Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Saga, Kaname
JAEA-Review 2025-003, 23 Pages, 2025/05
Diagnosis and treatment using radioisotopes (RI) in the medical field contribute to improving people's welfare. However, almost all medical RI distributed in Japan are imported from overseas. As a result, geopolitical influences and natural disasters lead to difficulties for importing them. Based on these backgrounds, in Japan, a specialized subcommittee on the production and utilization of medical radioisotopes was established within the Atomic Energy Commission, and in May 2022, it formulated the "Action Plan for Promotion of Production and Utilization of Medical Radioisotopes." Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) launched the NXR Development Center in FY2024 to separate and recycle valuable elements contained in high-level liquid waste (HLLW). The advantages of using HLLW are that it contains a wide variety of nuclides and in large quantities. Therefore, this report focused on the RI contained in HLLW and evaluated whether it can be supplied for medical use. Specifically, the target supply amount of Sr-90, the parent nuclide of Y-90 approved as a RI for medical use, and the amount of Sr-90 in HLLW were estimated. Based on the estimation, the feasibility of separating medical RI from HLLW in a reprocessing research facility was evaluated. As a result, the HLLW possibly contains an amount of RI equivalent to the domestic medical demand. Although it depends on the RI concentration in the HLLW, a small volume of HLLW, ranging from a few hundred milliliters to a few liters, could potentially produce an amount of medical RI equivalent to domestic demand. In addition, the equipment already installed in research facilities, such as NUCEF at JAEA, may be sufficient to produce the medical RI. It may be possible to meet domestic medical demand for Sr-90, as a source of Y-90, by processing a few hundred milliliters to a few liters of HLLW using an existing research facility.
Watanabe, Tomoaki; Aizawa, Naoto*; Chiba, Go*; Tada, Kenichi; Yamamoto, Akio*
Proceedings of International Conference on Mathematics and Computational Methods Applied to Nuclear Science and Engineering (M&C 2025) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2025/04
Currently, a major burnup calculation method for the nuclide composition of nuclear fuel conducts neutron transport calculations at each burnup step to account for changes in the neutron spectrum. While this method is highly accurate, the large computational cost of neutron transport calculations can be problematic. Therefore, a fast burnup calculation method based on neutron spectrum reconstruction with the proper orthogonal decomposition (POD) and regression model is investigated. In this method, dimensionality reduction by POD is applied to many neutron fluxes obtained from detailed burnup calculations for various input parameter sets, and regression models are constructed to connect the dimensionality-reduced neutron fluxes and parameters. By substituting arbitrary input parameters to the regression models, the neutron flux is reconstructed and the burnup calculation is performed. This method performs burnup calculations that consider changes in the neutron spectrum based on input conditions without neutron transport calculations. The present method was applied to a PWR UO fuel pin cell model. The results show the nuclide inventory can be calculated with a prediction accuracy within a few percent. In addition, it is found that the calculation error is dominated by the regression models, which implies the further improvement of the regression models leads to improving the accuracy.
fuel pin cell model. The results show the nuclide inventory can be calculated with a prediction accuracy within a few percent. In addition, it is found that the calculation error is dominated by the regression models, which implies the further improvement of the regression models leads to improving the accuracy.
Futemma, Akira; Sanada, Yukihisa; Nakama, Shigeo; Sasaki, Miyuki; Ochi, Kotaro; Sawahata, Yoshiro*; Kawasaki, Yoshiharu*; Iwai, Takeyuki*; Hiraga, Shogo*; Haginoya, Masashi*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2024-022, 170 Pages, 2025/03
On March 11, 2011, the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake caused a tsunami that led to the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident, releasing radioactive material into the environment. Since then, Aerial Radiation Monitoring (ARM) using manned helicopters has been employed to measure radiation distribution. As a commissioned project from the Nuclear Regulation Authority, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) utilizes this technology for emergency monitoring during nuclear facility accidents, aiming to provide prompt results by pre-arranging information on background radiation, topography, and control airspaces around nuclear power plants nationwide. In fiscal year 2023, the commissioned project included conducting ARM around the Sendai Nuclear Power Station and preparing related information. To enhance effectiveness during emergencies, ARM and the first domestic training flight of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) were conducted during the FY2023 Nuclear Energy Disaster Prevention Drill. Furthermore, UAVs radiation monitoring technology was advanced by selecting UAVs and investigating their performance. This report summarizes the results and technical issues identified providing insights to improve emergency preparedness.
Sakamoto, Masahiro; Okumura, Keisuke; Kanno, Ikuo; Matsumura, Taichi; Terashima, Kenichi; Riyana, E. S.; Mizokami, Masato*; Mizokami, Shinya*
JAEA-Research 2024-017, 14 Pages, 2025/03
In the TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), a trial retrieval of fuel debris with small-amount from Unit 2 is planned. The retrieved fuel debris will be transported out of 1F to Institutes in Ibaraki prefecture for analysis. The analyzed results will be utilized for the improvement of the processes (retrieval, transportation and storage) in the fuel debris management as feedback, and also for the development of technologies necessary in the future. The weight of fuel debris in the trial retrieval is planned to be a few grams. After the trial, the scale of retrieval will be expanded step by step. In the trial retrieval, a rational transportation container should be considered beforehand, according to the laws and regulations associated with the off-site transportation. The transportation container has a classification and the classification is decided according to the radioactivity of the material in the container. In this report, we evaluated the applicability of the Type A transport container to contribute to the safety assessment of retrieved fuel debris.
Takahashi, Yoshio*; Yamaguchi, Akiko; Yomogida, Takumi
Treatise on Geochemistry, 3rd edition, Vol.6, p.105 - 150, 2025/00
With the recent development of measurement techniques, new approaches to the environmental geochemistry of radionuclides have been applied for various research targets. In this review article, several topics within the last 10-15 years in the field of environmental geochemistry of radionuclides have been discussed. In particular, this article mainly focused on two topics, (i) studies on the migration of radionuclides emitted by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) accident in 2011 and (ii) the development of X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) spectroscopy and its application to the geochemical processes of radionuclides.
Asai, Shiho*; Horita, Takuma
Bunseki Kagaku, 73(10-11), p.569 - 578, 2024/10
The accurate estimation of the quantities and composition of long-lived radionuclides in radioactive waste is crucial for assessing the long-term safety of its disposal. Traditionally, theoretical predictions of the quantities of long-lived radionuclides obtained from burn-up calculation codes with evaluated nuclear data have been used especially for the safety assessment of high-level radioactive waste. However, such nuclear data used in theoretical predictions have not been sufficiently validated due to the scarcity of the reported measurement data. In this study, we aim to contribute to the improvement of the reliability of theoretical predictions by confirming them with the measured quantities of long-lived radionuclides per unit mass of uranium in spent nuclear fuel, which are output data obtained from the burnup calculation code. This involves measuring the long-lived radionuclides present in nuclear fuel pellets used in commercial nuclear reactors. Specifically, we focused on  Zr,
Zr,  Pd, and
Pd, and  Cs, which can be effectively measured using an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (ICP-MS). Besides the purpose of validating the nuclear data, this article also highlights viable measurement techniques for these radionuclides, along with examples demonstrating their applicability to long-lived radionuclides, including the preparation procedures for their measurement.
Cs, which can be effectively measured using an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (ICP-MS). Besides the purpose of validating the nuclear data, this article also highlights viable measurement techniques for these radionuclides, along with examples demonstrating their applicability to long-lived radionuclides, including the preparation procedures for their measurement.
Saga, Kaname
JAEA-Review 2024-038, 9 Pages, 2024/09
The purpose of this report is understanding the elements and radio isotopes with highly useful based on the current trends in the industrial field. The survey was conducted from the viewpoint of the abundance of elements and radio isotopes contained and the demand in the industrial field, and the following survey results were obtained. The economic scale of radio isotopes in the industrial field (including radiation use) has been increasing in recent years in the manufacturing, medical, and agricultural sectors. On the other hand, the domestic production of the utilized radio isotope is still small, and some radio isotopes are entirely imported. Radio isotopes such as Sr-90, Mo-100, Cs-137, and Am-241 from spent fuel are suitable for industrial use because of their abundance in spent fuel and half-lives. As for the utilization of elements, the industrial use of platinum group elements and rare earth elements were explored because these elements are high industrial value and low domestic self-sufficiency. The platinum group elements were evaluated to have the potential to be supplied in a certain amount as a new domestic production source based on their abundance in spent fuel. On the other hand, for rare earth elements, which have also low self-sufficiency rate, the ratio of the amount that could be supplied from spent fuel compared to the current annual supply was evaluated to be less than 1%, and therefore, no effect could be expected. The domestic recycling rate of rare earth elements is low, and the provision of numerical simulation technology, which improves the recycling rate, could highly contribute to the industries. This technology makes it possible to calculate the optimal operating conditions for the separation process, such as the number of processing stages and processing speed, in accordance with the elements to be separated and used.
Yomogida, Takumi; Ouchi, Kazuki; Morii, Shiori; Oka, Toshitaka; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Koma, Yoshikazu; Konno, Katsuhiro*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 14, p.14945_1 - 14945_11, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:31.14(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Particles containing alpha ( ) nuclides were identified from sediment in stagnant water in the Unit 3 reactor building of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDiNPS). We analyzed different concentrations of alpha nuclides samples collected at two sampling sites, torus room and Main steam isolation valve (MSIV) room. Most of the
) nuclides were identified from sediment in stagnant water in the Unit 3 reactor building of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDiNPS). We analyzed different concentrations of alpha nuclides samples collected at two sampling sites, torus room and Main steam isolation valve (MSIV) room. Most of the  -nuclides in the stagnant water samples of the torus room and the MSIV room were present in particle fractions larger than 10
-nuclides in the stagnant water samples of the torus room and the MSIV room were present in particle fractions larger than 10  m. We detected uranium-bearing particles in
m. We detected uranium-bearing particles in  m-size by scanning electron microscopy-energy dispersive X-Ray (SEM-EDX) observation. Other short lived
m-size by scanning electron microscopy-energy dispersive X-Ray (SEM-EDX) observation. Other short lived  -nuclides were detected by alpha track detection. The
-nuclides were detected by alpha track detection. The  -nuclide-containing particles with several tens to several hundred
-nuclide-containing particles with several tens to several hundred  m in size were mainly comprised iron (Fe) by SEM-EDX analysis. This study clarifies that the morphologies of U and other
m in size were mainly comprised iron (Fe) by SEM-EDX analysis. This study clarifies that the morphologies of U and other  -nuclides in the sediment of stagnant water in the FDiNPS's Unit 3 reactor building.
-nuclides in the sediment of stagnant water in the FDiNPS's Unit 3 reactor building.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Sugihara, Kenta*
Physical Review C, 109(5), p.054610_1 - 054610_12, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:74.11(Physics, Nuclear)Nuclide production cross sections are crucial in nuclear research, development, space exploration, and astrophysical investigations. Despite their importance, limited experimental data availability restricts the practicality of phenomenological approaches to comprehensive cross-section estimation. To address this, we propose a Gaussian process-based machine learning (ML) model capable of transferring knowledge from elements with abundant data to those with limited or no experimental data. Our ML model not only enables comprehensive cross-section estimations for various elements but also demonstrates predictive capabilities akin to physics models, even in regions with scarce training data.
 Be and
Be and  Al under direct muon-induced spallation in granite quartz and its implications for past high-energy cosmic ray fluxes
Al under direct muon-induced spallation in granite quartz and its implications for past high-energy cosmic ray fluxesSakurai, Hirohisa*; Kurebayashi, Yutaka*; Suzuki, Soichiro*; Horiuchi, Kazuho*; Takahashi, Yui*; Doshita, Norihiro*; Kikuchi, Satoshi*; Tokanai, Fuyuki*; Iwata, Naoyoshi*; Tajima, Yasushi*; et al.
Physical Review D, 109(10), p.102005_1 - 102005_18, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Secular variations of galactic cosmic rays (GCRs) are inseparably associated with the galactic activities and should reflect the environments of the local galactic magnetic field, interstellar clouds, and nearby supernova remnants. The high-energy muons produced in the atmosphere by high-energy GCRs can penetrate deep underground and generate radioisotopes in the rock. As long lived radionuclides such as  Be and
Be and  Al have been accumulating in these rocks, concentrations of
Al have been accumulating in these rocks, concentrations of  Be and
Be and  Al can be used to estimate the long-term variations in high-energy muon yields, corresponding to those in the high-energy GCRs over a few million years. This study measured the production cross sections for muon induced
Al can be used to estimate the long-term variations in high-energy muon yields, corresponding to those in the high-energy GCRs over a few million years. This study measured the production cross sections for muon induced  Be and
Be and  Al by irradiating positive muons with the momentum of 160 GeV/c on the synthetic silica plates and the granite core at the COMPASS experiment line in CERN SPS. In addition, it the contributions of the direct muon spallation reaction and the nuclear reactions by muon-induced particles on the production of long lived radionuclides in the rocks were clarified.
Al by irradiating positive muons with the momentum of 160 GeV/c on the synthetic silica plates and the granite core at the COMPASS experiment line in CERN SPS. In addition, it the contributions of the direct muon spallation reaction and the nuclear reactions by muon-induced particles on the production of long lived radionuclides in the rocks were clarified.
Futemma, Akira; Sanada, Yukihisa; Sasaki, Miyuki; Kawasaki, Yoshiharu*; Iwai, Takeyuki*; Hiraga, Shogo*; Haginoya, Masashi*; Matsunaga, Yuki*; Akutsu, Yuichiro*; Arai, Yoshinori*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2023-026, 161 Pages, 2024/03
By the accident at Tokyo Electric Power Company's (TEPCO's) Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), caused by tsunami triggered by the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake, a large amount of radioactive material was released into the surrounding environment. After the accident, Airborne Radiation Monitoring (ARM) via manned helicopter has been utilized as a method to quickly and extensively measure radiation distribution surrounding FDNPS. In order to utilize ARM and to promptly provide the results during a nuclear emergency, information on background radiation levels, topographical features, and controlled airspace surrounding nationwide nuclear facilities have been prepared in advance. In the fiscal year 2022, we conducted ARM around the Mihama Nuclear Power Station of Kansai Electric Power Company (KEPCO), the Tsuruga Power Station of Japan Atomic Power Company (JAPC), and the Ikata Power Station of Shikoku Electric Power Company (YONDEN), and prepared information on background radiation doses and controlled airspace. In addition, we have developed an aerial radiation detection system via unmanned airplane, which is expected to be an alternative to ARM, during a nuclear emergency. This report summarizes the results and technical issues identified.
Kimura, Yoshiki; Tsuchiya, Kenichi*
Radioisotopes, 72(2), p.121 - 139, 2023/07
Rapid and precise radioisotope identification in the scene of nuclear detection and nuclear security incidents is one of the challenging issues for the prompt response on the detection alarm or the incidents. A radioisotope identification algorithm using a deep artificial neural network model applicable to handheld gamma-ray detectors has been proposed in the present paper. The proposed algorithm automatically identifies gamma-emitting radioisotopes based on the count contribution ratio (CCR) from each of them estimated by the deep artificial neural network model trained by simulated gamma-ray spectra. The automated radioisotope identification algorithm can support first responders of nuclear detection and nuclear security incidents without sufficient experience and knowledge in radiation measurement. The authors tested the performance of the proposed algorithm using two different types of deep artificial neural network models in application to handheld detectors having high or low energy resolution. The proposed algorithm showed high performance in identifying artificial radioisotopes for actually measured gamma-ray spectra. It was also confirmed that the algorithm is applicable to identifying  U and automated uranium categorization by analyzing estimated CCRs by the deep artificial neural network models. The authors also com-pared the performance of the proposed algorithm with a conventional radioisotope identification method and discussed promising ways to improve the performance of the algorithm using the deep artificial neural network.
U and automated uranium categorization by analyzing estimated CCRs by the deep artificial neural network models. The authors also com-pared the performance of the proposed algorithm with a conventional radioisotope identification method and discussed promising ways to improve the performance of the algorithm using the deep artificial neural network.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Takeshita, Hayato; Maekawa, Fujio
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.01033_1 - 01033_4, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:68.83(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Futemma, Akira; Sanada, Yukihisa; Sasaki, Miyuki; Kawasaki, Yoshiharu*; Iwai, Takeyuki*; Hiraga, Shogo*; Haginoya, Masashi*; Matsunaga, Yuki*; Akutsu, Yuichiro*; Hokama, Tomonori; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2022-028, 127 Pages, 2023/02
A large amount of radioactive material was released by the nuclear disaster of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), Tokyo Electric Power Company, caused by the Great East Japan Earthquake and the following tsunami on March 11, 2011. After the nuclear disaster, airborne radiation monitoring via manned helicopter has been utilized to grasp rapidly and widely the distribution of the radioactive materials surrounding FDNPS. We prepare the data of background radiation dose, geomorphic characteristics and the controlled airspace surrounding nuclear facilities of the whole country in order to make effective use of the monitoring technique as a way of emergency radiation monitoring and supply the results during an accident of a facility. This report has summarized the knowledge noted above achieved by the aerial radiation monitoring around Ohi and Takahama nuclear power stations. In addition, the examination's progress aimed at introducing airborne radiation monitoring via an unmanned plane during a nuclear disaster and the technical issues are summarized in this report.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Kato, Masaaki*; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 38(2), p.347 - 358, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:49.56(Chemistry, Analytical)To develop remote isotopic analysis for the nuclids with small isotope shifts, Doppler-free fluorescence spectroscopy of Ca was performed using laser ablation plume. Counter-propagating laser beams from two external cavity diode lasers were used to irradiate the plume in order to excite the ground-state Ca atoms to the  D
D state through a double resonance scheme of
state through a double resonance scheme of  S
S

 P
P

 D
D . Subsequently, we measured fluorescence spectra associated with the relaxation from the
. Subsequently, we measured fluorescence spectra associated with the relaxation from the  D
D to
to  P
P states. The linewidth measured at 1 ms delay after ablation under helium gas pressure of 70 Pa was found to be less than 70 MHz, which was about 1/30 of the linewidth of the Doppler-limited fluorescence spectrum. A broad Gaussian pedestal was observed at less than 600 micro-second delay in the temporal variation in fluorescence spectra, and it was most likely due to the velocity-changing collision. Additionally, the pressure broadening rate coefficient for the second-step
states. The linewidth measured at 1 ms delay after ablation under helium gas pressure of 70 Pa was found to be less than 70 MHz, which was about 1/30 of the linewidth of the Doppler-limited fluorescence spectrum. A broad Gaussian pedestal was observed at less than 600 micro-second delay in the temporal variation in fluorescence spectra, and it was most likely due to the velocity-changing collision. Additionally, the pressure broadening rate coefficient for the second-step  P
P

 D
D transition was determined to be 46.0 MHz/torr from the spectra measured under various gas pressures. We evaluated analytical performances such as linearity of the calibration curve, limit of detection, and measurement accuracy using fluorescence signals of three naturally occurring Ca isotopes (i.e.,
transition was determined to be 46.0 MHz/torr from the spectra measured under various gas pressures. We evaluated analytical performances such as linearity of the calibration curve, limit of detection, and measurement accuracy using fluorescence signals of three naturally occurring Ca isotopes (i.e.,  Ca,
Ca, 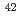 Ca, and
Ca, and 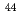 Ca). The limit of detection of isotopic abundance was estimated to be 0.09% from the 3-sigma criteria of the background. These results suggest that this spectroscopic technique is promising for remote isotopic analysis of nuclides with small isotope shifts.
Ca). The limit of detection of isotopic abundance was estimated to be 0.09% from the 3-sigma criteria of the background. These results suggest that this spectroscopic technique is promising for remote isotopic analysis of nuclides with small isotope shifts.
 Sr and
Sr and  Cs by AMS
Cs by AMSHonda, Maki; Martschini, M.*; Wieser, A.*; Marchhart, O.*; Lachner, J.*; Priller, A.*; Steier, P.*; Golser, R.*; Sakaguchi, Aya*
JAEA-Conf 2022-001, p.85 - 90, 2022/11
Accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) is an analytical method that combines mass spectrometry with a tandem accelerator, which has been used mainly in nuclear physics experiments. AMS is used to measure radionuclides with half-lives of 10 -10
-10 years. For radionuclides with half-lives of this order, the method of measuring their mass is 10
years. For radionuclides with half-lives of this order, the method of measuring their mass is 10 -10
-10 times more sensitive than measuring their activity. Because of this advantage, AMS has been widely applied in Earth and planetary sciences, atomic energy research, and other fields. Among the various studies, Wallner et al. (2021, 2016) have achieved excellent work in Earth and planetary sciences. For example, they have attained the ultra-sensitive analysis of
times more sensitive than measuring their activity. Because of this advantage, AMS has been widely applied in Earth and planetary sciences, atomic energy research, and other fields. Among the various studies, Wallner et al. (2021, 2016) have achieved excellent work in Earth and planetary sciences. For example, they have attained the ultra-sensitive analysis of  Fe and
Fe and  Pu in environmental samples. These are radionuclides produced by rapid-neutron-capture (
Pu in environmental samples. These are radionuclides produced by rapid-neutron-capture ( -process) nucleosynthesis. Our recent work shows that a new AMS system (VERA, University of Vienna), which combines laser isobaric separation and a typical AMS system, has been successfully applied to the ultra-sensitive determination of
-process) nucleosynthesis. Our recent work shows that a new AMS system (VERA, University of Vienna), which combines laser isobaric separation and a typical AMS system, has been successfully applied to the ultra-sensitive determination of  Sr and
Sr and  Cs in environment. For
Cs in environment. For  Sr in environmental samples, the
Sr in environmental samples, the  -ray measurement by the milking of the daughter nuclide
-ray measurement by the milking of the daughter nuclide  Y is still the principal method, which takes 3-6 weeks. The new AMS method has a detection limit of
Y is still the principal method, which takes 3-6 weeks. The new AMS method has a detection limit of  0.1 mBq, which is comparable to that of
0.1 mBq, which is comparable to that of  -ray measurement, with a more straightforward chemical treatment than
-ray measurement, with a more straightforward chemical treatment than  -measurement. Our achievement demonstrates that AMS can be a practical new method for determining
-measurement. Our achievement demonstrates that AMS can be a practical new method for determining  Sr in the environment.
Sr in the environment.
Okada, Shota; Murakami, Masashi; Kochiyama, Mami; Izumo, Sari; Sakai, Akihiro
JAEA-Testing 2022-002, 66 Pages, 2022/08
Japan Atomic Energy Agency is an implementing organization of burial disposal for low-level radioactive waste generated from research, industrial and medical facilities in Japan. Radioactivity concentrations of the waste are essential information for design of the disposal facility and for licensing process. A lot of the waste subjected to the burial disposal is arising from dismantling of nuclear facilities. Radioactive Wastes Disposal enter has therefore discussed a procedure to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations by theoretical calculation for waste arising from the dismantling of the research reactors facilities and summarized the common procedure. The procedure includes evaluation of radioactive inventory by activation calculation, validation of the calculation results, and determination of the disposal classification as well as organization of the data on total radioactivity and maximum radioactivity concentration for each classification. For the evaluation of radioactive inventory, neutron flux and energy spectra are calculated at each region in the reactor facility using two- or three-dimensional neutron transport code. The activation calculation is then conducted for 140 nuclides using the results of neutron transport calculation and an activation calculation code. The recommended codes in this report for neutron transport calculation are two-dimensional discrete ordinate code DORT, three-dimensional discrete ordinate code TORT, or Monte Carlo codes MCNP and PHITS, and for activation calculation is ORIGEN-S. Other recommendation of cross-section libraries and calculation conditions are also indicated in this report. In the course of the establishment of the procedure, Radioactive Wastes Disposal Center has discussed the commonly available procedure at meetings. It has periodically held to exchange information with external operators which have research reactor facilities. The procedure will properly be reviewed and be revised by reflecting future situ
Yomogida, Takumi; Ouchi, Kazuki; Oka, Toshitaka; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Koma, Yoshikazu; Konno, Katsuhiro*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 12(1), p.7191_1 - 7191_10, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:55.41(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Particles containing alpha ( ) nuclides were identified from sediment in stagnant water at the torus room of the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Station (FDiNPS)'s Unit 2 reactor. Several uranium-bearing particles were identified by SEM observation. These particles contained Zr and other elements which constituted fuel cladding and structural materials. The
) nuclides were identified from sediment in stagnant water at the torus room of the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Station (FDiNPS)'s Unit 2 reactor. Several uranium-bearing particles were identified by SEM observation. These particles contained Zr and other elements which constituted fuel cladding and structural materials. The  U/
U/ U isotope ratio in the solid fractions that included U particles was consistent with the nuclear fuel in the Unit 2 reactor, which indicated that the U particles had been derived from nuclear fuel. The particles with alpha-emitters detected by alpha track analysis were several tens to several hundred
U isotope ratio in the solid fractions that included U particles was consistent with the nuclear fuel in the Unit 2 reactor, which indicated that the U particles had been derived from nuclear fuel. The particles with alpha-emitters detected by alpha track analysis were several tens to several hundred  m in size. The EDX spectra showed that these particles mainly comprised iron, which indicated Pu, Am, and Cm were adsorbed on the Fe-baring particles. This study clarifies that the major morphologies of U and other
m in size. The EDX spectra showed that these particles mainly comprised iron, which indicated Pu, Am, and Cm were adsorbed on the Fe-baring particles. This study clarifies that the major morphologies of U and other  -nuclides were differed in the sediment of stagnant water in the torus room of FDiNPS's Unit 2 reactor.
-nuclides were differed in the sediment of stagnant water in the torus room of FDiNPS's Unit 2 reactor.
Shimada, Asako; Taniguchi, Yoshinori; Kakiuchi, Kazuo; Ohira, Saki; Iida, Yoshihisa; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Amaya, Masaki; Maruyama, Yu
Scientific Reports (Internet), 12(1), p.2086_1 - 2086_11, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:28.39(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
Takeshita, Hayato*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Hiroki*; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Maekawa, Fujio
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 511, p.30 - 41, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:67.39(Instruments & Instrumentation)Nuclide production cross sections for proton-induced reactions on Mn and Co at incident energies of 1.3, 2.2, and 3.0 GeV were measured by the activation method at the J-PARC. In total, 143 production cross sections of reaction products were obtained. Among them, the cross sections of  Mn(p,X)
Mn(p,X) S and
S and  Mn(p,X)
Mn(p,X) Ar were measured for the first time. The stable proton beam and well established beam monitoring system contributed to the reduction of the systematic uncertainties to typically less than 5%, which was better than those of the previous data. To examine the prediction capabilities of spallation reaction models and evaluated data library, the measured data were compared with the spallation reaction models in PHITS (INCL4.6/GEM, etc.), INCL++/ABLA07, and the JENDL/HE-2007 library. The comparison of the mean square deviation factors indicated that both INCL4.6/GEM and JENDL/HE-2007 showed better agreement with the measured data than the others.
Ar were measured for the first time. The stable proton beam and well established beam monitoring system contributed to the reduction of the systematic uncertainties to typically less than 5%, which was better than those of the previous data. To examine the prediction capabilities of spallation reaction models and evaluated data library, the measured data were compared with the spallation reaction models in PHITS (INCL4.6/GEM, etc.), INCL++/ABLA07, and the JENDL/HE-2007 library. The comparison of the mean square deviation factors indicated that both INCL4.6/GEM and JENDL/HE-2007 showed better agreement with the measured data than the others.