Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
松下 太樹*; 小沢 耀弘*; 荒木 康史; 藤本 純治*; 佐藤 昌利*
Physical Review B, 111(24), p.245131_1 - 245131_11, 2025/06
We investigate the intrinsic spin Nernst effect (SNE), a transverse spin current induced by temperature gradients, in topological Dirac semimetals (TDSMs) and magnetic Weyl semimetals (MWSMs) with Ising spin-orbit coupling. The intrinsic SNE is described by the spin Berry curvature, which reflects the geometric nature of TDSMs and MWSMs. We clarified that the intrinsic SNE becomes significant when the Fermi energy is near, but slightly deviates from, the energy of the point nodes. In this situation, Bloch electrons with strong spin Berry curvature contribute to the SNE while avoiding carrier compensation between electrons and holes. We found that in TDSMs with small Fermi surfaces, the spin Nernst angle, which measures the efficiency of the SNE, is larger than that observed in heavy metals. This suggests that TDSMs with small Fermi surfaces can achieve efficient heat-to-spin current conversion. In MWSMs, variation in the magnitude of the exchange coupling with magnetic moments significantly changes the SNE, affecting both the direction and magnitude of the spin Nernst current. This implies that ferromagnetic transitions can be used to reverse the spin Nernst current. These results provide the fundamentals for future topological spin caloritronics.
町田 晃彦*; 齋藤 寛之*; 青木 勝敏*; 小松 一生*; 服部 高典; 佐野 亜沙美; 舟越 賢一*; 町田 真一*; 佐藤 豊人*; 折茂 慎一*
Physical Review B, 111(22), p.224413_1 - 224413_6, 2025/06
Mn金属を高温高圧で水素化することにより形成される反強磁性Mn重水素化物、fcc -MnDxとhcp
-MnDxとhcp -MnDxの結晶構造と磁気構造をin-situ中性子粉末回折により調べた。重水素原子はfcc及びhcp金属格子の八面体格子間を部分的に占有していた。N
-MnDxの結晶構造と磁気構造をin-situ中性子粉末回折により調べた。重水素原子はfcc及びhcp金属格子の八面体格子間を部分的に占有していた。N el温度は
el温度は -MnD
-MnD で543(10)Kであった。
で543(10)Kであった。 -MnD
-MnD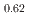 では、飽和磁気モーメントは0.82(1)
では、飽和磁気モーメントは0.82(1)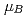 、N
、N el温度は347(3)Kであった。
el温度は347(3)Kであった。 -MnD
-MnD と
と -MnD
-MnD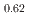 について決定されたN
について決定されたN el温度は、以前の研究で提案されたそれぞれのSlater-Pauling曲線によって予測されたものと一致した。更新されたN
el温度は、以前の研究で提案されたそれぞれのSlater-Pauling曲線によって予測されたものと一致した。更新されたN el温度は、電子バンド構造計算に基づくより正確なSlater-Pauling曲線の開発に示唆を与える。
el温度は、電子バンド構造計算に基づくより正確なSlater-Pauling曲線の開発に示唆を与える。
 Co
Co )Sn studied by
)Sn studied by  SR
SRCai, Y.*; Yoon, S.*; Sheng, Q.*; Zhao, G.*; Seewald, E. F.*; Ghosh, S.*; Ingham, J.*; Pasupathy, A. N.*; Queiroz, R.*; Lei, H.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 111(21), p.214412_1 - 214412_17, 2025/06
We study the magnetic properties of the metallic kagome system (Fe Co
Co )Sn by a combination of muon spin relaxation (
)Sn by a combination of muon spin relaxation ( SR), magnetic susceptibility, and scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) measurements in single crystal specimens with Co concentrations
SR), magnetic susceptibility, and scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) measurements in single crystal specimens with Co concentrations  = 0, 0.11, 0.8. In the undoped antiferromagnetic compound FeSn, we find possible signatures for a previously unidentified phase that sets in at
= 0, 0.11, 0.8. In the undoped antiferromagnetic compound FeSn, we find possible signatures for a previously unidentified phase that sets in at 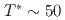 ~K, well beneath the Neel temperature
~K, well beneath the Neel temperature 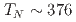 ~K as indicated by a peak in the relaxation rate 1/
~K as indicated by a peak in the relaxation rate 1/ observed in zero field (ZF) and longitudinal field (LF)
observed in zero field (ZF) and longitudinal field (LF)  SR measurements, with a corresponding anomaly in the ac and dc susceptibility, and an increase in the static width 1/
SR measurements, with a corresponding anomaly in the ac and dc susceptibility, and an increase in the static width 1/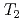 in ZF-
in ZF- SR measurements. No signatures of spatial symmetry breaking are found in STM down to 7~K. Related to the location and motion of muons in FeSn, we confirmed a previous report that about 40% of the implanted muons reside at a field-cancelling high symmetry site at
SR measurements. No signatures of spatial symmetry breaking are found in STM down to 7~K. Related to the location and motion of muons in FeSn, we confirmed a previous report that about 40% of the implanted muons reside at a field-cancelling high symmetry site at 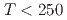 ~K, while an onset of thermal hopping changes the site occupancy at higher temperatures. In Fe
~K, while an onset of thermal hopping changes the site occupancy at higher temperatures. In Fe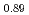 Co
Co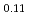 Sn, where disorder eliminated the field-cancellation effect, all the implanted muons exhibit precession and/or relaxation in the ordered state. In Fe
Sn, where disorder eliminated the field-cancellation effect, all the implanted muons exhibit precession and/or relaxation in the ordered state. In Fe Co
Co Sn, we find canonical spin glass behavior with freezing temperature
Sn, we find canonical spin glass behavior with freezing temperature 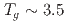 ~K; the ZF and LF-
~K; the ZF and LF- SR time spectra exhibit results similar to those observed in dilute alloy spin glasses CuMn and AuFe, with a critical behavior of
SR time spectra exhibit results similar to those observed in dilute alloy spin glasses CuMn and AuFe, with a critical behavior of  at
at 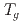 and
and 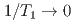 as
as 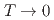 . The absence of spin dynamics at low temperatures makes a clear contrast to the spin dynamics observed by
. The absence of spin dynamics at low temperatures makes a clear contrast to the spin dynamics observed by  SR in many geometrically frustrated spin systems on insulating kagome, pyrochlore, and triangular lattices. The spin glass behavior of CoSn doped with dilute Fe moments is shown to originate primarily from the randomness of doped Fe moments rather than due to geometrical frustration of the underlying lattice.
SR in many geometrically frustrated spin systems on insulating kagome, pyrochlore, and triangular lattices. The spin glass behavior of CoSn doped with dilute Fe moments is shown to originate primarily from the randomness of doped Fe moments rather than due to geometrical frustration of the underlying lattice.
 phases in undoped and Ca-modified sodium niobates
phases in undoped and Ca-modified sodium niobates阿蘇 星侑*; 松尾 拓紀*; 米田 安宏; 森川 大輔*; 津田 健治*; 大山 研司*; 石垣 徹*; 野口 祐二*
Physical Review B, 111(17), p.174114_1 - 174114_12, 2025/05
高分解能放射光X線・中性子回折、収束電子線回折、密度汎関数理論(DFT)計算を組合せた解析により、Ca修飾NaNbO と非ドープNaNbO
と非ドープNaNbO の結晶構造、phase転移、相安定性を調べた。その結果、Ca修飾によって反強誘電体(AFE)-
の結晶構造、phase転移、相安定性を調べた。その結果、Ca修飾によって反強誘電体(AFE)- 相が200Kから800Kの広い温度範囲で安定化されること、NaNbO
相が200Kから800Kの広い温度範囲で安定化されること、NaNbO は格子膨張を伴う温度誘起等方圧によって安定化されるのに対し、Ca修飾NaNbO
は格子膨張を伴う温度誘起等方圧によって安定化されるのに対し、Ca修飾NaNbO は格子収縮を伴う組成誘起化学圧力によって安定化されることが示された。
は格子収縮を伴う組成誘起化学圧力によって安定化されることが示された。
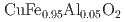
玉造 博夢; 内原 猛*; 満田 節生*; 石井 祐太*; 中尾 裕則*; 竹端 寛治*; 今中 康貴*
Physical Review B, 111(13), p.134403_1 - 134403_9, 2025/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In multiferroic CuFe Al
Al O
O , applying uniaxial pressure
, applying uniaxial pressure  generates a magnetoferroelectric phase distinct from the well-studied spin-driven ferroelectric phase associated with helical magnetic ordering in this system. Using a four-circle neutron diffractometer, the magnetic structure of the
generates a magnetoferroelectric phase distinct from the well-studied spin-driven ferroelectric phase associated with helical magnetic ordering in this system. Using a four-circle neutron diffractometer, the magnetic structure of the  -induced magnetoferroelectric phase is determined as the collinear sinusoidal type, which itself does not break the inversion symmetry in this system. Additionally, synchrotron radiation X-ray diffraction experiments are conducted to investigate how the triangular lattice in CuFe
-induced magnetoferroelectric phase is determined as the collinear sinusoidal type, which itself does not break the inversion symmetry in this system. Additionally, synchrotron radiation X-ray diffraction experiments are conducted to investigate how the triangular lattice in CuFe Al
Al O
O is distorted by applied
is distorted by applied  . Although lattice distortion during the magnetic phase transition in CuFe
. Although lattice distortion during the magnetic phase transition in CuFe Al
Al O
O is mitigated by the substitution of nonmagnetic Al
is mitigated by the substitution of nonmagnetic Al , the application of
, the application of  along the conjugate direction revives the "latent" spin-lattice coupling, causing the triangular lattice to distort during magnetic phase transition. The application of a magnetic filed considerably reduces
along the conjugate direction revives the "latent" spin-lattice coupling, causing the triangular lattice to distort during magnetic phase transition. The application of a magnetic filed considerably reduces  -induced ferroelectric polarization, but does not affect lattice distortion. These results indicate that
-induced ferroelectric polarization, but does not affect lattice distortion. These results indicate that  -induced ferroelectric polarization is not a consequence of the piezoelectric effect. Instead, the sinusoidal magnetic structure would contribute to the emergence of
-induced ferroelectric polarization is not a consequence of the piezoelectric effect. Instead, the sinusoidal magnetic structure would contribute to the emergence of  -induced ferroelectric polarization through spin-lattice coupling.
-induced ferroelectric polarization through spin-lattice coupling.
 under hydrostatic pressure; A Combined neutron, X-ray, Raman, and first-principles calculation study
under hydrostatic pressure; A Combined neutron, X-ray, Raman, and first-principles calculation studyEfthimiopoulos, I.*; Klotz, S.*; Kunc, K.*; Baptiste, B.*; Chauvigne, P.*; 服部 高典
Physical Review B, 111(13), p.134103_1 - 134103_13, 2025/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)X線回折、中性子回折、ラマン散乱、第一原理計算を用いて、ReO の高圧力下での挙動を15GPaまで包括的に調べた。常圧
の高圧力下での挙動を15GPaまで包括的に調べた。常圧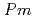 =3
=3 構造は0.7GPaで空間群
構造は0.7GPaで空間群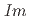 =3の立方晶相に連続的に相転移し、その後少なくとも15GPaまで安定であることがわかった。過去この圧力領域で報告されていた単斜晶
=3の立方晶相に連続的に相転移し、その後少なくとも15GPaまで安定であることがわかった。過去この圧力領域で報告されていた単斜晶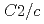 構造や菱面体晶
構造や菱面体晶 =3
=3 構造への転移は、試料に高輝度放射光X線を照射したことによる試料の劣化によるものであり、人工的なものであることが分かった。また今回、
構造への転移は、試料に高輝度放射光X線を照射したことによる試料の劣化によるものであり、人工的なものであることが分かった。また今回、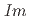 =3相の構造の圧力依存性と正確な状態方程式および天然試料と同位体濃縮
=3相の構造の圧力依存性と正確な状態方程式および天然試料と同位体濃縮 O試料のラマン散乱データを示した。このデータから、リジッドなReO
O試料のラマン散乱データを示した。このデータから、リジッドなReO 八面体が圧力とともに回転することによって、相転移および高密度化が起こることが分かった。
八面体が圧力とともに回転することによって、相転移および高密度化が起こることが分かった。
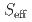 =
=  antiferromagnetic tetramer compound Yb
antiferromagnetic tetramer compound Yb SiO
SiO
長谷 正司*; 金子 耕士; 田端 千紘; 山内 宏樹; 辻井 直人*; D nni, A.*
nni, A.*
Physical Review B, 111(9), p.094403_1 - 094403_9, 2025/03
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We studied magnetic properties of Yb SiO
SiO having pseudospins of
having pseudospins of 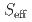 =
=  using magnetization, specific heat, and inelastic neutron scattering (INS) measurements. We observed cluster-like excitations in the INS measurements. We determined that the spin system in Yb
using magnetization, specific heat, and inelastic neutron scattering (INS) measurements. We observed cluster-like excitations in the INS measurements. We determined that the spin system in Yb SiO
SiO is the
is the 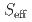 =
=  AFM tetramer with two exchange interactions of
AFM tetramer with two exchange interactions of 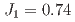 and
and 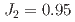 ~meV. The spin tetramer can explain the excitation energies,
~meV. The spin tetramer can explain the excitation energies, 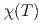 , magnetic specific heat at
, magnetic specific heat at 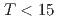 ~K, and the magnitude of the scattering vector (
~K, and the magnitude of the scattering vector ( ) dependence of the intensity [
) dependence of the intensity [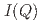 ] at 0.7 and 1.2 meV. The spin tetramer, however, cannot explain well
] at 0.7 and 1.2 meV. The spin tetramer, however, cannot explain well 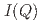 at 1.9 meV and
at 1.9 meV and 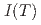 of the three excitations probably due to effects of weak inter-tetramer interactions.
of the three excitations probably due to effects of weak inter-tetramer interactions.
 with geometrically frustrated orthogonal antiferromagnetic dimer
with geometrically frustrated orthogonal antiferromagnetic dimer目時 直人; 山内 宏樹; 萩原 雅人; 綿貫 竜太*; 河村 聖子; 古府 麻衣子*; 中島 健次; 松田 雅昌*
Physical Review B, 111(10), p.104424_1 - 104424_9, 2025/03
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)フラストレートしたシャストリ・サザランド格子を有するNdB の磁気転移を理解する目的で中性子非弾性散乱実験を行った。
の磁気転移を理解する目的で中性子非弾性散乱実験を行った。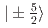 と
と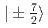 による準四重項状態が磁気秩序相で4つに分裂する。スペクトルは磁気相互作用
による準四重項状態が磁気秩序相で4つに分裂する。スペクトルは磁気相互作用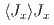 、磁気
、磁気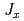 と四極子
と四極子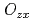 の結合、そして一軸的な結晶場により説明される。この
の結合、そして一軸的な結晶場により説明される。この 電子状態により、主たる秩序変数である面内磁気モーメント
電子状態により、主たる秩序変数である面内磁気モーメント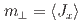 と結く誘起された2次的な秩序変数
と結く誘起された2次的な秩序変数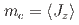 を説明することができた。幾何学的フラストレーションによってハイゼンベルグ相互作用が打ち消し合う状況で、磁気と四極子の結合が本質的な役割をすることが明らかになった。
を説明することができた。幾何学的フラストレーションによってハイゼンベルグ相互作用が打ち消し合う状況で、磁気と四極子の結合が本質的な役割をすることが明らかになった。
 Sb
Sb with a honeycomb network
with a honeycomb network足立 匡*; Ogawa, Taiki*; 小宮山 陽太*; 須村 拓也*; Saito-Tsuboi, Yuki*; Takeuchi, Takaaki*; Mano, Kohei*; Manabe, Kaoru*; 川端 幸樹*; 今津 毅士*; et al.
Physical Review B, 111(10), p.L100508_1 - L100508_6, 2025/03
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Chiral superconductivity exhibits the formation of novel electron pairs that breaks the time-reversal symmetry and has been actively studied in various quantum materials in recent years. However, despite its potential to provide definitive information, effects of disorder in the crystal structure on the chiral superconductivity has not yet been clarified, and therefore the investigation using a solid-solution system is desirable. We report muon-spin-relaxation ( SR) results of layered pnictide BaPtAs
SR) results of layered pnictide BaPtAs Sb
Sb with a honeycomb network composed of Pt and (As, Sb). We observed an increase of the zero-field
with a honeycomb network composed of Pt and (As, Sb). We observed an increase of the zero-field  SR rate in the superconducting (SC) state at the Sb end of
SR rate in the superconducting (SC) state at the Sb end of 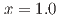 , suggesting the occurrence of a spontaneous magnetic field due to the time-reversal symmetry breaking in the SC state. On the other hand, a spontaneous magnetic field was almost and completely suppressed for the As-Sb mixed samples of
, suggesting the occurrence of a spontaneous magnetic field due to the time-reversal symmetry breaking in the SC state. On the other hand, a spontaneous magnetic field was almost and completely suppressed for the As-Sb mixed samples of 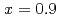 and 0.2, respectively, suggesting that the time-reversal symmetry-breaking SC state in
and 0.2, respectively, suggesting that the time-reversal symmetry-breaking SC state in 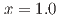 is sensitive to disorder. The magnetic penetration depth estimated from transverse-field
is sensitive to disorder. The magnetic penetration depth estimated from transverse-field  SR measurements at
SR measurements at 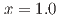 and 0.2 behaved like weak-coupling
and 0.2 behaved like weak-coupling  -wave superconductivity. These seemingly incompatible zero-field and transverse-field
-wave superconductivity. These seemingly incompatible zero-field and transverse-field  SR results of BaPtAs
SR results of BaPtAs Sb
Sb with
with 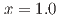 could be understood in terms of chiral
could be understood in terms of chiral  -wave superconductivity with point nodes on the three-dimensional Fermi surface.
-wave superconductivity with point nodes on the three-dimensional Fermi surface.
 with
with  = 2.1 K revealed by
= 2.1 K revealed by  Te NMR
Te NMR松村 拓輝*; 徳永 陽; 酒井 宏典; 神戸 振作; 他13名*
Physical Review B, 111(9), p.094507_1 - 094507_9, 2025/03
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To investigate the intrinsic magnetic properties of UTe , we performed
, we performed  Te-NMR measurements on the ultra-clean single-crystalline UTe
Te-NMR measurements on the ultra-clean single-crystalline UTe with superconducting transition temperature
with superconducting transition temperature  = 2.1 K and compared the results with those of the
= 2.1 K and compared the results with those of the  = 1.6 K sample. The broadening of the linewidth of the NMR spectrum in the a-axis magnetic field and the low-temperature magnetic fluctuations observed in the 1.6 K sample are suppressed in the ultra-clean sample, indicating that such magnetic properties originate from a tiny amount of U deficiency. The present results suggest that the magnetic properties in UTe
= 1.6 K sample. The broadening of the linewidth of the NMR spectrum in the a-axis magnetic field and the low-temperature magnetic fluctuations observed in the 1.6 K sample are suppressed in the ultra-clean sample, indicating that such magnetic properties originate from a tiny amount of U deficiency. The present results suggest that the magnetic properties in UTe are sensitive to the U deficiency. We also observed a peculiar angular dependence of the NMR quantities due to large magnetic anisotropy with the a-axis as the magnetic easy axis.
are sensitive to the U deficiency. We also observed a peculiar angular dependence of the NMR quantities due to large magnetic anisotropy with the a-axis as the magnetic easy axis.
 Fe
Fe O
O
Ba, Y.*; 山本 慧; 他6名*
Physical Review B, 111(10), p.104401_1 - 104401_15, 2025/03
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Ferrimagnet insulator yttrium iron garnet (Y Fe
Fe O
O , YIG) attracts much interest in magnonics and microwave applications due to its relatively low magnetic damping and long magnon relaxation time. The magnetoelastic interaction between YIG magnetization and surface acoustic waves (SAWs) has been the basis in the development of acoustic-surface-wave isolators. However, the investigation of SAW-driven magnetic resonance in YIG is limited by the low compatibility of YIG and SAW devices. In this work, we demonstrate nonreciprocal resonant SAW absorption in an on-chip YIG-SAW device integrated by the focused ion beam technique. We observed two distinct SAW absorption signals attributed to the perpendicular standing spin waves (PSSW). Furthermore, the large observed nonreciprocity is compared to theoretical predictions incorporating the influence of asymmetric surface conditions on PSSW mode profiles and nonreciprocal magnon-SAW coupling. The strongly nonreciprocal SAW attenuation in YIG offers a promising opportunity for highly efficient rf signal processing technologies.
, YIG) attracts much interest in magnonics and microwave applications due to its relatively low magnetic damping and long magnon relaxation time. The magnetoelastic interaction between YIG magnetization and surface acoustic waves (SAWs) has been the basis in the development of acoustic-surface-wave isolators. However, the investigation of SAW-driven magnetic resonance in YIG is limited by the low compatibility of YIG and SAW devices. In this work, we demonstrate nonreciprocal resonant SAW absorption in an on-chip YIG-SAW device integrated by the focused ion beam technique. We observed two distinct SAW absorption signals attributed to the perpendicular standing spin waves (PSSW). Furthermore, the large observed nonreciprocity is compared to theoretical predictions incorporating the influence of asymmetric surface conditions on PSSW mode profiles and nonreciprocal magnon-SAW coupling. The strongly nonreciprocal SAW attenuation in YIG offers a promising opportunity for highly efficient rf signal processing technologies.

Jin, H.*; Choi, E. S.*; Wu, H.-C.*; Curro, N. J.*; 那波 和宏*; 佐藤 卓*; 鬼柳 亮嗣; 大原 高志; Klavins, P.*; Taufour, V.*
Physical Review B, 111(3), p.035103_1 - 035103_7, 2025/01
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We report on neutron diffraction, magnetoresistance, magnetization and magnetic torque measurements under high magnetic field in the helical antiferromagnet CeVGe . This compound exhibits Kondo lattice coherence and helical antiferromagnetic (AFM) ordering at ambient pressure, similar to the well-studied CeRhIn
. This compound exhibits Kondo lattice coherence and helical antiferromagnetic (AFM) ordering at ambient pressure, similar to the well-studied CeRhIn . Our measurements reveal that CeVGe
. Our measurements reveal that CeVGe undergoes a magnetic transition from an incommensurate (ICM) AFM state to an up-up-down-down commensurate (CM) AFM structure, followed by a transition to a novel phase at higher fields. A quantum phase transition occurs around 21.3 T. This rich magnetic field phase diagram closely resembles that of CeRhIn
undergoes a magnetic transition from an incommensurate (ICM) AFM state to an up-up-down-down commensurate (CM) AFM structure, followed by a transition to a novel phase at higher fields. A quantum phase transition occurs around 21.3 T. This rich magnetic field phase diagram closely resembles that of CeRhIn . Furthermore, angle-dependent magnetoresistance measurements reveal that all transitions in CeVGe
. Furthermore, angle-dependent magnetoresistance measurements reveal that all transitions in CeVGe occur from the field component along the ab plane. These findings highlight the intricate interplay among exchange interactions, crystal field effects, ground state properties, and crystalline symmetries.
occur from the field component along the ab plane. These findings highlight the intricate interplay among exchange interactions, crystal field effects, ground state properties, and crystalline symmetries.
 Fe
Fe O
O
森 道康; Tomasello, B.*; Ziman, T.*
Physical Review B, 111(1), p.014407_1 - 014407_12, 2025/01
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The spin Seebeck effect (SSE) is a phenomenon of thermoelectric generation that occurs within a device consisting of a bilayer of a metal and a ferromagnet. When Tb Fe
Fe O
O (TbIG) is substituted for the ferromagnet, the effect goes to zero at low temperatures, yet it increases to positive values with the application of a magnetic field. This is opposite to the expectation that the SSE should be suppressed by a magnetic field due to the increase in
(TbIG) is substituted for the ferromagnet, the effect goes to zero at low temperatures, yet it increases to positive values with the application of a magnetic field. This is opposite to the expectation that the SSE should be suppressed by a magnetic field due to the increase in  magnon gap. In this paper, the crystal-field excitations (CFE) in TbIG are calculated within a mean field theory exploiting the parameters of Terbium Gallium Garnet Tb
magnon gap. In this paper, the crystal-field excitations (CFE) in TbIG are calculated within a mean field theory exploiting the parameters of Terbium Gallium Garnet Tb Fe
Fe O
O (TGG) from the neutron-scattering experimental literature. Like TGG, the primitive cell of TbIG hosts twelve Tb sites with six inequivalent magnetic sublattices, but due to the net
(TGG) from the neutron-scattering experimental literature. Like TGG, the primitive cell of TbIG hosts twelve Tb sites with six inequivalent magnetic sublattices, but due to the net ![$$[111]$$](/search/images/ERNTCMJRLUSA.gif) -molecular field from the tetrahedral and octahedral Fe ions, these can be classified into two distinct groups, the
-molecular field from the tetrahedral and octahedral Fe ions, these can be classified into two distinct groups, the 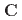 and the
and the 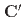 sites, which account for the "double umbrella" magnetic structure. We show that when an external magnetic field is applied along the [111] direction of the crystal, the lowest CFE of the
sites, which account for the "double umbrella" magnetic structure. We show that when an external magnetic field is applied along the [111] direction of the crystal, the lowest CFE of the 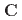 sublattices decreases. As a consequence of the magnetic field dependence of the lowest CFE, we find that at low temperatures the SSE in TbIG can result enhanced by an applied magnetic field.
sublattices decreases. As a consequence of the magnetic field dependence of the lowest CFE, we find that at low temperatures the SSE in TbIG can result enhanced by an applied magnetic field.
山根 結太*; 荒木 康史; 深見 俊輔*
Physical Review B, 111(14), p.144412_1 - 144412_9, 2025/00
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We study the Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction (DMI) appearing at the interface of a nonmagnetic/noncollinear-antiferromagnetic bilayer. The DMI is an antisymmetric exchange interaction between neighboring magnetic spins, arising in the absence of an inversion center between the spins, the explicit expression of which is dictated by system symmetry. We formulate the interfacial DMI for different crystalline orientations of the noncollinear antiferromagnet with a stacked-kagome lattice structure. From this formulation, we show that, when the kagome planes are perpendicular to the sample film plane, the DMI serves as a uniaxial magnetic anisotropy for the antiferromagnetic order parameter. Our findings reveal an important physical manifestation of a DMI, shedding light on microscopic mechanisms of the magnetic anisotropy in noncollinear antiferromagnets.
小手川 恒*; 中村 彰良*; Huyen, V. T. N.*; 新井 祐樹*; 藤 秀樹*; 菅原 仁*; 林 純一*; 武田 圭生*; 田端 千紘; 金子 耕士; et al.
Physical Review B, 110(21), p.214417_1 - 214417_8, 2024/12
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In this study, we show that the orthorhombic system TaMnP exhibits a large anomalous Hall conductivity (AHC) in spite of the small net magnetization. Neutron scattering experiment and the observation of the AH effect comprehensively suggest a dominant AF structure in TaMnP is represented by 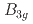 . The AHC is one of the largest among those observed in AF materials at zero fields. First-principles calculations suggest that the spin-orbit interaction originating in nonmagnetic Ta-5
. The AHC is one of the largest among those observed in AF materials at zero fields. First-principles calculations suggest that the spin-orbit interaction originating in nonmagnetic Ta-5 electrons significantly contributes to the enhancement of Berry curvatures in the momentum space. We found that the AF domain switching is triggered by the magnetic fields along all the crystal axes. This indicates that the AF domain determining the sign of the Hall response can be controlled even through the small net magnetization symmetrically different.
electrons significantly contributes to the enhancement of Berry curvatures in the momentum space. We found that the AF domain switching is triggered by the magnetic fields along all the crystal axes. This indicates that the AF domain determining the sign of the Hall response can be controlled even through the small net magnetization symmetrically different.
 SR study on the noncentrosymmetric superconductor NbGe
SR study on the noncentrosymmetric superconductor NbGe
Jiao, J. C.*; Chen, K. W.*; Hillier, A. D.*; 伊藤 孝; 髭本 亘; Li, Z.*; Lv, B.*; Xu, Z.-A.*; Shu, L.*
Physical Review B, 110(21), p.214516_1 - 214516_9, 2024/12
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We report on a muon spin relaxation ( SR) study on the polycrystalline noncentrosymmetric superconductor NbGe
SR) study on the polycrystalline noncentrosymmetric superconductor NbGe with superconducting transition temperature
with superconducting transition temperature  = 2.0-2.1 K. The zero-field
= 2.0-2.1 K. The zero-field  SR experiment indicates the absence of a spontaneous magnetic field in the superconducting state, showing the preservation of time-reversal symmetry in the superconducting state. The transverse-field
SR experiment indicates the absence of a spontaneous magnetic field in the superconducting state, showing the preservation of time-reversal symmetry in the superconducting state. The transverse-field  SR experiment is performed to map the phase diagram of NbGe
SR experiment is performed to map the phase diagram of NbGe , from which clear evidence of both type-I and type-II superconductivities is obtained. More importantly, we clearly delineate the region in the phase diagram where type-I and type-II superconductivities coexist.
, from which clear evidence of both type-I and type-II superconductivities is obtained. More importantly, we clearly delineate the region in the phase diagram where type-I and type-II superconductivities coexist.
藤澤 唯太*; Krishnadas, A*; Nakamura, Tomonori*; Hsu, C.-H.*; Smith, B. R. M.*; Pardo-Almanza, M*; Hiyane, Hoshu*; 永井 佑紀; 町田 理*; 岡田 佳憲*
Physical Review B, 110(22), p.224511_1 - 224511_5, 2024/12
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)エキゾチックな超伝導体の超伝導磁束の振る舞いを明らかにすることは、今後のデバイス開発にとって重要である。超伝導体LiTi O
O (111)の薄膜を作製し、磁場中での電子状態を走査型トンネル顕微鏡によって観測した。その際、接合部分の曲率に応じて超伝導磁束の状態が大きく変化することがわかった。そして、その変化は理論計算によっても確かめられた。この結果は、Josephson磁束を実験的な構造変化によってコントロールできる可能性を示唆しており、今後の新たなデバイス開発において重要な結果となるだろう。
(111)の薄膜を作製し、磁場中での電子状態を走査型トンネル顕微鏡によって観測した。その際、接合部分の曲率に応じて超伝導磁束の状態が大きく変化することがわかった。そして、その変化は理論計算によっても確かめられた。この結果は、Josephson磁束を実験的な構造変化によってコントロールできる可能性を示唆しており、今後の新たなデバイス開発において重要な結果となるだろう。
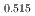 Gd
Gd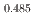 Mn
Mn O
O
石井 裕太*; 坂倉 輝俊*; 石川 喜久*; 鬼柳 亮嗣; Lustikova, J.*; 青山 拓也*; 大串 研也*; 若林 裕助*; 木村 宏之*; 野田 幸男*
Physical Review B, 110(18), p.184404_1 - 184404_7, 2024/11
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Neutron-scattering measurements were employed to investigate the magnetic ordering in Tb Gd
Gd Mn
Mn O
O (x = 0.485) enriched with the
(x = 0.485) enriched with the 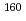 Gd isotope, a member of multiferroic RMn
Gd isotope, a member of multiferroic RMn O
O (R = rare-earth element) compounds. This material, at low temperatures, exhibits commensurate magnetic (CM) ordering, which drives electric polarization. Notably, electric polarization diminishes as the temperature decreases further, while the CM ordering persists. Magnetic structure analyses revealed that a cycloidal magnetic structure along the c axis transforms into a sinusoidal-like structure, resulting in the nonferroelectric phase, whereas a collinear magnetic structure in the ab plane exhibits no significant change. The findings suggest that the cycloidal magnetic structure plays a key role in inducing electric polarization in the CM ordering of the present material.
(R = rare-earth element) compounds. This material, at low temperatures, exhibits commensurate magnetic (CM) ordering, which drives electric polarization. Notably, electric polarization diminishes as the temperature decreases further, while the CM ordering persists. Magnetic structure analyses revealed that a cycloidal magnetic structure along the c axis transforms into a sinusoidal-like structure, resulting in the nonferroelectric phase, whereas a collinear magnetic structure in the ab plane exhibits no significant change. The findings suggest that the cycloidal magnetic structure plays a key role in inducing electric polarization in the CM ordering of the present material.
Chi, Z.*; 芝田 悟朗; 藤森 淳; 他15名*
Physical Review B, 110, p.184401_1 - 184401_8, 2024/11
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have studied the Co layer thickness dependences of magnetocrystalline anisotropy (MCA), Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction (DMI), and orbital moment anisotropy (OMA) in W/Co/Pt trilayers, in order to clarify their correlations with each other. We find that the MCA favors magnetization along the film normal and monotonically increases with decreasing effective magnetic layer thickness (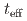 ). The magnitude of the Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya exchange constant (
). The magnitude of the Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya exchange constant (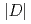 ) increases with decreasing
) increases with decreasing 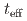 until
until 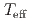
 1 nm, below which
1 nm, below which 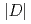 decreases. The MCA and
decreases. The MCA and 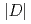 scale with 1/
scale with 1/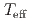 for
for 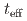 larger than
larger than 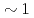 nm, indicating an interfacial origin. Using X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD), we find non-zero OMA when
nm, indicating an interfacial origin. Using X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD), we find non-zero OMA when 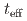 is smaller than
is smaller than 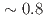 nm. The OMA increases with decreasing
nm. The OMA increases with decreasing 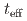 more rapidly than what is expected from the MCA, indicating that factors other than OMA contribute to the MCA at small
more rapidly than what is expected from the MCA, indicating that factors other than OMA contribute to the MCA at small 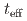 .
.
古谷 峻介*; 松尾 衛; 加藤 岳生*
Physical Review B, 110(16), p.165129_1 - 165129_13, 2024/10
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We theoretically investigate spin pumping into a quantum easy-plane ferromagnetic spin chain system. This quantum spin chain is effectively described by the Tomonaga-Luttinger (TL) liquid despite the ferromagnetic exchange interaction because of the easy-plane magnetic anisotropy. This TL liquid state has an extremely strong interaction that is hardly realized in other quantum antiferromagnetic chain systems or weakly interacting electron systems. We show how the strongly interacting TL liquid affects the ferromagnetic resonance that occurs in the ferromagnetic insulator. In particular, we discuss the dependence of the Gilbert damping on the temperature and the junction length. The Gilbert damping allows us to extract information about the above-mentioned strong interaction within the quantum ferromagnetic spin chain. We also point out that a well-known compound CsCuCl will be suitable for the realization of our setup.
will be suitable for the realization of our setup.