Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Luu, V. N.; 谷口 良徳; 宇田川 豊; 勝山 仁哉
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 442, p.114222_1 - 114222_15, 2025/10
被引用回数:0For near-term application, coated-Zr alloy claddings show potential for enhancing safety by providing better oxidation resistance and minimizing hydrogen absorption under design-basis accidents (DBA). This benefit could extend the burnup and operational cycles of fuel rods. In assessing safety, reactivity-initiated accidents (RIA) are considered as one of the DBA conditions. The current safety criteria for high-temperature oxidation failure, one of the failure modes linked to RIA, are defined by peak fuel enthalpy values that range from 205 to 270 cal/g. This wide variability presents challenges when attempting to generalize criteria for modified-Zr alloy claddings with superior oxidation resistance. Therefore, it may be more relevant to apply failure criteria based on embrittlement mechanisms, such as oxygen concentration in the  -Zr phase. This study aimed to assess the failure based on both peak fuel enthalpy and cladding embrittlement by analyzing previous NSRR experiments conducted with conventional materials using the RANNS fuel performance code. The findings suggest that the failure criteria associated with cladding embrittlement can provide a rational evaluation of failure behavior compared to the existing criterion based on peak fuel enthalpy. The local failure criterion leading to the formation of through-wall cracks during quenching is consistent with Chung's proposal (NUREG/CR-1344):
-Zr phase. This study aimed to assess the failure based on both peak fuel enthalpy and cladding embrittlement by analyzing previous NSRR experiments conducted with conventional materials using the RANNS fuel performance code. The findings suggest that the failure criteria associated with cladding embrittlement can provide a rational evaluation of failure behavior compared to the existing criterion based on peak fuel enthalpy. The local failure criterion leading to the formation of through-wall cracks during quenching is consistent with Chung's proposal (NUREG/CR-1344):  -Zr thickness of
-Zr thickness of  0.9 wt% oxygen is less than 0.1 mm, and this corresponds to approximately 35% BJ-ECR.
0.9 wt% oxygen is less than 0.1 mm, and this corresponds to approximately 35% BJ-ECR.
久保 光太郎; 森 憲治*; 村松 健
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 442, p.114176_1 - 114176_14, 2025/10
被引用回数:0Nuclear fuel cycle facilities are important elements for supporting the efficient use of energy resources by establishing a nuclear fuel cycle. However, given that the risks of these facilities are lower than those of nuclear power plants, it is considered reasonable to apply simplified assessment methods when evaluating seismic risks. In this study, a simplified quantification method is proposed for seismic risk assessment at such facilities. Traditional simplified methods have streamlined the assessment process by selecting only representative components, often neglecting others. In contrast, the proposed method simplifies the required computational processes while considering all components by applying Clark approximation. Clark approximation is a mathematical method for approximating the maximum of two normal distributions as a new normal distribution. The proposed method was validated by comparing its seismic probabilistic risk assessment with those performed using Monte Carlo simulations and traditional simplified methods. Results showed that although the proposed method overestimated the high confidence of low probability of failure by a relative difference of 0.15 compared with that of the Monte Carlo method under completely independent condition, the overall plant-level fragility curve was generally within the range of the 5% and 95% confidence fragility curves. The proposed method accounted for the impact of correlated failure, which is critical in seismic risk assessments. Thus, this method enabled the seismic risk assessment of nuclear fuel cycle facilities in a simplified manner without compromising accuracy, potentially contributing to examining risk mitigation measures and developing risk-informed safety regulations for these facilities.
佐藤 聡; 和田 裕貴; 柴本 泰照
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 437, p.114020_1 - 114020_14, 2025/06
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)沸騰遷移後(ポストBT)の熱伝達は、軽水炉における異常過渡および事故時の被覆管表面のドライアウト継続時間やピーク温度を分析する上で不可欠である。ドライアウト継続時間の評価には、リウェット現象が非常に重要だが、高流量および高熱流束条件下でのリウェット速度に関する実験データベースが不足しているため、モデルの開発および検証に十分なデータが存在しない。そこで、単管実験装置を用いて、幅広い熱水力条件下でステップ状の境界条件の変化によって生じるリウェット速度に関するデータベースを構築した。このデータベースと得られたリウェット速度の特性に基づいて、リウェット速度の実験的相関式を提案した。この相関式は、ステップ状過渡変化における液相または気相の質量フラックスの変化をパラメータとして用いることで、リウェット速度を正確に予測する。これは、再冠水過程と比較して、極めて高い質量流束条件下では、液膜前面近傍における気相または液相の質量流束の変化がリウェットに強く影響することを示唆している。
大西 貴士; 小山 真一*; 横山 佳祐; 森下 一喜; 渡部 雅; 前田 茂貴; 矢野 康英; 大木 繁夫
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 432, p.113755_1 - 113755_17, 2025/02
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The burning of minor actinide (MA) elements, such as neptunium (Np) and americium (Am), in fast reactors (FRs) has been proposed to reduce the volume of high-level radioactive waste. Evaluation of the transmutation behavior of Am for a wide spectral range from thermal to fast neutrons requires experimental validation based on the irradiation of Am targets with well-known isotopic compositions. Four samples each of two types of Am targets, Am-241 oxide and Am-243 oxide, were prepared and irradiated in the experimental fast reactor Joyo under fast neutron flux. Additionally, a ninth sample consisting of Am-241 oxide contained in a MgO pellet was prepared and irradiated in the JMTR under thermal neutron flux. All irradiated samples were analyzed by a radiochemical method. Indexes of the transmutation behavior such as the transmutation ratio, the ratio between burnup and accumulation of an actinide could be evaluated based on the analytical results.
松村 太伊知; 奥村 啓介; 坂本 雅洋; 寺島 顕一; Riyana E. S.; 近藤 千博*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 432, p.113791_1 - 113791_9, 2025/02
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Retrieving objects with a small amount of fuel debris, such as a few grams, will begin soon at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) at the start of decommissioning. Objects retrieved from the primary containment vessel are not necessarily fuel debris; fuel debris is an object from which neutrons are emitted because it contains nuclear-fuel material. However, the characteristics of the neutrons emitted by fuel debris are unknown. Fuel debris was categorized into five types according to the elapsed time from the accident, burnup, and fuel type (UO or mixed oxide). The number and energy spectra of (
or mixed oxide). The number and energy spectra of ( ,
,  ) and spontaneous fission neutrons emitted from 1 g of each fuel debris type were estimated using the SOURCES 4C code to obtain the neutron characteristics. The results showed that the average neutron energy is approximately 2.1 MeV, regardless of the type of fuel debris. However, the intensities of neutrons emitted from the fuel debris in 1F Units 2 and 3 varied by four orders of magnitude according to the fuel debris type.
) and spontaneous fission neutrons emitted from 1 g of each fuel debris type were estimated using the SOURCES 4C code to obtain the neutron characteristics. The results showed that the average neutron energy is approximately 2.1 MeV, regardless of the type of fuel debris. However, the intensities of neutrons emitted from the fuel debris in 1F Units 2 and 3 varied by four orders of magnitude according to the fuel debris type.
松下 健太郎; 江連 俊樹; 田中 正暁; 今井 康友*; 藤崎 竜也*; 堺 公明*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 432, p.113785_1 - 113785_16, 2025/02
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)ナトリウム冷却高速炉の安全設計の観点から、液面渦によるアルゴンカバーガスのガス巻込み現象(GE)を評価する手法の確立が必要となる。本研究では、GEを評価するインハウスツールである「StreamViewer」の評価モデルの高度化として、吸込み部から液面部にかけて連続する渦中心点を接続することで渦中心線を抽出し、渦中心線に沿った減圧量分布と水頭圧とのつり合いに基づいて渦のガスコア長さを評価する「PVLモデル」について提案した。PVLモデルの適用性確認として、矩形開水路体系における垂直平板による非定常後流渦試験の三次元数値解析結果に本モデルを適用し、その結果、PVLモデルを用いたStreamViewerによるGE評価によって、非定常渦流れの試験における入口流速とガスコア長さの関係を再現できることが確認された。
浜瀬 枝里菜; 三宅 康洋*; 今井 康友*; 堂田 哲広; 小野 綾子; 田中 正暁
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 432, p.113738_1 - 113738_12, 2025/02
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)ナトリウム冷却高速炉の安全性強化のため、浸漬型直接炉内冷却器(D-DHX)による自然循環崩壊熱除去システムの開発を進めている。D-DHXを用いた場合、炉心と炉上部プレナム間の相互作用(炉心-プレナム相互作用)が生じるため、炉容器全体を一括して取り扱う多次元熱流動評価手法(RV-CFD)の構築が必要となる。本研究では、実炉解析に向けて、集合体のモデル化に着目し、解析精度を確保しながら、計算負荷低減が可能なサブチャンネルを複数個合わせた疎メッシュサブチャンネルCFDモデルを開発し、RV-CFDの炉心部に適用した。PLANDTL-1試験解析の結果、自然循環時における炉心-プレナム相互作用を精度よく評価できることを確認した。
吉田 将冬; 井口 啓; 平野 宏志*; 北村 哲浩
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 431, p.113691_1 - 113691_16, 2025/01
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)プルトニウム燃料第二開発室は現在廃止措置段階にあり、2010年からグローブボックスの解体作業が行われている。従来のグローブボックス解体作業では、放射性核種を封じ込めるためグローブボックスをビニル製のテントで囲い、その中でエアラインスーツを着用した作業者が火花の生じる切断工具を用いて手作業で解体している。この従来の解体工法は長年使用されている実績があり、適宜改良・改善され体系化されている。しかし、作業員の負担が大きく、実作業時間を短くしなければならないこと、作業場が放射性物質で汚染されているため、万が一事故が発生した際の放射性物質吸引による内部被ばくのリスクが高いことなどいくつもの欠点が存在する。このような従来法の欠点を解消するため、現在小型油圧切断機及び遠隔操作技術を用いた新たなグローブボックス解体工法の開発を進めている。具体的には、遠隔解体装置を導入することでエアラインスーツ作業を減らし、解体作業の安全性を高めることそして、すべての機器を再利用することで廃棄物の発生を抑えることを目的としている。さらに、これらの目的の達成のためテント内で解体された資材をグローブ作業で処理するためのグローブ作業エリアを設計・検討試験を行っている。
 at temperature range 170 - 290
at temperature range 170 - 290 C
CLuu, V. N.; 中島 邦久
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 426, p.113402_1 - 113402_7, 2024/09
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)A field assessment at the Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Station revealed high radioactivity on the concrete shield plugs, which is estimated above 20 PBq for Cs-137 at units 2 and 3. This leads to significant interest in the retention of Cs on concrete during severe accidents (SA). However, the interaction of CsOH, as one of the main Cs forms released in SA, with concrete surfaces at elevated temperatures remains poorly researched. In this study, we have experimentally investigated the deposition behavior of CsOH on CaCO , which is the primary phase existing on the surface of concrete, under humid atmosphere. As a result, the chemical reaction enhanced deposition rate (N), and increased linearly with CsOH concentration (C
, which is the primary phase existing on the surface of concrete, under humid atmosphere. As a result, the chemical reaction enhanced deposition rate (N), and increased linearly with CsOH concentration (C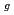 ), as following expression: N(
), as following expression: N( g/cm
g/cm
 s) = v
s) = v C
C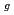 , where v
, where v is temperature-dependent deposition velocity as given by ln v
is temperature-dependent deposition velocity as given by ln v (cm/s) = -3785.8/T + 3.766, for T in the range of 170 and 290
(cm/s) = -3785.8/T + 3.766, for T in the range of 170 and 290  C. This empirical model can be integrated into severe accident codes to quantify the chemical trapping of cesium on concrete surfaces during ex-vessel release. Moreover, it can contribute to understanding the reasons behind the high dose rate on concrete shield plugs at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear power stations and aid in developing effective decommissioning practices for concrete structures.
C. This empirical model can be integrated into severe accident codes to quantify the chemical trapping of cesium on concrete surfaces during ex-vessel release. Moreover, it can contribute to understanding the reasons behind the high dose rate on concrete shield plugs at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear power stations and aid in developing effective decommissioning practices for concrete structures.
永塚 健太郎; 野口 弘喜; 長住 達; 野本 恭信; 清水 厚志; 佐藤 博之; 西原 哲夫; 坂場 成昭
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 425, p.113338_1 - 113338_11, 2024/08
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:91.70(Nuclear Science & Technology)高温ガス炉は固有の安全性を有し、二酸化炭素を排出することなく大量の水素や高温の熱供給が可能なことから、産業分野の脱炭素化に貢献できる。本報では、原子力機構で進めるHTTR(高温工学試験研究炉)を利用した炉心強制冷却喪失(LOFC)試験等の研究開発成果に加え、現在設計を進めるHTTRを用いた水素製造実証試験(HTTR-熱利用試験)の計画を紹介する。加えて、2030年代後半の運転開始に向け、基本設計が進められている高温ガス炉実証炉計画を紹介する。
Johnson, M.*; 江村 優軌; Clavier, R.*; 松場 賢一; 神山 健司; Brayer, C.*; Journeau, C.*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 423, p.113165_1 - 113165_14, 2024/07
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:75.80(Nuclear Science & Technology)日本原子力研究開発機構のMELT施設において、ナトリウム冷却高速炉のシビアアクシデントに関連する溶融ジェットとナトリウムの相互作用に関する実験的研究を行っている。X線イメージングと固化物の分析により、溶融ジェットと冷却材の接触界面でクラストが急速に形成され、熱的な微粒化現象が誘発されることを明らかにした。溶融ジェットと冷却材の接触界面における熱伝達計算の結果は、冷却材との接触から数ミリ秒以内に固体クラストが形成されることを示唆している。X線イメージングを用いたジェットへの冷却材巻き込みの観察結果に基づき、熱的な微粒化が促進されるメカニズムを提案する。
 compounds
compoundsFrazer, D.*; Saleh, T. A.*; 松本 卓; 廣岡 瞬; 加藤 正人; McClellan, K.*; White, J. T.*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 423, p.113136_1 - 113136_7, 2024/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)ナノインデンテーション法では、微小な試験片を用いてヤング率,硬度及びクリープ強度といった機械物性を評価することが可能である。本研究ではMOX燃料の代替物質として(U,Ce)O を用いて、高温ナノインデンテーション試験を実施した。試料のCe含有率は0.1、0.2及び0.3mol%とし、温度は800
を用いて、高温ナノインデンテーション試験を実施した。試料のCe含有率は0.1、0.2及び0.3mol%とし、温度は800 Cまでの測定を行い、ヤング率、硬度及びクリープ強度の評価を行った。温度の上昇に伴い、ヤング率は線形的に低下し、硬度は指数関数的に低下する結果が得られた。また、800
Cまでの測定を行い、ヤング率、硬度及びクリープ強度の評価を行った。温度の上昇に伴い、ヤング率は線形的に低下し、硬度は指数関数的に低下する結果が得られた。また、800 Cにおいては、応力指数n=4.7
Cにおいては、応力指数n=4.7 6.9のクリープ変形が得られた。
6.9のクリープ変形が得られた。
佐藤 一憲; 吉川 信治; 山下 拓哉; 下村 健太; Cibula, M.*; 溝上 伸也*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 422, p.113088_1 - 113088_24, 2024/06
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The accident progression of the in-vessel phase of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station Unit 1 was analyzed using the MAAP code. Although there is a large uncertainty in the initial stage of accident progression behavior in Unit 1 with little measurement data, it is presumed to have similarities to that of Unit 3. As a result, in Unit 1, since there was almost no alternative water injection during the in-vessel phase, cooling of the debris transferred to the lower plenum was small. It was likely that a large molten pool of metals had formed, and that the steam supply to the high-temperature core materials was suppressed and metal oxidation was relatively small. The analysis results for Unit 1 were compared with those for Units 2 and 3, and differences between units such as the thermal conditions of the debris that relocated to the pedestal and the degree of metal oxidation were shown.
Baccou, J.*; Glantz, T.*; Ghione, A.*; Sargentini, L.*; Fillion, P.*; Damblin, G.*; Sueur, R.*; Iooss, B.*; Fang, J.*; Liu, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 421, p.113035_1 - 113035_16, 2024/05
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:96.49(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Best-Estimate Plus Uncertainty (BEPU) framework, the use of best-estimate code requires to go through a Verification, Validation and Uncertainty Quantification process (VVUQ). The relevance of the experimental data in relation to the physical phenomena of interest in the VVUQ process is crucial. Adequacy analysis of selected experimental databases addresses this problem. The outcomes of the analysis can be used to select a subset of relevant experimental data, to encourage designing new experiments or to drop some experiments from a database because of their substantial lack of adequacy. The development of a specific transparent and reproducible approach to analyze the relevance of experimental data for VVUQ still remains open and is the topic of this contribution. In this paper, the concept of adequacy initially introduced in the OECD/NEA SAPIUM (Systematic APproach for model Input Uncertainty quantification Methodology) activity is formalized. It is defined through two key properties, called representativeness and completeness, that allows considering the multifactorial dimension of the adequacy problem. A new systematic approach is then proposed to analyze the adequacy of a set of experimental databases. It relies on the introduction of two sets of criteria to characterize representativeness and completeness and on the use of multi-criteria decision analysis method to perform the analysis. Finally, the approach is applied in the framework of the new OECD/NEA ATRIUM activity which includes a set of practical IUQ exercises in thermal-hydraulics to test the SAPIUM guideline in determining input uncertainties and forward propagating them on an application case. It allows evaluating the adequacy of eight experimental databases coming from the Super Moby-dick, Sozzi-Sutherland and Marviken experiments and identifying the most adequate ones.
上出 英樹; 浅山 泰; 若井 隆純; 江連 俊樹; 内堀 昭寛; 久保 重信; 竹内 正行
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 421, p.113062_1 - 113062_10, 2024/05
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)本報告では、設計支援解析評価手法の開発を通じて、プラントライフサイクル、リスクインフォームドアプローチ、持続可能性を考慮した日本のナトリウム冷却高速炉開発の進捗について、ARKADIAライフサイクル評価・設計支援システム、シビアアクシデント、自然循環、ナトリウム化学反応を対象とする安全設計・評価、リスクインフォームドアプローチをベースとした新しい規格基準体系、燃料サイクル技術の開発にかかる成果をまとめた。
Ho, H. Q.; 石井 俊晃; 長住 達; 小野 正人; 島崎 洋祐; 石塚 悦男; 澤畑 洋明; 後藤 実; Simanullang, I. L.*; 藤本 望*; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 417, p.112795_1 - 112795_6, 2024/02
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:23.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)External sources of neutron provide stable and sufficient neutron for initial startup of a nuclear reactor. They also provide signals for neutron detectors to monitor the safety of reactor during shutdown. In the high temperature engineering test reactor,  Cf is used as the external neutron source. However, the
Cf is used as the external neutron source. However, the  Cf sources must be renewed every approximately 7 years because of its relatively short half-life of 2.6 years. The renewal of
Cf sources must be renewed every approximately 7 years because of its relatively short half-life of 2.6 years. The renewal of  Cf sources requires a high cost and a very complicated procedure. This study investigated the feasibility of using BeO rods as the secondary neutron sources to avoid renewing the
Cf sources requires a high cost and a very complicated procedure. This study investigated the feasibility of using BeO rods as the secondary neutron sources to avoid renewing the  Cf neutron sources periodically. The BeO rods could exist in the reactor for a long time so that if the reactor operates long enough, the neutron flux at the wide-range monitoring detectors remains significant even if the reactor is shutdown for as long as 5 years. The results of this study indicated that using BeO rods as the secondary neutron sources would be an attractive option for the future HTGR design with a long-life fuel cycle.
Cf neutron sources periodically. The BeO rods could exist in the reactor for a long time so that if the reactor operates long enough, the neutron flux at the wide-range monitoring detectors remains significant even if the reactor is shutdown for as long as 5 years. The results of this study indicated that using BeO rods as the secondary neutron sources would be an attractive option for the future HTGR design with a long-life fuel cycle.
相馬 秀; 石垣 将宏*; 安部 諭; 柴本 泰照
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 416, p.112754_1 - 112754_18, 2024/01
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:23.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)The wall function (WF) enables analyzing condensation flow in a nuclear reactor containment vessel with reasonable computational costs. However, conventional wall treatments rely on the logarithmic laws for velocity, temperature, and concentration, limiting applicability. In this paper, we applied the analytical wall function approach to the condensation flow analysis of steam/air mixtures. This approach features the analytical integration of transport equations considering the buoyancy, the material property change, and the convective terms. We conducted CFD analysis with the analytical wall function models for the forced, mixed, and natural convection and confirmed good prediction, especially when the log law does not hold.
佐藤 一憲; 吉川 信治; 山下 拓哉; 下村 健太; Cibula, M.*; 溝上 伸也*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 414, p.112574_1 - 112574_20, 2023/12
Based on the updated knowledge from plant-internal investigations, experiments and computer-model simulations until now, the in-vessel phase of Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Station Unit 3 was analyzed using the MAAP code. In Unit 3, it is considered that ca. 40 percent of UO fuel was molten when core materials relocated to the lower plenum of the reactor pressure vessel. Initially relocated molten materials would have been fragmented by mixing with liquid water, while solid materials would have relocated later on. With this two-step relocation, debris in the lower plenum seems to have been permeable for coolant, thus debris seems to have been once cooled down effectively. Although the present MAAP analysis seems to slightly underestimate core-material oxidation during the relocation period, this probable underestimation was compensated for by an existing study that was considered more reliable, so that more realistic debris conditions in the lower plenum could be obtained. Probable debris reheat-up behavior was evaluated based on interpretation of the pressure data. This evaluation predicted that the fuel debris in the lower plenum was basically in solid-phase at the time when it relocated to the pedestal. With this study, basic validity of the former prediction of the Unit 3 accident progression behavior was confirmed, and detailed boundary conditions for future studies addressing the later phases were provided.
fuel was molten when core materials relocated to the lower plenum of the reactor pressure vessel. Initially relocated molten materials would have been fragmented by mixing with liquid water, while solid materials would have relocated later on. With this two-step relocation, debris in the lower plenum seems to have been permeable for coolant, thus debris seems to have been once cooled down effectively. Although the present MAAP analysis seems to slightly underestimate core-material oxidation during the relocation period, this probable underestimation was compensated for by an existing study that was considered more reliable, so that more realistic debris conditions in the lower plenum could be obtained. Probable debris reheat-up behavior was evaluated based on interpretation of the pressure data. This evaluation predicted that the fuel debris in the lower plenum was basically in solid-phase at the time when it relocated to the pedestal. With this study, basic validity of the former prediction of the Unit 3 accident progression behavior was confirmed, and detailed boundary conditions for future studies addressing the later phases were provided.
Pshenichnikov, A.; 永江 勇二
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 415, p.112729_1 - 112729_16, 2023/12
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The paper presents the results of a CLADS-MADE-03 BWR mock-up assembly degradation in high-temperature steam under a transient heating rate of 1 K/s, which are the assumed accident conditions for the beginning of the accident at the Unit 1 of the Fukushima Dai-Ichi Nuclear Power Station. In situ video investigations of the control blade provided visual evidences for the features of the control blade melt relocation. Based on the results, factors like an increase in the amount of core liquefied materials due to change of the melt composition, subsequent change in melt relocation features because of liquid/solid material ratio within the melt and B release and transport by aerosol formation were specially emphasized.
内堀 昭寛; 堂田 哲広; 青柳 光裕; 曽根原 正晃; 曽我部 丞司; 岡野 靖; 高田 孝*; 田中 正暁; 江沼 康弘; 若井 隆純; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 413, p.112492_1 - 112492_10, 2023/11
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:43.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)ナトリウム冷却高速炉に代表される革新炉に対し、安全性評価やそれに基づく設計最適化を自動で行うARKADIAを開発している。通常運転もしくは設計基準事象の範囲で設計最適化を行うARKADIA-Designについては、核特性-熱流動-炉心変形のマルチレベル連成解析手法等を中心技術として開発し、その基本的機能を確認した。シビアアクシデントまで含む範囲で安全性評価を行うARKADIA-Safetyの基盤技術として、炉内/炉外事象一貫解析手法の整備を進め、仮想的なシビアアクシデント事象を解析することで基本的機能を確認した。また、炉外事象に対する解析モデルの高度化、設計最適解の探索工程を合理化するAI技術の開発に着手した。