Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Baccou, J.*; Glantz, T.*; Ghione, A.*; Sargentini, L.*; Fillion, P.*; Damblin, G.*; Sueur, R.*; Iooss, B.*; Fang, J.*; Liu, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 421, p.113035_1 - 113035_16, 2024/05
In the Best-Estimate Plus Uncertainty (BEPU) framework, the use of best-estimate code requires to go through a Verification, Validation and Uncertainty Quantification process (VVUQ). The relevance of the experimental data in relation to the physical phenomena of interest in the VVUQ process is crucial. Adequacy analysis of selected experimental databases addresses this problem. The outcomes of the analysis can be used to select a subset of relevant experimental data, to encourage designing new experiments or to drop some experiments from a database because of their substantial lack of adequacy. The development of a specific transparent and reproducible approach to analyze the relevance of experimental data for VVUQ still remains open and is the topic of this contribution. In this paper, the concept of adequacy initially introduced in the OECD/NEA SAPIUM (Systematic APproach for model Input Uncertainty quantification Methodology) activity is formalized. It is defined through two key properties, called representativeness and completeness, that allows considering the multifactorial dimension of the adequacy problem. A new systematic approach is then proposed to analyze the adequacy of a set of experimental databases. It relies on the introduction of two sets of criteria to characterize representativeness and completeness and on the use of multi-criteria decision analysis method to perform the analysis. Finally, the approach is applied in the framework of the new OECD/NEA ATRIUM activity which includes a set of practical IUQ exercises in thermal-hydraulics to test the SAPIUM guideline in determining input uncertainties and forward propagating them on an application case. It allows evaluating the adequacy of eight experimental databases coming from the Super Moby-dick, Sozzi-Sutherland and Marviken experiments and identifying the most adequate ones.
 neutron diffraction study
neutron diffraction studyGong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Zheng, R.*; 眞山 剛*; Sun, B.*; 相澤 一也; Harjo, S.; 辻 伸泰*
Scripta Materialia, 225, p.115161_1 - 115161_5, 2023/03
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:45.58(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Deformation behavior during uniaxial compression at 21 K and 298 K in a commercial AZ31 magnesium alloy was studied by  neutron diffraction. Decreasing the deformation temperature resulted in a slight increase in yield stress (115 MPa
neutron diffraction. Decreasing the deformation temperature resulted in a slight increase in yield stress (115 MPa  139 MPa), but a remarkable enhancement in both the fracture stress (365 MPa
139 MPa), but a remarkable enhancement in both the fracture stress (365 MPa  551 MPa) and fracture strain (12.8%
551 MPa) and fracture strain (12.8%  16.5%). The low temperature sensitivity of the {10
16.5%). The low temperature sensitivity of the {10 2} extension twinning which governed the macroscopic yielding led to the slight increase in yield stress. At 21K, basal slip was suppressed, while the extension twinning was promoted resulted in higher twin volume fraction. In the late stage of deformation, the {10
2} extension twinning which governed the macroscopic yielding led to the slight increase in yield stress. At 21K, basal slip was suppressed, while the extension twinning was promoted resulted in higher twin volume fraction. In the late stage of deformation, the {10 1}-{10
1}-{10 2} double twinning was suppressed, which is considered to be the reason to delay the fracture at 21 K.
2} double twinning was suppressed, which is considered to be the reason to delay the fracture at 21 K.
 observation of twinning and detwinning in AZ31 alloy
observation of twinning and detwinning in AZ31 alloyGong, W.; Zheng, R.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; 相澤 一也; 辻 伸泰*
Journal of Magnesium and Alloys (Internet), 10(12), p.3418 - 3432, 2022/12
被引用回数:17 パーセンタイル:93.62(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Twinning and detwinning behavior of a commercial AZ31 magnesium alloy during cyclic compression-tension deformation with a total strain amplitude of 4% ( 2%) was evaluated using the complementary techniques of
2%) was evaluated using the complementary techniques of  neutron diffraction, identical area electron backscatter diffraction, and transmission electron microscopy. In-situ neutron diffraction demonstrates that the compressive deformation was dominated by twin nucleation, twin growth, and basal slip, while detwinning dominated the unloading of compressive stresses and subsequent tension stage. A large number of
neutron diffraction, identical area electron backscatter diffraction, and transmission electron microscopy. In-situ neutron diffraction demonstrates that the compressive deformation was dominated by twin nucleation, twin growth, and basal slip, while detwinning dominated the unloading of compressive stresses and subsequent tension stage. A large number of 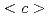 -component dislocations observed in twins and the detwinned regions were attributed to the dislocation transmutation during the twinning and detwinning. The accumulation of barriers including twin boundaries and various types of dislocations enhanced the interactions of migrating twin boundary with these barriers during twinning and detwinning, which is considered to be the origin for increasing the work hardening rate in cyclic deformation of the AZ31 alloy.
-component dislocations observed in twins and the detwinned regions were attributed to the dislocation transmutation during the twinning and detwinning. The accumulation of barriers including twin boundaries and various types of dislocations enhanced the interactions of migrating twin boundary with these barriers during twinning and detwinning, which is considered to be the origin for increasing the work hardening rate in cyclic deformation of the AZ31 alloy.
 neutron diffraction and electron microscopy study
neutron diffraction and electron microscopy studyZheng, R.*; Gong, W.; Du, J.-P.*; Gao, S.*; Liu, M.*; Li, G.*; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.; Ma, C.*; 尾方 成信*; et al.
Acta Materialia, 238, p.118243_1 - 118243_15, 2022/10
被引用回数:17 パーセンタイル:93.62(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Grain refinement can lead to the strengthening of metallic materials according to the Hall-Petch relationship. However, our recent results suggested that grain boundary sliding is the dominant deformation mode in bulk ultrafine grained (UFG) pure Mg at room temperature, leading to softening. Here, for the first time, we report that the Hall-Petch strengthening can be regained in bulk UFG pure Mg at cryogenic temperature. At 77K, the UFG pure Mg with a mean grain size of 0.6  m exhibited ultrahigh tensile yield strength and ultimate tensile strength of 309 MPa and 380 MPa, respectively. Combined
m exhibited ultrahigh tensile yield strength and ultimate tensile strength of 309 MPa and 380 MPa, respectively. Combined  neutron diffraction and electron microscopy investigation indicated that residual dislocation structures and deformation twins hardly formed in the UFG specimen during tensile test at 298K. In contrast, fast accumulation of lattice defects and remarkable reorientation were evident at 77K, suggesting that the grain-boundary-mediated process was suppressed and the plastic deformation was dominated by dislocation slip and deformation twinning. In addition, all the pure Mg specimens exhibited pronounced strain hardening at 77 K, which was mainly attributed to the suppressed grain boundary sliding and dynamic recovery. The mean dislocation density and relative fractions of dislocations with various Burgers vectors of the UFG specimen deformed at 77K were determined quantitatively from neutron diffraction data.
neutron diffraction and electron microscopy investigation indicated that residual dislocation structures and deformation twins hardly formed in the UFG specimen during tensile test at 298K. In contrast, fast accumulation of lattice defects and remarkable reorientation were evident at 77K, suggesting that the grain-boundary-mediated process was suppressed and the plastic deformation was dominated by dislocation slip and deformation twinning. In addition, all the pure Mg specimens exhibited pronounced strain hardening at 77 K, which was mainly attributed to the suppressed grain boundary sliding and dynamic recovery. The mean dislocation density and relative fractions of dislocations with various Burgers vectors of the UFG specimen deformed at 77K were determined quantitatively from neutron diffraction data.
Brumm, S.*; Gabrielli, F.*; Sanchez-Espinoza, V.*; Groudev, P.*; Ou, P.*; Zhang, W.*; Malkhasyan, A.*; Bocanegra, R.*; Herranz, L. E.*; Berda , M.*; et al.
, M.*; et al.
Proceedings of 10th European Review Meeting on Severe Accident Research (ERMSAR 2022) (Internet), 13 Pages, 2022/05
The current HORIZON-2020 project on "Management and Uncertainties of Severe Accidents (MUSA)" aims at applying Uncertainty Quantification (UQ) in the modeling of Severe Accidents (SA), particularly in predicting the radiological source term of mitigated and unmitigated accident scenarios. Within its application part, the project is devoted to the uncertainty quantification of different severe accident codes when predicting the radiological source term of selected severe accident sequences of different nuclear power plant designs, e.g. PWR, VVER, and BWR. Key steps for this investigation are, (a) the selection of severe accident sequences for each reactor design, (b) the development of a reference input model for the specific design and SA-code, (c) the selection of a list of uncertain model parameters to be investigated, (d) the choice of an UQ-tool e.g. DAKOTA, SUSA, URANIE, etc., (e) the definition of the figures of merit for the UA-analysis, (f) the performance of the simulations with the SA-codes, and, (g) the statistical evaluation of the results using the capabilities, i.e. methods and tools offered by the UQ-tools. This paper describes the project status of the UQ of different SA codes for the selected SA sequences, and the technical challenges and lessons learnt from the preparatory and exploratory investigations performed.
Liu, M.*; Gong, W.; Zheng, R.*; Li, J.*; Zhang, Z.*; Gao, S.*; Ma, C.*; 辻 伸泰*
Acta Materialia, 226, p.117629_1 - 117629_13, 2022/03
被引用回数:45 パーセンタイル:99.49(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)One hopeful path to realize good comprehensive mechanical properties in metallic materials is to accomplish homogeneous nanocrystalline (NC) or ultrafine grained (UFG) structure with low dislocation density. In this work, high pressure torsion deformation followed by appropriate annealing was performed on 316 stainless steel (SS). For the first time, we successfully obtained NC/UFG 316 SS having uniform microstructures with various average grain sizes ranging from 46 nm to 2.54  m and low dislocation densities. Among the series, an un-precedentedly high yield strength (2.34 GPa) was achieved at the smallest grain size of 46 nm, in which dislocation scarcity induced hardening accounting for 57% of the strength. On the other hand, exceptional strength-ductility synergy with high yield strength (900 MPa) and large uniform elongation (27%) was obtained in the fully recrystallized specimen having the grain size of 0.38
m and low dislocation densities. Among the series, an un-precedentedly high yield strength (2.34 GPa) was achieved at the smallest grain size of 46 nm, in which dislocation scarcity induced hardening accounting for 57% of the strength. On the other hand, exceptional strength-ductility synergy with high yield strength (900 MPa) and large uniform elongation (27%) was obtained in the fully recrystallized specimen having the grain size of 0.38  m. The high yield stress and scarcity of dislocation sources in recrystallized UFGs activated stacking faults and deformation twins nucleating from grain boundaries during straining, and their interaction with dislocations allowed for sustainable strain hardening, which also agreed with the plaston concept recently proposed. The multiple deformation modes activated, together with the effective strengthening mechanisms, were responsible for the outstanding comprehensive mechanical performance of the material.
m. The high yield stress and scarcity of dislocation sources in recrystallized UFGs activated stacking faults and deformation twins nucleating from grain boundaries during straining, and their interaction with dislocations allowed for sustainable strain hardening, which also agreed with the plaston concept recently proposed. The multiple deformation modes activated, together with the effective strengthening mechanisms, were responsible for the outstanding comprehensive mechanical performance of the material.
Zhang, P.*; Tang, X.*; Wang, Y.*; Wang, X.*; Gao, D.*; Li, Y.*; Zheng, H.*; Wang, Y.*; Wang, X.*; Fu, R.*; et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 142(41), p.17662 - 17669, 2020/10
被引用回数:21 パーセンタイル:74.59(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)固体トポケミカル重合(SSTP)は機能的な結晶性高分子材料を合成するための有望な方法であるが、溶液中で起こるさまざまな反応とは対照的に、非常に限られたタイプのSSTP反応しか報告されていない。ディールス・アルダー(DA)および脱水素-DA(DDA)反応は、溶液中で六員環を作るための教科書的反応であるが、固相合成ではほとんど見られない。本研究では、固体の1,4-ジフェニルブタジイン(DPB)を10-20GPaに加圧することで、フェニル基がジエノフィルとして、DDA反応することを複数の最先端の手法を用いて明らかにした。臨界圧力での結晶構造は、この反応が「距離選択的」であることを示している。つまり、フェニルとフェニルエチニル間の距離3.2 は、DDA反応は起こせるが、他のDDAや1,4-付加反応で結合を形成するには長すぎる。回収された試料は結晶性の肘掛け椅子型のグラファイトナノリボンであるため、今回の研究結果は、原子スケールの制御で結晶質炭素材料を合成するための新しい道を開く。
は、DDA反応は起こせるが、他のDDAや1,4-付加反応で結合を形成するには長すぎる。回収された試料は結晶性の肘掛け椅子型のグラファイトナノリボンであるため、今回の研究結果は、原子スケールの制御で結晶質炭素材料を合成するための新しい道を開く。
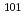 Pd
PdZhou, H. B.*; Zhou, X. H.*; Zhang, Y. H.*; Zheng, Y.*; Liu, M. L.*; Zhang, N. T.*; Chen, L.*; Wang, S. T.*; Li, G. S.*; Wang, H. X.*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 47(9), p.107_1 - 107_7, 2011/09
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:32.8(Physics, Nuclear)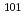 Pd原子核の高スピン状態を、タンデム加速器及び多重
Pd原子核の高スピン状態を、タンデム加速器及び多重 線検出装置GEMINI-IIを用いて、インビーム
線検出装置GEMINI-IIを用いて、インビーム 線核分光法で調べた。既知の
線核分光法で調べた。既知の
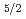 バンド, 1/2
バンド, 1/2 [550]バンドをより高スピン状態まで拡張した。発見されたバンド交差は
[550]バンドをより高スピン状態まで拡張した。発見されたバンド交差は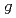
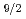 陽子の整列によるものであると解釈した。
陽子の整列によるものであると解釈した。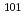 Pdの回転バンドの性質を周辺の核、及びcranked shell modelと比較・議論した。
Pdの回転バンドの性質を周辺の核、及びcranked shell modelと比較・議論した。
 [503] band of
[503] band of  Pt
PtLi, G. S.*; Zhou, X. H.*; Zhang, Y. H.*; Zheng, Y.*; Liu, M. L.*; Hua, W.*; Zhou, H. B.*; Ding, B.*; Wang, H. X.*; Lei, X. G.*; et al.
Journal of Physics G; Nuclear and Particle Physics, 38(9), p.095105_1 - 095105_9, 2011/09
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:11.77(Physics, Nuclear) Ptの高スピン状態をタンデム加速器と多重
Ptの高スピン状態をタンデム加速器と多重 線検出装置GEMINI-IIを用いて調べた。低スピン指標逆転現象が7/2
線検出装置GEMINI-IIを用いて調べた。低スピン指標逆転現象が7/2 [503]バンドで観測された。この現象は、中性子が7/2
[503]バンドで観測された。この現象は、中性子が7/2 [503]軌道から7/2
[503]軌道から7/2 [514]軌道に移ることによって起こるという解釈は、DonauとFrauendorfの反古典的近似による計算結果によって支持された。
[514]軌道に移ることによって起こるという解釈は、DonauとFrauendorfの反古典的近似による計算結果によって支持された。
Gong, W.; Zheng, R.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; 相澤 一也; 辻 伸泰*
no journal, ,
Extension twinning and detwinning play crucial roles in cyclic loading deformation of magnesium (Mg) and its alloys. The occurrences of twining and detwinning are accompanied by the motion of twin boundaries (TBs), and then the interaction between the TBs and lattice defects such as dislocations and various boundaries is the key factor for the mechanical properties. Because of the complex microstructures introduced by cyclic deformation, the work hardening mechanisms associated with twinning and detwinning in Mg alloys are still far from being understood. In the present study, twinning and detwinning behavior of a commercial AZ31 Mg alloy during cyclic compression-tension deformation was evaluated in multi-scale using in-situ neutron diffraction (ND), identical area electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD), and transmission electron microscopy techniques. The relationship between the mechanical responses in cyclic deformation and microstructures was investigated.
Gong, W.; Zheng, R.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; 辻 伸泰*
no journal, ,
Precipitation hardening in magnesium (Mg) alloys is generally due to the interactions between the precipitates and deformation modes. The precipitates formed in Mg alloys with rod-shaped or plate-shaped always keep a specific crystallographic orientation relationship with the HCP matrix. As a result, the rod-shaped or plated-shaped precipitates exhibit different interactions with the deformation modes depending on the geometric relationships between the precipitates and dislocation glide or twinning shear directions in the surrounding HCP lattices. Even many efforts have been devoted to clarify this phenomenon, the quantitative contributions of precipitation hardening on various deformation modes are still not fully understood. In-situ neutron diffraction can provide the bulk averaged crystallographic information such as lattice strains, dislocation density and texture for interpretating macroscopic deformation behavior. The Elastic-Plastic Self-Consistent (EPSC) polycrystal model is suitable to account for the deformation behavior in Mg alloys. In present study, the combination of in-situ neutron diffraction and EPSC modeling was employed to investigate the precipitation hardening behavior in a Z6 Mg alloy.
Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Zheng, R.*; 眞山 剛*; 相澤 一也; Harjo, S.; 辻 伸泰*
no journal, ,
Mg and its alloys possess great potential for a wide range of applications, particularly in cryogenic applications. However, the deformation mechanisms of Mg alloys at cryogenic temperatures are not fully understood due to the absence of appropriate methods. In this study, we investigated the deformation behavior of a commercial AZ31 alloy at cryogenic temperatures using in-situ neutron diffraction. The yield stress of AZ31 alloy significantly increased with decreasing temperature in tensile deformation, but slightly increased in compressive deformation. Interestingly, both the fracture strain and stress at 20 K exhibited a substantial increase compared to 298 K in compressive deformation. In-situ neutron diffraction experiments were conducted using the engineering diffractometer TAKUMI at J-PARC to reveal the deformation mechanisms in the AZ31 alloy at cryogenic temperatures. The stress-strain response of the AZ31 alloy with temperature will be discussed in relation to the temperature-dependent activity of deformation mechanisms.