Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Cs concentrations from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, phase III; Simulation with an identical source term and meteorological field at 1-km resolution
Cs concentrations from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, phase III; Simulation with an identical source term and meteorological field at 1-km resolutionSato, Yosuke*; Sekiyama, Tsuyoshi*; Fang, S.*; Kajino, Mizuo*; Qu rel, A.*; Qu
rel, A.*; Qu lo, D.*; Kondo, Hiroaki*; Terada, Hiroaki; Kadowaki, Masanao; Takigawa, Masayuki*; et al.
lo, D.*; Kondo, Hiroaki*; Terada, Hiroaki; Kadowaki, Masanao; Takigawa, Masayuki*; et al.
Atmospheric Environment; X (Internet), 7, p.100086_1 - 100086_12, 2020/10
The third model intercomparison project for investigating the atmospheric behavior of  Cs emitted during the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) accident (FDNPP-MIP) was conducted. A finer horizontal grid spacing (1 km) was used than in the previous FDNPP-MIP. Nine of the models used in the previous FDNPP-MIP were also used, and all models used identical source terms and meteorological fields. Our analyses indicated that most of the observed high atmospheric
Cs emitted during the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) accident (FDNPP-MIP) was conducted. A finer horizontal grid spacing (1 km) was used than in the previous FDNPP-MIP. Nine of the models used in the previous FDNPP-MIP were also used, and all models used identical source terms and meteorological fields. Our analyses indicated that most of the observed high atmospheric  Cs concentrations were well simulated, and the good performance of some models improved the performance of the multi-model ensemble. The analyses also confirmed that the use of a finer grid resolution resulted in the meteorological field near FDNPP being better reproduced. The good representation of the wind field resulted in the reasonable simulation of the narrow distribution of high deposition amount to the northwest of FDNPP and the reduction of the overestimation over the area to the south of FDNPP. In contrast, the performance of the models in simulating plumes observed over the Nakadori area, the northern part of Gunma, and the Tokyo metropolitan area was slightly worse.
Cs concentrations were well simulated, and the good performance of some models improved the performance of the multi-model ensemble. The analyses also confirmed that the use of a finer grid resolution resulted in the meteorological field near FDNPP being better reproduced. The good representation of the wind field resulted in the reasonable simulation of the narrow distribution of high deposition amount to the northwest of FDNPP and the reduction of the overestimation over the area to the south of FDNPP. In contrast, the performance of the models in simulating plumes observed over the Nakadori area, the northern part of Gunma, and the Tokyo metropolitan area was slightly worse.
Abe, Mitsushi*; Bae, S.*; Beer, G.*; Bunce, G.*; Choi, H.*; Choi, S.*; Chung, M.*; da Silva, W.*; Eidelman, S.*; Finger, M.*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(5), p.053C02_1 - 053C02_22, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:161 Percentile:99.30(Physics, Multidisciplinary)This paper introduces a new approach to measure the muon magnetic moment anomaly  and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)
and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)  at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure
at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure  and
and  using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for
using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for  is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of
is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of  e
e cm.
cm.
 Cs from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident; Simulations based on identical input data
Cs from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident; Simulations based on identical input dataSato, Yosuke*; Takigawa, Masayuki*; Sekiyama, Tsuyoshi*; Kajino, Mizuo*; Terada, Hiroaki; Nagai, Haruyasu; Kondo, Hiroaki*; Uchida, Junya*; Goto, Daisuke*; Qu lo, D.*; et al.
lo, D.*; et al.
Journal of Geophysical Research; Atmospheres, 123(20), p.11748 - 11765, 2018/10
Times Cited Count:49 Percentile:84.51(Meteorology & Atmospheric Sciences)A model intercomparison of the atmospheric dispersion of  Cs emitted following the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident was conducted by 12 models to understand the behavior of
Cs emitted following the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident was conducted by 12 models to understand the behavior of  Cs in the atmosphere. The same meteorological data, horizontal grid resolution, and an emission inventory were applied to all the models to focus on the model variability originating from the processes included in each model. The multi-model ensemble captured 40% of the observed
Cs in the atmosphere. The same meteorological data, horizontal grid resolution, and an emission inventory were applied to all the models to focus on the model variability originating from the processes included in each model. The multi-model ensemble captured 40% of the observed  Cs events, and the figure-of-merit in space for the total deposition of
Cs events, and the figure-of-merit in space for the total deposition of  Cs exceeded 80. Our analyses indicated that the meteorological data were most critical for reproducing the
Cs exceeded 80. Our analyses indicated that the meteorological data were most critical for reproducing the  Cs events. The results also revealed that the differences among the models were originated from the deposition and diffusion processes when the meteorological field was simulated well. However, the models with strong diffusion tended to overestimate the
Cs events. The results also revealed that the differences among the models were originated from the deposition and diffusion processes when the meteorological field was simulated well. However, the models with strong diffusion tended to overestimate the  Cs concentrations.
Cs concentrations.
Uchida, Kenichi*; Adachi, Hiroto; Kajiwara, Yosuke*; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Saito, Eiji
Solid State Physics, 64; Recent Advances in Magnetic Insulators; From Spintronics to Microwave Applications, p.1 - 27, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:18.01(Physics, Condensed Matter)Qiu, Z.*; Ando, Kazuya*; Uchida, Kenichi*; Kajiwara, Yosuke*; Takahashi, Ryo*; Nakayama, Hiroyasu*; An, Toshu*; Fujikawa, Yasunori*; Saito, Eiji
Applied Physics Letters, 103(9), p.092404_1 - 092404_4, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:120 Percentile:95.61(Physics, Applied)A platinum (Pt)/yttrium iron garnet (YIG) bilayer system with a well-controlled interface has been developed; spin mixing conductance at the Pt/YIG interface has been studied. A clear interface with good crystal perfection is experimentally demonstrated to be one of the important factors for an ultimate spin mixing conductance. The spin mixing conductance is obtained to be 1.3 10
10 m
m at the well-controlled Pt/YIG interface, which is close to a theoretical prediction.
at the well-controlled Pt/YIG interface, which is close to a theoretical prediction.
 Fe
Fe O
O
Kajiwara, Yosuke*; Uchida, Kenichi*; Kikuchi, Daisuke*; An, Toshu*; Fujikawa, Yasunori*; Saito, Eiji
Applied Physics Letters, 103(5), p.052404_1 - 052404_4, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:29.19(Physics, Applied)Heat-current-induced manipulation of spin relaxation in Y Fe
Fe O
O under an in-plane temperature gradient is investigated. We show that the linewidth of the ferromagnetic resonance spectrum, i.e., the spin relaxation, in an Y
under an in-plane temperature gradient is investigated. We show that the linewidth of the ferromagnetic resonance spectrum, i.e., the spin relaxation, in an Y Fe
Fe O
O film increases or decreases depending on the temperature-gradient direction and that this modulation is attributed to the spin-transfer torque caused by a thermally induced transverse spin-wave spin current in the Y
film increases or decreases depending on the temperature-gradient direction and that this modulation is attributed to the spin-transfer torque caused by a thermally induced transverse spin-wave spin current in the Y Fe
Fe O
O film. The experimental results also show that the spin-current magnitude generated by spin pumping in an attached Pt film is inversely proportional to the square of the modulated Gilbert damping constant, consistent with a phenomenological spin-pumping model.
film. The experimental results also show that the spin-current magnitude generated by spin pumping in an attached Pt film is inversely proportional to the square of the modulated Gilbert damping constant, consistent with a phenomenological spin-pumping model.
An, Toshu*; Vasyuchka, V. I.*; Uchida, Kenichi*; Chumak, A. V.*; Yamaguchi, Kazuya*; Harii, Kazuya; Oe, Junichiro*; Jungfleisch, M. B.*; Kajiwara, Yosuke*; Adachi, Hiroto; et al.
Nature Materials, 12(6), p.549 - 553, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:133 Percentile:96.12(Chemistry, Physical)Uchida, Kenichi*; Nonaka, Tatsumi*; Kikkawa, Takashi*; Kajiwara, Yosuke*; Saito, Eiji
Physical Review B, 87(10), p.104412_1 - 104412_6, 2013/03
Times Cited Count:104 Percentile:94.59(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The longitudinal spin Seebeck effect (LSSE) is investigated in various garnet ferritesY

 Fe
Fe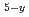

 O
O (
( = Gd, Ca;
= Gd, Ca;  = Al, Mn, V, In, Zr) by means of the inverse spin Hall effect in Pt films. The magnitude of the LSSE voltage in the Pt/Y
= Al, Mn, V, In, Zr) by means of the inverse spin Hall effect in Pt films. The magnitude of the LSSE voltage in the Pt/Y

 Fe
Fe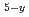

 O
O samples is found to be enhanced with increasing concentration of Fe in the garnet ferrites, which can be explained by a change in the spin-mixing conductance at the Pt/Y
samples is found to be enhanced with increasing concentration of Fe in the garnet ferrites, which can be explained by a change in the spin-mixing conductance at the Pt/Y

 Fe
Fe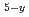

 O
O interfaces. We also investigate the dependence of the LSSE voltage on macroscopic magnetic parameters of Y
interfaces. We also investigate the dependence of the LSSE voltage on macroscopic magnetic parameters of Y

 Fe
Fe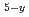

 O
O . The experimental results show that the LSSE voltage in the Pt/Y
. The experimental results show that the LSSE voltage in the Pt/Y

 Fe
Fe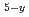

 O
O samples hasa positive correlation with the Curie temperature and the saturation magnetization, but no clear correlation with the gyromagnetic ratio and the Gilbert damping constant of the samples.
samples hasa positive correlation with the Curie temperature and the saturation magnetization, but no clear correlation with the gyromagnetic ratio and the Gilbert damping constant of the samples.
Jungfleisch, M. B.*; An, Toshu*; Ando, Kazuya*; Kajiwara, Yosuke*; Uchida, Kenichi*; Vasyuchka, V. I.*; Chumak, A. V.*; Serga, A. A.*; Saito, Eiji; Hillebrands, B.*
Applied Physics Letters, 102(6), p.062417_1 - 062417_4, 2013/02
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:84.33(Physics, Applied)Kirihara, Akihiro*; Uchida, Kenichi*; Kajiwara, Yosuke*; Ishida, Masahiko*; Nakamura, Yasunobu*; Manako, Takashi*; Saito, Eiji; Yorozu, Shinichi*
Nature Materials, 11(8), p.686 - 689, 2012/08
Times Cited Count:251 Percentile:98.50(Chemistry, Physical)Hou, D.*; Qiu, Z.*; Harii, Kazuya; Kajiwara, Yosuke*; Uchida, Kenichi*; Fujikawa, Yasunori*; Nakayama, Hiroyasu*; Yoshino, Tatsuro*; An, Toshu*; Ando, Kazuya*; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 101(4), p.042403_1 - 042403_4, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:80 Percentile:91.79(Physics, Applied)Inverse spin Hall effect has been investigated in bismuth(Bi)/permalloy(Py) bilayer films by using the spin pumping at room temperature. From the ferromagnetic-resonance-spectrum linewidth data, Bi is proved to be a good spin sink in our structure. We measured inverse spin Hall voltage and conductance of the Bi/Py bilayer and found that the inverse spin Hall current, 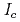 , decreases with increasing the Bi thickness, which is in contrast to the former understanding in similar bilayer systems, e.g., Pt/Py. We constructed a model to explain the thickness dependence of
, decreases with increasing the Bi thickness, which is in contrast to the former understanding in similar bilayer systems, e.g., Pt/Py. We constructed a model to explain the thickness dependence of 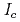 quantitatively, in which spin transport modulation near Bi/Py interface is considered.
quantitatively, in which spin transport modulation near Bi/Py interface is considered.
Uchida, Kenichi*; Ota, Takeru*; Adachi, Hiroto; Xiao, J.*; Nonaka, Tatsumi*; Kajiwara, Yosuke*; Bauer, G. E. W.*; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Saito, Eiji
Journal of Applied Physics, 111(10), p.103903_1 - 103903_11, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:127 Percentile:95.82(Physics, Applied)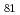 Fe
Fe /Pt films
/Pt filmsNakayama, Hiroyasu*; Ando, Kazuya*; Harii, Kazuya; Yoshino, Tatsuro*; Takahashi, Ryo*; Kajiwara, Yosuke*; Uchida, Kenichi*; Fujikawa, Yasunori*; Saito, Eiji
Physical Review B, 85(14), p.144408_1 - 144408_7, 2012/04
Times Cited Count:208 Percentile:98.03(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Geometric effects on the inverse spin Hall effect (ISHE) induced by the spin pumping driven by the ferromagnetic resonance (FMR) have been investigated quantitatively. We measured the FMR spectra and the electromotive force induced by the ISHE with changing the size and the thickness in Ni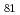 Fe
Fe /Pt films. The intensity of generated charge currents due to the ISHE changes systematically with changing the film geometry. The experimental results show a clear difference between Ni
/Pt films. The intensity of generated charge currents due to the ISHE changes systematically with changing the film geometry. The experimental results show a clear difference between Ni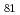 Fe
Fe and Pt thickness dependence of the ISHE induced by the spin pumping.
and Pt thickness dependence of the ISHE induced by the spin pumping.
Qiu, Z.*; Kajiwara, Yosuke*; Ando, Kazuya*; Fujikawa, Yasunori*; Uchida, Kenichi*; Tashiro, Takaharu*; Harii, Kazuya*; Yoshino, Tatsuro*; Saito, Eiji
Applied Physics Letters, 100(2), p.022402_1 - 022402_3, 2012/01
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:74.78(Physics, Applied)In a simple all-oxide system, spin pumping driven by spin wave resonances have been investigated by using the inverse spin-Hall effect (ISHE). In a lanthanum doped yttrium iron garnet (La:YIG)/indium tin oxide (ITO) bilayer film, the spin pumping generates and injects a spin current into the ITO layer, and an electromotive force signal is observed via the ISHE. The electromotive forces were measured depend on the out-of-plane magnetic-field-angle and the microwave excitation power, which were consistent with the theoretical prediction of the ISHE. The realization of the all-oxide spin pumping system extends possibilities for the oxide spintronics.
 Fe
Fe O
O /Pt hybrid structure
/Pt hybrid structureUchida, Kenichi*; An, Toshu*; Kajiwara, Yosuke*; Toda, Masaya*; Saito, Eiji
Applied Physics Letters, 99(21), p.212501_1 - 212501_3, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:49 Percentile:84.35(Physics, Applied)A spin current generated from a surface acoustic wave (SAW) was observed in an Y Fe
Fe O
O /Pt(YIG)/Pt hybrid structure. At the YIG/Pt interface, a SAW generated in the YIG layer was found to pump a spin current into the Pt layer, which was detected through the inverse spin-Hall effect in the Pt. The YIG/Pt lateral structure combined with a piezoelectric wedge transducer enables the systematic investigation of the spin-voltage distribution due to the SAW in the YIG. Since the observed phenomenon has high affinity with SAW-based electronics, it will pave the way for constructing spintronic SAW devices.
/Pt(YIG)/Pt hybrid structure. At the YIG/Pt interface, a SAW generated in the YIG layer was found to pump a spin current into the Pt layer, which was detected through the inverse spin-Hall effect in the Pt. The YIG/Pt lateral structure combined with a piezoelectric wedge transducer enables the systematic investigation of the spin-voltage distribution due to the SAW in the YIG. Since the observed phenomenon has high affinity with SAW-based electronics, it will pave the way for constructing spintronic SAW devices.
Uchida, Kenichi*; Xiao, J.*; Adachi, Hiroto; Oe, Junichiro; Takahashi, Saburo; Ieda, Junichi; Ota, Takeru*; Kajiwara, Yosuke*; Umezawa, Hiromitsu*; Kawai, Hirotaka*; et al.
Nature Materials, 9(11), p.894 - 897, 2010/11
Times Cited Count:1110 Percentile:99.87(Chemistry, Physical)Thermoelectric generation is an essential function in future energy-saving technologies. However, it has so far been an exclusive feature of electric conductors, a situation which limits its application; conduction electrons are often problematic in the thermal design of devices. Here we report electric voltage generation from heat flowing in an insulator. We reveal that, despite the absence of conduction electrons, the magnetic insulator LaY Fe
Fe O
O can convert a heat flow into a spin voltage. Attached Pt films can then transform this spin voltage into an electric voltage as a result of the inverse spin Hall effect. The experimental result require us to introduce a thermally activated interface spin exchange between LaY
can convert a heat flow into a spin voltage. Attached Pt films can then transform this spin voltage into an electric voltage as a result of the inverse spin Hall effect. The experimental result require us to introduce a thermally activated interface spin exchange between LaY Fe
Fe O
O and Pt. Our findings extend the range of potential materials for thermoelectric applications and provide a crucial piece of information for understanding the physics of the spin Seebeck effect.
and Pt. Our findings extend the range of potential materials for thermoelectric applications and provide a crucial piece of information for understanding the physics of the spin Seebeck effect.
Takeuchi, Shinji; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Amano, Kenji; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Hayano, Akira; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Oyama, Takuya; et al.
JAEA-Review 2009-017, 29 Pages, 2009/08
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is developing a geoscientific research project named the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project in crystalline rock environment in order to establish scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of HLW. Geoscientific research at the MIU project is planned to be carried out in three phases over a period of 20 years; Surface-based Investigation Phase (Phase 1), Construction Phase (Phase 2) and Operation Phase (Phase 3). Currently, the project is under the Construction Phase. This document presents the following 2009 fiscal year plan based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2002, (1) Investigation Plan, (2) Construction Plan, (3) Research Collaboration Plan, etc.
Nishio, Kazuhisa; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Mikake, Shinichiro; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Amano, Kenji; Oyama, Takuya; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Hama, Katsuhiro; Mizuno, Takashi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2009-002, 88 Pages, 2009/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is developing a geoscientific research project named Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to establish scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of HLW. Geoscientific research at MIU is planned to be carried out in three phases over a period of 20 years; Surface-based Investigation Phase (Phase I), Construction Phase (Phase II) and Operation Phase (Phase III). Currently, the project is under the Construction Phase. This document presents the following results of the research and development performed in 2007 fiscal year, as a part of the Construction Phase based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2002, (1) Investigation at the MIU Construction Site and the Shobasama Site, (2) Construction at the MIU Construction Site, (3) Research Collaboration.
Nishio, Kazuhisa; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Mikake, Shinichiro; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Amano, Kenji; Oyama, Takuya; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Hama, Katsuhiro; Yoshida, Haruo*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2009-001, 110 Pages, 2009/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is developing a geoscientific research project named Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project in crystalline rock environment in order to establish scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of HLW. Geoscientific research at MIU is planned to be carried out in three phases over a period of 20 years; Surface-based Investigation Phase (Phase 1), Construction Phase (Phase 2) and Operation Phase (Phase 3). Currently, the project is under the Construction Phase. This document presents the following results of the research and development performed in 2006 fiscal year, as a part of the Construction Phase based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2002, (1) Investigation at the MIU Construction Site, (2) Construction at the MIU Construction Site, (3) Research Collaboration.
Nishio, Kazuhisa; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Mikake, Shinichiro; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Amano, Kenji; Oyama, Takuya; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Hama, Katsuhiro; Yoshida, Haruo*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2008-073, 99 Pages, 2009/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is developing a geoscientific research project named Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project in crystalline rock environment in order to establish scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of HLW. Geoscientific research at MIU is planned to be carried out in three phases over a period of 20 years; Surface-based Investigation Phase (Phase 1), Construction Phase (Phase 2) and Operation Phase (Phase 3). Currently, the project is under the Construction Phase. This document presents the following results of the research and development performed in 2005 fiscal year, as a part of the Construction Phase based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2002, (1) Investigation at the MIU Construction Site, (2) Construction at the MIU Construction Site, (3) Research Collaboration.