Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kokubun, Yuji; Nakada, Akira; Seya, Natsumi; Nagaoka, Mika; Koike, Yuko; Kubota, Tomohiro; Hirao, Moe; Yoshii, Hideki*; Otani, Kazunori*; Hiyama, Yoshinori*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2023-052, 118 Pages, 2024/03
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai Reprocessing Plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and by law of Ibaraki Prefecture), the effluent control of liquid waste discharged from the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been performed. This report describes the effluent control results of the liquid waste in the fiscal year 2022. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other nuclear fuel material usage facilities were much lower than the limits authorized by the above regulations.
Tang, J.*; Seo, O.*; Rivera Rocabado, D. S.*; Koitaya, Takanori*; Yamamoto, Susumu*; Namba, Yusuke*; Song, C.*; Kim, J.*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Koyama, Michihisa*; et al.
Applied Surface Science, 587, p.152797_1 - 152797_8, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:75.56(Chemistry, Physical)The hydrogen absorption and diffusion mechanisms on cube-shaped Pd nanoparticles (NPs) which are important hydrogen-storage materials were studied using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and DFT calculations. In the surface region, hydrogen absorption showed almost similar behavior regardless of the NPs size. It was found that the octahedral sites are more favorable than the tetrahedral sites for hydrogen occupation. We also clarified that the hydrogen atoms absorbing on the smaller-sized Pd NPs diffuse to the subsurface more actively because of the weakened Pd-H bond by the surface disordering, which plays an important role in hydrogen adsorption at a low H pressure.
pressure.

 3H(D)
3H(D) O by neutron diffraction and effect of pH on structural formulas of nesquehonite
O by neutron diffraction and effect of pH on structural formulas of nesquehoniteYamamoto, Genichiro*; Kyono, Atsushi*; Abe, Jun*; Sano, Asami; Hattori, Takanori
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences, 116(2), p.96 - 103, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:49.61(Mineralogy)Neutron diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, and thermal analysis were performed to investigate the composition, structure, and formation conditions of the magnesium carbonate hydrate nesquehonite. The time-of-flight neutron diffraction revealed the crystal structure of the monoclinic space group  2
2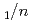 with lattice parameters of
with lattice parameters of  =7.72100(12)
=7.72100(12)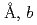 =5.37518(7)
=5.37518(7)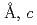 =12.1430(3)
=12.1430(3)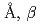 =90.165(4)
=90.165(4) , in which two deuterium atoms are coordinated to the O1, O2, and O6 atoms to form water molecules. The three water molecules in the structure suggests the structural formula of the nesquehonite should be MgCO
, in which two deuterium atoms are coordinated to the O1, O2, and O6 atoms to form water molecules. The three water molecules in the structure suggests the structural formula of the nesquehonite should be MgCO
 3H
3H O rather than Mg(HCO
O rather than Mg(HCO )(OH)
)(OH) 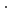 2H
2H O.
O.
Tang, J.*; Yamamoto, Susumu*; Koitaya, Takanori*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Tokunaga, Takuma*; Mukai, Kozo*; Matsuda, Iwao*; Yoshinobu, Jun*
Applied Surface Science, 480, p.419 - 426, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:49.16(Chemistry, Physical)Mass transports during hydrogen adsorption and absorption processes of PdCu alloys that has advantages of higher hydrogen diffusivity and economically lower-cost than the other Pd-alloys were studied. The research was made with a comparison of the well-known ordered phase of the bcc structure (the B2 phase) and a mixed phase of the fcc and B2 structures.  ultrahigh vacuum X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and ambient pressure X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy using synchrotron radiation were carried out to trace the chemical states of the Pd and Cu atoms as a function of temperatures. It is elucidated that the initial adsorption and absorption processes were similar in the two phases, but a hydrogen diffusion rate to the bulk was higher in the ordered phase than in the mixed one. We found the dynamics of the Pd and Cu atoms during the hydrogen adsorption/absorption processes largely depend on temperature. In the hydrogen atmosphere, the Pd atoms segregate at the surface below 373 K and Cu atoms segregate at the surface above 373 K. The present results agree well with the previous theoretical calculations and, thus, provide appropriate inputs toward developments of the hydrogen permeation materials.
ultrahigh vacuum X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and ambient pressure X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy using synchrotron radiation were carried out to trace the chemical states of the Pd and Cu atoms as a function of temperatures. It is elucidated that the initial adsorption and absorption processes were similar in the two phases, but a hydrogen diffusion rate to the bulk was higher in the ordered phase than in the mixed one. We found the dynamics of the Pd and Cu atoms during the hydrogen adsorption/absorption processes largely depend on temperature. In the hydrogen atmosphere, the Pd atoms segregate at the surface below 373 K and Cu atoms segregate at the surface above 373 K. The present results agree well with the previous theoretical calculations and, thus, provide appropriate inputs toward developments of the hydrogen permeation materials.
Yokoyama, Kenji; Yamamoto, Akio*; Kitada, Takanori*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(3), p.319 - 334, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:62.29(Nuclear Science & Technology)A new formulation of the cross-section adjustment methodology with the dimensionality reduction technique has been derived. This new formulation is proposed as the dimension reduced cross-section adjustment method (DRCA). Since the derivation of DRCA is based on the minimum variance unbiased estimation (MVUE), an assumption of normal distribution is not required. The result of DRCA depends on a user-defined matrix that determines the dimension reduced feature subspace. We have examine three variations of DRCA, namely DRCA1, DRCA2, and DRCA3. Mathematical investigation and numerical verification have revealed that DRCA2 is equivalent to the currently widely used cross-section adjustment method. Moreover, DRCA3 is found to be identical to the cross-section adjustment method based on MVUE, which has been proposed in the previous study.
Yoshida, Masafumi; Hanada, Masaya; Kojima, Atsushi; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Grisham, L. R.*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Shibata, Takanori*; Yamamoto, Takashi*; Akino, Noboru; Endo, Yasuei; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 96-97, p.616 - 619, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:70.16(Nuclear Science & Technology)In JT-60 Super Advanced for the fusion experiment, 22A, 100s negative ions are designed to be extracted from the world largest ion extraction area of 450 mm  1100 mm. One of the key issues for producing such as high current beams is to improve non-uniform production of the negative ions. In order to improve the uniformity of the negative ions, a tent-shaped magnetic filter has newly been developed and tested for JT-60SA negative ion source. The original tent-shaped filter significantly improved the logitudunal uniformity of the extracted H
1100 mm. One of the key issues for producing such as high current beams is to improve non-uniform production of the negative ions. In order to improve the uniformity of the negative ions, a tent-shaped magnetic filter has newly been developed and tested for JT-60SA negative ion source. The original tent-shaped filter significantly improved the logitudunal uniformity of the extracted H ion beams. The logitudinal uniform areas within a
ion beams. The logitudinal uniform areas within a  10 deviation of the beam intensity were improved from 45% to 70% of the ion extraction area. However, this improvement degrades a horizontal uniformity. For this, the uniform areas was no more than 55% of the total ion extraction area. In order to improve the horizontal uniformity, the filter strength has been reduced from 660 Gasus
10 deviation of the beam intensity were improved from 45% to 70% of the ion extraction area. However, this improvement degrades a horizontal uniformity. For this, the uniform areas was no more than 55% of the total ion extraction area. In order to improve the horizontal uniformity, the filter strength has been reduced from 660 Gasus cm to 400 Gasus
cm to 400 Gasus cm. This reduction improved the horizontal uniform area from 75% to 90% without degrading the logitudinal uniformity. This resulted in the improvement of the uniform area from 45% of the total ion extraction areas. This improvement of the uniform area leads to the production of a 22A H
cm. This reduction improved the horizontal uniform area from 75% to 90% without degrading the logitudinal uniformity. This resulted in the improvement of the uniform area from 45% of the total ion extraction areas. This improvement of the uniform area leads to the production of a 22A H ion beam from 450 mm
ion beam from 450 mm  1100 mm with a small amount increase of electron current of 10%. The obtained beam current fulfills the requirement for JT-60SA.
1100 mm with a small amount increase of electron current of 10%. The obtained beam current fulfills the requirement for JT-60SA.
Ito, Takanori*; Mori, Masashi*; Inukai, Manabu*; Nitani, Hiroaki*; Yamamoto, Takashi*; Miyanaga, Takashi*; Igawa, Naoki; Kitamura, Naoto*; Ishida, Naoya*; Idemoto, Yasushi*
Photon Factory News, 33(1), p.18 - 24, 2015/05
The effect of the annealing on the crystal and local structures of doped zirconia was investigated by multi-probe technique using synchrotron X-ray and neutron diffraction, and first principles calculation. It was revealed that the annealing process enhances the periodic distortion of some zirconia compounds by Rietveld/ maximum entropy methods applied to the SR-X-ray and neutron diffractions. In addition, the combined X-ray absorption spectroscopy and first-principles calculations results showed the ZrO polyhedra in zirconia were distorted by the annealing. Those results indicate that the degradation of oxide ionic conductivity by the annealing was related to the periodic distortion in zirconia.
polyhedra in zirconia were distorted by the annealing. Those results indicate that the degradation of oxide ionic conductivity by the annealing was related to the periodic distortion in zirconia.
Ito, Takanori*; Mori, Masashi*; Inukai, Manabu*; Nitani, Hiroaki*; Yamamoto, Takashi*; Miyanaga, Takashi*; Igawa, Naoki; Kitamura, Naoto*; Ishida, Naoya*; Idemoto, Yasushi*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 119(16), p.8447 - 8458, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:50.51(Chemistry, Physical)The effects of the annealing process on the crystal and local structures of the doped zirconia were investigated by Rietveld refinements of synchrotron X-ray and neutron diffraction, maximum entropy method (MEM), X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) and first principles calculation (FPC). This study reveals that the crystal structures of the sintered and annealed ((Zr Y
Y )O
)O and (Zr
and (Zr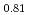 Sc
Sc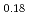 Ce
Ce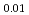 )O
)O ) are cubic with the space
) are cubic with the space 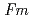 -3
-3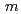 having large atomic displacement parameters (
having large atomic displacement parameters (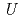 ). For the annealed (Zr
). For the annealed (Zr Y
Y )O
)O , the
, the 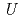 values reduce, and the electrons around the Zr/oxide ion sites gather at the center of each site. On the other hand, the annealed (Zr
values reduce, and the electrons around the Zr/oxide ion sites gather at the center of each site. On the other hand, the annealed (Zr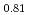 Sc
Sc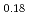 Ce
Ce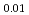 )O
)O shows the opposite tendency to that of the annealed (Zr
shows the opposite tendency to that of the annealed (Zr Y
Y )O
)O .
.
Suyama, Kenya; Sugawara, Takanori; Tada, Kenichi; Chiba, Go*; Yamamoto, Akio*
JAEA-Conf 2014-003, 76 Pages, 2015/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency organized an international conference PHYSOR 2014 on the reactor physics which is one of basic researches in the nuclear engineering, in cooperation with Research Reactor Institute of Kyoto University. PHYSOR is the world's largest scale international conference in the reactor physics field. It originates in the conference held in Marseille, France in 1990, which originally had been organized in the United States as a Physics of Reactors Topical Meeting of the reactor physics division of the American Nuclear Society every two years. More than 500 papers had been submitted and finally 472 papers were presented in the conference after the paper review process. This report contains the presented papers, which the PHYSOR organizing committee has decided to publish in an official JAEA report with the permission by authors, except for several selected papers to be published in the Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology of the Atomic Energy Society of Japan.
Kunimaru, Takanori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Sasao, Eiji; Hikima, Ryoichi; Tanno, Takeo; Sanada, Hiroyuki; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-018, 169 Pages, 2013/09
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based Investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III). The MIU Project has been ongoing the Phase II and the Phase III in 2011 fiscal year. This report shows the results of the investigation, construction and collaboration studies in fiscal year 2011, as a part of the Phase II and Phase III based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2010.
Komatsu, Mitsuru*; Nishigaki, Makoto*; Seno, Shoji*; Hirata, Yoichi*; Takenobu, Kazuyoshi*; Tagishi, Hirotaka*; Kunimaru, Takanori; Maekawa, Keisuke; Yamamoto, Yoichi; Toida, Masaru*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2012-001, 77 Pages, 2012/09
This research focused on methods of estimating the amounts of groundwater recharge, which are normally required as upper boundary conditions in groundwater flow analyses, based on measurements of infiltrating water in the ground, to systematize the methods and establish systems which are stable and measurable on site over a long time. Regarding developing measurement systems, fiber-optic strain measurement methods that enable multiple-point and long-distance measurement were used for measuring three quantities: suction pressure, soil moisture and volumetric water content rate obtained by applying water absorption swelling material, and each measurement was discussed. The results showed that the fiber-optic soil aquameter has two types of practical application: one for measuring suction pressure (Type I), and the other for measuring volumetric water content rate obtained by applying water absorption swelling material (Type III). Furthermore, by using measurement instruments in actual fields, the validity of the two methods for estimating the rainfall infiltration capacities of shallow-layer soils, that is, estimating the capacities either directly by measurements of soil water or from unsaturated hydraulic conductivities, was confirmed.
Kunimaru, Takanori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Kuboshima, Koji; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Mizuno, Takashi; Sato, Toshinori; et al.
JAEA-Review 2012-028, 31 Pages, 2012/08
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU project is planned in three overlapping phases; Surface-based Investigation Phase (Phase I), Construction Phase (Phase II) and Operation Phase (Phase III). Currently, the project is under the Construction Phase and the Operation Phase. This document introduces the research and development activities planned for 2012 fiscal year based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2010, construction plan and research collaboration plan, etc.
Kunimaru, Takanori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Ueno, Takashi; Tokuyasu, Shingo; Daimaru, Shuji; Takeuchi, Ryuji; et al.
JAEA-Review 2012-020, 178 Pages, 2012/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based Investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III). The MIU Project has been ongoing the Phase II. And Phase III started in 2010 fiscal year. This report shows the results of the investigation, construction and collaboration studies in fiscal year 2010, as a part of the Phase II based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2002.
Amano, Yuki; Yamamoto, Yoichi; Nanjo, Isao; Murakami, Hiroaki; Yokota, Hideharu; Yamazaki, Masanori; Kunimaru, Takanori; Oyama, Takahiro*; Iwatsuki, Teruki
JAEA-Data/Code 2011-023, 312 Pages, 2012/02
In the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project, ground water from boreholes, river water and precipitation have been analyzed for the environmental monitoring since the fiscal year 2001. This report shows the data set of water chemistry since the fiscal year 2001 to the fiscal year 2010.
Kunimaru, Takanori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Mizuno, Takashi; Sato, Toshinori; Ogata, Nobuhisa; et al.
JAEA-Review 2011-027, 30 Pages, 2011/08
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). Geoscientific research and the MIU project is planned in three overlapping phases; Surface-based Investigation Phase (Phase1), Construction Phase (Phase2) and Operation Phase (Phase3). Currently, the project is under the Construction Phase, and the Operation Phase. This document introduces the research and development activities planned for 2011 fiscal year plan based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2010, Investigation Plan, Construction Plan and Research Collaboration Plan, etc.
 -US
-US
Sugiyama, Kiyohiro*; Hirose, Yusuke*; Enoki, Kentaro*; Ikeda, Shugo*; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Tateiwa, Naoyuki; Haga, Yoshinori; Kida, Takanori*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Kindo, Koichi*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 80(Suppl.A), p.SA104_1 - SA104_3, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:27.45(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Kunimaru, Takanori; Ota, Kunio; Alexander, W. R.*; Yamamoto, Hajime*
JAEA-Research 2011-010, 52 Pages, 2011/06
Work has been currently ongoing to establish an appropriate quality management system (QMS), which is applicable to all aspects of the site characterisation process, in the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory project. A quality assurance (QA) audit of hydrochemical datasets for JAEA's deep boreholes HDB-1 to HDB-8 was carried out, along similar lines to that of the previous study for boreholes HDB-9 to HDB-11, by applying both the groundwater QA methodology employed in the recent site assessments in Sweden and a porewater QA regime proposed in this study. The results of the QA audit indicated that data were classified into low QA categories because mainly of a lack of relevant information, such as the records of groundwater sampling, which are necessary for more fully assessing the data quality. As such, a formalised field manual for hydrochemical sampling was developed. In addition, work to further improve the site characterisation QMS progressed.
Kunimaru, Takanori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Hayano, Akira; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Oyama, Takuya; Mizuno, Takashi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2011-007, 145 Pages, 2011/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). Geoscientific research and the MIU Project are planned in three overlapping phases; Surface-based Investigation Phase (Phase 1), Construction Phase (Phase 2) and Operation Phase (Phase 3). Currently, the project is under the Construction Phase. This document introduces the results of the research and development in fiscal year 2009, as a part of the Construction Phase based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2002, (1) Investigation at the MIU Construction Site and the Shobasama Site, (2) Construction at the MIU Construction Site, (3) Research Collaboration, etc. The goals of the Phase 2 are to develop and revise the models of the geological environment using the investigation results obtained during excavation and determine and assess changes in the geological environment in response to excavation, to evaluate the effectiveness of engineering techniques used for construction, maintenance and management of underground facilities, to establish detailed investigation plans of Phase 3.
Kunimaru, Takanori; Ota, Kunio; Alexander, W. R.*; Yamamoto, Hajime*
JAEA-Research 2010-035, 109 Pages, 2010/11
A quality management system (QMS) will save on effort by reducing errors and the requirement to re-sample and re-analysis and eventually lead to ensuring the reliability of the investigation results. In the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory project, work has been ongoing to develop an appropriate QMS which is applicable to surface-based investigations. A quality assurance (QA) audit of hydrochemical datasets for boreholes HDB-9 - 11 has been carried out by applying both the groundwater QA methodology employed in the recent site assessments in Sweden and the porewater QA regime newly proposed for assigning the QA categories. This QA audit exercise indicates that the HDB-9 - 11 hydrochemical data are classified into lower categories because mainly of contamination of waters by drilling fluids, poor time-series data coverage and oxidation of core materials and also clarifies areas where additional information/work would be required to the ongoing programme.
Takeuchi, Shinji; Kunimaru, Takanori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Hayano, Akira; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Oyama, Takuya; et al.
JAEA-Review 2010-029, 28 Pages, 2010/08
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). Geoscientific research and the MIU project is planned in three overlapping phases; Surface-based investigation phase (Phase1), Construction phase (Phase2) and Operation phase (Phase3). The project is currently under the construction phase, and the operation phase starts in 2010. This document introduces the research and development activities planned for 2010 fiscal year plan based on the MIU master plan updated in 2010, (1) Investigation plan, (2) Construction plan, (3) Research collaboration plan, etc.