Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kawano, Takahiro*; Mizuta, Naoki; Ueta, Shohei; Tachibana, Yukio; Yoshida, Katsumi*
JAEA-Technology 2023-014, 37 Pages, 2023/08
Fuel compact for High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) is fabricated by calcinating a matrix consisting of graphite and binder with the coated fuel particle. The SiC-matrixed fuel compact uses a new matrix made of silicon carbide (SiC) replacing the conventional graphite. Applying the SiC-matrixed fuel compact for HTGRs is expected to improve their performance such as power densities. In this study, the sintering conditions for applying SiC as the matrix of fuel compacts for HTGR are selected, and the density and thermal conductivity of the prototype SiC are measured.
Okita, Shoichiro; Mizuta, Naoki; Takamatsu, Kuniyoshi; Goto, Minoru; Yoshida, Katsumi*; Nishimura, Yosuke*; Okamoto, Koji*
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/05
Katsumi, Toshiyuki; Yoshida, Yasuhito*; Nakagawa, Ryo*; Yazawa, Shinya*; Kumada, Masashi*; Sato, Daisuke*; Thwe Thwe, A.; Chaumeix, N.*; Kadowaki, Satoshi
Journal of Thermal Science and Technology (Internet), 16(2), p.21-00044_1 - 21-00044_13, 2021/00
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:35.68(Thermodynamics)The effects of addition of CO and water vapor on characteristics of dynamic behavior of hydrogen/air premixed flames were elucidated experimentally. By Schlieren photography, wrinkles on the flame surface were clearly observed in low equivalence ratios. The propagation velocity increased monotonically as the flame radius became larger and flame acceleration was found. Increasing the addition of inert gas, the propagation velocity decreased, especially in the case of CO
and water vapor on characteristics of dynamic behavior of hydrogen/air premixed flames were elucidated experimentally. By Schlieren photography, wrinkles on the flame surface were clearly observed in low equivalence ratios. The propagation velocity increased monotonically as the flame radius became larger and flame acceleration was found. Increasing the addition of inert gas, the propagation velocity decreased, especially in the case of CO addition. Moreover, the Markstein length and the wrinkling factor decreased. This indicated that the addition of Co
addition. Moreover, the Markstein length and the wrinkling factor decreased. This indicated that the addition of Co or H
or H O promoted the unstable motion of hydrogen flames, which could be due to the enhancement of the diffusive-thermal effect. Based on the characteristics of dynamic behavior of hydrogen flames, the parameters used in the mathematical model on propagation velocity including flame acceleration was obtained, and then the flame propagation velocity under various conditions was predicted.
O promoted the unstable motion of hydrogen flames, which could be due to the enhancement of the diffusive-thermal effect. Based on the characteristics of dynamic behavior of hydrogen flames, the parameters used in the mathematical model on propagation velocity including flame acceleration was obtained, and then the flame propagation velocity under various conditions was predicted.
Kamiya, Kensaku; Honda, Mitsuru; Miyato, Naoaki; Urano, Hajime; Yoshida, Maiko; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Matsunaga, Go; Oyama, Naoyuki; Koide, Yoshihiko; Kamada, Yutaka; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 52(11), p.114010_1 - 114010_12, 2012/10
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:40.68(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Depending on the direction of the external tangential momentum input, substantial changes in not only toroidal but also poloidal flows for the carbon impurity ions are observed at around the 
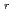 -well region. The shear in the edge
-well region. The shear in the edge 
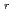 becomes wider in the co-NBI case, while the edge
becomes wider in the co-NBI case, while the edge 
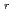 -well becomes deeper in the counter-NBI case.
-well becomes deeper in the counter-NBI case.
Usuki, Toshiyuki; Yoshida, Katsumi*; Yano, Toyohiko*; Miwa, Shuhei; Osaka, Masahiko
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 53(7), p.1078 - 1081, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The effects of sintering additives of magnesium silicates, i.e. enstatite (MgSiO ), steatite (MgSiO
), steatite (MgSiO ) and forsterite (Mg
) and forsterite (Mg SiO
SiO ), on the fabrication properties and characteristics of the silicon nitride ceramics based inert matrix fuels were experimentally investigated. CeO
), on the fabrication properties and characteristics of the silicon nitride ceramics based inert matrix fuels were experimentally investigated. CeO was selected as simulating element of AmO
was selected as simulating element of AmO . Sintered pellets were characterized in term of their densities, thermal conductivities and solubility to nitric acid. The densifications of sintered bodies were enhanced by using additives of magnesium silicates at relative low sintering temperature. The relative density of silicon nitride ceramics based inert matrix fuels with forsterite were achieved above 90% at 1723 K. The thermal conductivities of silicon nitride ceramics based inert matrix fuels varied according to sintering temperature, and those sintered at 1923 K were above 34 W/m K. The grain boundary phases in Silicon nitride ceramics based inert matrix fuels found to be dissolved into HNO
. Sintered pellets were characterized in term of their densities, thermal conductivities and solubility to nitric acid. The densifications of sintered bodies were enhanced by using additives of magnesium silicates at relative low sintering temperature. The relative density of silicon nitride ceramics based inert matrix fuels with forsterite were achieved above 90% at 1723 K. The thermal conductivities of silicon nitride ceramics based inert matrix fuels varied according to sintering temperature, and those sintered at 1923 K were above 34 W/m K. The grain boundary phases in Silicon nitride ceramics based inert matrix fuels found to be dissolved into HNO .
.
Shibanuma, Kiyoshi; Arai, Takashi; Kawashima, Hisato; Hoshino, Katsumichi; Hoshi, Ryo; Kobayashi, Kaoru; Sawai, Hiroaki; Masaki, Kei; Sakurai, Shinji; Shibama, Yusuke; et al.
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.9, p.276 - 281, 2010/08
The JT-60 SA project is a combined project of JA-EU satellite tokamak program under the Broader Approach (BA) agreement and JA domestic program. Major components of JT-60SA for assembly are vacuum vessel (VV), superconducting coils (TF coils, EF coils and CS coil), in-vessel components such as divertor, thermal shield and cryostat. An assembly frame (with the dedicated cranes), which is located around the tokamak, is adopted to carry out effectively the assembly of tokamak components in the tokamak hall, independently of the facility cranes in the building. The assembly frame also provides assembly tools and jigs with jacks to support temporarily the components as well as to adjust the components at right positions. In this paper, the assembly scenario and scequence of the major components such as VV and TFC and the concept of the assembly frame including special jigs and fixtures are discussed.
Sakanaka, Shogo*; Akemoto, Mitsuo*; Aoto, Tomohiro*; Arakawa, Dai*; Asaoka, Seiji*; Enomoto, Atsushi*; Fukuda, Shigeki*; Furukawa, Kazuro*; Furuya, Takaaki*; Haga, Kaiichi*; et al.
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.2338 - 2340, 2010/05
Future synchrotron light source using a 5-GeV energy recovery linac (ERL) is under proposal by our Japanese collaboration team, and we are conducting R&D efforts for that. We are developing high-brightness DC photocathode guns, two types of cryomodules for both injector and main superconducting (SC) linacs, and 1.3 GHz high CW-power RF sources. We are also constructing the Compact ERL (cERL) for demonstrating the recirculation of low-emittance, high-current beams using above-mentioned critical technologies.
Ida, Katsumi*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Yoshinuma, Mikiro*; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Nagaoka, Kenichi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Oyama, Naoyuki; Osakabe, Masaki*; Yokoyama, Masayuki*; Funaba, Hisamichi*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(9), p.095024_1 - 095024_9, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:71.94(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Dynamics of ion internal transport barrier (ITB) formation and impurity transport both in the Large Helical Device (LHD) heliotron and JT-60U tokamak are described. Significant differences between heliotron and tokamak plasmas are observed. The location of the ITB moves outward during the ITB formation regardless of the sign of magnetic shear in JT-60U and the ITB becomes more localized in the plasma with negative magnetic shear. In LHD, the low Te/Ti ratio ( 1) of the target plasma for the high power heating is found to be necessary condition to achieve the ITB plasma and the ITB location tends to expand outward or inward depending on the condition of the target plasmas. Associated with the formation of ITB, the carbon density tends to be peaked due to inward convection in JT-60U, while the carbon density becomes hollow due to outward convection in LHD. The outward convection observed in LHD contradicts the prediction by neoclassical theory.
1) of the target plasma for the high power heating is found to be necessary condition to achieve the ITB plasma and the ITB location tends to expand outward or inward depending on the condition of the target plasmas. Associated with the formation of ITB, the carbon density tends to be peaked due to inward convection in JT-60U, while the carbon density becomes hollow due to outward convection in LHD. The outward convection observed in LHD contradicts the prediction by neoclassical theory.
Murakawa, Hideki*; Ueda, Tadanobu*; Yoshida, Takehisa*; Sugimoto, Katsumi*; Asano, Hitoshi*; Takenaka, Nobuyuki*; Mochiki, Koichi*; Iikura, Hiroshi; Yasuda, Ryo; Matsubayashi, Masahito
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 605(1-2), p.127 - 130, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:82.24(Instruments & Instrumentation)Ida, Katsumi; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Oyama, Naoyuki; Ito, Kimitaka*; Yoshinuma, Mikiro*; Inagaki, Shigeru*; Kobuchi, Takashi*; Isayama, Akihiko; Suzuki, Takahiro; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 101(5), p.055003_1 - 055003_4, 2008/08
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:79.28(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A spontaneous transition phenomena between two meta-stable states of plasmas with internal transport barrier (ITB), that are characterized by different radial profiles of second derivative of ion temperature inside the ITB region where the ion temperature gradient is large, is observed in the steady-state phase of magnetic shear in the negative magnetic shear plasma in JT-60U tokamak. The curvature asymmetry factor evaluated from the radial profile of second derivative of ion temperature profiles changes from 0.08 (symmetric curvature ITB) to -0.43 (asymmetric curvature ITB) during transition phase.
Kamada, Yutaka; Leonard, A. W.*; Bateman, G.*; Becoulet, M.*; Chang, C. S.*; Eich, T.*; Evans, T. E.*; Groebner, R. J.*; Guzdar, P. N.*; Horton, L. D.*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
no abstracts in English
Ninomiya, Hiromasa; Akiba, Masato; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Fujiwara, Masami*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Inoue, Nobuyuki; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 49, p.S428 - S432, 2006/12
To contribute DEMO and ITER, the design to modify the present JT-60U into superconducting coil machine, named National Centralized Tokamak (NCT), is being progressed under nationwide collaborations in Japan. Mission, design and strategy of this NCT program is summarized.
Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Tamai, Hiroshi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Fujita, Takaaki; Takase, Yuichi*; Sakurai, Shinji; Kizu, Kaname; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Kurita, Genichi; Morioka, Atsuhiko; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 46(3), p.S29 - S38, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:41.68(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The National Centralized Tokamak (NCT) facility program is a domestic research program for advanced tokamak research to succeed JT-60U incorporating Japanese university accomplishments. The mission of NCT is to establish high beta steady-state operation for DEMO and to contribute to ITER. The machine flexibility and mobility is pursued in aspect ratio and shape controllability, feedback control of resistive wall modes, wide current and pressure profile control capability for the demonstration of the high-b steady state.
Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Akiba, Masato; Azechi, Hiroshi*; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Fujiwara, Masami*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hashizume, Hidetoshi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Horiike, Hiroshi*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.1599 - 1605, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.94(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 plasma operation
plasma operationTamai, Hiroshi; Akiba, Masato; Azechi, Hiroshi*; Fujita, Takaaki; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hashizume, Hidetoshi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Horiike, Hiroshi*; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ichimura, Makoto*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 45(12), p.1676 - 1683, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:45.44(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Design studies are shown on the National Centralized Tokamak facility. The machine design is carried out to investigate the capability for the flexibility in aspect ratio and shape controllability for the demonstration of the high-beta steady state operation with nation-wide collaboration, in parallel with ITER towards DEMO. Two designs are proposed and assessed with respect to the physics requirements such as confinement, stability, current drive, divertor, and energetic particle confinement. The operation range in the aspect ratio and the plasma shape is widely enhanced in consistent with the sufficient divertor pumping. Evaluations of the plasma performance towards the determination of machine design are presented.
Yoshida, Eiichi; Yaguchi, Katsumi*; Aoto, Kazumi
JNC TN9400 2004-061, 42 Pages, 2004/05
In sodium cooled fast reactors, when a very small-scale sodium leakage occurs to an air atmosphere through a fine crack of component or piping in the sodium systems, sodium may produce corrosive compounds by the chemical reactions with the air atmosphere, and corrosion damage of component materials may be induced. Therefore, evaluation of the corrosion behavior and the amount of damages of the component materials by the corrosive compound is important from the viewpoint of a design of a plant and maintenance management. The corrosion tests were conducted with the parameters NaOH concentration [55-100mass.% NaOH] and NaOH solution temperature [348-1027K] for the SUS304 stainless steel which is a typical structure material. The corrosion rate and corrosion crack susceptibility were examined. As the results, the corrosion rate of SUS304 was dependent on the temperature of NaOH solution, though the influence of NaOH concentration in solution was small. The different temperature dependency was shown in 55-85% NaOH solution and 100% NaOH. The activation energy was about 30kcal/mol in 55-85% NaOH solution and was about 9kcal/mol in 100% NaOH, respectively. The corrosion rate of this experiment was roughly in agreement with the reference values in NaOH solution obtained by the past experiments. The morphology of corrosion was general corrosion under all conditions. In the SCC experiment using the U-bend test specimen, TGSCC was observed under a part of condition. However, the observed region in this study was within the limits of the SCC boundary region of SUS304 in sodium-hydroxide solution.
Kato, Shoichi; Yoshida, Eiichi; Ishigami, Katsuo*; Yaguchi, Katsumi*
JNC TN9400 2003-108, 92 Pages, 2004/02
A high Cr-Mo steel is a candidate for structural materials of future advanced fast reactors, because of good thermal properties and high creep strength. In this study, creep, creep-fatigue and corrosion tests were carried out to confirm the long-term extrapolation of sodium environmental, effects on the mechanical properties of HCM12A (2001). The exposure to sodium was conducted using a sodium test apparatus constituted by austenitic steels. For the conditions of in-sodium test, the sodium temperature was 550 deg-C and the oxygen concentration in sodium was below 2 ppm. The creep and creep-fatigue strength data in sodium, and in the carburized sodium were within the scattered range of those in air under the same conditions. It is considered that the creep damage in the bulk of the material was dominant. The creep and creep-fatigue life calculated using the usual rule for air showed good agreement with the sodium experimental results. The maximum corrosion rate of HCM12A (2001) was 0.4 micro-m/year at 550 deg-C, and it was almost same as SUS304 and Mod.9Cr-1Mo steels. Corrosion allowance of HCM12A (2001), therefore, can be estimated conservatively by the equation defined in "the elevated temperature structural design guide of prototype fast reactor".
; Yoshida, Eiichi; Sakurai, Tadashi*; Yaguchi, Katsumi*
JNC TN9450 2003-001, 192 Pages, 2003/03
In order to evaluation of high temperature creep strength, creep tests under internal pressure on the fuel cladding tube for fast breeder reactor (FBR) has been preformed in New Technology Development Group. In this report, the result of the creep and creep-rupture properties on the advance austenitic stainless and high-Ni steels obtained up to this time was collected. Valuable test data totals 149 points including sodium environment test data. These data will be reflected in development and design for fuel cladding material. Contents of the data sheet are as follows ; (1)Material and number of data: 15Cr-20Ni steel (2 heats) 72 points, PNC1520 steel (1 heats) 6 points, 14Cr-25Ni steel (8 heats) 56 points, High-Ni steel (1 heat) 15 points (2)Test environment : In-air, In-argon gas and In-sodium (3)Test temperature : 600 C to 750
C to 750 C(873K to 1023K)
C(873K to 1023K)
Ninomiya, Hiromasa; Kitsunezaki, Akio; Shimizu, Masatsugu; Kuriyama, Masaaki; JT-60 Team; Kimura, Haruyuki; Kawashima, Hisato; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Sato, Masayasu; Isei, Nobuaki; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 42(1), p.7 - 31, 2002/07
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:27.27(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to establish scientific basis for the sustainment of highly integrated performance required in the advanced steady-state operation, JT-60U has been optimizing the discharge control scenarios of improved confinement plasmas and expanding the operation regions. Promising results toward the steady-state tokamak were obtained. The detail of such results is reported. JFT-2M has performed advanced and basic research for the development of high performance tokamak plasma as well as the structural material for a fusion reactor. The toroidal ripple reduction with ferritic steel plates outside the vacuum vessel was successfully demonstrated. No adverse effects were observed in the pre-testing on compatibility between ferritic steel plates, covering ~20% of the inside wall of the vacuum vessel, and plasma. The results of TRIAM-1M is also reported.
Yoshida, Kazuo; Yokobayashi, Masao; Tanabe, Fumiya; Kawase, Katsumi*; Komiya, Akitoshi*
JAERI-Data/Code 2001-023, 118 Pages, 2001/08
no abstracts in English