Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
塩谷 光平; 新山 友暁*; 下川 智嗣*
Materials Transactions, 66(6), p.704 - 711, 2025/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)ハイエントロピー合金(HEA)は、ほぼ等量ずつの5種類以上の元素により構成される多元系合金である。本論文では、HEAにおける粒界移動の分子動力学シミュレーションを実施し、HEAの各構成元素の濃度が粒界移動挙動に及ぼす影響を系統的に調査した。解析の結果、HEAの粒界移動に必要な駆動力は、粒界の移動が間欠的になるか、あるいは粒界移動速度が低下する条件において最大になることがわかった。また、最大の駆動力は粒界への元素の偏析度合いが最大になるときに達成された。さらに、粒界偏析の度合いはHEAの構成元素組成によってさまざまに制御可能であり、粒界偏析は粒界の移動に必要な駆動力や粒界移動速度といった粒界の移動挙動に強く影響を与えることがわかった。本研究は、HEAの元素組成が粒界移動挙動を決定する上で重要な役割を果たすことを示し、得られた結果は優れた機械的特性を有するHEAの設計に貢献するものである。
Fang, W.*; Liu, C.*; Zhang, J.*; 徐 平光; Peng, T.*; Liu, B.*; 諸岡 聡; Yin, F.*
Scripta Materialia, 249, p.116046_1 - 116046_6, 2024/08
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:57.76(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)The influence of interstitial carbon on the texture evolution of high-entropy alloys during cold rolling was investigated. To prevent carbide formation, elements with weak carbon affinity were carefully selected in the (FeMnCoNi)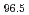 C
C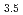 alloy. Neutron diffraction, electron channeling contrast imaging, and electron backscatter diffraction were used to analyze the texture and microstructure evolution in alloys with and without carbon addition. Though their texture components are similar at the early stage of deformation, the Brass and Goss textures in the carbon-containing alloy at 50% cold rolling reduction are obviously higher than those in the carbon-free alloy, while Copper and S textures are lower. A large number of deformation twins induced in the carbon containing alloy is attributed as the significant reason for the texture differences. This work helps to understand the impact of interstitial carbon on the texture evolution of high-entropy alloys, providing valuable insights for microstructure and performance optimization.
alloy. Neutron diffraction, electron channeling contrast imaging, and electron backscatter diffraction were used to analyze the texture and microstructure evolution in alloys with and without carbon addition. Though their texture components are similar at the early stage of deformation, the Brass and Goss textures in the carbon-containing alloy at 50% cold rolling reduction are obviously higher than those in the carbon-free alloy, while Copper and S textures are lower. A large number of deformation twins induced in the carbon containing alloy is attributed as the significant reason for the texture differences. This work helps to understand the impact of interstitial carbon on the texture evolution of high-entropy alloys, providing valuable insights for microstructure and performance optimization.
池田 陽一*; 梅本 好日古*; 松村 大樹; 辻 卓也; 橋本 勇輝*; 北澤 崇文*; 藤田 全基*
Materials Transactions, 64(9), p.2254 - 2260, 2023/09
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:44.33(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) and neutron diffraction experiments were carried out to clarify the typical features of the local structure of a family of medium-entropy alloys (CrCoNi, MnCoNi, and FeCoNi). A simple random cluster model was constructed for analyzing EXAFS spectra, and static and dynamic components of the mean-square relative displacement (MSRD) were separately extracted. In our analysis, the static MSRD of the MnCoNi sample was slightly larger than those of the CrCoNi and FeCoNi samples, whereas the dynamic MSRDs of these samples were almost identical. Based on the complementary neutron diffraction data, we argued that the origin of the large static displacement in the MnCoNi alloy can be associated with a short-range structural transformation through long-term structural relaxation.
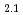 during high temperature deformation
during high temperature deformationJaladurgam, N. R.*; Lozinko, A.*; Guo, S.*; Harjo, S.; Colliander, M. H.*
Materialia, 22, p.101392_1 - 101392_4, 2022/05
The load redistribution between and within phases in eutectic high entropy alloy AlCoCrFeNi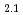 was measured using in-situ neutron diffraction during tensile deformation at 973 K. The load partitioning between phases is reversed compared to lower temperatures, with L1
was measured using in-situ neutron diffraction during tensile deformation at 973 K. The load partitioning between phases is reversed compared to lower temperatures, with L1 becoming the stronger phase. The evolution of the orientation-specific stresses and strains in the L1
becoming the stronger phase. The evolution of the orientation-specific stresses and strains in the L1 phase suggests that cube slip dominates the response. The low strength, internal load transfer and ideally plastic response of the B2 phase indicate a change in deformation mechanism compared to lower temperatures.
phase suggests that cube slip dominates the response. The low strength, internal load transfer and ideally plastic response of the B2 phase indicate a change in deformation mechanism compared to lower temperatures.
Yang, J.*; Ren, W.*; Zhao, X.*; 菊地 龍弥*; Miao, P.*; 中島 健次; Li, B.*; Zhang, Z.*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 99, p.55 - 60, 2022/02
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:53.14(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)物性測定と中性子散乱を組み合わせることにより、面心立方高エントロピー合金CrMnFeCoNiの磁気および熱輸送特性を調べた。DCおよびAC帯磁率は、温度領域全体で反強磁性および強磁性相互作用が共存する常磁性挙動を示し、それぞれ、常磁性から反強磁性への遷移、反強磁性から強磁性への遷移、およびスピン凍結に対応して、約80, 50、および20Kで3つの異常が見られる。電気伝導率と熱伝導率はNiに比べて大幅に低下しており、格子熱伝導率の温度依存性はガラスのようなプラトーを示す。非弾性中性子散乱測定は弱い非調和性を示唆し、熱輸送は欠陥散乱によって支配されると思われる。
Naeem, M.*; He, H.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Lin, W.*; Kai, J.-J.*; Wu, Z.*; Lan, S.*; Wang, X.-L.*
Acta Materialia, 221, p.117371_1 - 117371_18, 2021/12
被引用回数:67 パーセンタイル:97.82(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We studied the deformation behavior of CrFeCoNi high-entropy alloy by in situ neutron diffraction at room temperature, intermediate low temperature of 140 K, low temperatures of 40 K (no serrated deformation) and 25 K (with massive serrations). The contributions from different deformation mechanisms to the yield strength and strain hardening have been estimated. The athermal contributions to the yield strength were  183 MPa at all temperatures, while the Peierls stress increased significantly at low temperatures (from 148 MPa at room temperature to 493 MPa at 25 K). Dislocations contributed to
183 MPa at all temperatures, while the Peierls stress increased significantly at low temperatures (from 148 MPa at room temperature to 493 MPa at 25 K). Dislocations contributed to  94% strain hardening at room temperature. Although the dislocation strengthening remained the major hardening mechanism at very low temperatures, the planar faults contribution increased steadily from 6% at room temperature to 28% at 25 K.
94% strain hardening at room temperature. Although the dislocation strengthening remained the major hardening mechanism at very low temperatures, the planar faults contribution increased steadily from 6% at room temperature to 28% at 25 K.
 200 MeV ion irradiation
200 MeV ion irradiationPogrebnjak, A. D.*; Bagdasaryan, A. A.*; Horodeck, P.*; Tarelnyk, V.*; Buranich, V. V.*; 雨倉 宏*; 大久保 成彰; 石川 法人; Beresnev, V. M.*
Materials Letters, 303, p.130548_1 - 130548_4, 2021/11
被引用回数:25 パーセンタイル:79.76(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)ハイエントロピー合金ベースの(TiZrHfNbV)N窒化物コーティング材に高速重イオン(200MeV Xeイオンビーム)を照射し、陽電子消滅分光法を用いて照射影響を解析した。その結果、照射欠陥のうち、空孔が主な欠陥種であることが分かった。また、5 10
10 ions/cm
ions/cm の高照射量まで照射しても非晶質化や金属間化合物の形成は、検知されなかった。ハイエントロピー合金の高い耐照射性を示す結果となった。
の高照射量まで照射しても非晶質化や金属間化合物の形成は、検知されなかった。ハイエントロピー合金の高い耐照射性を示す結果となった。
Naeem, M.*; Zhou, H.*; He, H.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Lan, S.*; Wu, Z.*; Zhu, Y.*; Wang, X.-L.*
Applied Physics Letters, 119(13), p.131901_1 - 131901_7, 2021/09
被引用回数:20 パーセンタイル:77.31(Physics, Applied)We investigated the in situ deformation behavior of the CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy at a cryogenic temperature of 140 K and compared it with deformation at room temperature. The sample exhibited higher strength and larger ductility at the cryogenic temperature. The CrCoNi alloy remained single-phase face-centered cubic at room temperature, while deformation at 140 K resulted in a martensitic transformation to the hexagonal close-packed structure. The phase transformation, an additional deformation mechanism to stacking faults, twinning, and dis- location slip, resulted in a higher work hardening at cryogenic temperature. The study addresses the structure metastability in the CrCoNi alloy, which led to the formation of epsilon-martensite from the intrinsic stacking faults.
He, H.*; Naeem, M.*; Zhang, F.*; Zhao, Y.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Wang, B.*; Wu, X.*; Lan, S.*; Wu, Z.*; et al.
Nano Letters, 21(3), p.1419 - 1426, 2021/02
被引用回数:76 パーセンタイル:96.49(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)In CrCoNi, a so-called medium-entropy alloy, an fcc-to-hcp phase transformation has long been anticipated. Here, we report an in situ loading study with neutron diffraction, which revealed a bulk fcc-to-hcp phase transformation in CrCoNi at 15 K under tensile loading. By correlating deformation characteristics of the fcc phase with the development of the hcp phase, it is shown that the nucleation of the hcp phase was triggered by intrinsic stacking faults. The confirmation of a bulk phase transformation adds to the myriads of deformation mechanisms available in CrCoNi, which together underpin the unusually large ductility at low temperatures.
Lam, T.-N.*; Lee, S. Y.*; Tsou, N.-T.*; Chou, H.-S.*; Lai, B.-H.*; Chang, Y.-J.*; Feng, R.*; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.; Liaw, P. K.*; et al.
Acta Materialia, 201, p.412 - 424, 2020/12
被引用回数:43 パーセンタイル:90.26(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We examined fatigue-crack-growth behaviors of CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloys (HEAs) under as-fatigued and tensile-overloaded conditions using neutron-diffraction measurements coupled with diffraction peak-profile analyses. We applied both high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) and neutron-diffraction strain mapping for the complementary microstructure examinations. Immediately after a single tensile overload, the crack-growth-retardation period was obtained by enhancing the fatigue resistance, as compared to the as-fatigued condition. The combined mechanisms of the overload-induced larger plastic deformation, the enlarged compressive residual stresses and plastic-zone size, the crack-tip blunting ahead of the crack tip, and deformation twinning governed the pronounced macroscopic crack-growth-retardation behavior following the tensile overload.
Lam, T.-N.*; Tsai, C.-W.*; Chen, B.-K.*; Lai, B.-H.*; Liu, H.-C*; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.; Lin, B.-H.*; Huang, E.-W.*
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 51(10), p.5023 - 5028, 2020/10
被引用回数:14 パーセンタイル:56.20(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Substitution of Ge for Mn increases the elastic moduli of different 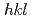 orientations of the CoCrFeMnNi-based high-entropy alloy. Our findings indicate that tuning minor element compositions may result in improved strength-ductility combination. The underlying deformation mechanisms of CoCrFeNiGe
orientations of the CoCrFeMnNi-based high-entropy alloy. Our findings indicate that tuning minor element compositions may result in improved strength-ductility combination. The underlying deformation mechanisms of CoCrFeNiGe were examined by
were examined by  neutron diffraction and analysis of the associated diffraction profiles during tensile deformation. The strain-hardening response of CoCrFeNiGe
neutron diffraction and analysis of the associated diffraction profiles during tensile deformation. The strain-hardening response of CoCrFeNiGe exhibited a dominant mechanism of mechanical twinning at moderate and large strains at room temperature. The evolution of the bulk work hardening rate was consistent with the convolutional multiple whole profile fitting results, which exhibited a continuous increase in twin formation probability.
exhibited a dominant mechanism of mechanical twinning at moderate and large strains at room temperature. The evolution of the bulk work hardening rate was consistent with the convolutional multiple whole profile fitting results, which exhibited a continuous increase in twin formation probability.
 Si
Si O
O
鈴木 恵理子; 中島 邦久; 逢坂 正彦; 大石 佑治*; 牟田 浩明*; 黒崎 健*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(7), p.852 - 857, 2020/07
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:42.20(Nuclear Science & Technology)軽水炉シビアアクシデント時の原子炉構造材へのセシウム(Cs)化学吸着・再蒸発挙動評価に資する熱力学特性データを得るため、化学吸着生成物であるCs Si
Si O
O 単体を調製し、1.9-302Kにおける熱容量の測定を行うことで、初めての実測値を得た。また、これより、室温における熱容量
単体を調製し、1.9-302Kにおける熱容量の測定を行うことで、初めての実測値を得た。また、これより、室温における熱容量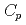
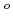 (298.15K)及び標準エントロピー
(298.15K)及び標準エントロピー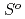 (298.15K)の実測値を取得し、それぞれ249.4
(298.15K)の実測値を取得し、それぞれ249.4  1.1 J K
1.1 J K mol
mol 、322.1
、322.1  1.3 J K
1.3 J K mol
mol であった。さらに、本研究で得られた標準エントロピーと、既往研究で報告されている標準生成エンタルピー
であった。さらに、本研究で得られた標準エントロピーと、既往研究で報告されている標準生成エンタルピー

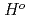 (298.15K)及び高温でのエンタルピー増加
(298.15K)及び高温でのエンタルピー増加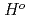 (
( )-
)-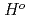 (298.15K)を用い、Cs
(298.15K)を用い、Cs Si
Si O
O の高温での標準生成ギブスエネルギーを実測値に基づき再評価し、既往文献値の妥当性を確認した。
の高温での標準生成ギブスエネルギーを実測値に基づき再評価し、既往文献値の妥当性を確認した。
Woo, W.*; Naeem, M.*; Jeong, J.-S.*; Lee, C.-M.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; He, H.*; Wang, X.-L.*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 781, p.139224_1 - 139224_7, 2020/04
被引用回数:58 パーセンタイル:94.69(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)To elucidate deformation behavior behind the exceptional mechanical properties of CrCoNi based medium entropy alloys, the deformation related microstructural parameters were determined by using in situ neutron diffraction and peaks profile analysis methods. Superior tensile strength and elongation of the CrCoNi alloy is relevant to higher twin fault probability (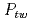 , up to 3.8%) and dislocation density (
, up to 3.8%) and dislocation density ( , up to 9.7
, up to 9.7  10
10 m
m ) compared to those (1.3% and 3.4
) compared to those (1.3% and 3.4  10
10 m
m , respectively) of the CrCoNiFe at 293K. Meanwhile, at 140K, the
, respectively) of the CrCoNiFe at 293K. Meanwhile, at 140K, the 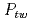 of the CrCoNiFe significantly increased up to 4.4% with the stable
of the CrCoNiFe significantly increased up to 4.4% with the stable  of
of  5.0
5.0  10
10 m
m and its mechanical properties overwhelm those of the CrCoNi at 273K. Such twinning dominant deformation mechanism at low temperature is also assured by lower stacking fault energy (SFE) of the CrCoNiFe at 140K compared to those of the CrCoNi and CrCoNiFe alloys at 293K.
and its mechanical properties overwhelm those of the CrCoNi at 273K. Such twinning dominant deformation mechanism at low temperature is also assured by lower stacking fault energy (SFE) of the CrCoNiFe at 140K compared to those of the CrCoNi and CrCoNiFe alloys at 293K.
Bae, J. W.*; Jung, J.*; Kim, J. G.*; Park, J. M.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Woo, W.*; Kim, H. S.*
Materialia, 9, p.100619_1 - 100619_15, 2020/03
In the present study, an integrated experimental-numerical analysis on ferrous medium-entropy alloy (FMEA) was conducted to understand the micromechanical response of the constituent phases in the FMEA at -137 C. The initial face-centered cubic (FCC) single phase microstructure of the FMEA was transformed to body-centered cubic (BCC) martensite during tensile deformation at -137
C. The initial face-centered cubic (FCC) single phase microstructure of the FMEA was transformed to body-centered cubic (BCC) martensite during tensile deformation at -137 C, resulting in improved low-temperature mechanical properties. The microstructure evolution due to deformation-induced phase transformation mechanism and strain partitioning behavior was analyzed using
C, resulting in improved low-temperature mechanical properties. The microstructure evolution due to deformation-induced phase transformation mechanism and strain partitioning behavior was analyzed using 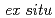 electron backscatter diffraction. The mechanical responses related to the stress partitioning between constituent phases and deformation-induced transformation rate were measured using
electron backscatter diffraction. The mechanical responses related to the stress partitioning between constituent phases and deformation-induced transformation rate were measured using  neutron diffraction in combination with the nanoindentation analysis.
neutron diffraction in combination with the nanoindentation analysis.
Lam, T.-N.*; Chou, Y.-S.*; Chang, Y.-J.*; Sui, T.-R.*; Yeh, A.-C.*; Harjo, S.; Lee, S. Y.*; Jain, J.*; Lai, B.-H.*; Huang, E.-W.*
Crystals (Internet), 9(8), p.420_1 - 420_8, 2019/08
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:61.54(Crystallography)An equal-molar CoCrFeMnNi, face-centered-cubic (fcc) high-entropy alloy (HEA) and a nickel-based superalloy are studied using in situ neutron diffraction experiments. With continuous measurements, the evolution of diffraction peaks is collected for microscopic lattice strain analyses. Cyclic hardening and softening are found in both metallic systems. However, as obtained from the diffraction-peak-width evolution, the underneath deformation mechanisms are quite different. The CoCrFeMnNi HEA exhibits distinct lattice strain and microstructure responses under tension-compression cyclic loadings.
星川 晃範; 井川 直樹; 山内 宏樹; 石井 慶信
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 66(10), p.1810 - 1814, 2005/10
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:25.21(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)メタンハイドレートのStructure Iと呼ばれる構造では、水分子が水素結合により12面体と14面体の二種類のカゴを作り、これらのカゴを積み重ねた結晶構造をしている。しかし、カゴに内包されたメタン分子中の水素の原子座標などは特定されていない。そこで、内包されたメタンの構造を明らかにするため、原研のJRR-3に設置してあるHRPDを用いて回折パターンを測定し、Rietveld法とマキシマムエントロピー法による精密構造解析を行った。水素と重水素では中性子散乱長の符号が異なることから、重水とメタン(CH )でメタンハイドレート試料を合成し、カゴ中の重水素とメタンの水素を区別した。カゴの種類によりメタンの構造に違いがあり、さらに中性子散乱長密度分布がカゴの種類により違うことが明らかになった。
)でメタンハイドレート試料を合成し、カゴ中の重水素とメタンの水素を区別した。カゴの種類によりメタンの構造に違いがあり、さらに中性子散乱長密度分布がカゴの種類により違うことが明らかになった。
松下 智裕*; 吉越 章隆; 安居院 あかね
Europhysics Letters, 71(4), p.597 - 603, 2005/08
被引用回数:32 パーセンタイル:76.76(Physics, Multidisciplinary)一般的に光電子ホログラフィー法はホログラムから3次元的な原子配列をフーリエ変換で再構成しているが、現実的には原子で散乱された電子波は理想的なs波でないため、単純なフーリエ変換で3次元実空間に戻すのは難しい。われわれはフーリエ変換を用いずに単一エネルギーのホログラムから3次元実空間を再構成するのにマキシマムエントロピー法を利用する方法を提案し、Si(100)シングルエネルギー光電子ホログラムに適応し3次元電子像を精度よく再構成した。
星川 晃範; 井川 直樹; 山内 宏樹; 石井 慶信; Stern, L. A.*
Proceedings of 5th International Conference on Gas Hydrates (ICGH-5), Volume 5, p.1619 - 1626, 2005/06
メタンハイドレートのStructure Iと呼ばれる構造では、水分子が水素結合により12面体と14面体の二種類のカゴを作り、これらのカゴを積み重ねた結晶構造をしている。しかし、カゴに内包されたメタン分子中の水素の原子座標などは特定されていない。そこで、内包されたメタンの構造を明らかにするため、原研のJRR-3に設置してあるHRPDを用いて回折パターンを測定し、Rietveld法とマキシマムエントロピー法による精密構造解析を行った。水素と重水素では中性子散乱長の符号が異なることから、重水とメタン(CH )でメタンハイドレート試料を合成し、カゴ中の重水素とメタンの水素を区別した。カゴの種類によりメタンの構造に違いがあり、さらにデバイワラー因子の温度依存性及び中性子散乱長密度分布がカゴの種類により違うことが明らかになった。
)でメタンハイドレート試料を合成し、カゴ中の重水素とメタンの水素を区別した。カゴの種類によりメタンの構造に違いがあり、さらにデバイワラー因子の温度依存性及び中性子散乱長密度分布がカゴの種類により違うことが明らかになった。
井川 直樹; 石井 慶信; 星川 晃範; 山内 宏樹; 下山 智隆
JAERI-Tech 2004-067, 23 Pages, 2004/11
従来よりも微細な氷を用いることでメタンハイドレートを合成した。中性子回折実験及びメタンハイドレート分解実験によるメタンガス放出量の測定の結果、合成したメタンハイドレートが、実験精度以内で、不純物や未反応の氷を含まない高品質なものであることがわかった。なお、メタンハイドレートの中性子回折データを用いてRietveld解析を行い、さらにMEM解析を行った結果、メタンハイドレート中の各構成原子の散乱長に基づく各原子位置の密度分布を可視することができた。
諫山 明彦; 岩間 尚文*; 正和 武志*; 細田 陽介*; 伊世井 宣明; 石田 真一; 佐藤 正泰
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1, 42(9A), p.5787 - 5796, 2003/09
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:15.37(Physics, Applied)フーリエ変換分光装置(FTS)ではマイケルソン干渉計を用いて電子サイクロトロン放射(ECE)から電子温度分布を得ている。マイケルソン干渉計では走査鏡をスキャンする(走査時間:約20ms)ことにより干渉信号を得ていて、この間プラズマの電子温度は変化しないと仮定している。しかし、ELMy Hモードプラズマでは、ELMにより発生した非熱的放射パルス(パルス幅:100 s程度)により干渉信号が歪み、電子温度分布測定が不可能になる。今回、非熱的放射パルスを検出・除去する手法を開発し、さらに、欠損の生じた干渉信号に最大エントロピー法(MEM)を適用して電子温度分布を得ることに成功した。また、最大エントロピー法を適用する際、スペクトルの平滑度を決めるパラメータ(「正規化パラメータ」)を最適化する必要があるが、今回は線形問題で用いられている最小GCV(GeneralizedCross Validation)規準を非線形問題であるMEMに適用した。その結果、最小GCV規準はMEMの正規化パラメータの決定に有用であることがわかった。今回開発した手法をJT-60U実験時の信号に適用した結果、一連のデータを放電間に自動処理できる可能性があることがわかった。
s程度)により干渉信号が歪み、電子温度分布測定が不可能になる。今回、非熱的放射パルスを検出・除去する手法を開発し、さらに、欠損の生じた干渉信号に最大エントロピー法(MEM)を適用して電子温度分布を得ることに成功した。また、最大エントロピー法を適用する際、スペクトルの平滑度を決めるパラメータ(「正規化パラメータ」)を最適化する必要があるが、今回は線形問題で用いられている最小GCV(GeneralizedCross Validation)規準を非線形問題であるMEMに適用した。その結果、最小GCV規準はMEMの正規化パラメータの決定に有用であることがわかった。今回開発した手法をJT-60U実験時の信号に適用した結果、一連のデータを放電間に自動処理できる可能性があることがわかった。