Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Saito, Takumi*; Nishi, Shusaku*; Amano, Yuki; Beppu, Hikari*; Miyakawa, Kazuya
ACS ES&T Water (Internet), 3(12), p.4103 - 4112, 2023/12
Sato, Takumi; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Morishita, Kazuki; Marufuji, Takato; Ishikawa, Takashi; Fujishima, Tadatsune; Nakano, Tomoyuki
JAEA-Technology 2023-016, 41 Pages, 2023/09
This report summarizes the results of the stabilization treatments of post-experiment nuclear materials in Plutonium Fuel Research Facility (PFRF) from August 2018 to March 2021. Based on the management standards for nuclear materials enacted after the contamination accident that occurred at PFRF on June 6, 2017, the post-experiment nuclear materials containing plutonium (Pu): samples mixed with organic substances that cause an increase in internal pressure due to radiolysis (including X-ray diffraction samples mixed with epoxy resin and plutonium powder which caused contamination accidents), carbides and nitrides samples which is reactive in air, and chloride samples which may cause corrosion of storage containers, were selected as targets of the stabilization. The samples containing organic materials, carbides and nitrides were heated in an air flow at 650  C and 950
C and 950  C for 2 hours respectively to remove organic materials and convert uranium (U) and Pu into oxides. U and Pu chlorides in LiCl-KCl eutectic melt were reduced and extracted into liquid Cd metal by a reaction with lithium (Li) -cadmium (Cd) alloy and converted to U-Pu-Cd alloy at 500
C for 2 hours respectively to remove organic materials and convert uranium (U) and Pu into oxides. U and Pu chlorides in LiCl-KCl eutectic melt were reduced and extracted into liquid Cd metal by a reaction with lithium (Li) -cadmium (Cd) alloy and converted to U-Pu-Cd alloy at 500  C or higher. All of the samples were stabilized and stored at PFRF. We hope that the contents of this report will be utilized to consider methods for stabilizing post experiment nuclear materials at other nuclear fuel material usage facilities.
C or higher. All of the samples were stabilized and stored at PFRF. We hope that the contents of this report will be utilized to consider methods for stabilizing post experiment nuclear materials at other nuclear fuel material usage facilities.
Kumagai, Yuta; Kimura, Atsushi*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa*; Watanabe, Masayuki
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 191, p.109831_1 - 109831_8, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Physical)In this study, we investigated and compared the effects of a high-silica zeolite (HMOR) on the radiation-induced degradation of three aromatic chlorides, 2-chlorophenol (2-ClPh), 2-chloroaniline (2-ClAn), and 2-chlorobenzoic acid (2-ClBA), in order to examine its potential to reduce the influence of ions in water matrix in the irradiation treatment of water-soluble organic compounds. In the presence of ions reactive to radicals, the degradation of 2-ClPh in water was inhibited, but the combined use of HMOR much improved the degradation yield. This improvement was attributed to high performance of HMOR in adsorption of 2-ClPh. Similarly, HMOR was effective for adsorption of 2-ClAn and facilitated the 2-ClAn degradation by irradiation. In contrast, HMOR was poor at adsorption of 2-ClBA and consistently the degradation of 2-ClBA in the water-HMOR mixture was inhibited by the radical scavenger. These results demonstrate that HMOR can mitigate the influence of radical scavengers in water.
Morishita, Kazuki; Sato, Takumi; Onishi, Takashi; Seki, Takayuki*; Sekine, Shinichi*; Okitsu, Yuichi*
JAEA-Technology 2021-024, 27 Pages, 2021/10
In the case of Plutonium (Pu)-bearing organic materials, organic materials are decomposed by alpha rays emitted mainly from Pu to generate hydrogen gas and other substances. Therefore, to safely store Pu-bearing organic materials for an extended period of time, organic materials must be eliminated. In addition, carbide and nitride fuels must be converted into oxides for safe storage in order to prevent the exothermal reaction of these fuels with oxygen/moisture in air. A survey of the literature on the stabilization treatment of Pu-bearing organic materials confirmed that organic materials can be decomposed and removed by heating at 950  C (1223.15 K) or greater in air. Furthermore, based on the calculated thermodynamic parameters of oxidation reaction of carbide and nitride fuels in air, it was estimated that these fuels would be oxidized in air at 950
C (1223.15 K) or greater in air. Furthermore, based on the calculated thermodynamic parameters of oxidation reaction of carbide and nitride fuels in air, it was estimated that these fuels would be oxidized in air at 950  C because the equilibrium oxygen partial pressure in the oxidation reaction at 950
C because the equilibrium oxygen partial pressure in the oxidation reaction at 950  C was lower than 2.1
C was lower than 2.1 10
10 Pa (oxygen partial pressure in air). Therefore, it was decided to stabilize Pu-bearing organic materials by heating at 950
Pa (oxygen partial pressure in air). Therefore, it was decided to stabilize Pu-bearing organic materials by heating at 950  C in air to remove the organic materials and oxidize the carbide and nitride fuels. As a mock-up test to remove the organic materials, thin sheets of epoxy resin were heated in air. The changes in appearance and weight before and after heating in air showed that organic materials can be removed. After the mock-up test, Pu-bearing organic materials were also stabilized by heating in the similar condition.
C in air to remove the organic materials and oxidize the carbide and nitride fuels. As a mock-up test to remove the organic materials, thin sheets of epoxy resin were heated in air. The changes in appearance and weight before and after heating in air showed that organic materials can be removed. After the mock-up test, Pu-bearing organic materials were also stabilized by heating in the similar condition.
Kong, L.*; Gong, J.*; Hu, Q.*; Capitani, F.*; Celeste, A.*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Li, N.*; Yang, W.*; Liu, G.*; et al.
Advanced Functional Materials, 31(9), p.2009131_1 - 2009131_12, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:81.42(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The soft nature of organic-inorganic halide perovskites renders their lattice particularly tunable to external stimuli such as pressure, undoubtedly offering an effective way to modify their structure for extraordinary optoelectronic properties. However, these soft materials meanwhile feature a general characteristic that even a very mild pressure will lead to detrimental lattice distortion and weaken the critical light-matter interaction, thereby triggering the performance degradation. Here, using the methylammonium lead iodide as a representative exploratory platform, we observed the pressure-driven lattice disorder can be significantly suppressed via hydrogen isotope effect, which is crucial for better optical and mechanical properties previously unattainable.
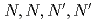 -tetraoctyl-diglycolamide from organic acid
-tetraoctyl-diglycolamide from organic acidSasaki, Yuji; Matsumiya, Masahiko*; Nakase, Masahiko*; Takeshita, Kenji*
Chemistry Letters, 49(10), p.1216 - 1219, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:43.66(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Lanthanide (Ln) extractions from organic acids to  -dodecane by
-dodecane by 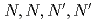 -tetraoctyl-diglycolamide (TODGA) were conducted. Four organic acids (lactic acid, malonic acid, tartaric acid, and citric acid) were employed. Although these acids stabilize lanthanides in the aqueous phase, a distribution ratio (
-tetraoctyl-diglycolamide (TODGA) were conducted. Four organic acids (lactic acid, malonic acid, tartaric acid, and citric acid) were employed. Although these acids stabilize lanthanides in the aqueous phase, a distribution ratio ( ) greater 1 was obtained for heavy Ln. Ln patterns (
) greater 1 was obtained for heavy Ln. Ln patterns ( (Ln) against atomic number of Ln) show maximum values of Ho and Er. In order to obtain high
(Ln) against atomic number of Ln) show maximum values of Ho and Er. In order to obtain high  values, the addition of HNO
values, the addition of HNO in aqueous phase is found to be effective.
in aqueous phase is found to be effective.
Terashima, Motoki; Endo, Takashi*; Miyakawa, Kazuya
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(4), p.380 - 387, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:20.94(Nuclear Science & Technology) -radiation and H
-radiation and H O
O induced oxidative dissolution of uranium(IV) oxide in aqueous solution containing phthalic acid
induced oxidative dissolution of uranium(IV) oxide in aqueous solution containing phthalic acidKumagai, Yuta; Jonsson, M.*
Dalton Transactions (Internet), 49(6), p.1907 - 1914, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)This study aims to reveal possible involvements of organic acids in the oxidative dissolution of UO . Using phthalic acid as a model compound, we have measured adsorption on UO
. Using phthalic acid as a model compound, we have measured adsorption on UO and investigated effects on the reaction between H
and investigated effects on the reaction between H O
O and UO
and UO and on oxidative dissolution induced by
and on oxidative dissolution induced by  -irradiation. Significant adsorption of phthalic acid was observed even at neutral pH. However, the reaction between H
-irradiation. Significant adsorption of phthalic acid was observed even at neutral pH. However, the reaction between H O
O and UO
and UO in phthalic acid solution induced oxidative dissolution of U(VI) similarly to aqueous bicarbonate solution. These results indicate that even though phthalic acid adsorbs on the UO
in phthalic acid solution induced oxidative dissolution of U(VI) similarly to aqueous bicarbonate solution. These results indicate that even though phthalic acid adsorbs on the UO surface, it is not involved in the interfacial reaction by H
surface, it is not involved in the interfacial reaction by H O
O . In contrast, the dissolution of U by irradiation was inhibited in aqueous phthalic acid solution, whereas H
. In contrast, the dissolution of U by irradiation was inhibited in aqueous phthalic acid solution, whereas H O
O generated by radiolysis was consumed by UO
generated by radiolysis was consumed by UO . The inhibition suggests that radical species derived from phthalic acid was involved in the redox reaction process of UO
. The inhibition suggests that radical species derived from phthalic acid was involved in the redox reaction process of UO .
.
Ikeura, Hiromi*; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 58(SI), p.SIIC04_1 - SIIC04_4, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)The electronic structure of the unoccupied conduction band of polycrystalline chloroaluminum phthalocyanine was investigated by X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) near the Cl K-edge. XAS spectra were recorded in total electron yield (TEY) and partial Auger electron yield (AEY) modes. Partial AEY spectra were measured using normal and spectator Cl KL L
L Auger yields as a function of photon energy. Although the TEY spectrum showed a broad shape; that was difficult to deconvolute curve fitting, the normal and spectator AEY spectra clearly showed that
Auger yields as a function of photon energy. Although the TEY spectrum showed a broad shape; that was difficult to deconvolute curve fitting, the normal and spectator AEY spectra clearly showed that 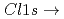
 *(Cl-Al) transition splits into two competitive peaks attributed to the core excitons (localized with a core hole) and conduction band (delocalized without a core hole). The existence of a band-like peak in the Cl K-edge XAS is evidence that the Cl axial ligand participates in forming the conduction band. Thus, band-like electron transport is expected to occur in the oligomer-like (-Al-Cl-Al-) site.
*(Cl-Al) transition splits into two competitive peaks attributed to the core excitons (localized with a core hole) and conduction band (delocalized without a core hole). The existence of a band-like peak in the Cl K-edge XAS is evidence that the Cl axial ligand participates in forming the conduction band. Thus, band-like electron transport is expected to occur in the oligomer-like (-Al-Cl-Al-) site.
Lin, P.*; Xu, C.*; Kaplan, D. I.*; Chen, H.*; Yeager, C. M.*; Xing, W.*; Sun, L.*; Schwehr, K. A.*; Yamazaki, Hideo*; Kokubu, Yoko; et al.
Science of the Total Environment, 678, p.409 - 418, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:48.08(Environmental Sciences)Nagasaki sediments containing bomb-derived Pu provided a unique opportunity to explore the long term geochemical behavior of Pu. Through a combination of selective extractions and molecular characterization via electrospray ionization Fourier-transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry, we determined that 55  3% of the
3% of the  Pu was preferentially associated with more persistent organic matter compounds in Nagasaki sediments, particularly those natural organic matter (NOM) stabilized by Fe oxides. Other organic matter compounds served as a secondary sink of these
Pu was preferentially associated with more persistent organic matter compounds in Nagasaki sediments, particularly those natural organic matter (NOM) stabilized by Fe oxides. Other organic matter compounds served as a secondary sink of these 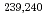 Pu (31
Pu (31  2% on average), and less than 20% of the
2% on average), and less than 20% of the 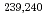 Pu was immobilized by inorganic mineral particles. While present long-term disposal and environmental remediation modeling assume that solubility limits and sorption to mineral surfaces control Pu subsurface mobility, our observations suggest that NOM undoubtedly plays an important role in sequestering Pu. Ignoring the role of NOM in controlling Pu fate and transport is not justified in most environmental systems.
Pu was immobilized by inorganic mineral particles. While present long-term disposal and environmental remediation modeling assume that solubility limits and sorption to mineral surfaces control Pu subsurface mobility, our observations suggest that NOM undoubtedly plays an important role in sequestering Pu. Ignoring the role of NOM in controlling Pu fate and transport is not justified in most environmental systems.
Taguchi, Mitsumasa*; Kumagai, Yuta; Kimura, Atsushi*
IAEA-TECDOC-1855, p.106 - 116, 2018/00
The technology for the decomposition of trace amounts of halogenated pharmaceuticals/antibiotics was developed in wastewater by use of the combination method of zeolite adsorbent and ionizing radiation. HMOR, a hydrophobic high-silica mordenite-type zeolite, was employed to concentrate 2-chlorophenol (2-ClPh) as a simple model of halogenated pharmaceuticals/antibiotics. HMOR adsorbed above 99% of 2-ClPh from dilute aqueous solutions. The yield of Cl production in HMOR mixture corresponded to the aqueous solution containing 10 fold higher concentration of dissolved 2-ClPh. Clofibrate and triclosan, one of chlorinated pharmaceuticals/antibiotics, in real wastewater were treated by use of the combination method of HMOR and ionizing radiation. Production yield of Cl
production in HMOR mixture corresponded to the aqueous solution containing 10 fold higher concentration of dissolved 2-ClPh. Clofibrate and triclosan, one of chlorinated pharmaceuticals/antibiotics, in real wastewater were treated by use of the combination method of HMOR and ionizing radiation. Production yield of Cl by use of the adsorbent was about twice higher than that in aqueous solution, and HMOR was contributed for effective reduction of chlorinated pharmaceuticals/antibiotics in real wastewater.
by use of the adsorbent was about twice higher than that in aqueous solution, and HMOR was contributed for effective reduction of chlorinated pharmaceuticals/antibiotics in real wastewater.
Manabe, Sachi; Matsubara, Natsumi; Saegusa, Jun; Takeishi, Minoru
KEK Proceedings 2016-8, p.281 - 285, 2016/10
no abstracts in English
 Cs in forest surface environments; Application to a contaminated forest site near Fukushima and assessment of potential impacts of soil organic matter interactions
Cs in forest surface environments; Application to a contaminated forest site near Fukushima and assessment of potential impacts of soil organic matter interactionsOta, Masakazu; Nagai, Haruyasu; Koarashi, Jun
Science of the Total Environment, 551-552, p.590 - 604, 2016/05
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:72.55(Environmental Sciences)A model for  Cs transfer in forest was developed to assess behavior of Fukushima-derived
Cs transfer in forest was developed to assess behavior of Fukushima-derived  Cs. The model simulation well reproduced observed 3 year migration of
Cs. The model simulation well reproduced observed 3 year migration of  Cs in organic layer and mineral soil. Long-term predictions indicated that more than 90% of the deposited
Cs in organic layer and mineral soil. Long-term predictions indicated that more than 90% of the deposited  Cs remains in the top 5 cm soil till 30 years, suggesting that forest acts as a long-term reservoir of
Cs remains in the top 5 cm soil till 30 years, suggesting that forest acts as a long-term reservoir of  Cs with limited loss via groundwater pathway. Impacts of soil organic matter (SOM) on
Cs with limited loss via groundwater pathway. Impacts of soil organic matter (SOM) on  Cs dynamics were investigated by modifying parameters of
Cs dynamics were investigated by modifying parameters of  Cs turnover. The results showed that SOM-induced reduction of
Cs turnover. The results showed that SOM-induced reduction of  Cs adsorption, slower fixation of
Cs adsorption, slower fixation of  Cs by clay and enhanced mobilization of the fixed
Cs by clay and enhanced mobilization of the fixed  Cs elevate soil-to-plant transfer of
Cs elevate soil-to-plant transfer of  Cs by increasing fraction of dissolved
Cs by increasing fraction of dissolved  Cs. A substantial proportion (27%
Cs. A substantial proportion (27%  73%) of
73%) of  Cs in these soils was delivered to horizons deeper than 5 cm decades later. These results suggested that SOM significantly influences behavior of
Cs in these soils was delivered to horizons deeper than 5 cm decades later. These results suggested that SOM significantly influences behavior of  Cs over long-term.
Cs over long-term.
Aosai, Daisuke*; Saeki, Daisuke*; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Matsuyama, Hideto*
Colloids and Surfaces A; Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 495, p.68 - 78, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:1.64(Chemistry, Physical)The transport of radionuclides by organic colloids in deep groundwater is one of the important issues for the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste. Because of their low concentration, it is difficult to directly analyze organic colloids in deep groundwater. In this study, hydrodynamic conditions were optimized, and surfaces of nanofiltration membranes were modified using a cationic phosphorylcholine polymer for preventing membrane fouling. Deep groundwater, obtained at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory in Japan, was condensed. The recovery yield of the organic colloids in the deep groundwater condensation test at 5-fold condensation was improved from 62% to 92% by the optimized hydrodynamic conditions and membrane surface modification for prevention of membrane fouling. The composition of organic colloids in the condensates was analyzed using pyrolysis gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry.
Ikeura, Hiromi*; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro
Molecular Crystals and Liquid Crystals, 622(1), p.50 - 54, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Organic electrically conducting  -stacked molecules are widely regarded as promising materials for future application of nanoelectronics. Direct measurements of electronic structures of unoccupied states in organic semiconductors lead to better understanding of mechanism of electron conduction. For probing unoccupied partial density of states (DOS), X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) is commonly used, where selective excitation of the 1s core electron to the unoccupied conduction band is possible. However, XAS cannot distinguish localized and delocalized features without comparing any theoretical approach. In this work, the core-hole-clock method in resonant Auger spectroscopy (RAS) has been applied to probe electron delocalization through the empty conduction band in the attosecond domain for the purpose of exploring electronic materials with high-speed electron transport. We will discuss some organic molecules such as pentacenes.
-stacked molecules are widely regarded as promising materials for future application of nanoelectronics. Direct measurements of electronic structures of unoccupied states in organic semiconductors lead to better understanding of mechanism of electron conduction. For probing unoccupied partial density of states (DOS), X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) is commonly used, where selective excitation of the 1s core electron to the unoccupied conduction band is possible. However, XAS cannot distinguish localized and delocalized features without comparing any theoretical approach. In this work, the core-hole-clock method in resonant Auger spectroscopy (RAS) has been applied to probe electron delocalization through the empty conduction band in the attosecond domain for the purpose of exploring electronic materials with high-speed electron transport. We will discuss some organic molecules such as pentacenes.
Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Baba, Yuji; Hirao, Norie; Honda, Mitsunori; Izumi, Toshinori; Ikeura, Hiromi*
Molecular Crystals and Liquid Crystals, 622(1), p.44 - 49, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The molecular orientation is one of the important factors for controlling various properties in organic semiconductor materials. Films are usually heterogeneous. Thus they exist as a mixture of microscopic domains which have a variety of orientation directions. Therefore, it is essential to observe selectively microscopic domains with different orientation direction. In this work, we have developed the photoelectron emission microscopy (PEEM) system combined with the linearly polarized vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) light or synchrotron radiation (SR) X-rays. PEEM images (FOV = ca.50 micro m) for poly(3-hexylthiophene), P3HT thin films were observed under the UV irradiation with various polarization angles, including in-plain and out-of-plain polarization. Morphologies at some bright parts are different each other. The resultant observation suggests that it enables us to distinguish oriented micro-domains with specific directions of polymer chain axis from other amorphous parts.
Aosai, Daisuke*; Saeki, Daisuke*; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Matsuyama, Hideto*
Colloids and Surfaces A; Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 485, p.55 - 62, 2015/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:11.41(Chemistry, Physical)To analyze organic colloids in deep groundwater, concentration techniques using adsorption resins and reverse osmosis membranes have been widely applied, because their concentrations in deep groundwater are very low and detection of the organic colloids in raw groundwater is difficult. However, these techniques have respective disadvantages such as chemical disturbance and membrane fouling caused by cations. To overcome their disadvantages, we propose a new concentration method using nanofiltration membranes to concentrate organic colloids rapidly without chemical disturbance and to selectively remove monovalent and divalent ions, which may cause inorganic and/or organic fouling. Concentration performance of the NF and RO membranes for aqueous solutions for humic acids was evaluated using a laboratory-scale membrane test unit. The time course of permeate flux and concentration of humic acids were measured. These membranes were applied to the concentration of actual groundwater.
 films prepared by reactive sputtering deposition
films prepared by reactive sputtering depositionYamamoto, Shunya; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Miyashita, Atsumi; Yoshikawa, Masahito
Materials Research Express (Internet), 2(2), p.026401_1 - 026401_8, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:14.43(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The effects of deposition temperature and film thickness on the structural and gasochromic properties of tungsten trioxide films used for the optical detection of diluted cyclohexane have been investigated. The tungsten trioxide films were prepared on SiO substrates by magnetron sputtering, with the deposition temperature ranging from 300 to 550
substrates by magnetron sputtering, with the deposition temperature ranging from 300 to 550 C in an Ar and O
C in an Ar and O gas mixture. The gasochromic properties of the films, coated with a catalytic Pt layer, were examined by exposing them up to 5% cyclohexane in N
gas mixture. The gasochromic properties of the films, coated with a catalytic Pt layer, were examined by exposing them up to 5% cyclohexane in N gas. We found that (001)-oriented monoclinic tungsten trioxide films, with a columnar structure, grew at deposition temperatures between 400 and 450
gas. We found that (001)-oriented monoclinic tungsten trioxide films, with a columnar structure, grew at deposition temperatures between 400 and 450 C. The gasochromic characterization of the tungsten trioxide films revealed that (001)-oriented tungsten trioxide films, with cauliflower-like surface morphology, were appropriate for the optical detection of cyclohexane.
C. The gasochromic characterization of the tungsten trioxide films revealed that (001)-oriented tungsten trioxide films, with cauliflower-like surface morphology, were appropriate for the optical detection of cyclohexane.
Avramov, P. V.*; Kuzubov, A. A.*; Sakai, Seiji; Otomo, Manabu*; Entani, Shiro; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Eleseeva, N. S.*; Pomogaev, V. A.*; Naramoto, Hiroshi*
Journal of Porphyrins and Phthalocyanines, 18(7), p.552 - 568, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:5.22(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Baba, Yuji; Shimoyama, Iwao; Hirao, Norie; Honda, Mitsunori; Izumi, Toshinori; Ikeura, Hiromi*
Photon Factory Activity Report 2013, Part B, P. 546, 2014/00
The molecular orientation is one of the important factors for controlling various properties in organic semiconductor materials. Films are usually heterogeneous. Thus they exist as a mixture of microscopic domains which have a variety of orientation directions. Therefore, it is essential to observe selectively microscopic domains with different orientation direction. In this work, we have developed the photoelectron emission microscope (PEEM) system combined with the linearly polarized vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) light or synchrotron radiation (SR) X-rays. PEEM images for poly(3-hexylthiophene), P3HT thin films were observed under synchrotron X-ray irradiation with linearly polarization. In conclusion, it was found that PEEM with polarized synchrotron can be a powerful tool that gives information of molecular orientation in nano-meter scale.