Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Okuno, Hiroshi; Kawakami, Takeshi; Watanabe, Fumitaka; Horikoshi, Hidehiko*
Journal of Disaster Research, 18(8), p.911 - 917, 2023/12
In response to residents' concerns about the radiation health effects following the nuclear accidents at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of the Tokyo Electric Power Company in March 2011, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) established a telephone consultation system. Eight toll-free telephone lines were prepared, and employees with knowledge of radiation health effects were assigned for consultation. Approximately 35,000 consultations were conducted from March 17, 2011, to September 18, 2012. The results of the text mining analysis revealed that the greatest source of anxiety was the impact on children's health from radiation. The JAEA's system for telephone consultation was improved following this telephone consultation experience. The description of telephone hotlines in the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) guide, GSG-14, was discussed for further improvements of the JAEA's telephone consultation system.
Hamamoto, Shimpei; Shimizu, Atsushi; Inoi, Hiroyuki; Tochio, Daisuke; Homma, Fumitaka; Sawahata, Hiroaki; Sekita, Kenji; Watanabe, Shuji; Furusawa, Takayuki; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 388, p.111642_1 - 111642_11, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:51.78(Nuclear Science & Technology)Following the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident in 2011, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency adapted High-Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) to meet the new regulatory requirements that began in December 2013. The safety and seismic classifications of the existing structures, systems, and components were discussed to reflect insights regarding High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactors (HTGRs) that were acquired through various HTTR safety tests. Structures, systems, and components that are subject to protection have been defined, and countermeasures to manage internal and external hazards that affect safety functions have been strengthened. Additionally, measures are in place to control accidents that may cause large amounts of radioactive material to be released, as a beyond design based accident. The Nuclear Regulatory Commission rigorously and appropriately reviewed this approach for compliance with the new regulatory requirements. After nine amendments, the application to modify the HTTR's installation license that was submitted in November 2014 was approved in June 2020. This response shows that facilities can reasonably be designed to meet the enhanced regulatory requirements, if they reflect the characteristics of HTGRs. We believe that we have established a reference for future development of HTGR.
Watanabe, Fumitaka; Okuno, Hiroshi
Proceedings of 18th International Symposium on the Packaging and Transport of Radioactive Materials (PATRAM 2016) (DVD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2016/09
This paper shows our calculations on the effects of a radiological release by assuming a severe accident in nuclear material transportation. Following recalculations of safe distance from the point of a severe accident during transportation of a transportation cask TN12 typically used in France containing spent nuclear fuel, and calculations to replicate the "Regulatory Guide: Emergency Preparedness for Nuclear Facilities", a similar calculation was made for a spent fuel transportation cask NFT-14P that was typically utilized in Japan instead of TN12. The safe distance was calculated to be about 30 m. The above calculations were made with the HotSpot codes which adopted the Gauss plume model and had been developed by the USA. Some additional calculations were made with EyesAct, which was developed and used in Japan, adopting also the Gauss plume model, to compare calculation results.
Homma, Fumitaka; Inoi, Hiroyuki; Watanabe, Shuji; Fukutani, Koji*
JAEA-Technology 2013-034, 57 Pages, 2013/12
Emergency generator of HTTR started in the blackout occurred just after an Tohoku Pacific Ocean Earthquake on March 11, 2011 with an intensity of 5 upper on the Japanese seven stage seismic scale and its duration time was long. In addition, we suffer from multiple severe aftershocks just after the start of emergency generators. Emergency generator of HTTR was able to supply output electric power sufficiently and stably to required loads. We carried on integrity check of the emergency generator for the HTTR after the earthquake. In particular, we put emphasis on finding faults caused by thee earthquake shaking. As a result, we found that the erosion in a combustion liner, and the condition of erosion was very strange and rare. Therefore, we carried out investigations of causes of erosion, and change of specifications for combustion liner to prevent erosion. This measure improve the reliability for the further Large-Scale earthquake.
Kanamori, Masashi; Shirakawa, Yusuke; Yamashita, Toshiyuki; Okuno, Hiroshi; Terunuma, Hiroshi; Ikeda, Takeshi; Sato, Sohei; Terakado, Naoya; Nagakura, Tomohiro; Fukumoto, Masahiro; et al.
JAEA-Review 2010-037, 60 Pages, 2010/09
When a nuclear emergency occurs in Japan, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) provides technical support to the National government, local governments, police, fire station and license holder etc. They are designated public organizations conforming to the basic law on emergency preparedness and the basic plan for disaster countermeasures. The Nuclear Emergency Assistance & Training Center (NEAT) of JAEA provides a comprehensive range of technical support activities to an off-site center in case of a nuclear emergency. Specifically, NEAT gives technical advice and information, provides for the dispatch of specialist as required, supplies emergency equipments and materials to the national government and municipal office. NEAT provide various lectures and training course concerning nuclear disaster prevention for those personnel taking an active part in emergency response organizations at normal time. And NEAT researches on nuclear disaster prevention and also cooperate with international organizations. This annual report summarized the activities of JAEA/NEAT in the fiscal year 2009.
Nagai, Haruyasu; Watanabe, Fumitaka; Endo, Kuniaki
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 51(11), p.816 - 818, 2009/11
, 51(11), p.816 - 818, 2009/11
It is important to consider and develop countermeasures against Radiological Dispersal Device (RDD) incident in an urban environment. In the U.S. functions of countermeasure against terrorist attack has been developed, maintained and disseminated to the public by conducting regular emergency exercises. Here, we review the full-scale emergency exercise against RDD incident in an urban environment (EMPIRE09) held at Albany in the State of New York in June 2009. The National Response Framework of the U.S. for nuclear and radiological incidents is also explained. Finally, as our recommendation to the domestic countermeasures against terrorist attack, analyses on the difference of emergency response frameworks between Japan and the U.S. and important items to be considered are provided for consideration of the state of countermeasure against RDD incident in an urban environment.
Kanamori, Masashi; Hashimoto, Kazuichiro; Terunuma, Hiroshi; Ikeda, Takeshi; Omura, Akiko; Terakado, Naoya; Nagakura, Tomohiro; Fukumoto, Masahiro; Watanabe, Fumitaka; Yamamoto, Kazuya; et al.
JAEA-Review 2009-023, 61 Pages, 2009/09
When a nuclear emergency occurs in Japan, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) provides technical support to the National government, local governments, police, fire station and license holder etc. They are Designated Public Organizations conforming to the Basic Law on Emergency Preparedness and the Basic Plan for Disaster Countermeasures. The Nuclear Emergency Assistance and Training Center (NEAT) of JAEA provides a comprehensive range of technical support activities to an Off-Site Center in case of a nuclear emergency. Specifically, NEAT gives technical advice and information, provides for the dispatch of specialist as required, supplies emergency equipments and materials to the Joint Council of Nuclear Disaster Countermeasures, which meets at the Off-Site Center. NEAT provide various lectures and training course concerning nuclear disaster prevention for those personnel taking an active part in emergency response organizations at normal time. And NEAT researches on nuclear disaster prevention and also cooperate with international organizations. This annual report summarized the activities of JAEA/NEAT in the fiscal year 2008.
Esaka, Fumitaka; Watanabe, Kazuo; Onodera, Takashi; Lee, C. G.; Magara, Masaaki; Sakurai, Satoshi; Usuda, Shigekazu
Applied Surface Science, 255(4), p.1512 - 1515, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:39.14(Chemistry, Physical)Isotope ratio analysis of individual uranium particles in environmental samples taken at nuclear facilities is one of the key techniques for nuclear safeguards. For accurate analysis, we developed a combined technique of single particle manipulation, which was carried out in scanning electron microscope (SEM), and SIMS. This technique gives information on particle size as well as isotope ratios for each particle. In the present study, the particle size dependence of the precision of uranium isotope ratio is investigated by using the SEM-SIMS technique. In the analysis of individual particles of a CRM U050 (5% enriched uranium) sample, even if the particle diameter was 0.5  m, the analysis with the precision of
m, the analysis with the precision of  U/
U/ U isotope ratio within 5% was possible. In the presentation, the results obtained for the other uranium particles having different isotopic composition will also be presented.
U isotope ratio within 5% was possible. In the presentation, the results obtained for the other uranium particles having different isotopic composition will also be presented.
Watanabe, Fumitaka; Yamamoto, Kazuya; Sajiki, Kenjiro; Yasu, Sadanori*; Igarashi, Miyuki*
JAEA-Technology 2008-025, 63 Pages, 2008/03
The larger the scale of an accident, the more closely cooperation is needed between concerned parties for appropriate and timely response, especially if they are located apart from each other. The past nuclear accidents revealed that they failed to share important information with each other and such a situation caused unnecessary confusion in public information. Based on lessons learned from accidents, JAEA developed the Emergency Information Clearinghouse (ECHO). Information is fed into a secured server from each PC. Unified information on the server can be chronologically listed through a web browser. This web-based system enables separately located parties to share proper information in a timely manner and minimize the load of managing a great deal of information. The ECHO has been in operation 24/7 on a network for nuclear emergency response and connects nationwide 22 off-site centers, and several authorities concerned. The system has been used during for training and drills.
Watanabe, Fumitaka
Proceedings of 2nd International Joint Topical Meeting on Emergency Preparedness and Response and Robotics and Remote Systems (CD-ROM), p.9 - 14, 2008/03
The JCO criticality accident in 1999 revealed that parties concerned had no effective tools to share important information about the accident with each other and such a situation caused unnecessary confusion and unease in society. Based on lessons learned from the accident, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) developed the Emergency Information Clearinghouse (ECHO) in 2002. ECHO is in operation as an information tool on a dedicated-line network for nuclear emergency response. ECHO connects nationwide 22 off-site centers, central government emergency operations centers, and the Nuclear Emergency Assistant and Training Center (NEAT) of JAEA. Various points to be improved have been suggested through the practical use in nuclear emergency drills. ECHO has become an efficient information sharing tool through several improvements. The system enables the parties separately located to share proper information in a timely manner and minimize the load of managing a large amount of information.
Zhang, X. Z.*; Esaka, Fumitaka; Esaka, Konomi; Magara, Masaaki; Sakurai, Satoshi; Usuda, Shigekazu; Watanabe, Kazuo
Spectrochimica Acta, Part B, 62(10), p.1130 - 1134, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:71.59(Spectroscopy)The capability of inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) for the determination of uranium isotope ratios in individual particles was determined. For this purpose, we developed an experimental procedure including single particle transfer with a manipulator, chemical dissolution and isotope ratio analysis. As the result, the  U/
U/ U isotope ratio for the particle with the diameter between 0.5 and 3.9
U isotope ratio for the particle with the diameter between 0.5 and 3.9  m was successfully determined with the deviation from the certified ratio within 1.8%. The developed procedure was successfully applied to the analysis of a simulated environmental sample prepared from a mixture of indoor dust (NIST SRM 2583) and uranium particles (NBL CRM U050, U350 and U950a). From the results, the proposed procedure was found to be an alternative analytical tool for nuclear safeguards.
m was successfully determined with the deviation from the certified ratio within 1.8%. The developed procedure was successfully applied to the analysis of a simulated environmental sample prepared from a mixture of indoor dust (NIST SRM 2583) and uranium particles (NBL CRM U050, U350 and U950a). From the results, the proposed procedure was found to be an alternative analytical tool for nuclear safeguards.
Lee, C. G.; Iguchi, Kazunari; Inagawa, Jun; Suzuki, Daisuke; Esaka, Fumitaka; Magara, Masaaki; Sakurai, Satoshi; Watanabe, Kazuo; Usuda, Shigekazu
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 272(2), p.299 - 302, 2007/05
Times Cited Count:49 Percentile:93.75(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
Esaka, Fumitaka; Esaka, Konomi; Lee, C. G.; Magara, Masaaki; Sakurai, Satoshi; Usuda, Shigekazu; Watanabe, Kazuo
Talanta, 71(3), p.1011 - 1015, 2007/02
Times Cited Count:66 Percentile:87.15(Chemistry, Analytical)A new technique to measure  U/
U/ U and
U and  U/
U/ U isotope ratios for individual particles in safeguards environmental samples was developed, which was a combination of particle isolation under scanning electron microscope (SEM) and secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS). In order to verify the effectiveness of the technique, the
U isotope ratios for individual particles in safeguards environmental samples was developed, which was a combination of particle isolation under scanning electron microscope (SEM) and secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS). In order to verify the effectiveness of the technique, the  U/
U/ U and
U and  U/
U/ U isotope ratios were measured for individual particles in a simulated environmental sample containing uranium standard (NIST CRM U010) and Pb metal particles. The deviations of the
U isotope ratios were measured for individual particles in a simulated environmental sample containing uranium standard (NIST CRM U010) and Pb metal particles. The deviations of the  U/
U/ U and
U and  U/
U/ U isotope ratios from the certified values increased with increasing the signal intensity ratio of
U isotope ratios from the certified values increased with increasing the signal intensity ratio of  Pb to
Pb to  U, which was due to the interferences by Pb molecular ions. By the isolation of individual uranium particles prior to SIMS analysis, the interferences were eliminated. The effectiveness of the technique was also confirmed by the analysis of a real sample taken at a laboratory in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA).
U, which was due to the interferences by Pb molecular ions. By the isolation of individual uranium particles prior to SIMS analysis, the interferences were eliminated. The effectiveness of the technique was also confirmed by the analysis of a real sample taken at a laboratory in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA).
Esaka, Fumitaka; Esaka, Konomi; Magara, Masaaki; Sakurai, Satoshi; Usuda, Shigekazu; Watanabe, Kazuo
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 251(1), p.218 - 222, 2006/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:27.62(Instruments & Instrumentation)Individual Cu particles were transferred, with a manipulator attached to a scanning electron microscope, onto individual Si carriers for subsequent quantitative analysis by means of total-reflection X-ray fluorescence spectrometry. By applying an internal standard to the carriers prior to the particle transfer, the amounts of Cu were successfully determined for the particles with diameters between 3.04 and 8.84 micrometer. The deviations of the measured values from the calculated ones were within 10%. However, the deviations were more than 33% if particle diameters were greater than 10.17 micrometer. This suggests that in such a case the fluorescent X-ray is not emitted from all parts of the particle. Even if particle diameters were greater than 10.17 micrometer, the amounts of Cu could be determined with the deviations within 9% when the particles were dissolved with HNO solution. This technique was also successfully applied to the measurement of individual brass particles.
solution. This technique was also successfully applied to the measurement of individual brass particles.
Usuda, Shigekazu; Yasuda, Kenichiro; Kokubu, Yoko; Esaka, Fumitaka; Lee, C. G.; Magara, Masaaki; Sakurai, Satoshi; Watanabe, Kazuo; Hirayama, Fumio; Fukuyama, Hiroyasu; et al.
International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 86(9), p.663 - 675, 2006/08
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:39.28(Chemistry, Analytical)The IAEA introduced the environmental sample analysis method, as a powerful tool to detect undeclared nuclear activities, into strengthened safeguards system. The principle of the method is that nuclear signatures can be evidenced if trace amount of nuclear materials in environmental samples taken from inside and outside of nuclear facilities are accurately analyzed. Currently, isotope ratios of uranium and plutonium in "swipe" samples are measured, which are collected in nuclear facilities. In future, the subject of environmental sample analysis will expand to soil, sediment, vegetation, water and airborne dust taken from outside of the nuclear facilities. If physical and chemical form of the nuclear materials is identified, we may estimate their origin, treatment process and migration behavior. This paper deals with the developed analytical techniques for the safeguards environmental samples, the current R&D on techniques related to estimation of the physical and chemical form, and possible analytical methodologies applicable to ultra-trace amounts of nuclear materials.
Lee, C. G.; Iguchi, Kazunari; Esaka, Fumitaka; Magara, Masaaki; Sakurai, Satoshi; Watanabe, Kazuo; Usuda, Shigekazu
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 245(2), p.440 - 444, 2006/04
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:49.64(Instruments & Instrumentation)The etching rates of fission track detectors made of polycarbonate containing uranium particles were measured after thermal neutron irradiation with fluence of 8 10
10 n/cm
n/cm , in order to study the influence of uranium enrichment on the etching rate that was calculated from the weight loss by etching. There is a strong correlation between the etching rate of detector and the enrichment E of uranium particle: the former increases as the latter increases. Particularly, the etching rate per particle was proportional to E
, in order to study the influence of uranium enrichment on the etching rate that was calculated from the weight loss by etching. There is a strong correlation between the etching rate of detector and the enrichment E of uranium particle: the former increases as the latter increases. Particularly, the etching rate per particle was proportional to E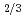 rather than E
rather than E , which is probably due to the overlapping of fission tracks. The etching behaviors of detector revealed that the existence of two different etching rate regions, a nonlinear region in the beginning of etching process and a subsequent constant region, which was explained as the opening of fission tracks and the broadening of opened tracks, respectively.
, which is probably due to the overlapping of fission tracks. The etching behaviors of detector revealed that the existence of two different etching rate regions, a nonlinear region in the beginning of etching process and a subsequent constant region, which was explained as the opening of fission tracks and the broadening of opened tracks, respectively.
Lee, C. G.; Iguchi, Kazunari; Esaka, Fumitaka; Magara, Masaaki; Sakurai, Satoshi; Watanabe, Kazuo; Usuda, Shigekazu
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 2, 45(10), p.L294 - L296, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:55.64(Physics, Applied)We have developed an effective method for fission track (FT) sample preparation to perform particle analysis of the safeguards environmental samples by the FT-thermal ionization mass spectrometry (TIMS) method. In this method, a fission track detector and the layer containing particles are separated. The main feature of the developed FT sample is that the detection of a particle from the corresponding fission track can be performed correctly and in a simple manner by fixing each one end of the detector and the particle layer and by using an etching tool. It is expected that this method will enhance the effectiveness of particle analysis.
Sakurai, Satoshi; Magara, Masaaki; Usuda, Shigekazu; Watanabe, Kazuo; Esaka, Fumitaka; Hirayama, Fumio; Lee, C. G.; Yasuda, Kenichiro; Inagawa, Jun; Suzuki, Daisuke; et al.
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-27-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2006/00
no abstracts in English
Iguchi, Kazunari; Esaka, Konomi; Lee, C. G.; Inagawa, Jun; Esaka, Fumitaka; Onodera, Takashi; Fukuyama, Hiroyasu; Suzuki, Daisuke; Sakurai, Satoshi; Watanabe, Kazuo; et al.
Radiation Measurements, 40(2-6), p.363 - 366, 2005/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:58.78(Nuclear Science & Technology)In particle analysis for safeguards environmental samples, the fission track technique is very important to detect sub-micrometer particles containing uranium. In the technique the authors developed, the particles were recovered onto the polycarbonate membrane filter. The filter was dissolved in solvent and dried to form a thin film of detector, in which the particles were confined. After thermal neutron irradiation and etching, the particles of interest in the detector were easily identified with fission tracks, and were picked up for isotope ratio analysis. It was found, however, that the particles in the vicinity of the detector surface may fall off during the etching process. Therefore, optimization of the etching condition is required. In this work, the effects of etching time and enrichment of uranium in particles were investigated. Preliminary results suggest that etching time should be shorter with the increase in the enrichment.
Watanabe, Fumitaka; Matsui, Tomoaki; Nomura, Tamotsu
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2005/10
None