oshima, Takeshi
Proceedings of 7th International Congress on Laser Advanced Materials Processing (LAMP 2015) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2015/08
A short pulse laser (the nanosecond and femtosecond) was applied to hydrogen absorbing alloys surface layer, and a surface modification experiment was put into effective to aim at improvement of hydrogen adsorption functionally. It was investigated about correlation between an initial hydrogen absorption reaction rate of hydrogen alloys and a laser irradiation in this research. The laser irradiation condition was done with pulse width 100 fsec and energy 0.2 - 3.4 mJ/pulse. It blazed down on hydrogen absorbing alloys (LaNi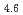 Al
Al ) and changed local order in the surface. As a result, the initial hydrogen absorption reaction rate was 1.5 - 3.0 times as fast as a irradiated sample, and the result and laser irradiated sample found out that a hydrogen absorption function improves. A laser irradiation can conclude to be effective in surface modification of the hydrogen storage materials.
) and changed local order in the surface. As a result, the initial hydrogen absorption reaction rate was 1.5 - 3.0 times as fast as a irradiated sample, and the result and laser irradiated sample found out that a hydrogen absorption function improves. A laser irradiation can conclude to be effective in surface modification of the hydrogen storage materials.
Abe, Hiroshi; Aone, Shigeo*; Morimoto, Ryo*; Uchida, Hirohisa*
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 580(Suppl.1), p.S219 - S221, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:30.03(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Abe, Hiroshi; Orimo, Satoshi; Kishimoto, Masahiko*; Aone, Shigeo*; Uchida, Hirohisa*; Daido, Hiroyuki; Oshima, Takeshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 307, p.218 - 220, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.99(Instruments & Instrumentation)We investigated the structure changes of a hydrogen storage alloy by ion irradiations, and its absorption property in order to obtain basic data and to elucidate relevant mechanisms of hydrogen absorption by the influence of the irradiation. In previous studies, the induction of vacancies in a hydrogen absorption alloy was found to be effective to increase in the hydrogen absorption rate. As well known, the rate of hydrogen absorption strongly depends upon the surface state of a hydrogen storage alloy because the dissociation of hydrogen molecules or water molecules needs electron change with the surface in the H gas or electrochemical reaction process. In this study, ion irradiations were made at a room temperature using the laser driven proton beam method, at Kansai Photon Science Institute, Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The beam treatment has several unique properties such as short pulse duration, high peak current, low transverse emittance, and wide energy range from KeV to MeV. The irradiation was used to modify the alloy surface using this equipment. From obtained results, the initial hydrogen absorption rate was found improved by the laser driven proton beam rather more effectively than a mono-energetic proton beam. Discussion is made on the correlation among proton irradiation (laser driven proton or mono-energetic proton) and the initial hydrogen absorption rate of the alloy. We argue about the usefulness of an energy spread beam.
gas or electrochemical reaction process. In this study, ion irradiations were made at a room temperature using the laser driven proton beam method, at Kansai Photon Science Institute, Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The beam treatment has several unique properties such as short pulse duration, high peak current, low transverse emittance, and wide energy range from KeV to MeV. The irradiation was used to modify the alloy surface using this equipment. From obtained results, the initial hydrogen absorption rate was found improved by the laser driven proton beam rather more effectively than a mono-energetic proton beam. Discussion is made on the correlation among proton irradiation (laser driven proton or mono-energetic proton) and the initial hydrogen absorption rate of the alloy. We argue about the usefulness of an energy spread beam.
 and TbFe
and TbFe
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Kohara, Shinji*; Ito, Masayoshi*; Abe, Hiroshi; Takeuchi, Mitsuaki*; Uchida, Hirohisa*; Matsumura, Yoshihito*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 38(1), p.109 - 112, 2013/03
We performed local structure analysis of SmFe and TbFe
and TbFe in the crystallization process from amorphous by using synchrotron X-ray pair-distribution function (PDF) method. The giant mangetostrictive materials of these compounds can be controlled its property by ion irradiation. In amorphous TbFe
in the crystallization process from amorphous by using synchrotron X-ray pair-distribution function (PDF) method. The giant mangetostrictive materials of these compounds can be controlled its property by ion irradiation. In amorphous TbFe and SmFe
and SmFe , the mosaic block size was small and the short-range order structure owing to Fe-Fe network maintained. In crystalline SmFe
, the mosaic block size was small and the short-range order structure owing to Fe-Fe network maintained. In crystalline SmFe , a rigid long-range order structure of Fe-Fe and Sm-Sm network coexisted and it had a large mosaic block size. On the other hand, in crystalline TbFe
, a rigid long-range order structure of Fe-Fe and Sm-Sm network coexisted and it had a large mosaic block size. On the other hand, in crystalline TbFe , Fe-Fe network degraded by Tb-Tb network owing to its lattice tolerance.
, Fe-Fe network degraded by Tb-Tb network owing to its lattice tolerance.
Okamura, Hiroki*; Tsuchida, Takashi*; Okada, Masao*; Yamagata, Ryohei; Seito, Hajime; Haruyama, Yasuyuki; Kaneko, Hirohisa
2011 Nen (Dai-29-Kai) Denki Setsubi Gakkai Zenkoku Taikai Koen Rombunshu, p.367 - 368, 2011/09
no abstracts in English
Abe, Hiroshi; Aone, Shigeo*; Morimoto, Ryo*; Uchida, Hirohisa*; Oshima, Takeshi
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 36(1), p.133 - 135, 2011/03
The introduction of vacancies in Pd was found to be effective for an increase in the initial hydrogen absorption rate in a previous study. Also, it was reported that the initial hydrogen absorption rate depends strongly on the surface conditions of metals. Heavy ions with keV ranges can create severe damage and high densities of vacancy near the surface of materials. As well known, the formation of hydride phases can be facilitated by the presence of vacancy because vacancy acts as hydrogen trapping site to form hydrides. Thus, the hydrogen absorption characteristics of Pd may be improved by the irradiation of heavy ions. As a result, the initial hydrogen absorption rate increased due to ion irradiation, and the value became 3 10 times higher than un-irradiated Pd.
10 times higher than un-irradiated Pd.
Tsuchida, Takashi*; Yamagata, Ryohei; Seito, Hajime; Haruyama, Yasuyuki; Kaneko, Hirohisa; Kashimura, Shinji*
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 22, 2011/01
There are a lot of restrictions of electric installations in a high radiation environment. For example longevity of electric devices would be shortened remarkably in a high radiation environment. It becomes impossible also for lighting equipments to keep an original function under a high radiological environment due to deterioration of insulation resistance of ballasts and luminous flux decrease of lamps, etc. The authors developed radiation-resistant lighting. This research aims to verify those functionality and safety under  -ray irradiation conditions.
-ray irradiation conditions.
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Abe, Hiroshi; Oshima, Takeshi; Uchida, Hirohisa*
Journal of Applied Physics, 107(9), p.093505_1 - 093505_6, 2010/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:33.25(Physics, Applied)An Mg-Fe alloy system prepared through mechanical alloying was structurally analyzed. Mechanical alloying can produce single-phase bcc alloys using Mg concentrations up to about 15 mol%. Use of conventional average structure analysis and X-ray pair-distribution function method enabled the long-range and short-range order structures of the Mg-Fe alloys to be bridged. The substituted Mg atoms were randomly arranged in the low-Mg composition but started to have an order structure. The partially ordered Mg-Fe alloy undergoes an austenitic (cubic) to martensitic (orthorhombic) phase change, as increasing Mg composition.
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Abe, Hiroshi; Oshima, Takeshi; Morimoto, Ryo*; Uchida, Hirohisa*; Mizuki, Junichiro
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 33(4), p.1053 - 1056, 2008/12
The effect of ion irradiation on palladium (Pd) metal was investigated by hydrogen-absorption measurements, SEM microscopy and synchrotron X-ray diffraction. N irradiation was made with an acceleration energy 350 keV. The initial hydrogen absorption rate of the irradiated Pd was three times larger than that of non-irradiated Pd. The microscopic structure was investigated by using the pair-distribution function (PDF) obtained by X-ray diffraction. Although the average structure of the Pd was f.c.c, the Pd atoms displaced and two occupancy sites are revealed. This site occupancy is closely related with the hydrogen-absorption rate.
irradiation was made with an acceleration energy 350 keV. The initial hydrogen absorption rate of the irradiated Pd was three times larger than that of non-irradiated Pd. The microscopic structure was investigated by using the pair-distribution function (PDF) obtained by X-ray diffraction. Although the average structure of the Pd was f.c.c, the Pd atoms displaced and two occupancy sites are revealed. This site occupancy is closely related with the hydrogen-absorption rate.
Abe, Hiroshi; Aone, Shigeo*; Uchida, Hirohisa*; Oshima, Takeshi
JAEA-Review 2008-055, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2007, P. 145, 2008/11
no abstracts in English
Abe, Hiroshi; Morimoto, Ryo*; Sato, Fumiatsu*; Azuma, Yorito*; Uchida, Hirohisa*
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 408-412, p.348 - 350, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:53.71(Chemistry, Physical)Mm(misch metal) based hydrogen storage alloys are applied to the negative electrode of the Ni-H battery and other hydrogen storage systems. In such pratical applications, various surface processes of hydrogen molecules often become rate contolling. Therefore, the improvement of the alloy surface is of great importance to promote the initial activation and hydriding rate. We have reported that the alkaline pretreatment of an alloy surfece exhibits a high durability against CO attack. Since low energy ion irradiation is quite useful for surface modification of materials, the hydriding proerties of a Mm is expected on electrochemical hydriding rate of the alloy. As a result, the ion irradiation Mm was found to induce a higher hydriding rate than that of the un-irradiation one.
Abe, Hiroshi; Morimoto, Ryo*; Sato, Fumiatsu*; Azuma, Yorito*; Uchida, Hirohisa*
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 404-406, p.288 - 292, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:50.78(Chemistry, Physical)The effect of ion irradiation on the rate of electrochemical hydriding rate of palladium (Pd) was investigated. In this study, ion irradiation onto the Pd surface was made with H , He
, He , Ar
, Ar and N
and N in the acceleration energy range from 30 to 350 keV, and in the ion dose up to 1
in the acceleration energy range from 30 to 350 keV, and in the ion dose up to 1  10
10 cm
cm . As the ion dose was increased, the initial rate of hydriding of Pd was increased. The ion irradiatiion treatment of the surface of a metal induces high concentrations of vacancy. The increased hydriding rate may be caused by the induction of high concentration of vacancy whichi traps hydrogen atoms, and this seems to accelerate the rates of hydride nucleation and growth in the surface. The ion irradiation was found as an effective way to enhance the rate of the initial activation of Pd in the electrochemical hydriding process.
. As the ion dose was increased, the initial rate of hydriding of Pd was increased. The ion irradiatiion treatment of the surface of a metal induces high concentrations of vacancy. The increased hydriding rate may be caused by the induction of high concentration of vacancy whichi traps hydrogen atoms, and this seems to accelerate the rates of hydride nucleation and growth in the surface. The ion irradiation was found as an effective way to enhance the rate of the initial activation of Pd in the electrochemical hydriding process.
Ishikawa, Hirohisa; Yui, Mikazu; Uchida, Masahiro; Kamei, Gento
JNC TN8200 2003-004, 151 Pages, 2004/03
To commemorate the 10th anniversary of the ENTRY, a laboratory in JNC Tokai for R&D in the field of geological disposal of radioactive waste, an international workshop was held in JNC Tokai, during the term of Sept 22 to 24, 2003. A technical tour for the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory site was also done before the workshop, on October 20 to 21, to deepen understanding the background of discussion in the workshop.The workshop contained two sessions. The topic of each session was 1. long-term transition of the near-field and 2. cooperation among the performance assessment, in-situ experiment, and laboratory experiment, respectively. In the session 1, we mainly discussed the thermal-hydrological-mechanical-chemical (THMC) coupled processes for the near-field performance assessment, especially focusing on chemical degradation effects by cement materials and the status of mechanistic understanding radionuclide migration. Silicate dissolution kinetic model, including smectite dissolution in a hyper alkaline solution, was also discussed. Then, we discussed a relevant linkage among laboratory experiments, model (simulation experiment) and database development, in-situ experiment and natural analogue.In the session 2, we discussed (1) methodology for understanding the site based on the surface and boreholes investigations, (2) identification of remained uncertainty after the surface and boreholes investigations, (3) the critical measurement at the surface and boreholes investigations, (4) feedback items from performance assessment to site characterization and (5) required data besides the site investigation. This report contains the minutes of discussion in the workshop. Presented materials were also appended with permission from the speakers.
Kamei, Gento; Ishikawa, Hirohisa; Yui, Mikazu; Uchida, Masahiro; Aoki, Kazuhiro
Saikuru Kiko Giho, (21), p.95 - 98, 2003/12
None
Abe, Hiroshi; Uchida, Hirohisa*; Azuma, Yorito*; Uedono, Akira*; Chen, Z. Q.*; Ito, Hisayoshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 206(1-4), p.224 - 227, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:77.46(Instruments & Instrumentation)Palladium(Pd) is used for the purification of H gas and as a catalyst for the dissociation of H
gas and as a catalyst for the dissociation of H molecules. Therefore, much work has been made until now. Since low energy ion irradiation, i.e., ion implantation is quite useful for surface modification of materials, the hydrogen absorption properties of Pd is expected to be improved by ion irradiation. In this work, we aimed at investigating the effect of ion irradiation on the hydrogen absorption rate of Pd. Ion irradiation was made with H
molecules. Therefore, much work has been made until now. Since low energy ion irradiation, i.e., ion implantation is quite useful for surface modification of materials, the hydrogen absorption properties of Pd is expected to be improved by ion irradiation. In this work, we aimed at investigating the effect of ion irradiation on the hydrogen absorption rate of Pd. Ion irradiation was made with H , He
, He and Ar
and Ar in an acceleration energy rage from 30 to 350keV up to a dose of 1 x 10
in an acceleration energy rage from 30 to 350keV up to a dose of 1 x 10 /cm
/cm . As a result, ion irradiated Pd sample was found to induce a higher absorption rate than that of the unirradiated one. The initial hydrogen results suggest that defects introduced in Pd by ion irradiation facilitate tha rate of nucleation and growth of hydride.
. As a result, ion irradiated Pd sample was found to induce a higher absorption rate than that of the unirradiated one. The initial hydrogen results suggest that defects introduced in Pd by ion irradiation facilitate tha rate of nucleation and growth of hydride.
Abe, Hiroshi; Uedono, Akira*; Uchida, Hirohisa*; Komatsu, A.*; Okada, Sohei; Ito, Hisayoshi
Materials Science Forum, 363-365, p.156 - 158, 2001/05
no abstracts in English
Hatanaka, Koichiro; Watari, Shingo*; Kanazawa, Yasuo*; Uchida, Masahiro; Ishiguro, Katsuhiko; Ishikawa, Hirohisa
PNC TN8410 95-377, 57 Pages, 1995/11
None
Abe, Hiroshi; Morimoto, Ryo*; Uchida, Hirohisa*; Oshima, Takeshi
no journal, ,
Regarding the hydrogen storage in metals, it was reported that the absorption concentration of hydrogen atoms and the hydrogen absorption rate depend strongly on the surface state of metals. For the surface modification of materials, ion implantaton/irradiation with both lon and high energy are known to be a quite useful method. These facts give the possibility that the hydrogen absorptivity in Pd is improved by surface modification using ion irradiation.
Aone, Shigeo*; Abe, Hiroshi; Uchida, Hirohisa*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English