Influence of interstitial carbon on bulk texture evolution of carbide-free high-entropy alloys during cold rolling using neutron diffraction
中性子回折による無炭化物ハイエントロピー合金冷間圧延中のバルク集合組織変化に及ぼす格子間炭素の影響
Fang, W.*; Liu, C.*; Zhang, J.*; 徐 平光 

 ; Peng, T.*; Liu, B.*; 諸岡 聡
; Peng, T.*; Liu, B.*; 諸岡 聡 
 ; Yin, F.*
; Yin, F.*
Fang, W.*; Liu, C.*; Zhang, J.*; Xu, P. G.; Peng, T.*; Liu, B.*; Morooka, Satoshi; Yin, F.*
The influence of interstitial carbon on the texture evolution of high-entropy alloys during cold rolling was investigated. To prevent carbide formation, elements with weak carbon affinity were carefully selected in the (FeMnCoNi)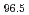 C
C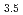 alloy. Neutron diffraction, electron channeling contrast imaging, and electron backscatter diffraction were used to analyze the texture and microstructure evolution in alloys with and without carbon addition. Though their texture components are similar at the early stage of deformation, the Brass and Goss textures in the carbon-containing alloy at 50% cold rolling reduction are obviously higher than those in the carbon-free alloy, while Copper and S textures are lower. A large number of deformation twins induced in the carbon containing alloy is attributed as the significant reason for the texture differences. This work helps to understand the impact of interstitial carbon on the texture evolution of high-entropy alloys, providing valuable insights for microstructure and performance optimization.
alloy. Neutron diffraction, electron channeling contrast imaging, and electron backscatter diffraction were used to analyze the texture and microstructure evolution in alloys with and without carbon addition. Though their texture components are similar at the early stage of deformation, the Brass and Goss textures in the carbon-containing alloy at 50% cold rolling reduction are obviously higher than those in the carbon-free alloy, while Copper and S textures are lower. A large number of deformation twins induced in the carbon containing alloy is attributed as the significant reason for the texture differences. This work helps to understand the impact of interstitial carbon on the texture evolution of high-entropy alloys, providing valuable insights for microstructure and performance optimization.