Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Zhang, Y.-J.*; 梅田 岳昌*; 諸岡 聡; Harjo, S.; 宮本 吾郎*; 古原 忠*
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 55(10), p.3921 - 3936, 2024/10
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In this study, a series of eutectoid steels with Mn addition up to 2 mass% were isothermally transformed at various temperatures from 873 K to 973 K to clarify the pearlite growth kinetics and the underlying thermodynamics at its growth front. The microscopic observation indicates the acceleration in pearlite growth rate and refinement in lamellar spacing by decreasing the transformation temperature or the amount of Mn addition. After analyzing the solute distribution at pearlite growth front via three-dimensional atom probe, no macroscopic Mn partitioning across pearlite/austenite interface is detected, whereas Mn segregation is only observed at ferrite/austenite interface. Furthermore, in-situ neutron diffraction measurements performed at elevated temperatures reveals that the magnitude of elastic strain generated during pearlite transformation is very small.
Zhou, L.*; Zhang, H.*; Qin, T. Y.*; Hu, F. F.*; 徐 平光; Ao, N.*; Su, Y. H.; He, L. H.*; Li, X. H.*; Zhang, J. R.*; et al.
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 55(7), p.2175 - 2185, 2024/07
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:75.40(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)High-speed railway S38C axles undergo surface induction hardening for durability, but are susceptible to fatigue cracks from foreign object impact. The neutron diffraction method was employed to measure the residual strain in S38C axles, obtaining microscopic lattice distortion data, for the gradient layer at a depth of 8 mm under the surface. The results showed that after induction-hardening, the microscopic lattice distortion had a gradient distribution, decreasing with the distance from the surface. However, in the case of impacting speed of 600 km/m, the average microscopic lattice distortion increased with the distance from the surface, reaching a maximum augmentation of 55 pct. These findings indicate a strong experimental basis, and improve our understanding of the relationship between macroscopic residual stress and decision-making, in regard to operation and maintenance.
 muon spin relaxation method and first-principles calculations
muon spin relaxation method and first-principles calculations都留 智仁; 西村 克彦*; 松田 健二*; 布村 紀男*; 並木 孝洋*; Lee, S.*; 髭本 亘; 松崎 禎市郎*; 山口 正剛; 海老原 健一; et al.
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 54(6), p.2374 - 2383, 2023/06
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:25.24(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)高強度Al合金の水素脆化感受性は、Al合金の実用化において重要な課題として認識されているが、水素のトラップまたは分布の特定は困難であった。本研究では、実験とシミュレーションに基づいた効果的なアプローチにより、Al合金中の潜在的なトラップサイトを探索することを提案する。Al-0.5%Mg, Al-0.2%Cu, Al-0.15%Ti, Al-0.011%Ti, Al-0.28%V, Al-0.015%V (at.%)に対して、5から300Kの温度範囲でゼロフィールドミュオンスピン緩和実験が行われた。双極子場の幅の温度変化から、Al-0.5%Mgに3つのピーク、Al-0.2%Cuに4つのピーク、Al-0.011%TiとAl-0.015%Vに3つのピークがあることが明らかにされた。観測されたピークに対応するミュオントラップサイトの原子配置は、溶質及び溶質-空孔ペア周りの水素のトラップエネルギーに対する第一原理計算を用いてよく同定された。ミュオンピーク温度とトラップエネルギーの間に線形関係が抽出されたことにより、Al合金において水素と強い結合エネルギーを持つ合金元素とその複合体の可能性を探ることができる。
古賀 紀光*; 梅澤 修*; 山本 正之*; 山本 卓*; 山下 享介; 諸岡 聡; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 52(3), p.897 - 901, 2021/03
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:16.41(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Small ball rebound hardness tests demonstrated characteristic hardening at 700 K in the ultra-low carbon and pearlitic steels. The equilibrium phase diagram of Fe-C binary alloy calculated using Thermo-Calc exhibited dissolving of cementite above 700 K. Moreover, in-situ heating neutron diffraction measurement demonstrated the increase of lattice parameter by dissolving of cementite above 700 K. Therefore, it can be concluded that the characteristic hardening above 700 K can be attributed to the solid solute carbon.
海老原 健一; 杉山 優理*; 松本 龍介*; 高井 健一*; 鈴土 知明
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 52(1), p.257 - 269, 2021/01
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:40.46(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)応力腐食割れの原因の1つと考えられている水素脆化に関し、近年、材料の変形時に水素により過剰生成した空孔が直接の原因と考える水素助長ひずみ誘起空孔モデルが提案されている。しかし、その定量的考察はあまりなされておらず、誘起空孔の挙動の定量的評価が必要である。このことから、本研究では、水素添加と同時にひずみを与えた純鉄の薄膜試料の水素熱脱離スペクトルを、空孔及び空孔クラスターの挙動を考慮したモデルでシミュレーションした。モデルでは、9個の空孔からなる空孔クラスター(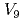 )までを考慮し、空孔及び空孔クラスターの水素トラップエネルギーとして、分子静力学で見積もった値を用いた。また、拡散に関するパラメータも原子レベル計算で評価した値を用いた。結果として、モデルは、全体としてスペクトルを再現し、時効処理の温度に対するスペクトルの変化も再現した。一方、実験との2つの特徴的な違いも現れ、その考察から、
)までを考慮し、空孔及び空孔クラスターの水素トラップエネルギーとして、分子静力学で見積もった値を用いた。また、拡散に関するパラメータも原子レベル計算で評価した値を用いた。結果として、モデルは、全体としてスペクトルを再現し、時効処理の温度に対するスペクトルの変化も再現した。一方、実験との2つの特徴的な違いも現れ、その考察から、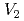 及び
及び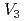 の拡散はモデルより遅いこと、また、水素と共にひずみを与える際に、空孔クラスターも生成されることの可能性が見出された。本モデルは、照射で生成した空孔の挙動の考察にも応用可能と考える。
の拡散はモデルより遅いこと、また、水素と共にひずみを与える際に、空孔クラスターも生成されることの可能性が見出された。本モデルは、照射で生成した空孔の挙動の考察にも応用可能と考える。
Lam, T.-N.*; Tsai, C.-W.*; Chen, B.-K.*; Lai, B.-H.*; Liu, H.-C*; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.; Lin, B.-H.*; Huang, E.-W.*
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 51(10), p.5023 - 5028, 2020/10
被引用回数:14 パーセンタイル:56.94(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Substitution of Ge for Mn increases the elastic moduli of different 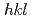 orientations of the CoCrFeMnNi-based high-entropy alloy. Our findings indicate that tuning minor element compositions may result in improved strength-ductility combination. The underlying deformation mechanisms of CoCrFeNiGe
orientations of the CoCrFeMnNi-based high-entropy alloy. Our findings indicate that tuning minor element compositions may result in improved strength-ductility combination. The underlying deformation mechanisms of CoCrFeNiGe were examined by
were examined by  neutron diffraction and analysis of the associated diffraction profiles during tensile deformation. The strain-hardening response of CoCrFeNiGe
neutron diffraction and analysis of the associated diffraction profiles during tensile deformation. The strain-hardening response of CoCrFeNiGe exhibited a dominant mechanism of mechanical twinning at moderate and large strains at room temperature. The evolution of the bulk work hardening rate was consistent with the convolutional multiple whole profile fitting results, which exhibited a continuous increase in twin formation probability.
exhibited a dominant mechanism of mechanical twinning at moderate and large strains at room temperature. The evolution of the bulk work hardening rate was consistent with the convolutional multiple whole profile fitting results, which exhibited a continuous increase in twin formation probability.
齋藤 圭*; 平出 哲也; 高井 健一*
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 50(11), p.5091 - 5102, 2019/11
被引用回数:35 パーセンタイル:84.22(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)低温熱脱離分析法(L-TDS)と陽電子消滅法(PAS)を用い、擬へき開破壊を示す焼戻しマルテンサイト鋼中の種々のトラップサイトの中から、水素存在下塑性ひずみにより導入された格子欠陥からの脱離による水素ピークを分離し同定する試みを行った。水素の存在下において塑性ひずみを付与した鋼試験片をL-TDSにより測定することで、2つのピーク、すなわち元から存在していた脱離と新たな脱離の分離を可能にした。PASの結果からL-TDSによって新たに見出された脱離は空孔型欠陥に対応することが明らかとなった。水素存在下における塑性ひずみは、破面から1.5mm以内に形成される格子欠陥濃度を原子比で約10 オーダーまで著しく増大させた。これらの結果は、水素存在下における塑性変形がナノボイド核形成と合体をもたらし、焼戻しマルテンサイト鋼の擬へき開破壊をもたらすことを示している。
オーダーまで著しく増大させた。これらの結果は、水素存在下における塑性変形がナノボイド核形成と合体をもたらし、焼戻しマルテンサイト鋼の擬へき開破壊をもたらすことを示している。
 neutron diffraction line profile analysis
neutron diffraction line profile analysisHarjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; 友田 陽*; Gong, W.*; 相澤 一也; Tichy, G.*; Shi, Z.*; Ung r, T.*
r, T.*
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 48(9), p.4080 - 4092, 2017/09
被引用回数:64 パーセンタイル:92.67(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) neutron diffraction during tensile deformation of lath martensite steel containing 0.22 mass% of carbon, is performed using TAKUMI of J-PARC. The diffraction peaks at plastically deformed states exhibit asymmetries as the reflection of redistributions of the stress and dislocation densities/arrangements in lath-packets where the dislocation glides are favorable (soft packet) and unfavorable (hard packet). The dislocation density is as high as 10
neutron diffraction during tensile deformation of lath martensite steel containing 0.22 mass% of carbon, is performed using TAKUMI of J-PARC. The diffraction peaks at plastically deformed states exhibit asymmetries as the reflection of redistributions of the stress and dislocation densities/arrangements in lath-packets where the dislocation glides are favorable (soft packet) and unfavorable (hard packet). The dislocation density is as high as 10 m
m at the as-quenched state, and then during tensile straining, the load and the dislocation density become different between the two lath-packets. The dislocation character and arrangement vary also in the hard packet, but hardly change in the soft packet. The hard packet plays an important role in the high work hardening in martensite, which could be understood by taking into account not only the increase of the dislocation density but also the change in dislocation arrangement.
at the as-quenched state, and then during tensile straining, the load and the dislocation density become different between the two lath-packets. The dislocation character and arrangement vary also in the hard packet, but hardly change in the soft packet. The hard packet plays an important role in the high work hardening in martensite, which could be understood by taking into account not only the increase of the dislocation density but also the change in dislocation arrangement.
Ung r, T.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; 友田 陽*; Rib
r, T.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; 友田 陽*; Rib rik, G.*; Shi, Z.*
rik, G.*; Shi, Z.*
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 48(1), p.159 - 167, 2017/01
被引用回数:60 パーセンタイル:91.36(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Based on high-resolution neutron diffraction experiments we will show that in lath martensite steels the initially homogeneous dislocation structure is disrupted by plastic deformation, to produce a composite on the length scale of martensite lath packets. The diffraction patterns of plastically strained martensitic steel reveal characteristically asymmetric peak profiles in the same way as has been observed in materials with heterogeneous dislocation structures. Lath packets oriented favorably or unfavorably for dislocation glide become soft or hard. The lath packet type develops by work softening or work hardening in which the dislocation density becomes smaller or larger compared to the initial average one. The decomposition into soft and hard lath packets is accompanied by load redistribution between the two lath packet types. The composite behavior of plastically deformed lath martensite opens a new way to understand the elastic-plastic response in this class of materials.
佐藤 裕*; 粉川 博之*; 藤井 啓道*; 矢野 康英; 関尾 佳弘
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 46(12), p.5789 - 5800, 2015/12
被引用回数:18 パーセンタイル:60.59(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)PNC-FMSとSUS316鋼の異材接合に摩擦攪拌接合(Friction stir welding)を適用し、系統的に強度と組織の評価を実施した。その結果、接合欠陥の生じない健全な継手を得ることができた。なお、本研究の一部は、文部科学省原子力基礎基盤戦略研究イニシアチブにより実施された「摩擦攪拌接合によるNa高速炉心材料の新たな接合技術に関する研究」の成果である。
山口 正剛
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 42(2), p.319 - 329, 2011/02
被引用回数:146 パーセンタイル:98.06(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The microscopic mechanism of grain boundary embrittlement in metals by solute segregation has been not well understood for many years. From first-principles calculations, we show here that the calculated cohesive energy (= surface energy - grain boundary energy) of bcc Fe  3(111) symmetrical tilt grain boundary is reduced by the segregation of sulfur and phosphorous, while it is increased by the segregation of boron and carbon. The rate of the decrease/increase in the cohesive energy was excellently proportional to the experimental shift in the ductile-to-brittle transition temperature of high-purity iron with increasing segregation. It indicates that the change in the cohesive energy of grain boundary plays a key role in the grain boundary embrittlement.
3(111) symmetrical tilt grain boundary is reduced by the segregation of sulfur and phosphorous, while it is increased by the segregation of boron and carbon. The rate of the decrease/increase in the cohesive energy was excellently proportional to the experimental shift in the ductile-to-brittle transition temperature of high-purity iron with increasing segregation. It indicates that the change in the cohesive energy of grain boundary plays a key role in the grain boundary embrittlement.
山口 正剛; 海老原 健一; 板倉 充洋; 門吉 朋子*; 鈴土 知明; 蕪木 英雄
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 42(2), p.330 - 339, 2011/02
被引用回数:137 パーセンタイル:97.82(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The microscopic mechanism of grain boundary embrittlement in metals by hydrogen trapping (segregation) has been not well understood for many years. From first-principles calculations, we show here that the calculated cohesive energy of bcc Fe  3(111) and fcc Al(Cu)
3(111) and fcc Al(Cu)  5(012) symmetrical tilt grain boundaries with varying the trapping density of hydrogen can be significantly reduced by hydrogen trapping; it indicates that the reduction of the cohesive energy of the grain boundary may cause the hydrogen-induced grain-boundary embrittlement in Fe, Al, and Cu, although the possibility of hydrogen trapping at grain boundary is very different among those metals. Considering the "mobile" effect of hydrogen during fracture, more hydrogen atoms coming from solid solution state can be trapped on the gradually formed two fracture surfaces in addition to the already trapped "immobile" hydrogen atoms at the grain boundary before fracture.
5(012) symmetrical tilt grain boundaries with varying the trapping density of hydrogen can be significantly reduced by hydrogen trapping; it indicates that the reduction of the cohesive energy of the grain boundary may cause the hydrogen-induced grain-boundary embrittlement in Fe, Al, and Cu, although the possibility of hydrogen trapping at grain boundary is very different among those metals. Considering the "mobile" effect of hydrogen during fracture, more hydrogen atoms coming from solid solution state can be trapped on the gradually formed two fracture surfaces in addition to the already trapped "immobile" hydrogen atoms at the grain boundary before fracture.
西山 裕孝; Liu, X.*; 亀田 純*
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 39(5), p.1118 - 1131, 2008/05
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:20.13(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Mechanisms of neutron-irradiation hardening in phosphorus (P), sulfur (S) and/or copper (Cu) doped ferritic alloys have been studied by applying a rate theory to temperature dependence of the yield strength. In P-doped alloys, neutron irradiation below 563 K brings about a remarkable increase in the athermal stress and activation energy due to more extensive dispersion of fine ( 1.7 nm) P-rich precipitates than Cu-rich precipitates. During neutron irradiation above 668 K, precipitation hardening occurs to some extent in Cu-doped and S-doped alloys, compared to small or negligible hardening in the P-doped alloys. In alloys with low to moderate contents of various dissolved impurities subjected to the high-temperature irradiation, the formation of kink pairs becomes considerably difficult. Differing dynamic interactions of dissolved and precipitated impurities with the nucleation and growth of dislocations are discussed, giving rise to irradiation hardening.
1.7 nm) P-rich precipitates than Cu-rich precipitates. During neutron irradiation above 668 K, precipitation hardening occurs to some extent in Cu-doped and S-doped alloys, compared to small or negligible hardening in the P-doped alloys. In alloys with low to moderate contents of various dissolved impurities subjected to the high-temperature irradiation, the formation of kink pairs becomes considerably difficult. Differing dynamic interactions of dissolved and precipitated impurities with the nucleation and growth of dislocations are discussed, giving rise to irradiation hardening.