Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
alloy using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopyMiyazaki, Hidetoshi*; Akatsuka, Tatsuyoshi*; Kimura, Koji*; Egusa, Daisuke*; Sato, Yohei*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Takagi, Yasumasa*; Yasui, Akira*; Ozawa, Kenichi*; Mase, Kazuhiko*; et al.
Materials Transactions, 64(6), p.1194 - 1198, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.80(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigated the electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy using hard and soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy and electronic band structure calculations to understand the mechanism of the phase stability of this material. Electronic structure of the Mg
alloy using hard and soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy and electronic band structure calculations to understand the mechanism of the phase stability of this material. Electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy showed a semi-metallic electronic structure with a pseudo-gap at the Fermi level. The observed electronic structure of the Mg
alloy showed a semi-metallic electronic structure with a pseudo-gap at the Fermi level. The observed electronic structure of the Mg Zn
Zn Y
Y alloy suggests that the presence of a pseudogap structure is responsible for phase stability.
alloy suggests that the presence of a pseudogap structure is responsible for phase stability.
 Sn and Mg
Sn and Mg Si single crystals
Si single crystalsSaito, Wataru*; Hayashi, Kei*; Huang, Z.*; Sugimoto, Kazuya*; Oyama, Kenji*; Happo, Naohisa*; Harada, Masahide; Oikawa, Kenichi; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Hayashi, Koichi*; et al.
ACS Applied Energy Materials (Internet), 4(5), p.5123 - 5131, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:63.28(Chemistry, Physical) Si single crystals" [AIP Advances 10, 035115 (2020)]
Si single crystals" [AIP Advances 10, 035115 (2020)]Hayashi, Kei*; Saito, Wataru*; Sugimoto, Kazuya*; Oyama, Kenji*; Hayashi, Koichi*; Happo, Naohisa*; Harada, Masahide; Oikawa, Kenichi; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Miyazaki, Yuzuru*
AIP Advances (Internet), 11(2), P. 029903_1, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology) -Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus
-Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus  B
BYang, Z. H.*; Kubota, Yuki*; Corsi, A.*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Sun, X.-X.*; Li, J. G.*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Michel, N.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yuan, C. X.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 126(8), p.082501_1 - 082501_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:58 Percentile:95.97(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A quasifree ( ,
,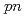 ) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus
) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus  B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for
B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for  and
and  orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for
orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for  . Our finding of such a small
. Our finding of such a small  component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in
component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in  B. The present work gives the smallest
B. The present work gives the smallest  - or
- or  -orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of
-orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of  or
or  orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
 Si single crystals
Si single crystalsHayashi, Kei*; Saito, Wataru*; Sugimoto, Kazuya*; Oyama, Kenji*; Hayashi, Koichi*; Happo, Naohisa*; Harada, Masahide; Oikawa, Kenichi; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Miyazaki, Yuzuru*
AIP Advances (Internet), 10(3), p.035115_1 - 035115_7, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:69.37(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology) Ni from the (
Ni from the ( ,
,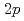 ) reaction
) reactionElekes, Z.*; Kripk ,
,  *; Sohler, D.*; Sieja, K.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Authelet, G.*; Baba, Hidetada*; et al.
*; Sohler, D.*; Sieja, K.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Authelet, G.*; Baba, Hidetada*; et al.
Physical Review C, 99(1), p.014312_1 - 014312_7, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:71.31(Physics, Nuclear)The nuclear structure of the  Ni nucleus was investigated by (
Ni nucleus was investigated by ( ,
,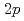 ) reaction using a NaI(Tl) array to detect the deexciting prompt
) reaction using a NaI(Tl) array to detect the deexciting prompt  rays. A new transition with an energy of 2227 keV was identified by
rays. A new transition with an energy of 2227 keV was identified by 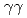 and
and 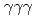 coincidences. Our shell-model calculations using the Lenzi, Nowacki, Poves, and Sieja interaction produced good candidates for the experimental proton hole states in the observed energy region, and the theoretical cross sections showed good agreement with the experimental values. Although we could not assign all the experimental states to the theoretical ones unambiguously, the results are consistent with a reasonably large Z = 28 shell gap for nickel isotopes in accordance with previous studies.
coincidences. Our shell-model calculations using the Lenzi, Nowacki, Poves, and Sieja interaction produced good candidates for the experimental proton hole states in the observed energy region, and the theoretical cross sections showed good agreement with the experimental values. Although we could not assign all the experimental states to the theoretical ones unambiguously, the results are consistent with a reasonably large Z = 28 shell gap for nickel isotopes in accordance with previous studies.
Miyazaki, Akemi; Kawaguchi, Kenichi*
Nihon Kenchiku Gakkai Kozokei Rombunshu, 597, p.69 - 76, 2005/11
The objective of our research is to examine the wave propagation properties of framed structures. Those structures tend to become larger and higher recently. On the case of those structures it may be possible that the structure is locally damaged before it becomes vibration state by an external force. It is seemed that for such structures then the investigation and estimation of dynamic structural behaviour from the view point of wave propagation become important. For these purposes, we planned and carried out impact hammer experiments on some lattice-type plates. In this paper the experiment results performed on three lattice-type plates and one continuum plate are shown. The results show that wave propagation properties of lattice-type plates depend on wave propagation properties of the members consist of those lattice-type plates. Preliminary experiments for evaluating the effect of the boundary conditions performed in advance of the experiments for lattice-type plate models are also shown.
; ; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro; ; Kato, Noriyoshi; Miyazaki, Hitoshi; Tanimoto, Kenichi
JNC TN9410 2002-010, 62 Pages, 2002/11
The vaporizer in extinguishing of Large Equipment Dismantling Facility (LEDF)that cost is considering as a plan to cut down as part of a rationalization design highly. When the vaporizer is deleted, it becomes here where liquefied carbon dioxide is emitted in the direct cell, it is necessary to grasp the action and extinguishing performance of the pressure change in the cell by rapid evaporation test of the emitted liquefied carbon dioxide. So pressure action inside the fire laboratory in liquefied carbon dioxide release and a putting out the fire tests due to the combustion time of the combustible were enforced by using the general fire laboratory with Demonstration Test on Extinguishing of the cell (I) in the llth year of Heisei. However, since these tests are after laboratory without airtightness, it needs to grasp the pressure action at the time of liquefied carbon dioxide discharge under the airtight high conditions of having assumed the still more nearly actual cell. The cell (II) Demonstration Test on Extinguishing using the vessel of Sodium Leak Fire and Aerosol test rig (SOLFA-2) container inside of OEC was carried out. The results were as follows. (1)In order to grasp the pressure action of the vessel, the internal pressure of SOLFA-2 was set as -50mmH O, and emitted liquefied carbon dioxide. Consequently, the tendency for the pressure in the vessel to descend rapidly immediately after liquefied carbon dioxide discharge, and to descend gently-sloping through the process which goes up gradually after that and goes abruptly up for a short time was seen. (2)The process which goes abruptly up in an above-mentioned short time is considered to be the factors with main what some liquefied carbon dioxide emitted in the vessel changed to dry ice, and was deposited taken and sublimating surrounding heat, and evaporating again. (3)It sets to total flooding system and the average minimum temperature in the vessel becomes about -48
O, and emitted liquefied carbon dioxide. Consequently, the tendency for the pressure in the vessel to descend rapidly immediately after liquefied carbon dioxide discharge, and to descend gently-sloping through the process which goes up gradually after that and goes abruptly up for a short time was seen. (2)The process which goes abruptly up in an above-mentioned short time is considered to be the factors with main what some liquefied carbon dioxide emitted in the vessel changed to dry ice, and was deposited taken and sublimating surrounding heat, and evaporating again. (3)It sets to total flooding system and the average minimum temperature in the vessel becomes about -48 C, and at ...
C, and at ...
; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro; ; ; Kato, Noriyoshi; Miyazaki, Hitoshi; Tanimoto, Kenichi
JNC TN9410 2002-008, 68 Pages, 2002/07
In order to rationalize for Large Equipment Dismantling Facility (LEDF), the plan of removing vaporizer belong to Cell-fire-extinguishing-system was investigated. When a vaporizer is cut down, It is necessary to grasp a fire-extinguishing performance. The fire-extinguishing performance check examination by liquefaction carbon dioxide in the cell fire-extinguishing examination (I) was carried out in 1999 fiscal year. As the result, The good performance was obtained to polyethylene. But there was the deep-seated fire about a piece of wood. Then, The check items were carbon dioxide (CO ) concentration and CO
) concentration and CO concentration holding time for the deep-seated fire in the cell fire-extinguishing examination (III). The results were as follows; (1)By use of the combustion model in which a piece of wood and cotton were put is lit, temperature inside model, mass reduction, and combustion situation were examined. The model burned remarkably in 30
concentration holding time for the deep-seated fire in the cell fire-extinguishing examination (III). The results were as follows; (1)By use of the combustion model in which a piece of wood and cotton were put is lit, temperature inside model, mass reduction, and combustion situation were examined. The model burned remarkably in 30 60 min. The peak temperature rise to 680
60 min. The peak temperature rise to 680  C(MAX), and attained smoldering after (ignition) 70 min. Moreover, in order to determine the generating conditions of a deep-seated fire, the situation of CO
C(MAX), and attained smoldering after (ignition) 70 min. Moreover, in order to determine the generating conditions of a deep-seated fire, the situation of CO extinguishing after ignition by the time lag of 50
extinguishing after ignition by the time lag of 50 90 min were examined. The model around ignition 50 minutes was the most difficult to extinguish, and it turned out that they are the conditions which were most suitable for the deep-seated fire examination model of an exam. (2)In order to decide on CO
90 min were examined. The model around ignition 50 minutes was the most difficult to extinguish, and it turned out that they are the conditions which were most suitable for the deep-seated fire examination model of an exam. (2)In order to decide on CO concentration and concentration holding time required for fire extinguishing of the deep-seated fire in LEDF, The fire-extinguishing performance was investigated by 40
concentration and concentration holding time required for fire extinguishing of the deep-seated fire in LEDF, The fire-extinguishing performance was investigated by 40  65% of CO
65% of CO concentration. Consequently, CO
concentration. Consequently, CO concentration required for deep-seated fire extinguishing was understood that 60% or more was required when safety was taken into consideration at 50% or more. Moreover, when it was 50% or more of CO
concentration required for deep-seated fire extinguishing was understood that 60% or more was required when safety was taken into consideration at 50% or more. Moreover, when it was 50% or more of CO concentration and the holding time of CO
concentration and the holding time of CO concentration ...
concentration ...
; ; ; Kato, Noriyoshi; Miyazaki, Hitoshi; Tanimoto, Kenichi
JNC TN9410 2002-006, 49 Pages, 2002/07
Construction of LEDF (Large Equipment Dismantling Facility) is being planned by Waste Management Section. This purpose of LEDF is the melting treatment of the radioactive waste in OEC (O-arai Engineering Center) and the waste package in JAERI (O-arai Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute). It is also considered about the disposal plan of the future. Therefore LEDF has the sorting process of waste because of the removal of problematic substances. But that process is conducted using its human eyes. This process needs automatic operation because of high classification accuracy, high reliability, burden reduction of a worker. Then we select EXFS (Energy dispersive X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometer), and conducted the measurement of waste (a sample) with this device. That purpose is to confirm an application as the sorting device. A confirmation result is shown in the following. (1)Sorting performance Measurement is possible without pretreatment, if it is metal. However, sorting is difficult when paint, plating, impurities, etc. are shown in the surface. (2)Measurement position It is necessary to set a gap of the measurement thing from a measurement position to 4㎜ or less. (3)Radiation influence Because the background had risen by the influence of a radiant ray, the distinction of Fluorescence X-ray became difficult. Therefore the distinction of materials became impossible. Aluminum is influenced specially by it. As a conclusion, the application nature of EXFS thing Sorting System is high. But there is a bad influence by radiation. Therefore, difficult is installation into the cell. In order to apply EXFS to LEDF, it is necessary to place it outside the cell and to use as the help of the visual inspection.
Donomae, Yasushi; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro; Kikuchi, Yutaka; Kato, Noriyoshi; Miyazaki, Hitoshi; Tanimoto, Kenichi
JNC TN9410 2001-021, 73 Pages, 2002/01
In order to rationalize for Large Equipment Dismantling Facility (LEDF), the plan of removing vaporizer belong to Cell-fire-extinguishing-system was investigated. In this test, in order to study the behavior of pressure in cell, when the liquefaction carbon dioxide (liq-CO ) is emitted, and the performanee of extinguishing fires, the test of behavior of pressure and the extinguishing fires take effect. Also the extinguishing fires test used water-mist take effect for complement liq-CO
) is emitted, and the performanee of extinguishing fires, the test of behavior of pressure and the extinguishing fires take effect. Also the extinguishing fires test used water-mist take effect for complement liq-CO . The results as follows; (1)In the test of behavior of pressure, Liq-CO
. The results as follows; (1)In the test of behavior of pressure, Liq-CO was emitted test room under -40mmAq negative pressure. Room pressure was increase about 0.8mmAq/sec at first. After 29sec, the pressure was increase slowly about 0.1mmAq/sec. After 120sec, the increase was drastic about 1.5mmAq/s. (2)In the test of extinguishing fires by liq-CO
was emitted test room under -40mmAq negative pressure. Room pressure was increase about 0.8mmAq/sec at first. After 29sec, the pressure was increase slowly about 0.1mmAq/sec. After 120sec, the increase was drastic about 1.5mmAq/s. (2)In the test of extinguishing fires by liq-CO , under -40mmAq, Polyethylene and wooden chips + cotton (crib) was burn. Polyethylene was extinguished perfectly, but the embers remained in cribs. While the room pressure was increase about 1.3mmAq/sec for 10sec at first. After 30 sec, the pressure was increase about 1mmAq/sec. On the other hand, the drastic increase of pressure disappeared between 100sec to 120sec by change the nozzle size from 14mm
, under -40mmAq, Polyethylene and wooden chips + cotton (crib) was burn. Polyethylene was extinguished perfectly, but the embers remained in cribs. While the room pressure was increase about 1.3mmAq/sec for 10sec at first. After 30 sec, the pressure was increase about 1mmAq/sec. On the other hand, the drastic increase of pressure disappeared between 100sec to 120sec by change the nozzle size from 14mm to 10mm
to 10mm . (3)In the test of extinguishing fires by water-mist, Cribs was extinguished perfectly, but Polyethylene was extinguished difficulty under the same condition of liq-CO
. (3)In the test of extinguishing fires by water-mist, Cribs was extinguished perfectly, but Polyethylene was extinguished difficulty under the same condition of liq-CO test. (4)Therefore the results, It's coped with the fire extinguishing and the keeping negative pressure for LEDF cells. Therefore nozzle size is fitted cell volume as changing 14mm
test. (4)Therefore the results, It's coped with the fire extinguishing and the keeping negative pressure for LEDF cells. Therefore nozzle size is fitted cell volume as changing 14mm to 10mm
to 10mm . (5)As the performance of extinguishing fires by liq-CO
. (5)As the performance of extinguishing fires by liq-CO , It is necessity the concentration of above 50% CO
, It is necessity the concentration of above 50% CO for combustibles as cribs, remaining the embers. (6)On the other hand, It is necessity most study for the adoption of water-mist. Therefore water-mist was not effective for polyethylene, and it needed water ...
for combustibles as cribs, remaining the embers. (6)On the other hand, It is necessity most study for the adoption of water-mist. Therefore water-mist was not effective for polyethylene, and it needed water ...
; Kato, Noriyoshi; Miyazaki, Hitoshi; Tanimoto, Kenichi
JNC TN9410 2001-018, 114 Pages, 2001/09
Construction of LEDF (Large equipment dismantling facility) which has the in-can type incineration-melting furnace is planned. The in-can type incineration-melting furnace performs incineration and melting solidification of radioactive waste within the canister made from ceramics, and is characterized by discarding the canister. On the other hand, as for this furnace, the amount of incineration is restrained to canister capacity, Therefore, how to repeat incineration and melting can be considered as a method of increasing the amount of incineration. However, we were anxious about the contact time of the melt and a canister extending, the amount of wear of canister base material increasing, or the heat load (heat cycle) to a canister increasing, and the material intensity of canister base material falling, in order that this method may repeat incineration and melting. then, the tests used imitation waste, are the conditions which repeat (1,3, 10 bathes) the incineration temperature of 1000  C, and the melt temperature of 1500
C, and the melt temperature of 1500  C, and investigated change of the amount of wear of canister base material and high temperature bend strength. The result is as follows. (1) The amount of wear of canister base material was 0.09 mm/h at the maximum. This result was a sufficiently few value, even if compared with the conventional result (1.0 mm/h). Moreover, the high temperature bend strength of canister base material is about 3 Mpa on an average, and change was seen before and after the examination to which heat load is applied. (2) These tests showed that the factor which spoils the soundness of a canister was oxidization degradation of the canister base material by peeling from the base material of Glaze (glass coating material). The portion embrittlement by oxidization degradation is locally worn down by contact of the melt. (3)Heat-resistant temperature of Glaze is about 1300
C, and investigated change of the amount of wear of canister base material and high temperature bend strength. The result is as follows. (1) The amount of wear of canister base material was 0.09 mm/h at the maximum. This result was a sufficiently few value, even if compared with the conventional result (1.0 mm/h). Moreover, the high temperature bend strength of canister base material is about 3 Mpa on an average, and change was seen before and after the examination to which heat load is applied. (2) These tests showed that the factor which spoils the soundness of a canister was oxidization degradation of the canister base material by peeling from the base material of Glaze (glass coating material). The portion embrittlement by oxidization degradation is locally worn down by contact of the melt. (3)Heat-resistant temperature of Glaze is about 1300  C. At the melting operation temperature of 1500
C. At the melting operation temperature of 1500  C, and ...
C, and ...
Kondo, Hitoshi; ; Namekawa, Takashi; ; Miyazaki, Hitoshi; Tanimoto, Kenichi
JNC TN9410 2001-006, 43 Pages, 2000/12
In order to make a contribution to the clearance level decision work of the research facility which handle radioisotope (RI), fuel and so on, the amount of waste from decommissioning the facility was investigated. The investigation were the estimation of the amount of decommissioning waste and the evaluation of the amount of clearance level waste for four facilities which are Fuel Monitorring Facility (FMF), Alpha-Gamma Facility (AGF), Materials Monitoring Facility (MMF), and Waste Dismantling Facility (WDF). The result of estimation and valuation are as follows. (1)The amount of the decommissioning waste for FMF is about 71500 tons. (Concrete is about 67500 tons, metal is about 3,600 tons, and others is about 300 tons.) (2)The amount of the decommissioning waste for AGF is about 14200 tons. (Concrete is about 13300 tons, metal is about 600 tons, and others is about 200 tons.) (3)The amount of the decommissioning waste for MMF is about 18000 tons. (Concrete is about 17100 tons, metal is about 700 tons, and others is about 100 tons.) (4)The amount of the decommissioning waste for WDF is about 28600 tons. (Concrete is about 27900 tons, metal is about 700 tons, and others is about 20 tons.) (5)All concrete waste and over 70% of metal waste is included the clearance level or non-radioactive waste. (6)By excluding a waste under the clearance level from a disassembly waste, the radioactive waste for the decommissioning the facility can be drastically reduced.
; ; Kato, Noriyoshi; Miyazaki, Hitoshi; Tanimoto, Kenichi
JNC TN9410 2000-002, 149 Pages, 1999/12
LEDF (Large Equipment Dismantling Facility) is the solid waste processing technology development facility that carries out high-volume reduction and low dosage processing. The high-volume reduction processing of the high dose  -waste configured with combustible waste, pvc & rubber, spent ion exchange resin, and noncombustible waste have been planned the incinerating and melting facility using the in-can type high frequency induction heating in LEDF. This test is intended to clarify the design data. It was confirmed that the incinerating and melting performance, molten solid properties and exhaust gas processing performance with pilot testing equipment and bench scale equipment. The result of this test are as follows. (1)Processing speed is 6.7kg/h for the combustible waste, 13.0kg/h for the ion exchange resin, and 30.0kg/h for the noncombustible waste. For above optimum processing conditions are as follows. (a)Operating temperature is 1000
-waste configured with combustible waste, pvc & rubber, spent ion exchange resin, and noncombustible waste have been planned the incinerating and melting facility using the in-can type high frequency induction heating in LEDF. This test is intended to clarify the design data. It was confirmed that the incinerating and melting performance, molten solid properties and exhaust gas processing performance with pilot testing equipment and bench scale equipment. The result of this test are as follows. (1)Processing speed is 6.7kg/h for the combustible waste, 13.0kg/h for the ion exchange resin, and 30.0kg/h for the noncombustible waste. For above optimum processing conditions are as follows. (a)Operating temperature is 1000 C for the combustible waste, 1300
C for the combustible waste, 1300 C for the ion exchange resin, 1500
C for the ion exchange resin, 1500 C for the noncombustible waste. (b)Air flow is 90Nm
C for the noncombustible waste. (b)Air flow is 90Nm /h. Air temperature is 300
/h. Air temperature is 300 C. Air velocity is 20m/s. (2)Incineration time per day is 5h. Warm-up time and incineration time from the stop of waste charging is 0.5h. Melting time per day is 5h inconsideration of heating hold time of incinerated ash and melting of quartz. Warm-up time is 0.5h. (3)The system decontamination factor in Co, Cs and Ce with pilot testing equipment is 10
C. Air velocity is 20m/s. (2)Incineration time per day is 5h. Warm-up time and incineration time from the stop of waste charging is 0.5h. Melting time per day is 5h inconsideration of heating hold time of incinerated ash and melting of quartz. Warm-up time is 0.5h. (3)The system decontamination factor in Co, Cs and Ce with pilot testing equipment is 10 or more. (4)Design data of the iron doped silica gel judged to be have a applicability as RuO
or more. (4)Design data of the iron doped silica gel judged to be have a applicability as RuO gas absorber is as follows. (a)Its diameter distribute in the range of 0.8-1.7mm. (b)To have a decontamination factor of 10
gas absorber is as follows. (a)Its diameter distribute in the range of 0.8-1.7mm. (b)To have a decontamination factor of 10 can achieve for retention time of 3 seconds and its life time is about 1 year. (5)In terms of the distribution of the nuclear species in molten solid is evenly distributed. It was also confirmed that the distribution of main elements in ceramic layer is ...
can achieve for retention time of 3 seconds and its life time is about 1 year. (5)In terms of the distribution of the nuclear species in molten solid is evenly distributed. It was also confirmed that the distribution of main elements in ceramic layer is ...
; ; Miyazaki, Hitoshi; ; Tanimoto, Kenichi; Terunuma, Seiichi
PNC TN9420 95-011, 13 Pages, 1994/10
None
; Miyazaki, Hitoshi; ; Tanimoto, Kenichi; Terunuma, Seiichi
PNC TN9420 94-010, 103 Pages, 1994/04
None
Hirai, Keizo*; Komatsu, Masafumi*; Akama, Akio*; Noguchi, Kyotaro*; Nagakura, Junko*; Ohashi, Shinta*; Saito, Tetsu*; Kawasaki, Tatsuro*; Yazaki, Kenichi*; Ikeda, Shigeto*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shimada, Koji; Tateishi, Ryo*; Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Sasaki, Akimichi; Tanaka, Yukumo; Miyazaki, Masashi; Yasue, Kenichi; Niwa, Masakazu; Sueoka, Shigeru; Umeda, Koji; et al.
no journal, ,
Activity evaluation of crush zones encountered in basement rock is an issue of the seismic safety assessment of nuclear plant and geological isolation of radioactive wastes. The selection of crush zone of which has been evaluated should be defined as the latest one by means of turn determination of crush zone activity based on stratigraphic or structural geological method. A lesson from granitic basement rock (Kojaku granite) holding the fast breeder reactor "Monju" is presented. The Kojaku Granite form the oval Tsuruga peninsula (ca. 8km in width) on the southeastern coast of the Sea of Japan and the age is 68.5 plus/minus 0.7Ma (Zircon U-Pb age).1. Stratigraphy-oriented turn determination of crush zone activity. (1.1) Turn determination using cover sediments. (1.2) Turn determination using dyke, mineral and clay vein. 2. Structural-oriented turn determination of crush zone activity.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Shimada, Koji; Sasaki, Akimichi; Tanaka, Yukumo; Miyazaki, Masashi; Yasue, Kenichi; Niwa, Masakazu; Sueoka, Shigeru; Umeda, Koji; Ikeda, Makinori
no journal, ,
The Nuclear Regulation Authority instructed to develop a further additional research plan regarding the crushed zones on the Monju site against the JAEA on September 25. The JAEA developed a research plan in response to this instruction, and, the stripping investigation with expansion of the area, the additional detailed geographical and geological surveys around the mountains/terrace boundary, and the marine seismic surveys in the coastal waters, were conducted. The fracture zones were grouped into 2 systems called  -system and
-system and  -system in the on-site investigation. We examined the cross-cutting relationships and displacements of the fracture zones and confirmed that the
-system in the on-site investigation. We examined the cross-cutting relationships and displacements of the fracture zones and confirmed that the  -system was formed after the
-system was formed after the  -system. From the investigation results so far, similar to the results of the compilation report of April 31, 2010, no clear evidence was observed to support that on-site crushed zones are active faults.
-system. From the investigation results so far, similar to the results of the compilation report of April 31, 2010, no clear evidence was observed to support that on-site crushed zones are active faults.