Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakajima, Kenji; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Ito, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Endo, Hitoshi*; Fujita, Masaki*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Gong, W.*; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(3), p.9_1 - 9_59, 2017/12
The neutron instruments suite, installed at the spallation neutron source of the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), is reviewed. MLF has 23 neutron beam ports and 21 instruments are in operation for user programs or are under commissioning. A unique and challenging instrumental suite in MLF has been realized via combination of a high-performance neutron source, optimized for neutron scattering, and unique instruments using cutting-edge technologies. All instruments are/will serve in world-leading investigations in a broad range of fields, from fundamental physics to industrial applications. In this review, overviews, characteristic features, and typical applications of the individual instruments are mentioned.
Seto, Hideki; Ito, Shinichi; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Endo, Hitoshi*; Nakajima, Kenji; Shibata, Kaoru; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kawakita, Yukinobu; et al.
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta; General Subjects, 1861(1), p.3651 - 3660, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:82.01(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)J-PARC, Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex provides short pulse proton beam at a repetition rate 25 Hz and the maximum power is expected to be 1 MW. Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) has 23 neutron beam ports and 21 instruments have already been operated or under construction / commissioning. There are 6 inelastic / quasi-elastic neutron scattering spectrometers and the complementary use of these spectrometers will open new insight for life science.
Takahashi, Nobuaki*; Murata, Hirohiko*; Mitsubori, Hitoshi*; Sakuraba, Junji*; Soga, Tomohiro*; Aoki, Yasushi*; Kato, Takanori*; Saito, Yuichi; Yamada, Keisuke; Ikenaga, Noriaki*; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 85(2), p.02C306_1 - 02C306_3, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:10.46(Instruments & Instrumentation)Ishikawa, Nobuyuki; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Fujita, Kaoru; Yamada, Yumi*; Okazaki, Hitoshi*; Suzuki, Shinichi*
Proceedings of 2012 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP '12) (CD-ROM), p.483 - 489, 2012/06
The development of safety protection system for JSFR is progressed in terms of logic circuits, selection of trip signals and its setting values for reactor trip. In addition, it is necessitated to evaluate the satisfaction for requirements of the safety protection system by safety analyses considering comprehensive parameter ranges. For this purpose, we will report the current status of the development focusing on the evaluation results for satisfaction of safety protection system based on safety standard.
Yamada, Fumitaka; Sonobe, Hitoshi; Igarashi, Hiroshi
JAEA-Review 2007-061, 67 Pages, 2008/02
In JAEA, various systems associated with the collaboration with industries and universities are enacted. These systems have been operated considering the needs of JAEA's program, industry and academia, resultantly contributed, for example, to basic research and the project development. Activities under these systems contain personal exchanges, the publication of the accomplishments and utilization of those, in R&D concerning geological disposal technology of HLW. These activities have progressed in PNC and JNC, through JAEA. The accomplishments from these systems have contributed to the advancement of the national program on the geological disposal of HLW. In this report, the progress of the R&D under these systems was investigated from the beginning of their operation. The contribution to the R&D on geological disposal technology of HLW was also studied. On the basis of these studies, the future utilization of the systems of the collaboration was also discussed.
 Sb
Sb Te
Te ; Ring statistics analogy between the crystal and amorphous states
; Ring statistics analogy between the crystal and amorphous statesKohara, Shinji*; Kato, Kenichi*; Kimura, Shigeru*; Tanaka, Hitoshi*; Usuki, Takeshi*; Suzuya, Kentaro; Tanaka, Hiroshi*; Moritomo, Yutaka*; Matsunaga, Toshiyuki*; Yamada, Noboru*; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 89(20), p.201910_1 - 201910_3, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:216 Percentile:97.97(Physics, Applied)The three-dimensional atomic configuration of amorphous Ge Sb
Sb Te
Te were derived by reverse Monte Carlo simulation with synchrotron-radiation X-ray diffraction data. The authors found that amorphous Ge
were derived by reverse Monte Carlo simulation with synchrotron-radiation X-ray diffraction data. The authors found that amorphous Ge Sb
Sb Te
Te can be regarded as "even-numbered ring structure", because the ring statistics is dominated by four- and six-fold rings analogous to the crystal phase. On the other hand, the formation of Ge-Ge homopolar bonds in amorphous GeTe constructs both odd- and even-numbered rings. They believe that the unusual ring statistics of amorphous Ge
can be regarded as "even-numbered ring structure", because the ring statistics is dominated by four- and six-fold rings analogous to the crystal phase. On the other hand, the formation of Ge-Ge homopolar bonds in amorphous GeTe constructs both odd- and even-numbered rings. They believe that the unusual ring statistics of amorphous Ge Sb
Sb Te
Te is the key for the fast crystallization speed of the material.
is the key for the fast crystallization speed of the material.
 SiO
SiO determined by high
determined by high 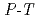 in situ X-ray diffractometry
in situ X-ray diffractometryKatsura, Tomoo*; Yamada, Hitoshi*; Shimmei, Toru*; Kubo, Atsushi*; Ono, Shigeaki*; Kanzaki, Masami*; Yoneda, Akira*; Walter, M. J.*; Ito, Eiji*; Urakawa, Satoru*; et al.
Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 136(1-2), p.11 - 24, 2003/04
Times Cited Count:184 Percentile:93.71(Geochemistry & Geophysics)no abstracts in English
Takano, Hitoshi*; Sugimoto, Yoshihiro*; Yamashita, Tadashi*; Yamada, Naoyuki*
JNC TJ6420 2003-011, 127 Pages, 2003/02
Drilling and high resolution electrical survey was carried out to make a geological structure model around mill tailing yard. Following by drill investigation, Distribution of the granite which became fragility was confirmed by the development of fractures with hydrothermal vein. However, fresh bedrock is distributed deeper than 40m. Permeability of weathering granite is about in 1.15 10
10 m/sec. The value agrees previous findings. In fresh granite, permeability is 4.33
m/sec. The value agrees previous findings. In fresh granite, permeability is 4.33 10
10 m/sec, and it value is larger than existing data. It is for developing of fractures in fresh granite. At high resolution electrical survey, analysis is done by 3 dimensions. By analyzing it with 3 dimensions, good resistivity distribution was provided. From resistivity distribution, tailing, weathered granite or sedimentary rock and fresh granite are classified. Resistivity distribution was taken out from lines or seismic exploration refraction method, and compared between two methods. As a result, low resistivity region is fitted low velocity zone and high resistivity region is fitted high velocity zone. Topography and 4 geological models are created. These models are output as versatile text data to show relation of a coordinate and the point of contact.
m/sec, and it value is larger than existing data. It is for developing of fractures in fresh granite. At high resolution electrical survey, analysis is done by 3 dimensions. By analyzing it with 3 dimensions, good resistivity distribution was provided. From resistivity distribution, tailing, weathered granite or sedimentary rock and fresh granite are classified. Resistivity distribution was taken out from lines or seismic exploration refraction method, and compared between two methods. As a result, low resistivity region is fitted low velocity zone and high resistivity region is fitted high velocity zone. Topography and 4 geological models are created. These models are output as versatile text data to show relation of a coordinate and the point of contact.
Ohara, Kazuhiro*; Kusano, Joichi; Inoue, Hitoshi*; Takaishi, Kazutoshi*; Yamada, Takayuki*; Ouchi, Nobuo; Ota, Tomoko*
Dai-50-Kai Sosei Kako Rengo Koenkai Koen Rombunshu, p.199 - 200, 1999/10
no abstracts in English
Ashida, Takashi; Sonobe, Hitoshi; Yamada, Kazuo
PNC TN8600 91-003, 38 Pages, 1991/06
no abstracts in English
Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Shibata, Kaoru; Yamada, Takeshi*; Endo, Hitoshi*; Ito, Shinichi*; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Nakajima, Kenji; Kawamura, Seiko; Kawakita, Yukinobu; et al.
no journal, ,
 powder) in mechanical treatment cell at Tokai Reprocessing Plant
powder) in mechanical treatment cell at Tokai Reprocessing PlantFuruuchi, Yuta; Sato, Shinji; Yatabe, Hitoshi; Yokota, Satoru; Yamada, Takashi; Yahagi, Fumio; Terunuma, Hirotaka; Tokoro, Takeshi; Takahashi, Akihiro; Iijima, Shizuka; et al.
no journal, ,
Clean-up activity of spent fuel powder (UO powder) in mechanical treatment cell was performed for the purpose of the preparation of decommissioning at TRP. For the clean-up activity, we selected an inexpensive vacuum cleaner and made tools, that was improved taking into account of use by means of a crane or a manipulator in the high dose cell, and applied it after a mock-up test. We report our experience and knowledge provided through this clean-up activity.
powder) in mechanical treatment cell was performed for the purpose of the preparation of decommissioning at TRP. For the clean-up activity, we selected an inexpensive vacuum cleaner and made tools, that was improved taking into account of use by means of a crane or a manipulator in the high dose cell, and applied it after a mock-up test. We report our experience and knowledge provided through this clean-up activity.
Saegusa, Yu; Nishino, Saki; Horie, Koji; Yatabe, Hitoshi; Yamada, Takashi; Oyama, Daisuke; Uchida, Naoki
no journal, ,
All the spent fuel stored in the Tokai Reprocessing Plant is transported to the overseas reprocessing plant. When spent fuel transportation, we use dry type cask instead of wet type cask. Therefore, equipment of the wet type cask is not used. And the equipment is some possibility of interfere with cask because the equipment is stored in the transport route. So, we were dismantled receiving and storage process equipment as preparation work for spent fuel transportation. In dismantlement work, we selected cutting equipment after scrutinizing size and shape of equipment, contamination and workability. Moreover, we have taken safety measures during work such as fire prevention and contamination control. As a result, the work was completed as originally planned.
Watanabe, Kazuki; Okada, Jumpei; Yokota, Satoru; Oyama, Daisuke; Yamada, Takashi; Yatabe, Hitoshi; Horie, Koji; Uchida, Naoki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yokota, Satoru; Okada, Jumpei; Watanabe, Kazuki; Yatabe, Hitoshi; Yamada, Takashi; Horie, Koji; Furuuchi, Yuta; Uchida, Naoki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Takahashi, Naoki; Kobayashi, Daisuke; Yoshimoto, Katsunobu; Lee, J.-Y.*; Wakabayashi, Hitoshi*; Tochihara, Yutaka*; Yamada, Minoru*; Tanaka, Hideki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Zheng, X.; Hosoyamada, Ryuji*; Shiotsu, Hiroyuki; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Shibamoto, Yasuteru; Maruyama, Yu
no journal, ,
Accident tolerant fuel (ATF) can significantly impact risk assessment and other safety issues due to altered characteristics such as cladding oxidation and hydrogen generation at high temperatures. This study employs a dynamic probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) approach and the severe accident analysis code of MELCOR to investigate the effects on a pressurized water reactor (PWR) after implementing ATF (Cr-coated zircaloy and FeCrAl). It focuses on evaluating the effects of ATF from the perspectives of reducing the generation of oxidation heat and hydrogen, and delaying the onset of core damage. By assessing the risk curves, this research aims to demonstrate the expected effects of the ATF implementation.